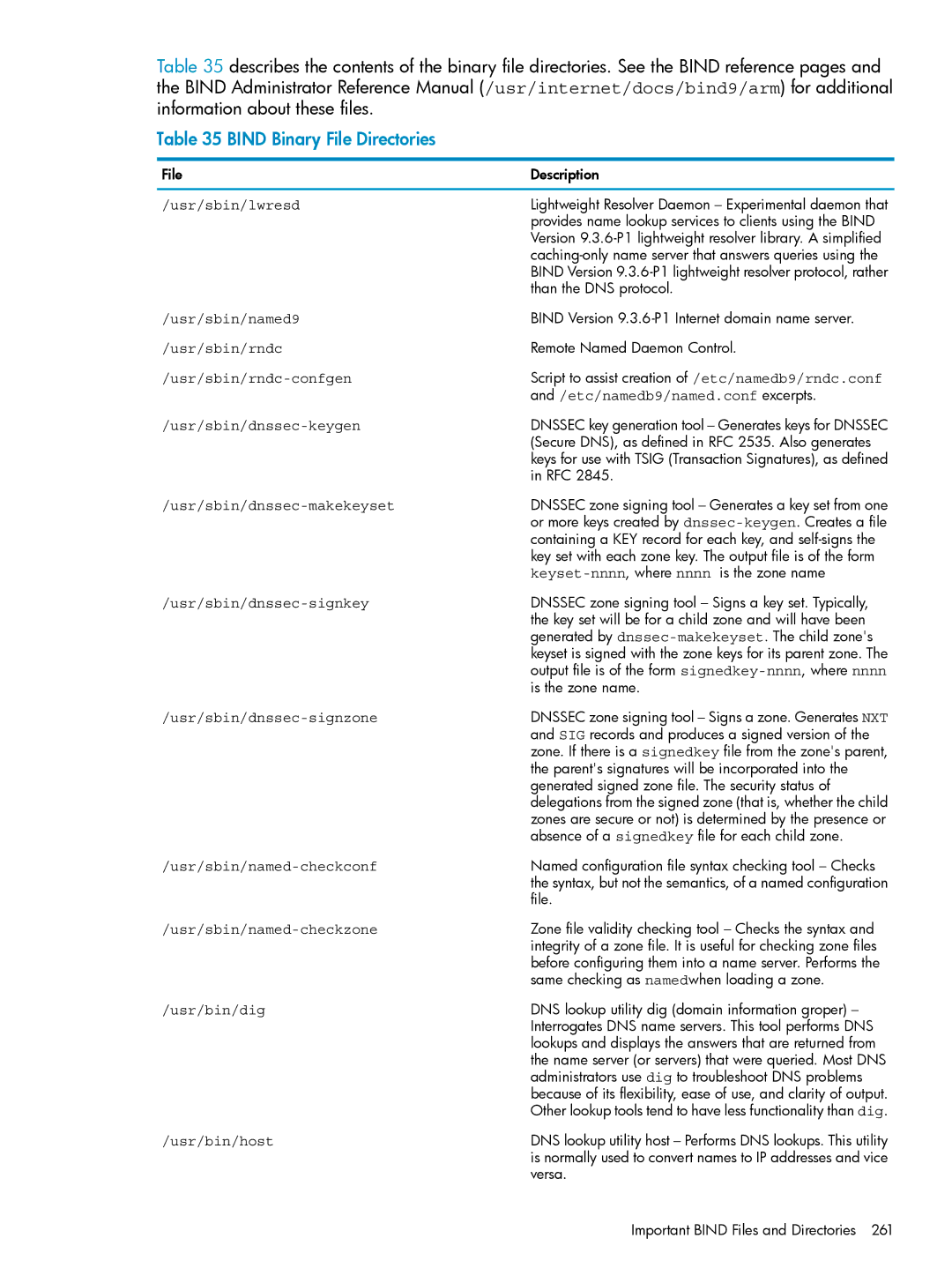
Table 35 describes the contents of the binary file directories. See the BIND reference pages and the BIND Administrator Reference Manual (/usr/internet/docs/bind9/arm) for additional information about these files.
Table 35 BIND Binary File Directories
File | Description |
/usr/sbin/lwresd | Lightweight Resolver Daemon – Experimental daemon that |
| provides name lookup services to clients using the BIND |
| Version |
| |
| BIND Version |
| than the DNS protocol. |
/usr/sbin/named9 | BIND Version |
/usr/sbin/rndc | Remote Named Daemon Control. |
Script to assist creation of /etc/namedb9/rndc.conf | |
| and /etc/namedb9/named.conf excerpts. |
| DNSSEC key generation tool – Generates keys for DNSSEC |
| (Secure DNS), as defined in RFC 2535. Also generates |
| keys for use with TSIG (Transaction Signatures), as defined |
| in RFC 2845. |
| DNSSEC zone signing tool – Generates a key set from one |
| or more keys created by |
| containing a KEY record for each key, and |
| key set with each zone key. The output file is of the form |
| |
| DNSSEC zone signing tool – Signs a key set. Typically, |
| the key set will be for a child zone and will have been |
| generated by |
| keyset is signed with the zone keys for its parent zone. The |
| output file is of the form |
| is the zone name. |
| DNSSEC zone signing tool – Signs a zone. Generates NXT |
| and SIG records and produces a signed version of the |
| zone. If there is a signedkey file from the zone's parent, |
| the parent's signatures will be incorporated into the |
| generated signed zone file. The security status of |
| delegations from the signed zone (that is, whether the child |
| zones are secure or not) is determined by the presence or |
| absence of a signedkey file for each child zone. |
| Named configuration file syntax checking tool – Checks |
| the syntax, but not the semantics, of a named configuration |
| file. |
| Zone file validity checking tool – Checks the syntax and |
| integrity of a zone file. It is useful for checking zone files |
| before configuring them into a name server. Performs the |
| same checking as namedwhen loading a zone. |
/usr/bin/dig | DNS lookup utility dig (domain information groper) – |
| Interrogates DNS name servers. This tool performs DNS |
| lookups and displays the answers that are returned from |
| the name server (or servers) that were queried. Most DNS |
| administrators use dig to troubleshoot DNS problems |
| because of its flexibility, ease of use, and clarity of output. |
| Other lookup tools tend to have less functionality than dig. |
/usr/bin/host | DNS lookup utility host – Performs DNS lookups. This utility |
| is normally used to convert names to IP addresses and vice |
| versa. |
Important BIND Files and Directories 261