Digi Connect Family
Page
Chapter Introduction
Chapter Command Descriptions
Contents
Who 258
Modem Emulation Commands
Index 271
Contents
Chapter
T r o d u c t i o n
Quick Reference for Configuring Features
Quick Reference for Configuring Features
Feature/Task Commands
Guide
Feature/Task Commands
Configure an IP Address
Access the Command Line
Access the Command Line
Basic Command Information
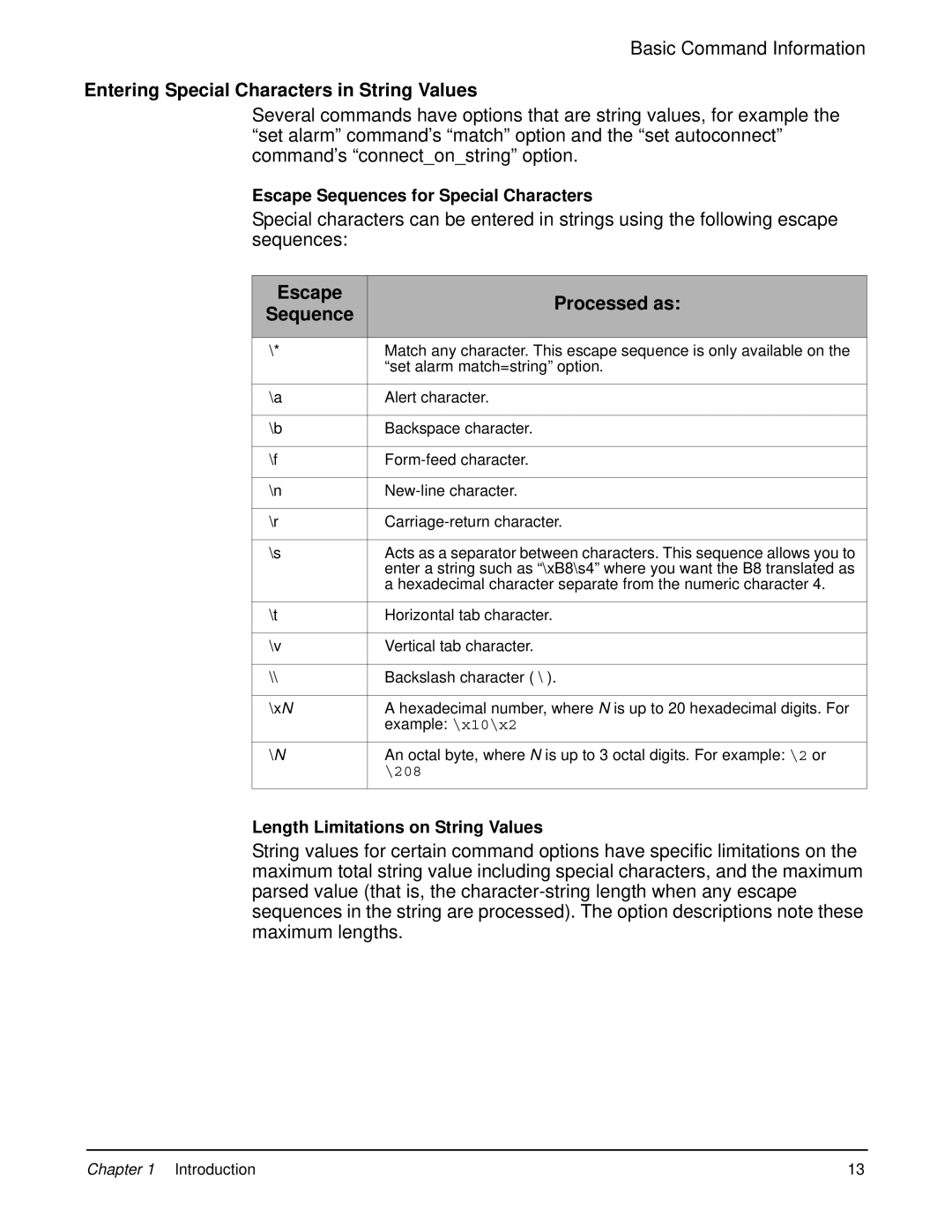
Escape Processed as Sequence
Entering Special Characters in String Values
Escape Sequences for Special Characters
Length Limitations on String Values
Identifying the User Model for Your Digi Connect Product
User Models and User Permissions in Digi Connect Products
One-user Model
Two-user Model
Increasing Security for Digi Device Users
Login Suppression Feature
User Models and User Permissions in Digi Connect Products
Verifying Device Support for Commands
Verifying Device Support for Commands
From=serveripaddressfilename
To=serveripaddressfilename
Host ip address
Boot
Load file
See also
Examples
Close
Session Type Default Escape Keys
Connection number
Serial port
Ip address
Dhcpserver
Display Dhcp server status
Assigned expired
Assigned active
Reserved active
Reserved inactive
Released
Offered pre-lease
Unavailable Address
Set dhcpserver on
Display
Arp
Options Accesscontrol
Buffers
Ddns
Device
Gpio
Memory
Serial
Switches
Sockets
Spd
Display Virtual Private Network VPN status information
Display device information
State
Output
Ip address
Primary dns addr
Reset status
No service
Last reset reason
Administrative
Non-administrative
Session successes
Lcp echo requests
Session failures
Session consecutive failures
Total bypasses
Total link down requests
Tail=number
Display buffers
Tftp=serverfilename
Server
Display port buffering information on the screen
Set buffer on
Output buffering information to a Tftp server
Output multi-port buffering information to a Tftp server
Exit
Displaying Online Help on
Help and ? help and ?
Ethernet
Info
Icmp
Statistics, see Output on
Displays statistics from the wireless Ethernet wlan table
Displays statistics from the TCP table
Displays statistics from the UDP table
Ethernet statistics
Statistic Description
Icmp statistics
IP statistics
Serial statistics
UDP statistics
TCP statistics
Wireless Wlan statistics
Display Icmp statistics
Range
Kill
Connection id
Binary=onoff
Options
Crmod=onoff
Id=number
Newpass
Name=string
Count=0n
Ipaddress
Interval=milliseconds
Size=bytes
Provision
Enter phone numbers as numbers only with no dashes
Given you
Display current provisioning parameters
Manually provision the module for a SIP-only network
Nai=network access id
Spc=service programming code MSL
Mdn=mobile directory number
Min=mobile ID number
Priha=primary host agent IP address
Ha=home address
Secha=secondary host agent IP address
Hass=host agent shared secret
Type=otasp
Type=iota
Otaspnumber= Otasp number for example, *228
Program args
Tftp server ipfilename
Quit
=serial port s=session
Auth command. The revert auth command revert authentication
Revert multiple settings
Revert
Time
Options all
Alarm
Auth
Autoconnect port=range
Ekahau
Login
Forwarding
Host
Pmodem port=range
Service
Pppoutbound port=range
Profile port=range
Phase1
Vpn allglobaltunnelphase1phase2
Phase2
Wireless
User=user name -luser name
Options Esc
Send
Options Enabled=onoff
Set accesscontrol
Off
Autoaddsubnets=onoff
Netmask 255.255.255.0 to access this device server
Subnets will be allowed to access this device server
Subnip1-32=ipaddress
Subnmask1-32= mask
Configure alarms with general options applies to all alarms
Set alarm
Configure alarms for a range set multiple alarms
Devices supported Purpose Required permissions Syntax
Configure alarms based on mobile signal strength GSM
Configure alarms based on data pattern matching
Configure alarms based on signal strength Cdma
Configure alarms based on mobile temperature
Mailserverip=ipaddress
State= onoff
From=string
Cwm=onoff
Cc=string
To=string
Highpins=list of highpins
Pins=list of pins
Lowpins=list of lowpins
Reminderinterval=seconds
Reminder=onoff
Triggerinterval=seconds
Mode=match
Time=max time
Celldata=byte count threshold
Mode=mobiletemp
Mode=configchange
Mode=1xevdounavail
Mode=mobileunavail
Set alarm #1 mode to Gpio mode
Error conditions triggering alarms
Set alarm #1 to designate which pins trigger alarm
Enable alarm #1
Gpio input, Gpio output, or standard serial
Set alarm Turn alarm #10 on
Set snmp on
Set autoconnect
Rlogin
Service=rawrloginssltelnet
State=onoff
Trigger=alwaysdatadcddsrstring
Description=string
Nodelay=onoff
Ipaddress=ipaddress
Ipport=ipport
Set network on
Network IP destination when data arrives on the serial port
Set serial on
Set tcpserial on
Set bsc
Serialmode=bisync3270bisync3275
State=disabledenabled
Baudrate=baud rateexternalclock
Baud rate
Textconversion=onoff
Codeset=asciiebcdic
Pollingaddress=0x followed by 2 hex digits
Selectionaddress=0x followed by 2 hex digits
Rxtimeout=milliseconds
Noresponsemessage=0x followed by up to 64 hex digits
Poweronmessage=0x followed by up to 64 hex digits
Txretries option
Port
Options Clear
Size
Data will not be buffered and all data will be cleared from
On mode and the buffer size to 64 kilobytes
Buffer
Pause
Registered with that service
Update requests will be rejected
For a user to display Dynamic DNS settings set permissions
Ddnsupdater=read
Disabled
Service=disableddyndnsorg
Action=updatenowclearstatus
Updatenow
Standardhttp
Ddpassword=password
Alternatehttp
Securehttp
Nochg
Dynamic DNS service
Display on
Command. See dhcpserver on
User interface’s Network Configuration settings
For a user to display Dhcp server settings set permissions
Set dhcpserver set dhcpserver
Action=setrevert
Item=scope
Set
Revert
Startip=ip address
Offerdelay=0-5000
Endip=ip address
Leasetime=timeinfinite
Range=1-16all
Item=reservation
Ip=ip address
Clientid=client MAC address
Range=1-4all
Item=exclusion
First address in the exclusion block
Disable all reservations that were previously added
Using the web UI
IP address, which is the purpose of a reservation
Is, reservations override exclusions
102 Command Descriptions
Dhcpserver on
Web user interface, the online help for Network Settings
Dhcp terminology and managing Dhcp server operation
Set ekahau set ekahau
Wireless device
Digi Connect Wi-EM only
Proprietary hardware components
Server=hostnameip address
Id=device id
Name=device name
Set identifiers
Enable Ekahau Client
Options Duplex
Set ethernet
Half
Full
100
Speed
Privileges
Set forwarding
Staticrouteindex=1-8
Options ipforwarding=onoff
Action=addchangedelete
Add
Mask=subnet mask
Net=destination ip address
Gateway=ip address
Metric=1-16
Routing information
Settings under Network Configuration
Set nat on
Devices supported Purpose
Set gpio
Options Range=1-n
Mode=serialinputoutput
Signals
Pin Number Default Serial Signal Signal Direction
Messages or Snmp traps when Gpio pins change
Default serial signal settings for Gpio pins
Options Add
Set group
Remove
Id=range
Defaultaccess=nonecommandlinemenu
Commandline=onoff
Commandline
Name= string
Permissions Examples
Default
Options Name=name
Device support
Set ia
Configure network-based masters set ia master
Configure serial-port connected devices set ia serial
Serial settings, which include
Instead of a set ia command with no options
Serial= range
Serial options
Chartimeout=3-99999 ms applies to master or slave
Slavetimeout=10-99999 ms applies to slave only
Idletimeout=0=disabled1-99000 seconds
Table=1..8 applies to master only
Medium
Priority=highmediumlow
Modbus options
Chartimeout=3-99000 ms
Modbusrtu Modbusascii Modbustcp Messagetimeout=100-99000 ms
Master=range
Type=tcpudp
126 Command Descriptions
Addroute=route index
Table options
Moveroute=fromrouteindex,torouteindex
Route options
Port=serial port
Mapto=protocol address
Configuration settings in the Web user interface
Settings for the Digi Connect WAN IA
Revert on page 61. The revert ia command options revert any
Existing IA configuration settings
Options Suppress=onoff
Set login
Quitkey=key
Previouskey=key
Quitlabel=string
Previouslabel=string
Presskeylabel=string
Sortby=nonekeylabel
Title=string subtitle=string
Key
Label
Horizontal
Direction=horizontalvertical
Vertical
Item=1-32
Submenu=string
Command=string
Menu displayed to the user upon selecting the menu item
Contains spaces, enclose it in double quotes
Set mgmtconnection
Timedperiod=period
Lkaupdateenabled=onoff
Timedoffset=immediateoneperiodrandomtime
Immediate
Retry timeout interval feature
Clntreconntimeout=nonetimeout
Display current connection settings
Set values for the client connection
Set mgmtglobal
Settings set permissions s-mgmtglobal=rw
Set permissions s-mgmtglobal=read
Options Deviceid=hex string
Tcpnodelayenabled=onoff
Rcicompressionenabled=onoff
Tcpkeepalivesenabled=onoff
Revertdeviceid
Connidletimeout=nonetimeout value
Options Networktype=modempppethernet802.11
Set mgmtnetwork
Modemppp
802.11
Proxypassword=string
Proxylogin=string
Connectionmethod=autononemtmdhproxy
Mdh
Mdhrxkeepalive=time
Mtwaitcount=count
Mdhtxkeepalive=time
Mdhwaitcount=count
Settings set permissions s-router=rw
Protocol forwarding settings
Set nat set nat
Supported are
Poenabled1-64=onoff
Prenabled1-4=onoff
Maxentries=64-1024
Prnumber1-4=greesp
Pocount=1-64=number of ports in range, minimum
Poproto1-64=tcpudp
Poexternal1-64=number of ports in range, minimum
Pointernal1-64=number of ports in range, minimum
Set network
Setting user permissions for commands
Network level
Where
Ip=device ip address
Ip address options
Gateway=gateway ip
Submask=device submask
TCP retransmit options
TCP keepalive options
Arpttl=1-20 minutes
ARP options
Garp=30-3600 seconds
Set passthrough
Remote Device Management and IP Pass-through
Using Pinholes to Manage the Digi Cellular Family Device
Http=passterminate
Options State=enableddisabled
Https=passterminate
Telnet=passterminate
Surelink=passterminate
Connectware=passterminate
Ping=passterminate
On page 14 for more information
Set permissions
Help
Permission descriptions
Set permissions
Boot=noneexecute
Backup=noneexecute
Execute
Self
Accesscontrol=nonereadrw
Rlogin=noneexecute
Connect=noneexecute
Dhcpserver=noneexecute
Ddnsupdater=nonereadrw
Alarm=nonereadrw
Login=nonereadrw
Autoconnect=noner-selfreadrw-selfw-self-rrw
Permissions=nonereadrw
Service=nonereadrw
Pmodem=noner-selfreadrw-selfw-self-rrw
Ppp=nonereadrw
Vpn=nonereadrw
User=nonereadrw
Wlan=nonereadrw
Status=nonereadrw
Disables modem emulation
Enables modem emulation
Configure modem emulation
Display modem-emulation settings
Disables Telnet processing
Enables Telnet processing
Modem Emulation Commands for descriptions of Digi
Specific commands for modem-emulation configurations
Set pppoutbound
Pap
Authmethod=nonePAPCHAPboth
Chap
Both
Addressmask=ip address mask
Defaultgateway=yesno
Protocolcompression=onoff
Addresscompression=onoff
Lcpkaquiettime=10-86400 seconds
Lcpkeepalive=onoff
Asyncmap=hex string
000A0000
N1-4=phonenumber
Ipcpdnsenabled=onoff
Loginscript=chat script
Display pppstats command displays the current status of PPP
Dialscript=chat script
Port as a console to access the command line interface
Or displays the current port-profile settings
Set profile set profile
Option’s description
Options Port=port
Localconfig
Profile=profile
Consolemanagement
Tunneling
Tcpsockets
Udpsockets
Set putty
Displays current terminal-emulation settings
For it to process
Height=10-60
Width=80132
Hostport=/com/0/com/1/vcom/0
Keyboardport=/com/0/com/1No Keyboard
Block
Cursortype=noneblockunderlinevertical
Underline
Blinkcursor=onoff
Characterset=host charset
Character Set name Description
Set putty Complete list of allowed character sets is
Key mapping terminal emulation options
Keymaprange=1-32
Deletekeymaprange=1-32
Inseq=00-FF
Outseq=00-FF
Would enter
Emulation settings
Now, to delete the first 2 entries
One enter
Set python
Command=filename
Options Range=1
Options State
Options Keepalive=onoff
Set realport
Exclusive=onoff
Probecount, probeinterval, garbagebyte, and overridedhcp
Set service keepalive=onoff, or clients such as autoconnect
Set rtstoggle
Postdelay=delay
Predelay=delay
Altpin=onoff
Set serial
Csize=5678
Baudrate=bps
Flowcontrol=hardwaresoftwarenone
Hardware
Options Range= range
Set service
Ipport=network port
Delayedack=0-1000
Base network port number + serial port number
Port Number
Service Services Provided Network
Command Descriptions 195
Index numbers and changing default port numbers
Device is configured for IP passthrough
Service table
Set surelink on
Options Trapdestip=ipaddress
Setsenabled=onoff
Publiccommunity=string
Privatecommunity=string
Authfailtrap=onoff
Logintrap=onoff
Coldstarttrap=onoff
Linkuptrap=onoff
Display current socket tunnel settings
Configure a socket tunnel
Set sockettunnel
End initiated the tunnel
Toport=port number
Fromport=port number
Set surelink set surelink
Connection-failure settings can be disabled as well
Ping Test
TCP Connection Test
Systemresetconnectfailures=1-2550=off
Moduleresetconnectfailures=1-2550=off
Display current SureLink settings
Options for Hardware reset thresholds
Ping
Test=pingtcpdns
Trigger=intervalidle
Dns
Interval
Ipport=1-65535
Interval=10-65535
Dnsfqdn1=dns fqdn
Dnsfqdn2=dns fqdn
Statistics on page 35 for descriptions of these statistics
Display pppstats command displays connection and activity
Configure MEI settings
Set switches set switches
Display current MEI settings
Used
Options Range=range
Wires=twofour
Mode=232485
232
Current switch settings
Display on page 27. The display switches command displays
Revert on page 61. The revert switches command reverts
Set switches configuration
Options Description=string
Set system
Location=string
Contact=string
This command affects the following TCP serial connections
Serial settings
Connections made using the autoconnect feature
For a user to display the TCP serial settings for any line
Sidstring=socketid string
Endpattern=string
Sendtime=01-65535ms
Strippattern=onoff
Revert on Show on
Configure terminal settings
Command line of the device
Display current terminal settings
Set term
For a user to display the UDP serial settings for any line
Another service, the data will be sent to the serial port
Connect WAN and ConnectPort Display
Are logged in set permissions s-udpserial=r-self
Sendcount= bytes
Port= range
Sendtime=0 time
Clostime=time
Sidstring=string
Range=1-64
UDP port of the destination to which data is sent
UDP serial settings
Identifies the range of UDP destinations to be displayed
Data to be sent on to the network destination
Display user configuration attributes
Change user configuration attributes
For a user to display user configuration attributes
For a user to display and set user configuration attributes
Associate
Maximum of 32 users can be defined
Two groups
Disassociate
User cannot use group access rights Default is off
Groupaccess=onoff
User is not allowed to access the custom menu interface
Gid=number
Defaultgroup=nonegidgname
Defaultaccess=nonecommandlinemenugroup
Group
Gid
Tftphostfilename
Publickey=tftphostfilenameclear
Tftphost
Splashtime=0-30 seconds
Set video
Server=vnc server ipaddrdns name
Password=vnc server password
Port=vnc server network port
Server services are enabled and disabled by the set service
Configured globally
Remote Access VNC Client Settings
VPN Settings and VPN Tunnel Settings
Security associations SAs
Display current VPN settings
Set IKE/ISAKMP SA Phase 2 Options
Set IKE/ISAKMP SA Phase 1 Options
Display current VPN settings
Identity=fqdnuser fqdnip address
Dhgroup=125
Identity=ip-address
Pfs=onoff
Name=tunnel name
Tunnel options
Newname=tunnel name
Manually-keyed options
Remotevpnendpoint=fqdnip address
Mode=manually-keyed
Inboundspi=256
Md5
Inboundauthentication=nonemd5sha1
Sha1
Inboundauthkey=ascii keyhex key
Inboundenckey=ascii keyhex key
Outboundauthentication=nonemd5sha1
Outboundspi=256
Outboundauthkey=ascii keyhex key
Isakmp options
Encryption Authentication SA Lifetime
Mode=isakmp
Sharedkey=ascii keyhex key
Authentication=md5sha1
Set vpn phase1
Authmethod=sharedkeydssrsa
Sharedkey
Salifetime=10-232
Set vpn phase2
Salifetimedata=0-232
Tunnel=1-2
Encryption=nonedes3desaes
Authentication=nonemd5sha1
Salifetime=60-232
Salifetimedata=0 232 kilobytes
Settings
Configuring
Set wlan
PSK
Authentication methods and associated data fields
Inner and outer protocols
Configure wireless settings
Ssid=string
Open
Authentication=
Wepauth
Wpapsk
Wep
Encryption=open,wep,tkip,ccmp,any
Tkip
Ccmp
Gtc
Password=string
Mschapv2
Otp
WepkeyN=hex string
Psk=string
User permissions for commands
Issued to the device
Settings... column to go to the command descriptions
Show
Show
Command Descriptions 251
Display network configuration settings
Configuration table entry or range of entries
Display settings for a particular user
Command Descriptions 253
Session number
Ip addr
Telnet
Tcp port
Connect
Options Statusconnectdisconnect
Disconnect
Set vpn on page 228. The set vpn command configures VPN
This command enables the tunnel at index 1 to be used
This command
Connections Management page in the Web user interface from
Who who
To set permissions who=execute to use this command. See
Displays active connections to and from the device
None at this time
Modem Emulation Cable Signals
What Is Modem Emulation?
What Is Modem Emulation?
Modes of Operation
Common User Scenarios for Modem Emulation
User Scenario Diagram a
User Scenario Diagram B
Outgoing Modem Emulation Connection
Connection Scenarios for Modem Emulation
Incoming Modem Emulation Connection
Modem Emulation Pooling
Accepted But Ignored AT Commands
About the Commands in this Chapter
Emulation configuration scenario
Modem Emulation AT Command Set
Function Result Command Code
Modem Emulation Commands 265
Function Result
Command
Register Definitions
Register Function Range Units Default
Register Function Range Units Default
Result Codes
Emulation commands
Short Long Form
270 Modem Emulation Commands
D e
ESP
GRE
PSK
Self user permission
198
Snmp