NS7520 Hardware Reference
Page
Part number/version 90000353D Release date March
Page
Contents
A p t e r 4 B B u s M o d u l e
A p t e r 7 M e m o r y C o n t r o l l e r M o d u l e
A p t e r
A p t e r 1 0 S e r i a l C o n t r o l l e r M o d u l e
D e
About this guide
Who should read this guide
What’s in this guide
Conventions used in this guide
To read about See
Documentation updates
Related documentation
Customer support
For Contact information
Page
About the NS7520
NS7520 Features
Key features and operating modes of the major NS7520 modules
O u t t h e N S 7 5 2
7 5 2 0 F e a t u r e s
NS7520 module block diagram
NS7520 overview
Operating frequency
Pinout and Packaging
NS7520 packaging dimensions
Symbol Min Nom Max
Packaging
NS7520 pinout and dimensions
NS7520 BGA layout
Pinout detail tables and signal descriptions
Column Description
Symbol Pin Description
System bus interface
System bus interface pinout
External bus
ADDR7
ADDR6
ADDR5
ADDR4
Do not USE
Signal descriptions
System bus interface signal description
Mnemonic Signal Description
Chip select controller
Chip select controller pinout
Busy
Chip select controller signal description
Mnemonic Signal
Ethernet interface MAC
Ethernet interface MAC pinout
Ethernet interface MAC signal description
COL
CRS
No connect pins
No connect pins
Serial Other Pin Serial channel Signal Description
General-purpose I/O
RTS PORTC4 RXCB/RIB Reset
PORTA3 Rxda DACK1
PORTA2 Dsra Amux
DSR
Gpio signal
Serial signal
Other signal
Serial channel Other Description
System clock and reset
Clock generation and reset signal description
System clock pinout
System mode test support
System mode and system reset pinout
Plltst
Bisten
ARM debugger signal description
Jtag test ARM debugger
Jtag test pinout
Trst termination
Power supply
Power supply pinout
Signal Pin Description
GND
Working with the CPU
ARM Thumb concept
CPU performance
ARM mode
Working with ARM exceptions
ARM performance
ARM
Summary of ARM exceptions
Exception priorities
Exception vector table
Exception vector table
Vector Description Address
Reset exception
Detail of ARM exceptions
Undefined exception
SWI exception
Abort exception
IRQ exception
Firq exception
Entering and exiting an exception software action
Entering an exception
Exiting an exception
Reset Undef
Exception entry/exit summary
Exception entry/exit by exception type
Abort P
Hardware Interrupts
Firq and IRQ lines
Interrupt controller
Interrupt sources
W . d i g i . c o m
Page
BBus Module
BBus masters and slaves
Cycles and BBus arbitration
BBus masters and slaves
Module Master Slave
Address decoding
BBus address decoding
Address range Module
Page
SYS Module
Signal description
Signal mnemonic Signal name Description
Jtag support
ARM debug
System clock generation NS7520 clock module
External oscillator vs. internal PLL circuit
Using the external oscillator
NS7520 clock module block diagram
External oscillator mode hardware configuration
Using the PLL circuit
PLL mode hardware configuration
PLL mode hardware configuration
Setting the PLL frequency
PLL Settings register Setting the PLL frequency on bootup
PLL Settings register bit definition
Bits Access Mnemonic Reset Description D3109 Reserved
Bits Access Mnemonic Reset Description
MHz A87 A65 A40 ND+1 PLL Settings reg
Output divider
PLL multiplier
MHz A87 A65 A40 ND+1 PLL Settings reg
PLL Control register bit definition
Pllcnt
Sysclk frequency
ND+1 PLL Settings register
MHz
Reset circuit sources
NS7520 bootstrap initialization
Address bit Name Description
GEN Module
Module configuration
GEN module address configuration
GEN module hardware initialization
Address Register
GEN module registers
System Control register
Address FFB0
General information
Bclk output disable
Software watchdog enable
Software watchdog reset/interrupt select
Software watchdog timeout in seconds
Bus monitor enable
Enable access to internal chip registers in CPU
User mode
Bits Access Mnemonic Reset
Description Enable ARM CPU
DMA module test mode
Bus interface TEA/LAST configuration
CPU disable
DMA module reset
TA input synchronizer
Last reset caused by external reset
System Status register
System Status register bit definition
NS7520 revision ID
Last reset caused by watchdog timer
Last reset caused by PLL update
Last reset caused by software reset
Product ID defined by external resistor jumpers
Software Service register
Timer Control registers
Software Service register bit definition
Address FFB0 000C
Timer Control registers bit definition
Timer enable
Timer interrupt enable
Timer interrupt mode
Timer prescaler
Timer clock source
Initial timer count
Timer Status registers
Timer Status registers bit definition
Timer interrupt pending
Current timer count
Porta Configuration register
Porta mode configuration
Porta register bit definition
Porta data direction
Porta Configuration
Porta configuration
Adata
Porta data register
PORTA1 Gpio Gpio OUT SER1CTS DONE1OUT PORTA0 SER1SPISENABLE
Inputs
Outputs
IN/SER1DCD
Portc Configuration register
Portc mode
Portc register bit definition
Portc data direction
Portc configuration
Portc configuration
Cdata
Portc data register
PORTC1 Gpio Gpio OUT LEVELIRQ1=CDIR1 PORTC0 LEVELIRQ0=CDIR0
Interrupts
PORTC30
Interrupt controller registers
Address FFB0 0030 / 0034
Interrupt Enable registers bit definition
D01
Page
Memory Controller Module
Pin configuration
MEM module pin configuration by memory type
Mode A2714 A130 CSx
About the MEM module
Mode A2714 A130
Sdram
RAS CAS
MEM module configuration
Setting the chip select address range
Memory controller register map
Address Mnemonic Register
Memory Space
Memory Module Configuration register
Enable Dram refresh
Mmcr bit definition
Refresh count value
Enable external address multiplexing
Enable A27 output
Rcyc
Refresh cycle count
A27 and A26 bit settings
Enable A26 output
Enable A25 output
AMUX2
Chip Select Base Address register
Chip Select Base Address register bit definition
Base
Base address
Dram configuration mode
Peripheral page size
Dram address multiplexer select
External TA configuration
Dram internal address multiplexer mode
Burst memory cycle enable
Force Bclk at end of memory cycle
Write-protect the chip select
Eeprom
Valid bit
Chip Select Option Register a
Chip Select Option Register a bit definition
Mask
Mask Address
When DRSEL=0
When DRSEL=1 and DMODE=2’b00
When DRSEL=1 and DMODE=2’b01 at full speed
When DRSEL=1 and DMODE=10
Burst access size in beats
Bsize
Port size
Read cycle mode
Write cycle mode
OE Ctrl
WE Ctrl
Chip Select Option Register B
Chip Select Option Register B bit definition
Static memory Sram controller
Sync
Single cycle read/write
Sync Write Sync Read
Burst cycles
Async Read
Using the internal multiplexer
NS7520 Dram address multiplexing
000 001 010 011 100 101 110 111
7 5 2 0 D R a M a d d r e s s m u l t i p l e x i n g
Internal Dram multiplexing Mode
NS7520 multiplexed address outputs
Dram
Using the external multiplexer
Dram refresh
FP/EDO Dram controller
Normal FP Dram bus cycles
FP Dram Write FP Dram Read
FP/EDO Dram burst cycles
FP Dram burst cycles
X32 Sdram configuration
NS7520 Sdram interconnect
X32 Sdram interconnect
X16 Sdram configuration
BA1
BA0
BA1 Bclk CLK VCC CKE
NS7520 signal 16M Sdram signal 64M Sdram signal
X16 Sdram interconnect
CAS3 RAS CAS2 CAS1 CAS0
Udqm
X8 Sdram configurations
NS7520 signal 16M Sdram signal
X8 Sdram interconnect
Bclk CLK VCC CKE
Sdram A10/AP support
Command definitions
Sdram command definitions
Mux mode X32 X16
Command
Bsize configuration
CAS latency Bcyc configuration
Memory timing fields Sdram
Burst length
Sdram Mode register
Sdram Mode register settings
Full
Address Field Value
Sdram read cycles
Sdram normal read
Sdram burst read
Sdram write cycles
Sdram normal write
Sdram burst write
Peripheral page burst size
Example
Wait Bcyc
Page
DMA Module
DMA module
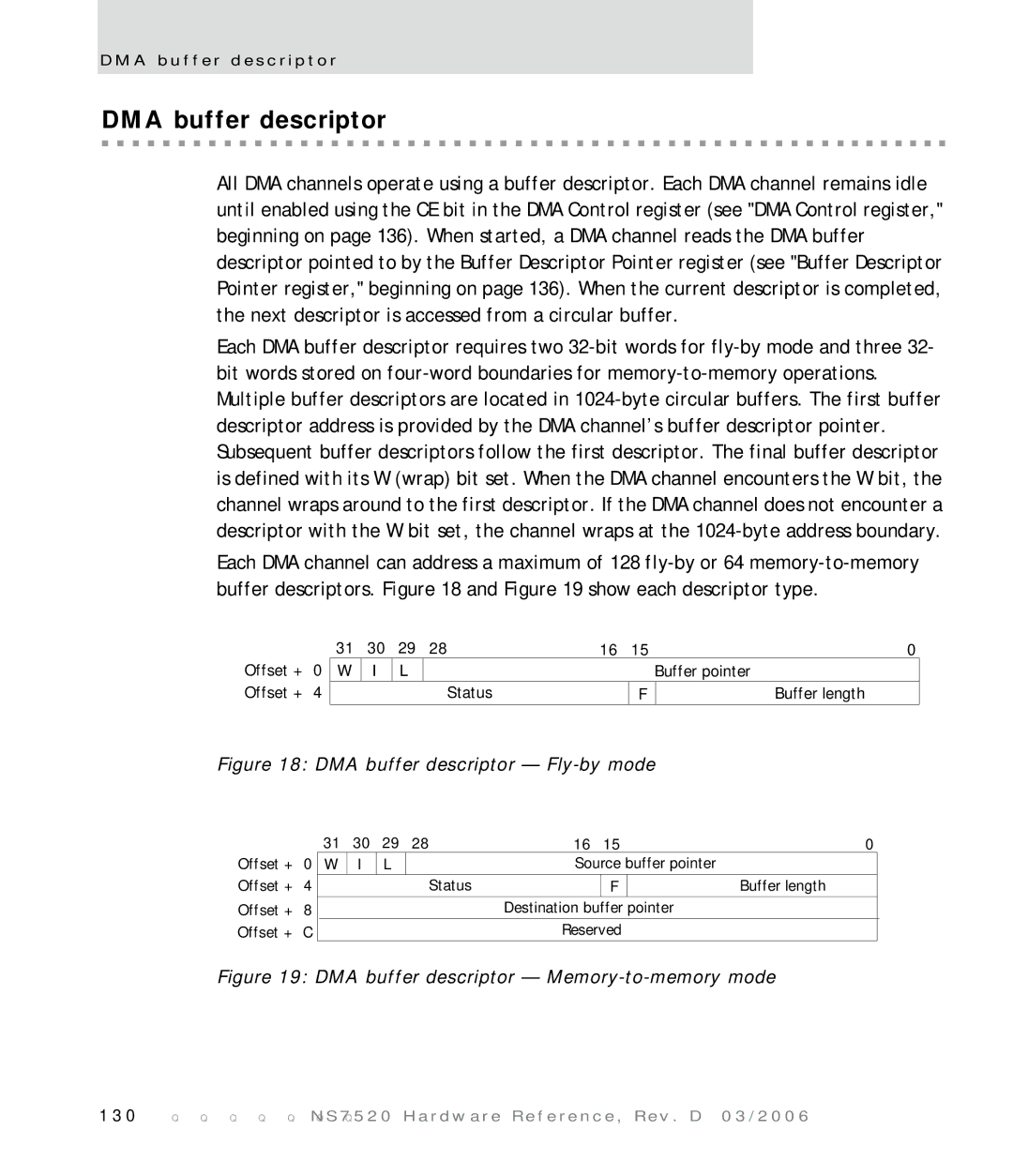
Fly-by operation transfers
Memory-to-memory operation
DMA fly-by transfers
DMA buffer descriptor Fly-by mode
DMA buffer descriptor
Buffer descriptor bit definitions
Buffer descriptor bit definitions
Bit Description
Buffer descriptor field definitions
Buffer descriptor field definitions
Field Description
Channel Base address DMA channel peripheral Fly-by mode
DMA channel assignments
DMA channel assignments
DMA channel registers
Address map
Address Description
Address Description
Buffer Descriptor Pointer register
DMA Control register
DMA channel enable
DMA operation mode
DMA Control register bit definition
Channel abort request
Burst transfer enable
Memory-to-memory mode
BTE
REQ
Channel request source
Sinc
Source address increment
Dinc
Destination address increment
Data operand size
Current DMA channel state shown in binary
Current DMA channel buffer descriptor index
DMA Status/Interrupt Enable register
DMA Status/Interrupt Enable register bit definition
Error completion interrupt pending
Normal completion interrupt pending
Premature complete interrupt enable
Normal completion interrupt enable
Error completion interrupt enable
Buffer not ready interrupt enable
Ethernet transmitter considerations
Ethernet receiver considerations
External peripheral DMA support
Signal description
External DMA configuration
Memory-to-memory mode
Signal Description
DMA controller reset
Hardware needed for external memory-to-memory DMA transfers
Page
Ethernet Module
Ethernet front-end EFE
Fifo
Transmit and receive FIFOs
EFE transmit processing
EFE receive processing
Receive buffer descriptor selection
DMA
External CAM filtering
MAC module block diagram
MAC module
Other modules in the diagram include
EFE configuration
EFE register map
Address Register Register description
Maxf
Supp
Test
Mcfg
Ethernet General Control register Egcr bit definitions
Address FF80
Erxetx Erxdmaetxdma Erxlngetxwm Erxshtefulld Erxbad
Erxregetxreg Erfifohetfifoh Erxbretxbc
Ethernet General Control register bit definition
Enable transmit Fifo
Enable transmit DMA
Do not set this bit when operating the Ethernet
Receiver in interrupt service mode
Enable Transmit Data register ready interrupt
Enable transmit data Fifo half empty interrupt
Enable transmit buffer complete interrupt
Enable full-duplex operation
MAC software reset
Invert the transmit clock input
PSOS pNA buffer descriptors
Insert transmit source address
Endec mode and NS7520 pins
Endec control signal cross-reference
External interface mode
Mode field Output based on EFE CSR bit
Ethernet General Status register Egsr bit definitions
Ethernet General Status register bit definition
Rxfdbrxskip Rxregrtxrege Rxfifohtxfifoh Rxbrtxbc
Receive Fifo data available
Receive register ready
Receive Fifo half full
Receive buffer ready
Receive buffer skip
Transmit register empty
Transmit Fifo half empty
Transmit buffer complete
Endec status signal cross-reference
Ethernet Fifo Data register
Address FF80 0008 / FF80 000C secondary address
Writing to the Ethernet Fifo Data register
Reading from the Ethernet Fifo Data register
Ethernet Transmit Status register
Ethernet Fifo Data register bit definition
Ethernet Transmit Status register bit definition
Fifo data FF80
Packet transmitted OK
Broadcast packet transmitted
Multicast packet transmitted
Transmit abort late collision
Txaed
Transmit abort excessive deferral
Txaec
Transmit abort excessive collisions
Txaur
Transmit aborted underrun
Txaj
Transmit abort jumbo
Transmit CRC error
Txdef
Transmit packet deferred
Txcrc
Ethernet Receive Status register
Txcolc
Transmit collision count
Ethernet Receive Status register bit definition
Receive buffer size in bytes
Receive carrier event previously seen
Receive data violation event previously seen
Receive packet has CRC error
Receive packet has dribble bit error
Receive broadcast packet
Receive multicast packet
Receive packet has code violation
Receive packet is too long
Receive packet is too short
MAC Configuration Register
Rover
Receive overflow
MAC Configuration Register 1 bit definition
Receive enable
RX flow control
Pass ALL receive frames
MAC Configuration Register 2 bit definition
Auto detect pad enable
Vlan pad enable
PAD/CRC enable
CRC enable
Pad operation table
PAD operation
Back-to-Back Inter-Packet-Gap register
Back-to-Back Inter-Packet-Gap register bit definition
Back-to-back inter-packet-gap
Non-Back-to-Back Inter-Packet-Gap register
Address FF80 040C
Non-Back-to-Back Inter-Packet-Gap register bit definition
Non back-to-back inter-packet-gap part
Collision Window/Collision Retry register
Collision Window/Collision Retry register bit definition
Collision window
Retransmission maximum
Maximum Frame register
Maximum Frame register bit definition
Maximum frame length
PHY Support register
PHY Support register bit assignment
Enable Jabber protection
Bit mode
Test register
Address FF80 041C
Test backpressure
Test pause
Shortcut pause quanta
MII Management Configuration register
MII Management Configuration register bit definition
Reset MII management
Clock select
Clks field settings
Scani
Scan increment single scan for read data
Clks field Sysclk ratio MHz example
MII Management Command register
MII Management Command register bit definition
Automatically scan for read data
Single scan for read data
MII Management Address register
MII Management Address register bit definition
MII PHY device address
MII PHY register address
MII Management Write Data register
Address FF80 042C
MII Management Write Data register bit definition
MII write data
MII Management Read Data register
MII Management Read Data register bit definition
MII read data
MII Management Indicators register
MII Management Indicators register bit definition
Read data not valid
Automatically scan for read data in progress
Smii Status register
Station Address registers
Smii Status register bit definition
Station Address Register
Station Address Register 1 bit definition
Station Address Register 2 bit definition
Station address octet
Station Address Register 3 bit definition
OCTET3
OCTET4
OCTET5
Station Address Filter register
Address FF80 05C0
Station Address Filter register bit definition
Register hash table
Multicast hash table entries and bit definitions
Address FF80 05D0
Address FF80 05D4
Address FF80 05D8
Address FF80 05DC
HT2 bit definition
HT3 bit definition
Calculating hash table entries
W . d i g i . c o m
Page
W . d i g i . c o m
Page
Serial Controller Module
Supported features
RTS, CTS, DTR, DSR, DCD, RI
Serial port block diagram
Bit-rate generator
Uart mode
Serial protocols
SPI mode
Fifo management
Transmit Fifo interface
Operating in Endian modes
Terminology What’s being written Value
Processor interrupts vs. DMA
Receive Fifo interface
Using processor interrupts
Using DMA
SPI master mode
Signals
Configuration
SPI master transmitter
SPI slave mode
SPI master receiver
Signals
SPI slave transmitter
SPI slave receiver
General-purpose I/O configurations
SPI slave mode 0 and 1 two-byte transfer
Configuration
Operating Mode Serial Port Maximum Rate
Serial port performance
N f i g u r a t i o n
Serial Channel registers
Serial Channel 1, 2 Control Register a
Address FFD0 0000
Serial Channel Control Register a
Parity enable
Stick parity
Even parity select
Number of stop bits
Enable the transmitter with active CTS
Remote loopback
Local loopback
General-purpose output 1/General-purpose
Enable receive DMA requests
Data terminal ready active
Request-to-send active
Receiver interrupt condition
Receiver interrupt enable bits
Enable transmit DMA requests
Receiver interrupts
Transmitter interrupt condition
Transmitter interrupt enable bits
Transmitter interrupts
Serial Channel 1, 2 Control Register B
Address FFD0 0004
Serial Channel Control Register B bit definition
Enable receive character GAP timer
SCC mode
Rcgt
Bitordr
Enable active RTS only while transmitting
Transmit encoding
Receive data encoding
Differential Manchester 111. a 1 is
Serial Channel 1, 2 Status Register a
Address FFD0 0008
Serial Channel Status Register a bit definition
Character Match1
Character Match2
Character Match3
Buffer GAP timer
Character GAP timer
Bgap
Cgap
Current ring indicator state
DCD
Current data carrier detect state
Current data set ready state
Receive framing error interrupt pending
Receive parity error interrupt pending
Receive break interrupt pending
Receive overrun interrupt pending
Rrdy
Receive register ready interrupt pending
Receive Fifo half-full interrupt pending
Receive buffer closed interrupt pending
Receive Fifo full
Change in DCD interrupt pending
Change in RI interrupt pending
Change in DSR interrupt pending
Change in CTS interrupt pending
Transmit register empty interrupt pending
Transmit Fifo half-empty interrupt pending
Transmit buffer closed interrupt pending
Serial Channel 1, 2 Bit-Rate registers
Address FFD0 000C / 4C
Tempty
Bit-rate generator enable
Timing mode
Serial Channel Bit-Rate register bit definition
Receive clock source
Transmit clock source
Drive receive clock external
Drive transmit clock external
Clkmux
BRG input clock
Transmit clock invert
Receive clock invert
If Dpll is not used and you are not using
If Dpll is not used but you are using
When Dpll is used in the application,
Tdcr
Rdcr
Receive divide clock rate
Tics
Transmit internal clock source
Rics
Receiver internal clock source
With the 18.432MHz crystal using Xtale as the clock source
Max baudrates with different clock sources
Nreg
With the 18.432MHz crystal using Sysclk as the clock source
16X @ 55.296MHz
X1 mode X8 mode X16 mode
Serial Channel 1, 2 Fifo registers
Address FFD0 0010
Bit rate examples
Serial Channel 1, 2 Receive Buffer Gap Timer
Address FFD0 0014
Data
Data
Serial Channel 1, 2 Receive Character Gap Timer
Register diagram and bit assignment
Serial Channel Receive Buffer Gap Timer bit definition
Address FFD0 0018
Serial Channel Receive Character Gap Timer bit definition
CT value
Serial Channel 1,2 Receive Match register
Serial Channel 1, 2 Receive Match Mask register
Address FFD0 001C / 5C
Address FFD0 0020
Serial Channel Receive Match Mask register bit definition
RMMB1
RMMB2
RMMB3
Page
Electrical Characteristics
DC characteristics
Recommended operating conditions
Recommended operating thermal conditions
Sym Parameter Conditions Min Typ Max Unit
Input/Output characteristics
Pad pullup and pulldown characteristics
DC characteristics inputs
DC characteristics outputs
Internal pullup characteristics
AC characteristics
AC electrical specifications
Absolute maximum ratings
Maximum voltage ratings
Estimated Signal Load pF Device loads
System loading details
PORTA3, PORTA1, PORTC3, PORTC1
MDC, MDIO, TXEN, TXER, TXD30
Oscillator Characteristics
Signal Derating ns/pF
Output buffer derating by load capacitance
MDC, TXD30, TXER, TXEN, TDO
NS7520
Timing Diagrams
TimingSpecifications
Resettiming
Reset timing parameters
Num Description Min Typ Max Units
Sram timing
Sram timing parameters
Num Description Min Max Unit
Sram read
CS* controlled read wait =
Sram burst read
CS* controlled read wait = 0, Bcyc =
Sram write
CS controlled write internal and external, wait =
Sram burst write
Sram OE read
OE* controlled read wait =
Sram OE burst read
Sram WE write
WE* controlled write wait =
Sram WE burst write
Sdram timing
Sdram timing parameters
Sdram read
Sdram read, CAS latency =
Active Read Inhibit Prechg Bterm
Sdram burst read
Sdram burst read
Sdram write
Sdram write
Sdram burst write
Sdram burst write
Sdram load mode
Sdram refresh
FP Dram timing
FP Dram timing parameters
FP Dram read
Fast Page read
FP Dram burst read
Fast Page burst read
FP Dram write
Fast Page write
FP Dram burst write
Fast Page burst write
Fprefreshcycles
Fast page refresh Rcyc =
CAS3 CAS2 CAS1 CAS0 RF1 RF2 RF3 RF4 RF5 RF8
Ethernet timing
Ethernet timing parameters
Ethernet PHY timing
Ethernet cam timing
Jtag arm ice timing diagram
Jtag timing
Jtag arm ice timing parameters
Num Description Min Max Units
Jtag bscan timing diagram
Jtag bscan timing parameters
External DMA timing
External DMA timing parameters
Fly-by external DMA
Memory-to-memory external DMA
Serial internal timing characteristics
Serial external timing characteristics
Serial internal/external timing
2T SYS
Synchronous serial internal clock
Synchronous serial external clock
Gpio timing diagram
Gpio timing
Gpio timing parameters
Page
Index
CPU
Non-Back-to-BackInter-Packet-Gap register
FP Dram
Portc
NET+ARM
PORTC0
Receiver interrupts 229 transmitter interrupts
Undefined exception 32
Page