FR-F500
This section is specifically about safety matters
Safety Instructions
Additional instructions
Treat as industrial waste
Emergency stop
Contents
104
100
102
103
Watt-hour meter clear/actual operation hour meter clear
163
195
184
192
Chapter
Chapter Outline
Pre-Operation Information
Precautions for operation
Installation
Wiring
Name Description
Basic Configuration
Basic configuration
Japanese Harmonic Suppression Guideline
Without front cover
Structure
Appearance and structure
Front view
FR-F520-0.75K to 11K, FR-F540-0.75K to 11K
Removal and reinstallation of the front cover
FR-F520-30K to 55K, FR-F540-30K to 55K
Removal and reinstallation of the operation panel
Chapter
97inches1.97inches
Installation
Instructions for installation
Clearances around the inverter
Vertical mounting
Wiring cover and handling 22K or less
For installation in an enclosure
NFB
Description of control circuit terminals
Symbol Terminal Name Description
Type Symbol Terminal Name Description
Description of main circuit terminals
IPF
Type
Terminal Name Description
RUN
Inverter Capacity 75K 5K or more
Wiring of the main circuit
Wiring instructions
Overall wiring length 1.5K or more
Motor Capacity Ground Cable Gauge 200V class 400V class
FR-F520-11K
Terminal block layout
FR-F520-1.5K, 2.2K, 3.7K FR-F520-45K
FR-F520-5.5K, 7.5K FR-F520-55K
Terminal names in parentheses are those of the EC version
400V class FR-F540-0.75K, 1.5K, 2.2K, 3.7K FR-F540-30K, 37K
FR-F540-5.5K, 7.5K, 11K FR-F540-45K, 55K
FR-F540-15K, 18.5K, 22K
Cables, crimping terminals, etc
Connection of the power supply and motor
Model FR-F520-5.5K to 55K, FR-F540-5.5K to 55K
Connection procedure
Model FR-F520-0.75K to 3.7K, FR-F540-0.75K to 3.7K
Terminal screw size M3.5 Tightening torque 1.2 N⋅ m
Wiring of the control circuit
Changing the control logic
Current flow related to RUN signal
How to use terminals STOP, CS and PC
System configuration example
Connection to the PU connector
Recommended cable connector
PU connector pin-outs
Max m
Wiring method
Wiring of one RS-485 computer and one inverter
RS-485 terminal Computer
Connection of the FR-BU brake unit option
Connection of stand-alone option units
Connection of the conventional BU brake unit option
Connection of the FR-HC high power factor converter option
Connection of the power factor improving DC reactor option
Connection of the FR-RC power regeneration converter option
MC1
Interlock Power Supply MC2 Leakage current
Design information
Harmonics RF Noise
Other wiring
Power harmonics
Class Circuit Type
Received Power 5th 7th 11th 13th 17th 19th 23rd Over 23rd
Japanese harmonic suppression guidelines
Conversion Factors for FR-F500 Series
Equivalent Capacity Limits
Harmonic Content Values at the fundamental current of 100%
FR-HC
Harmonic suppression techniques
ACL, DCL
Inverter-generated noises and reduction techniques
Bundle them
Data line filter
Noise Path Measures
Following measures must be taken
Its Reduction by Noise Filters
Noise Induced to Signal Cables by Inverter Output
Data examples
Noise Terminal Voltage of Inverter and Example
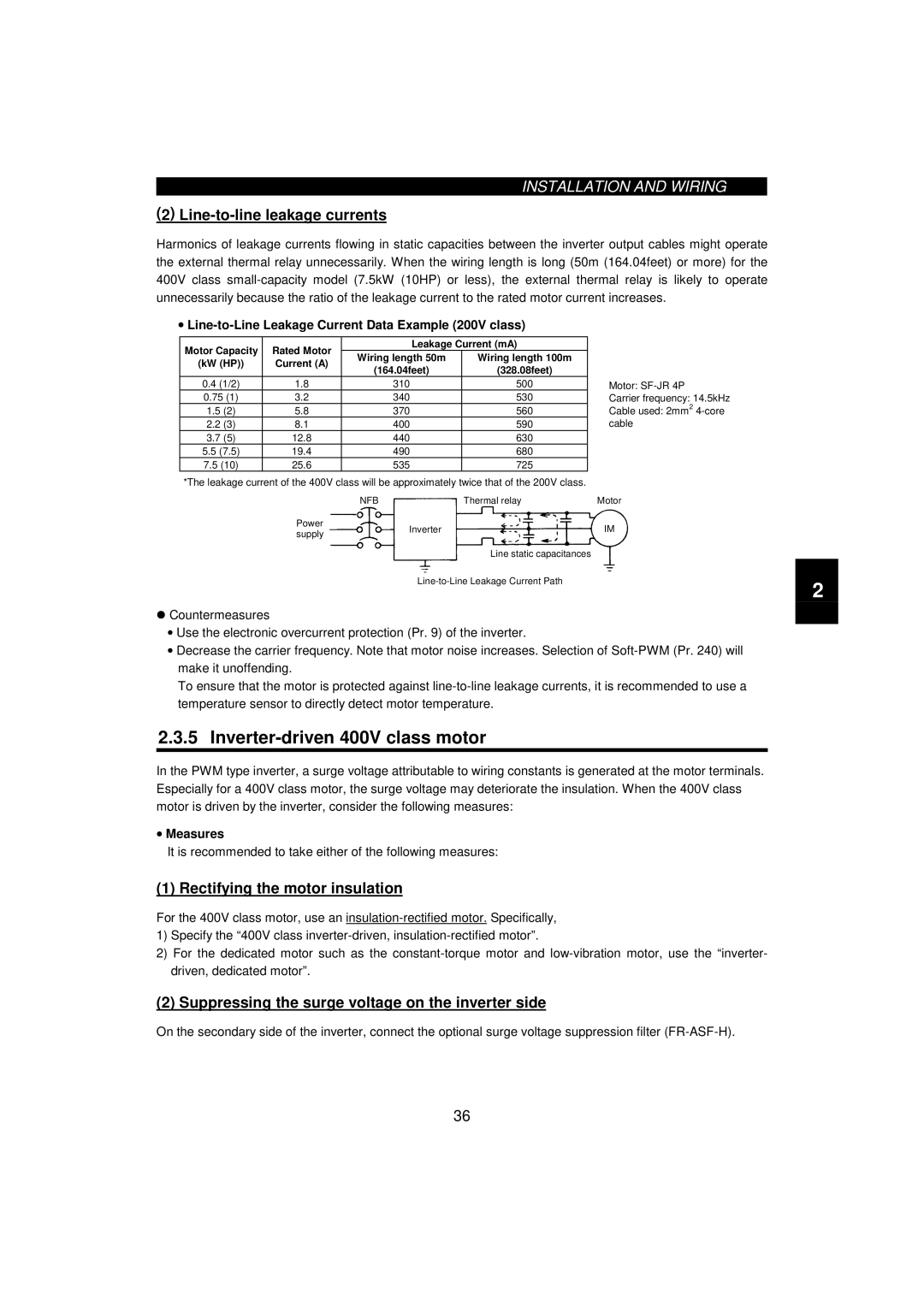
# Countermeasures
Leakage currents and countermeasures
To-ground leakage currents
# Example of counter measures against noise
Suppressing the surge voltage on the inverter side
Inverter-driven 400V class motor
Line-to-line leakage currents
Rectifying the motor insulation
400V class
Peripheral devices
Selection of peripheral devices
Example
Short circuit ratings
Standard to comply UL 508C 1 Installation
Wiring of the power supply and motor
Branch circuit protection
Our view of transistorized inverters for the EMC Directive
Instructions for compliance with the European standards
Motor overload protection
EMC Directive
Maximum Altitude 000 m 10,000 m
Low Voltage Directive
During operation Storage During transportation
90% RH or less
Unit mm2
Earthing EC version
Earthing and Earth Leakage Current
Earthing methods
OPERATION/CONTROL
Devices and parts to be prepared for operation
External operation mode factory setting
PU operation mode
External/PU combined operation mode
Communication operation mode
Before switching power on, check the following
Power on
Unit indications, operating status indications
Operation Panel
Names and functions of the operation panel FR-DU04
Key indications
Monitoring
Frequency setting
Used to set the running frequency in the PU operation mode
Parameter setting method
Alarm history
Operation mode
Help mode
User clear
Alarm history clear
Parameter clear
All clear
#Parameter setting mode
Copy mode
Pr user group read selection
Parameter Checking and Setting
Simple mode parameter list
Parameter checking
Name Application
Parameter Factory Setting
Main parameter settings
Setting of maximum frequency Pr maximum frequency
Setting of minimum frequency Pr minimum frequency
0Hz at 4mADC, 60Hz at
Application Setting
Selection of load pattern Pr load pattern selection
Gain
Pre-operation checks
Operation
Description Image
Operation at 60Hz
External jog operation
Motor is decelerated to a stop
PU jog operation
Start Press
Stop Press
Hold down the key to change the frequency
Decelerates when Pr = 9999 to a stop
Step Description
Start
Parameters
Parameter list
Parameter List
Setting Tion
F4 fourth frequency voltage
Minimum Factory Refer Cust Func Parameter Setting
PID
Can be accessed when Pr =
Function rewrite prevention
List of Parameters Classified by Purposes of Use
Torque boost Pr , Pr
Setting
Parameter Factory Setting Range Remarks
Parameter Function Details
120Hz To 120Hz
Pr maximum frequency Pr minimum frequency
Use Pr to set the lower limit of the output frequency
9999 To 120Hz Function invalid
Base frequency, base frequency voltage Pr , Pr , Pr
8888
60Hz To 120Hz 30Hz 10Hz 24 to 9999
Parameter Factory Setting Setting Range Remarks
Multi-speed operation Pr to Pr , Pr to Pr.27
Acceleration/deceleration time Pr , Pr , Pr , Pr , Pr , Pr
To 3600 s minimum setting increments 0.1 s
To 360 s minimum setting increments 0.01 s
Factory Setting Range Remarks
Decelerationtime s
Electronic overcurrent protection Pr
Pr electronic thermal O/L relay
Acceleration
To 10 s
DC injection brake Pr to Pr
Operated at
Value Operated
5Hz To 60Hz
Starting frequency Pr
Pr starting frequency
Pr load pattern selection
Parameter Factory Setting Range
Output Characteristics
Load pattern selection Pr
Related parameters
Pr jog acceleration/deceleration timereference frequency
Jog operation Pr , Pr
Pr jog frequency
Pr MRS input selection
Wiring example
Pr Setting Specifications of MRS Signal
MRS input selection Pr
149
Parameter Number Factory Setting Setting Range Remarks
Stall prevention Pr , Pr , Pr , Pr , Pr , Pr
To 120Hz 148
Compensated
Multi-speed input compensation Pr
Pr multi-speed input compensation
Not compensated
Function Description
Acceleration/deceleration pattern Pr , Pr.140 to Pr.143
Pr regenerative function selection
Setting When using the brake unit, power return converter
When using the high power factor converter FR-HC
Regenerative brake duty Pr.30
Pr.3335Hz Pr.3430Hz
Frequency jump Pr to Pr
144 4, 6, 8, 10 104, 106, 108
Pr speed display Pr speed setting switch-over
Running Speed Parameter Setting Unit Pr Setting
Speed display Pr , Pr
Pr up-to-frequency sensitivity
Factory Setting Setting Range Setting Capacity
Automatic torque boost Pr , Pr
Up-to-frequency sensitivity Pr
Output frequency detection Pr , Pr , Pr
Output Signal
6Hz To 120Hz 9999 Same as Pr Setting
Output Signal
Second stall prevention function is not activated
Pr Setting Operation
Second stall prevention Pr , Pr
120%
Set Pr to Pr and Pr in accordance with the following table
Parameter Number Factory Setting Setting Range
100
Output frequency monitor
Output current monitor
Set value 17, 24 monitor
To 120Hz Rated output
Setting Parameter
Monitoring reference Pr , Pr
Maximum output voltage of terminal AM is 10VDC
164
Parameter Factory Setting Remarks
9999 1 to No restart
Frequency 162 Search No frequency 163
To the load inertia moment, torque 165
Parameter Setting Description
Pr remote setting function selection
Remote setting function selection Pr
FrequencyOutput
Ordinary operation
Intelligent mode selection Pr
Pr intelligent mode selection
Operation Mode Description Automatically Set
Setting Reference Current
Setting Pr Reference I for intelligent mode
Pr Ref. I for intelligent mode accel
Pr Ref. I for intelligent mode decel %
P24
Use Pr to select alarms to be reset for retry
Errors Reset for Retry Setting
Retry function Pr , Pr to Pr
To 10 times Not output 101 to Output
Use Pr to set the number of retries at alarm occurrence
Retry is not made
Motor
Applied motor Pr
Pr applied motor
Refer to the following list and set the parameters
Pr PWM frequency selection Pr Soft-PWM setting
Parameter Factory Setting Description
PWM carrier frequency Pr , Pr
To 5, 10 to
Voltage input Pr
Pr 0-5V/0-10V selection
Related parameters
Pr filter time constant
Reset Selection PU Disconnection Detection
Input filter time constant Pr
Key from the PU during
Pr Setting Output Terminals
Alarm code output selection Pr
Pr alarm code output selection
Alarm code output
Parameter Name
Pr parameter write disable selection
Parameter write inhibit selection Pr
Pr reverse rotation prevention selection
Reverse rotation prevention selection Pr
To 4, 6 to
Operation mode selection Pr
Pr operation mode selection
External signal input terminal STF, STR
X12 MRS Function/Operation
Switch-over mode
PU operation interlock
X12 MRS
Operation mode external signal switching function
X16 Signal Operation Mode
Operating Condition
Parameter Number
Confirm the settings of Pr , Pr and Pr
38 V/F control frequency voltage Pr to Pr
Computer link operation Pr to Pr
123 9999 To 150ms 124
Parameter Factory Setting Range Number
Parameter Description Setting
117 118 192 119 Data length 120 121 To 10 122 9999
Data format
Required after no data error ACK. Refer to
Computer programming Communication protocol
Control codes
Data definitions
Reply data from inverter to computer during data read
Send data from computer to inverter during data read
Stop bit length Bit Bits Data length Parity check
Response time
= Data sending time s
Number of Bits
HFF
Instruction Data
H7F
Return
Instructions for the program
Instruction
Setting items and set data
H6D
HFA
H7A
H6E
HEC
Error Code List
Error Definition Inverter Operation
H6C
Operation Mode Operation Location
Communication specifications for RS-485 communication
Operation at alarm occurrence
Communication error
Pr = 20
Setting Basic PID control configuration
PID control Pr to Pr
Pr = 10
PID action overview
Reverse action Forward action
Sink logic
Pr =
Deviation
Entry Description
O signals
Signal
Function Description Remarks
132
Parameter setting
Adjustment procedure
Gain K = 1/proportional band 9999
Start
Calibration example
Detector output calibration
Set point input calibration
138 139 9999 To 60.0Hz No automatic
135 136
137
NFB MC1
Sink logic, Pr = 7, Pr = 6, Pr = 17, Pr = 18, Pr =
Roles of the magnetic contactors MC1, MC2, MC3
Signals
Magnetic Place of Installation Role
Signal Terminal Used Description
Sets the MC2 and MC3 operation interlock time
Parameter Name Setting Description
Commercial power To 60.0Hz 139
Operation sequence
OFF OFF →
Operation procedure
Operation procedure for running Operation pattern
Signal on-off after parameter setting
Pr to Pr % Refer to Pr Pr , Pr % Refer to Pr
Related parameters Pr to Pr
Zero current detection Pr , Pr
Zero current detection level
Zero current detection period
Pr stall prevention operation selection
RT signal activated condition selection Pr
Pr RT signal activated condition
Stall prevention function and current limit function Pr
101 Driving
#...Operation not #...Not activated Acceleration
Deceleration
100 Driving
Related parameters Pr RUN terminal function selection
OL signal output timer Pr
Pr OL signal waiting time
157 To 25 s No signal output
Batch deletion
User group selection Pr , Pr to Pr
Examples of use
160 9999 10, 11 173 174
Jog operation selection JOG
Input terminal function selection Pr to Pr
184 Current input selection AU For the NA and EC 185
Setting Signal Functions Relevant Parameters
Refer to the following table and set the parameters
Output terminal function selection Pr to Pr
Sleep
Commercial power supply Inverter switch-over MC1
Commercial power supply Inverter switch-over MC3 125
FAN
199
User initial value setting Pr
Pr users initial value setting
Setting example
Pr cooling fan operation selection
Output phase failure protection selection Pr
Pr output phase failure protection selection
Cooling fan operation selection Pr
150%
Override bias/gain Pr , Pr
Pr override bias Pr override gain
50%
Advanced PID control Pr to Pr NA, EC versions only
Pr =1
Pr motor switch-over selection = 0 Basic Method
Pr motor switch-over selection = 1 Alternative Method
Pr =0
Pr motor switch-over selection = 0 Basic Method Example
Pr motor switch-over selection = 2 Direct Method
System configuration
DC24V
Parameter Number Name
Parameter Number Name Additional Setting Description
Signal name Function
Start
Motor switch-over timing
Start Stop
Name Setting Range
Stopstart
Output stop detection
Sleep
Status transition chart
M1 operation
Supply operation
Commercial power
EC version 50Hz
Calibration of terminal AM
Meter frequency meter calibration Pr , Pr
Pr FM terminal calibration Pr AM terminal calibration
Calibration of terminal FM
When operation panel FR-DU04 is used
Operation procedure
To 20mA To 120Hz
Frequency setting voltage current bias and gain Pr to Pr
902 0Hz To 60Hz 903
904 4mA 0Hz To 20mA To 60Hz 905
Mode
Power-on monitoring mode
Mode
Least significant
#Parameter setting mode
#Setting change
⋅ 9 times
To 90 to Current setting of gain frequency
Press to change the set frequency Press for 1.5 s
# Analog voltage A/D value % Across terminals
#Press
Once to display the current For 0V 0mA, 100% for
Analog voltage calibration value 5V 10V, 20mA
990 Without beep, 1 With beep
Buzzer control Pr
Pr buzzer control
Protective Functions
Major faults
Errors Alarms
Error alarm definitions
Decrease the acceleration time
OC During Dec
OV During Acc
Check for too slow acceleration
Remedy the instantaneous power failure
Instantaneous power failure is within 15ms
Find the cause of instantaneous power failure occurrence
Check for a ground fault in the motor and connection cable
Set the ambient temperature to within the specifications
Ground Fault
Output side ground fault overcurrent protection
Parameter storage device alarm
Option slot alarm 1 to
Check for a wrong option function setting and operation
Check the communication cable for wire breakage
CPU error
Find the cause of alarm occurrence
CPU Fault
Fault
Check for a short circuit in the PC terminal output
Check for a short circuit in the PU connector cable
Output phase failure protection
P24
Minor fault
Stop selection
Reduce the load volume or the frequency of operation
PU stop Stop made by pressing
Key of the PU has been set in Pr PU
Actual Digital
To know the operating status at the occurrence of an alarm
Correspondences between digital and actual characters
Key to reset the inverter
Alarm code output
Resetting the inverter
Motor rotates in opposite direction
Troubleshooting
Speed greatly differs from the setting
Motor remains stopped
Speed does not increase
Operation mode is not changed properly
Power lamp is not lit
Motor current is large
Periodic inspection
Precautions for Maintenance and Inspection
Precautions for maintenance and inspection
Check items
Daily and Periodic Inspection
Insulation resistance test using megger
Pressure test
Analog meter Converter Across terminals
Inspection Description Periodic Method Crlterlon Instrument
Disconnect cables
Tester Polarity Measured Value
Checking method
Module device numbers and terminals to be checked
Assumes the use of an analog meter
Smoothing capacitor in main circuit
Replacement of parts
Part Name Standard Replacement Interval Description
Cooling fan
Relays
Inverter replacement
Smoothing capacitors
Typical Measuring Points and Instruments
Measurement of main circuit voltages, currents and power
Measurement of voltages and currents
10VDC
Measuring Points and Instruments
Measuring Point
5VDC
Specifications
Model specifications
Standard Specifications
36.0
Voltage, frequency Permissible AC
Collector output
Common specifications
Setting To +10V, 11 bits/-5 to +5V
Alarm
Unit mm inches
Outline drawings
Unit mm inches
# FR-F520-5.5K, 7.5K, 11K # FR-F540-5.5K, 7.5K, 11K
W1 W2 H H1 FR-F540-30K,37K 340 270 320 550 195 71.5
Inverter Type FR-F520-37K 340 270 320 550 530 195 71.5
FR-F520-45K 450 380 430 550 525 250 154
FR-F520-55K 480 410 460 700 675 250 154
# Operation panel FR-DU04
Outline drawing Panel cutting dimension drawing
Chapter Options
Stand-alone options
Option List
193
Name Type Function
Inboard dedicated options
Appendices
Read
Appendix Data Code List
Multi-speed setting speed
Data Codes
PID
118 Communication speed
Read Write
Name Read
Func
Auxiliary motor stop delay frequency
Motor switch-over selection
Output stop cancel process value level
Auxiliary motor start delay frequency
Print Data Manual Number Revision
Manual number is given on the bottom left of the back cover