Serial #
Manuale del proprietario e dinstallazione
Before You Throw Away Your Old Refrigerator or Freezer
How to Connect Electricity section
Refrigerants
Mains lead replacement
HOW to Connect Electricity
Ambient Room Temperature Limits
About the temperature controls
Unit will have one of the temperature controls shown below
Refrigerator temperature cannot be changed during TurboCool
How to Use
About TurboCool
How it Works
About CustomCool. on some models
How to Use
ExpressThaw ExpressChill
CustomCool Chart
Installing the Filter Cartridge
When to Replace the Filter
About the water filter
Water Filter Cartridge on some models
About the shelves and bins
About the refrigerator doors
Refrigerator Doors
Refrigerator Door Bins and Freezer Door Tilt-Out Bins
QuickSpace Shelf
Slide-Out Spillproof Shelf
Removable Beverage Rack
Freezer Baskets
Divider Deep Freezer Baskets
Slide-Out Freezer Shelves
Fixed Freezer Shelves
Loading the Freezer Compartment
About the freezer compartment
Freezer Performance
About crisper removal
About the crispers and pans
Automatic Icemaker
About the automatic icemaker
Ice Storage Drawer
To Use the Dispenser
About the ice and water dispenser. on some models
Locking the Dispenser on some models
Dispenser Light on some models
Cleaning the Outside
Care and cleaning of the refrigerator
Cleaning the Inside
Ice Storage Drawer on Dispenser Models
Preparing for Vacation
Behind the Refrigerator
Preparing to Move
Freezer Compartment
Replacing the light bulbs
Dispenser
This light is located above the top drawer
Panels less than 6 mm thick
Trim kits and decorator panels
Mm or Raised Panel
Read these instructions completely and carefully
Freezer Panel Without Dispenser With Dispenser
Dimensions for Custom Wood Panels
Insert the Bottom Freezer Panel on dispenser models
Inserting the door panels
Attach the Top Trim on the Freezer and Refrigerator Doors
These pieces are tucked inside the refrigerator door handle
Install the Side Trim
Removing the Doors
Removing and replacing the doors
Replacing the Doors
Before YOU Begin
Dimensions
Refrigerator Location
Clearances
To adjust the rollers on 21′ and 23′ models
To adjust the rollers on 25′, 27′ and 29′ models
Rollers
Door Alignment
For Built-In Style models
Dimensions and Specifications
Reattach the access cover
Installing the Water Line
Before YOU Begin
Connect the Tubing to the Refrigerator
Start the Icemaker
Turn the Water on and Plug in the Refrigerator
You may hear the fans spinning at high speeds
Normal operating sounds
New high efficiency compressor may run faster
Cycle, you may hear the ice cubes dropping into
Problem Possible Causes What To Do
Before you call for service…
Ice cubes have
See Care and cleaning
Odor/taste
Small or hollow cubes
Actual temperature not
Temperatures are OK
Equal to Set temperature
Select Temp feature is
Important Safety Instructions
Special Safety Instructions for Australia and New Zealand
Shut Off the Main Water Supply
Before You Begin
Connecting the Tubing to the Refrigerator
Connecting the Tubing to the Shutoff Valve
Plug In the Refrigerator
Turn the Water On
Start the Icemaker
Page
Fonctionnement
Réfrigérants
Avant de jeter votre vieux réfrigérateur ou congélateur
Branchement Électrique
Remplacement du cordon d’alimentation
Classe de Symbole Température ambiante Maximale Minimale
Les commandes de température des
Limites de température ambiante dans la pièce
Pas l’alimentation électrique du réfrigérateur
Commandes de Température interne Commande cadran Interne
Les commandes de température
Au sujet de TurboCool
Les commandes de température suite
Fonctionnement
Utilisation
Comment il fonctionne
Au sujet de CustomCool. sur certains modèles
Comment l’utiliser
Tableau CustomCool
Le filtre à eau
Installation de la cartouche du filtre
Cartouche du filtre à eau
Quand remplacer le filtre
Étagères et bacs
Les portes du réfrigérateur
Portes du réfrigérateur
Dispositif de retenue de bouteille
Panier mobile à breuvage
Étagère QuickSpace
Support à bouteilles de vin/boissons sur certains modèles
Étagère coulissante anti-déversement
Paniers du congélateur
Paniers du bas du congélateur
Étagères de congélateur coulissantes
Clayettes de congélateur fixes
Performance du congélateur
Compartiment congélateur
Chargement du compartiment congélation
Retrait des conteneurs
Les tiroirs et conteneurs à légume
Tiroir à glaçons
Machine à glaçons automatique
Pour obtenir de la glace, tirez le tiroir vers
’avant
Pour utiliser le distributeur
Le distributeur d’eau et de glaçons. sur certains modèles
Verrouillage du distributeur
Eclairage du distributeur
Tiroir à glace
Entretien et nettoyage du réfrigérateur
Nettoyage de l’extérieur
Nettoyage de l’intérieur
Départ en vacances
Derrière le réfrigérateur
Déménagement
Compartiment réfrigérateur-lampe supérieure
Remplacement des ampoules
Compartiment réfrigérateur-lampe inférieure
Compartiment congélateur
Panneaux de moins de 6 mm d’épaisseur
Kits de moulures et de panneaux décoratifs
Panneau de 19 mm ou surélevé
Veuillez lire toutes les directives attentivement
Panneau du Panneaux du Congélateur sans
Dimensions pour les panneaux de bois sur mesure
Distributeur
Insérez les panneaux du congélateur et du réfrigérateur
Installation des panneaux de porte
Installez la moulure latérale
Démontage des portes
Démontage et remontage des portes
Remontage des portes
Avant DE Commencer
Emplacement DU Réfrigérateur
Alimentation D’EAU DE LA Machine À Glaçons
Dégagements
Alignement DES Portes
Roulettes
Dimensions ET Spécifications
Installation DE LA Conduite D’EAU
Avertissement
Avant DE Commencer
Branchez LE Tuyau À Votre Réfrigérateur
Installation DE LA Conduite D’EAU Suite
Remettez le couvercle d’accès
Ouvrez LE Robinet D’EAU ET Branchez LE Réfrigérateur
Mettez EN Marche LA Machine À Glaçons
CustomCool
Bruits normaux de fonctionnement
Sur les modèles équipés d’une machine à glaçons
Après un cycle de fabrication de glaçons, vous pouvez
Problème
Avant d’appeler un réparateur…
Problème Causes possibles Correctifs
Signal sonore
Consultez Remplacement des ampoules
En éclaboussant
Fonctionne, mais ne
Les aliments ne se
La commande de
Dégèlent pas/ne se
Refroidissent pas
Instrucciones de seguridad Instrucciones de manejo
Freezer
Refrigerantes
Antes de desechar su antiguo frigorífico o
Reemplazo del cable
Cómo Conectar LA Electricidad
Rango de Símbolo Temperatura Ambiente Máximo Mínimo
Límites de temperatura ambiente en el entorno
Controles de Temperatura interna
Los controles de la temperatura
Controles de ajuste Externos
Cómo funciona
TurboCool
Cómo usar
Cómo utilizarlo
CustomCool. en algunos modelos
El gráfico CustomCool
Instalar el cartucho del filtro
El filtro de agua
Tapón de derivación del filtro
¿Cuando se debe reemplazar el filtro?
Los estantes y recipientes del frigorífico
Puertas del frigorífico
Puertas del frigorífico
Recipiente para botellas
Estante QuickSpace
Estante deslizable a prueba de derramamientos
Colgador de bebidas extraíble
Estante de vino/bebidas en la puerta en algunos modelos
Cestas del congelador
Divisor Cestas hondas del congelador
Estantes deslizantes del congelador
Estantes fijos del congelador
Cómo llenar el congelador
El compartimento del congelador
Rendimiento del congelador
Las bebidas gaseosas no deben guardarse en el congelador
Gavetas para frutas y vegetales
Gavetas y recipientes
Gavetas con humedad ajustable
Recipiente convertible para carnes
Advertencia Conéctelo
El dispositivo automático para hacer hielo
Cajón de almacenamiento de hielo
Dispositivo automático para hacer hielo
Para usar el dispensador
El dispensador de agua y de hielo. en algunos modelos
Para bloquear el dispensador
Luz del dispensador en algunos modelos
Limpiar el exterior
Cuidado y limpieza del frigorífico
Limpiar el interior
Preparación para vacaciones
Atrás del frigorífico
En caso de mudanza
Compartimento del frigorífico-Luz inferior
Reemplazo de bombillas
Compartimento del congelador
Dispensador
Paneles de menos de 6 mm de espesor
Molduras y paneles decorativos
Panel de 19 mm o panel levantado
Lea las instrucciones completamente y debidamente
Panel del congelador Paneles del Sin dispensador Congelador
Dimensiones de los paneles de madera hechos a medida
Las áreas superiores de los paneles necesitan recortarse
Inserte el panel del congelador y panel del frigorífico
Cómo insertar los paneles de la puerta
Lea las instrucciones completa y detenidamente
Instalación de la moldura lateral
Cómo retirar las puertas
Cómo retirar y reemplazar las puertas
Cómo reponer las puertas
Ubicación DEL Frigorífico
Antes DE Iniciar
Área
Alineación DE LAS Puertas
Rodillos
Instalación DE LA Toma DE Agua
Dimensiones Y Especificaciones
Antes DE Empezar
Sólo a tomas de agua potable
Vuelva a colocar la cubierta de acceso
Conecte EL Tubo AL Frigorífico
Hielo
Encienda EL Agua Y Conecte EL Frigorífico
Sonidos normales de operación
Antes de solicitar un servicio…
Problema Causas Posibles Qué hacer
Para hacer hielo no
Dispositivo automático
Vea Instalar la línea de agua
El dispensador de hielo
Dispositivo para hacer
Hielo picado No sale agua pero el
Hielo funciona
El agua chorrea del
No funciona la luz
Del frigorífico
Interior
Vea Reemplazar las bombillas
Notas
108
Istruzioni per l’uso
Di alcuni problemi -142 Rumorosità normali di funzionamento
Refrigeranti
Prima di smaltire il vecchio freezer/frigo
Sostituzione dei cavi principali
Collegamento Elettrico
Classi di Simbolo Temperatura ambiente Massime Minime
Limiti delle temperature ambiente
Molto Temperata 32C 10C 16C Sub-Tropicale 38C 18C 43C
Regolazione delle temperature
Modo di impiego
Come funziona
Come funziona il CustomCool
Istruzioni per l’uso del CustomCoolsolo in alcuni modelli
Come si usa
Tabella per l’uso del CustomCool
Istruzioni per il CustomCoolsolo in alcuni modelli
Istruzioni per il filtro dell’acqua
Installazione della cartuccia del filtro dell’acqua
Cartuccia del filtro dell’acqua
Quando cambiare il filtro
Porte del frigorifero
Istruzioni per le porte del frigorifero
Ferma bottiglie
Contenitori larghi
Ripiano retrattile di QuickSpace
Ripiani scorrevoli raccogligocce
Rastrelliera rimovibile per le bottiglie
Ripiano per vino e bevande sulla porta su alcuni modelli
Divisore Cestelli profondi del freezer
Ripiani e cestelli
Cestelli del freezer
Ripiani del freezer estraibili
Riempimento del freezer
Come utilizzare il freezer
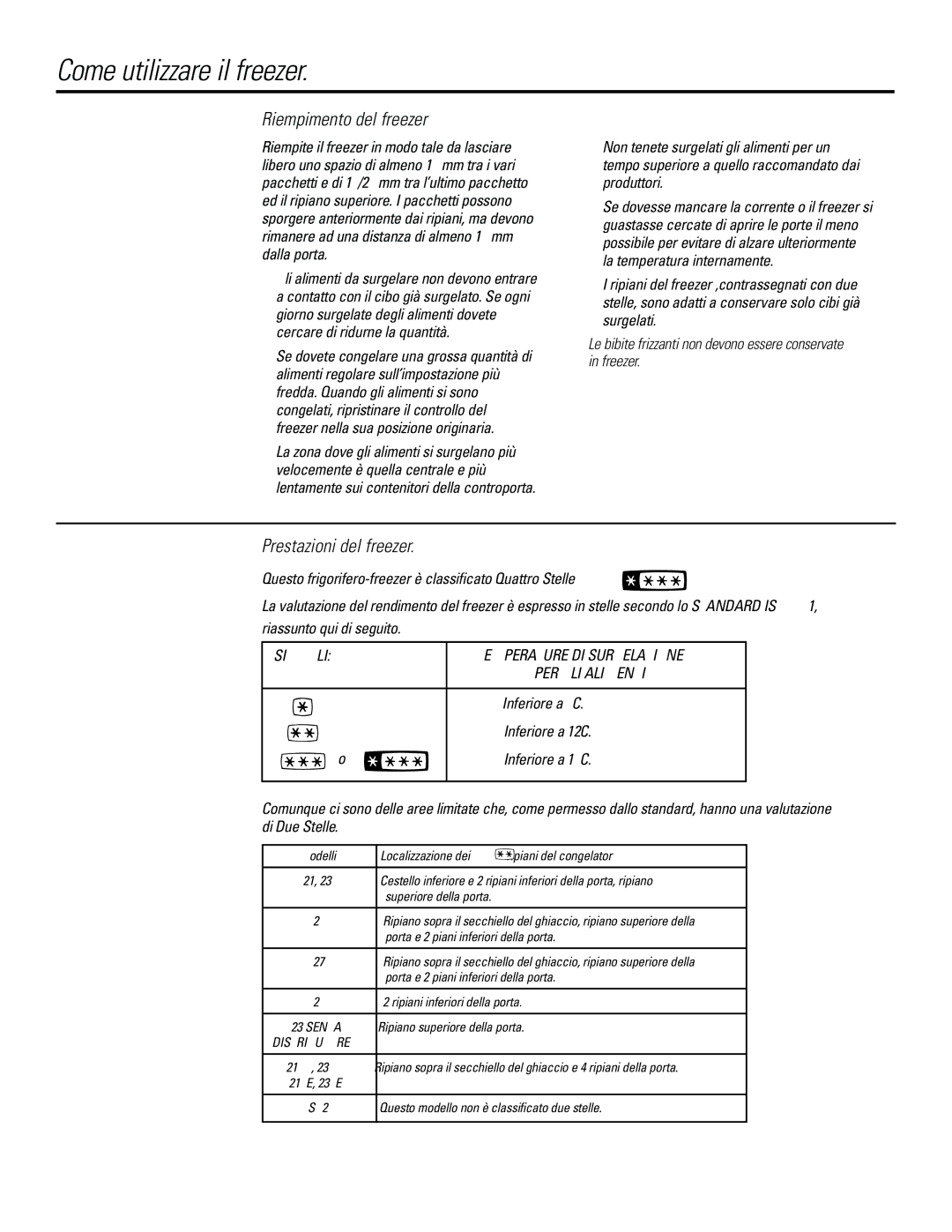
Prestazioni del freezer
Le bibite frizzanti non devono essere conservate in freezer
Cassetti per frutta e verdura
Informazioni sui ripiani e cassetti
Regolazione dell’umidità
Cassetto a temperatura convertibile per la carne
Fabbricatore di ghiaccio automatico
Fabbricatore automatico di ghiaccio
Cassetto del ghiaccio
Allacciatevi solo ad acqua potabile
Come usare il distributore
Distributore di acqua e ghiaccio solo in alcuni modelli
Blocaggio distributore in alcuni modelli
Produzione rapida di ghiaccio
Pulizia dell’esterno
Manutenzione e pulizia del frigorifero
Pulizia interna
Per estrarlo
Prima di un periodo di vacanze
Parte posteriore del frigorifero
Trasloco del frigorifero
Comparto frigorifero-luce superiore
Sostituzione delle lampadine
Comparto frigorifero-luce inferiore
Comparto freezer
Pannelli con spessore inferiore a 6 mm
Kit cornici e pannelli di rivestimento
Pannelli da 19 mm o con rilievo
Leggere attentamente e completamente e queste istruzioni
Pannello freezer senza Distributore Con distributore
Installazione del pannello del freezer e del frigorifero
Installazione dei pannelli delle porte
Leggere completamente e attentamente queste istruzioni
Le cornici laterali sono attaccate alle maniglie
Installazione della cornice laterale
Rimozione delle porte
Smontaggio e rimontaggio delle porte
Montaggio delle porte
Prima DI Iniziare
Dimensioni
Posizione DEL Frigorifero
Spaziature
Allineamento Dele Porte
Regolazione Delle Ruote
Le ruote hanno tre funzioni
Per regolare le ruote sui modelli 25, 27 e
Dimensioni E Specifiche solo modelli incorporati
Riattaccare il coperchio di accesso
Installazione Della Tubazione DELL’ACQUA
Prima DI Iniziare
Connessione solo a fonti di acqua potabile
Accendete IL Fabbricatore DI Ghiaccio
Whoosh
Rumorosità normali di funzionamento
Prima di chiamare l’assistenza…
Problemi Possibili Cause Cosa Fare
Lenta
Non funziona
Cubetti sono piccoli e
Irregolari
Funziona
Lacqua fuoriesce dal
Nessuna erogazione di
Acqua o ghiaccio
All’interno. Con tempo
Selezionate
Accendono
Vedere sezione Sostituzione lampadine
143
144
De série
Escreva aqui o modelo e o número de série
Congelador velho
Antes de jogar fora seu frigorífico ou
Frigorígenos
Substituição do condutor principal
Como Conectar a Electricidade
Classe de Símbolo Temperatura ambiente Máxima Mínima
Limites de temperatura do ambiente de funcionamento
Na medida do necessário para compensar tais factores
Sobre os controlos de temperatura
Como funciona
Sobre a função TurboCool
Como utilizar
Como utilizar
Sobre a função CustomCool. em alguns modelos
Diagrama da Função CustomCool
Cartucho do filtro de água
Sobre o filtro de água
Quando trocar o filtro
Instalação do cartucho do filtro
Sobre as prateleiras e recipientes
Sobre as portas do frigorífico
As portas do frigorífico
Retentor de garrafas
Porta-bebidas removível
Prateleira QuickSpace
Porta-vinho/bebidas da porta em alguns modelos
Cestas do congelador
Divisor Cestas da arca frigorífica
Prateleiras do congelador que deslizam para fora
Prateleiras fixas do congelador
Para carreguar do compartimento do congelador
Sobre o compartimento do congelador
Desempenho do congelador
Sobre a remoção dos compartimentos
Sobre os compartimentos e gavetas
Compartimentos de frutas e vegetais
Gaveta de carne conversível
Dispensador automático de gelo
Sobre o dispensador automático de gelo
Gaveta de armazenagem de gelo
Para ter acesso ao gelo, puxe a gaveta para a
Para utilizar o dispensador
Sobre o dispensador de gelo e água. em alguns modelos
Para trancar o dispensador
Luz do dispensador em alguns modelos
Gaveta de armazenagem de gelo nos modelos de dispensador
Manutenção e limpeza do frigorífico
Limpeza exterior
Limpeza do interior
Preparação para as férias
Parte traseira do frigorífico
Preparação para uma mudança
Compartimento do frigorífico Lâmpada inferior
Troca das lâmpadas
Compartimento do congelador
Compartimento do frigorífico Lâmpada superior
Painéis com menos de 6 mm de espessura
Remates e painéis decorativos
Painéis de 19 mm ou elevados
Leia estas instruções completa e cuidadosamente
As áreas no topo dos painéis devem ser cortadas dos painéis
Dimensões para os painéis de madeira feitos sob medida
Insira o painel do congelador e o painel do frigorífico
Instalação dos painéis das portas
Instale o remate lateral
Remoção das portas
Remover e recolocar das portas
Recolocação das portas
168
Localização do Frigorífico
Antes DE Começar
Vãos Livres
Dimensões
Alinhamento DAS Portas
Rodas
As rodas servem a três propósitos
Para ajustar as rodas nos modelos 25′, 27′ e 29′
Para os modelos Built-in Style
Dimensões E Especificações
Antes DE Começar
Instalação do Sistema DE Fornecimento DE Água
Conecte a Tubulação AO Frigorífico
ATENÇÃO! Conecte apenas a um fornecimento de água potável
Ligue O Dispensador DE Gelo
Ligue a Água E Insira a Ficha do Frigorífico NA Tomada
Sons normais de operação
Antes de chamar o serviço de atendimento…
Problema Causas possíveis Que fazer
Têm odor e/ou sabor
Os cubos de gelo
Veja Manutenção e limpeza
Congelação dos cubos
Do frigorífico
Há um odor a emanar
Porta não fecha bem
Forma-se humidade no
178
Modell- und Seriennr. hier eintragen Modell
Serie
Auch Abschnitt Elektrischer Anschluss
Kühlmittel
Den Kühlschrank oder Tiefkühltruhe entsorgen
Ersatz desHauptleitungsanschlusses
Elektrischer Anschluss
Temperaturregler an
Temperaturklasse Symbol Maximum Minimum
Raumtemperaturgrenzen
Raumtemperatur
Temperaturregler
Wirkungsweise
Temperaturregler Forts
Bedienungsweise
Bedienungsweise
CustomCool. an bestimmten Modellen
CustomCool Tabellen
Wasserfilter Patrone
Wasserfilter
Ersetzen des Filters
Einbau der Filterpatrone
Regale und Behälter
Kühlschranktüren
Kühlschranktüren
Kühlschrank Türbehälter und Gefrierfach Aufkippbehälter
QuickSpace Regal
Herausziehbares, rutschfestes Regal
Entfernbares Getränkegestell
Wein-/Getränkegestell in Tür bei manchen Modellen
Gefrierfach-Körbe
Trennwand Gefrierfach-Körbe
Herasuschiebbare Gefrierfach-Regale
Feste Gefrierfachregale
Beladung des Gefrierfachs
Das Gefrierfach
GefrierfachNutzleistung
Kühlhaltefach
Kühlhaltefächer und Schubladen
WARNUNG! Nur an
Automatischer Eismacher
Automatischer Eismacher
Eisschublade
Benutzung des Verteilers
Eis- und Wasserverteiler. an bestimmten Modellen
Wichtiges über den Verteiler
Eisschublade an Verteilermodellen
Pflege und Reinigung des Kühlschrankes
Reinigung des Abtropfregals
Reinigung der Innenseite
Ferienvorbereitungen
Hinter dem Kühlschrank
Umzug
Kühlschrank muss immer aufrecht stehen
Kühlschrankfach oberes Licht
Ersetzen der Glühbirne
Kühlschrankfach unteres Licht
Gefrierfach
Verkleidung unter 6 mm Dicke
Zierleisten und dekorative Verkleidungen
Mm oder überhöhte Verkleidung
Diese Anleitungen sorgfältig und vollständig lesen
Dimensionen für die sonderangefertigte Holzverkleidungen
Einsetzen der Verkleidung in die Gefrierfachtür
Einsetzen der Türverkleidung
Einsetzen der unteren Gefrierfachtürverkleidung
Anleitungen sorgfältig und vollständig lesen
Diese Teile befinden sich auf der Innenseite am Türgriff
Anbringen der seitlichen Leiste
Abnehmen der Tür
Abnehmen und Einsetzen der Türen
Einsetzen der Tür
VOR Beginn
Dimensionen
Wasserleitung ZUM Eismacher
Standort DES Kühlschrankes
Rollen
Installationsanleitungen
Türenabgleich
Für eingebaute Modelle
Dimensionen UND Spezifikationen
VOR Beginn
Installationsanleitungen Installation DER Wasserleitung
Anschluss DER Leitung AN DEN Kühlschrank
Trinkwasserleitung anschliessen
Wasser Anstellen UND Kühlschrank Einstecken
Eismacher Anstellen
Normale Betriebsgeräusche
Ehe Sie den Kundendienst anrufen
Problem Mögliche Ursachen Was kann man tun?
Eiswürfel haben einen
Häufiges Brummen
Geruch oder Geschmack
Siehe Pflege und Reinigung
Orange Kühlschrank hat einen
Gespendet Gefrierfach erscheint
Geruch
Tür lässt sich nicht
Anmerkungen
Serienr
Veiligheidsinformatie . . . . .214 Gebruiksaanwijzingen
Koelmiddelen
Waarschuwing
Vervanging van de hoofdkabel
Aansluiting OP HET Stroomnet
Grenzen omgevingstemperatuur
Temperatuurregeling CustomCool-modellen
Omgevingstemperatuur
Temperatuurklasse Symbool Maximum Minimum
Interne draaiknop Externe setpoint Bedieningselementen
Temperatuurregeling
Werking
Temperatuurregeling Vervolgd
Gebruiksaanwijzing
Gebruiksaanwijzing
CustomCool. sommige modellen
CustomCool-tabel
Waterfilter
Installatie van de filtercartridge
Cartridge van de waterfilter sommige
Vervanging van de filter
Rekken en bakken
Deuren van de koelkast
Deuren van de koelkast
Fleshouder
QuickSpace-rek
Uitschuifbaar morsvrij rek
Verwijderbaar drankrek
Deur Wijnrek/Drankrek met sommige modellen
Manden in vriesvak
Verdeling Manden in diepvriesgedeelte
Uitschuifbare rekken in vriesvak
Vaste rekken in vriesvak
Vullen van diepvriesgedeelte
Diepvriesgedeelte
Rendement van de diepvriezer
Verwijderen van het groentevak
Groentevakken en laden
Automatische ijsmachine
Automatische ijsmachine
IJslade
Trek de lade uit om bij het ijs te kunnen
Gebruiksaanwijzing voor de verdeler
IJs- en waterverdeler. sommige modellen
Vergrendelen van de verdeler
Belangrijke informatie in verband met de verdeler
Berglade voor ijs modellen met verdeler
Onderhoud en schoonmaak van de koelkast
Schoonmaken van de buitenkant
Schoonmaken van de binnenkant
Vakantieregeling
Achter de koelkast
Verhuizen
Koelgedeelte licht bovenaan
Vervangen van lampjes
Koelgedeelte licht onderaan
Diepvriesgedeelte
Minder dan 6 mm dikke panelen
Sierkits en decoratieve panelen
Paneel van 19 mm of verhoogd paneel
Lees alle instructies heel aandachtig
Paneel van vriesvak
Afmetingen van op maat gemaakte houten panelen
Zonder verdeler
Verdeler
Plaatsen van panelen van vriesvak en van koelgedeelte
Plaatsen van deurpanelen
Installeren van sierpaneel op zijkant
Verwijderen van de deuren
Verwijderen en terugplaatsen van de deuren
Terugplaatsen van de deuren
Plaats VAN DE Koelkast
Voordat U Begint
Vrije Ruimten
Afmetingen
Uitlijnen VAN DE Deuren
Wieltjes
239
Waarschuwing
Installatie VAN DE Waterleiding
Voordat U Begint
Buis OP Koelkast Aansluiten Vervolg
Ijsmachine Starten
Hoor jij wat ik hoor? Deze geluiden zijn normaal
Normale geluiden
Probleem Mogelijke oorzaken Oplossing
Voordat u met een monteur contact opneemt …
Voordat u met een monteur contact opneemt…
Hebt Cubed ICE
Maar de temperaturen
Oranje schijn
De koelkast ruikt
246
√‰ËÁ›Â˜ ÏÂÈÙÔ˘ÚÁ›·˜
248 æ˘ÎÙÈο
¶ÚÈÓ ÂÙ¿ÍÂÙ ÙÔ ·ÏÈfi Û·˜ „˘ÁÂ›Ô ‹ ÙÔÓ ·ÏÈfi Û·˜ ηٷ„‡ÎÙË
„ µÁ¿ÏÙ ÙȘ fiÚÙ˜ Î·È ÂÙ¿ÍÙ ÙȘ ͯˆÚÈÛÙ¿
„ ∂¿Ó ÙÔ „˘ÁÂ›Ô ¤¯ÂÈ ÎÏÂȉ·ÚÈ¿, ·¯ÚËÛÙ¤„Ù ÙËÓ
∞ÓÙÈηٿÛÙ·ÛË ÙÔ˘ ηψ‰›Ô˘ Û‡Ó‰ÂÛ˘ ÛÙÔ ÎÂÓÙÚÈÎfi ‰›ÎÙ˘Ô
·ÙËÁÔÚ›· ‡Ì‚ÔÏÔ
¶ÂÚÈÔÚÈÛÌÔ› ıÂÚÌÔÎÚ·Û›·˜ ÂÚÈ‚¿ÏÏÔÓÙÔ˜ ¯ÒÚÔ˘
¶ÏËÚÔÊÔڛ˜ Û¯ÂÙÈο Ì ٷ ¯ÂÈÚÈÛÙ‹ÚÈ· ıÂÚÌÔÎÚ·Û›·˜
¶È¤ÛÙ ÙÔ ‰È·ÎfiÙÔ˘ TurboCool. £· ·Ó¿„ÂÈ Ô ‰Â›ÎÙ˘
¶ÂÚÈÔÚÈÛÌÔ› ıÂÚÌÔÎÚ·Û›·˜ ¯ÒÚÔ˘
∆Ô CustomCool TM Â›Ó·È ¤Ó· Û‡ÛÙËÌ· ÌÂ
¶ÏËÚÔÊÔڛ˜ Û¯ÂÙÈο Ì ÙÔ CustomCoolTM Û ÔÚÈṲ̂ӷ ÌÔÓ٤Ϸ
¿ÊËÌ· CustomCool TM
‡Ó‰ÂÛÌÔ˜ ·Ú¿Î·Ì„˘ Ê›ÏÙÚÔ˘
‡ÛÈÁÁ· Ê›ÏÙÚÔ˘ ÓÂÚÔ‡
¢ÂÓ ˘¿Ú¯Ô˘Ó fiÏ· Ù· ÂÍ·ÚÙ‹Ì·Ù· Û fiÏ· Ù· ÌÔÓ٤Ϸ
¶fiÚÙ˜ „˘Á›Ԣ
ªÂÁ¿ÏÔÈ ·ÔıË΢ÙÈÎÔ› ¯ÒÚÔÈ
ªÈÎÚÔ› ·ÔıË΢ÙÈÎÔ› ¯ÒÚÔÈ
¿ÊÈ QuickSpaceTM
˘ÚfiÌÂÓÔ Ú¿ÊÈ Ô˘ ‰ÂÓ ÛÙ¿˙ÂÈ
∞Ê·ÈÚÔ‡ÌÂÓË ı‹ÎË ÌԢηÏÈÔ‡
¿ÊÈ fiÚÙ·˜ ÁÈ· ÎÚ·Û› / ·Ó·„˘ÎÙÈο Û ÌÂÚÈο ÌÔÓ٤Ϸ
˘ÚfiÌÂÓ· Ú¿ÊÈ· ηٷ„‡ÎÙË
·Ï¿ıÈ· ηٷ„‡ÎÙË
·ıÂÚ¿ Ú¿ÊÈ· ηٷ„‡ÎÙË
¿Ú¯Ô˘Ó ‰‡Ô ÂȉÒÓ ÛÙ·ıÂÚ¿ Ú¿ÊÈ· ηٷ„‡ÎÙË
∞fi‰ÔÛË ÙÔ˘ ηٷ„‡ÎÙË
∆ÔÔı¤ÙËÛË ÙÚÔÊ›ÌˆÓ ÛÙÔ ¯ÒÚÔ ÙÔ˘ ηٷ„‡ÎÙË
¿Ùˆ ·fi -18C
· ·Ó ·Ê·ÈÚ¤ÛÂÙ ÙÔ Î¿Ùˆ Û˘ÚÙ¿ÚÈ ÊÚ¤ÛÎˆÓ ÙÚÔʛ̈Ó
˘ÚÙ¿ÚÈ· ÊÚ¤ÛÎˆÓ ÙÚÔÊ›ÌˆÓ Ì ڢıÌÈ˙fiÌÂÓË ˘ÁÚ·Û›·
¿Óˆ Î·È ¤Íˆ
ÂÚÈÛÙÚ¤ÊÔÓÙ·˜ ÙȘ Ûùëó ·ÛÊ·ÏÈṲ̂ÓË ı¤ÛË
˘ÚÙ¿ÚÈ ·Ôı‹Î¢Û˘ ¿ÁÔ˘
∞˘ÙfiÌ·ÙË ·ÁÔÌ˯·Ó‹
¤Íˆ Î·È ·Ó·ÛËÎÒÛÙ ÙÔ ¤Ú· ·fi ÙÔ ÛÙÔ
„ ªÂ ÂÈÏÂÁ̤ÓË ÙË ı¤ÛË Cubed ICE, ‰ÂÓ
· Ó· ¯ÚËÛÈÌÔÔÈ‹ÛÂÙ ÙÔ ‰È·ÓÔ̤·
·ı·ÚÈÛÌfi˜ ÙˆÓ ÂÛˆÙÂÚÈÎÒÓ ¯ÒÚˆÓ
˘ÚÙ¿ÚÈ ·Ôı‹Î¢Û˘ ¿ÁÔ˘ ÛÙ· ÌÔÓ٤Ϸ Ì ‰È·ÓÔ̤·
¶ÚÔÂÙÔÈÌ·Û›· fiÙ·Ó ÚfiÎÂÈÙ·È Ó· ʇÁÂÙ ÁÈ· ‰È·ÎÔ¤˜
¶›Ûˆ ·fi ÙÔ „˘Á›Ô
¶ÚÔÂÙÔÈÌ·Û›· ÁÈ· ÌÂÙ·ÎfiÌÈÛË
fiÚÙ˜ ·ÓÔȯ٤˜
ÃÒÚÔ˜ „˘Á›Ԣ-¿Ùˆ ʈ˜
ÃÒÚÔ˜ „˘Á›Ԣ-∂ʈ˜
¢È·ÓÔ̤·˜
ΜÁ¿ÏÙ ÙÔ „˘ÁÂ›Ô ·ÙËÓ
¶Ï·›ÛÈ· ¿¯Ô˘˜ ÏÈÁfiÙÂÚÔ˘ ·fi 6 ¯ÈÏ
¢È·‚¿ÛÙ fiϘ ÙȘ Ô‰ËÁ›Â˜ ÚÔÛÂÎÙÈο
19 ¯ÈÏ. ‹ ÀÂÚ˘„ˆÌ¤ÓÔ Ï·›ÛÈÔ
¢È·ÛÙ¿ÛÂȘ ÙˆÓ ÈÔ Û˘ÓıÈÛÌ¤ÓˆÓ Í‡ÏÈÓˆÓ Ï·ÈÛ›ˆÓ
ÙÔ˘ „˘Á›Ԣ Î·È ÙÔ Â¿Óˆ Ï·›ÛÈÔ ÙÔ˘ ηٷ„‡ÎÙË
∂ÈÛ·ÁˆÁ‹ ÙˆÓ Ï·ÈÛ›ˆÓ ı˘ÚÒÓ
269
∂·Ó·Û˘Ó‰¤ÛÙ ÙËÓ ÏÂÍÔ‡‰· ηψ‰›ˆÛ˘
∂·Ó·ÙÔÔı¤ÙËÛË ÙˆÓ ı˘ÚÒÓ
21’ Î·È 23’ 25’, 27’ Î·È 29’ ¶Ï¢ڤ˜
271
∂¿Óˆ
¶›Ûˆ
∆· ÚÔ‰¿ÎÈ· Â͢ËÚÂÙÔ‡Ó 3 ÛÎÔÔ‡˜
272
· Ó· Ú˘ıÌ›ÛÂÙ ٷ ÚÔ‰¿ÎÈ· ÛÙ· ÌÔÓ٤Ϸ 25, 27 ηÈ
· Ó· Ú˘ıÌ›ÛÂÙ ٷ ÚÔ‰¿ÎÈ· ÛÙ· ÌÔÓ٤Ϸ 21 ηÈ
273
¢π∞∆∞∂π ∞𠶃√¢π∞ƒ∞º∂
· ÌÔÓ٤Ϸ fiÔ˘ ¯ÚËÛÈÌÔÔÈ›ٷÈ
¶ƒ√√Ã∏! ˘Ó‰¤ÂÙ ÙÔ „˘ÁÂ›Ô ÌfiÓÔ Ì ·ÚÔ¯‹ fiÛÈÌÔ˘ ÓÂÚÔ‡
‚ϤÂÙ Ûùëó ÂÈÎfiÓ·
ÙËÓ ¤ÓˆÛË
Ù˘ ·ÁÔÌ˯·Ó‹˜ Â›Ó·È Ûùëó ı¤ÛË
275
Òûùâ Ó· ʤÚÂÈ ·ÚÎÂÙfi ÓÂÚfi Ûùëó ·ÁÔÌ˯·Ó‹
Àƒ¡∞∂π
¶Úfi‚ÏËÌ· ¶Èı·Ó¤˜ ·Èٛ˜ ∆È Ó· οÓÂÙÂ
¶ÚÈÓ Î·Ï¤ÛÂÙ οÔÈÔÓ ÁÈ· ÂÈÛ΢‹
278
279
280