Polycom DMA 7000 System Operations Guide
USA
Contents
Device Management
Local Cluster Configuration
Integrations with Other Systems 163
MCU Management 131
Superclustering 227
Conference Manager Configuration 193
Site Topology 283
Call Server Configuration 237
Users and Groups 311
System Management and Maintenance 347
Contents
DMA Operations Guide
431
System Reports 407
Index 539
Introduction to the Polycom DMA System
Polycom DMA 7000 System Overview
Conference Manager
Polycom DMA System’s Primary Functions
Call Server
RealPresence Platform API
SVC Conferencing Support
Two-server Cluster Configuration
Polycom DMA System’s Three Configurations
Superclustering
Single-server Configuration
Port Protocol Description
See Signaling Settings on
System Capabilities and Constraints
System Port Usage
Port Protocol Description
Be changed see Signaling Settings on
See Security Settings on
Accessing the Polycom DMA System
Polycom Solution Support
Working in the Polycom DMA System
Polycom DMA System User Roles and Their Access Privileges
Settings Dialog Box
Field Input Requirements
DMA Operations Guide Working in the Polycom DMA System
Menu/Icon Admin Provisioner Auditor
Management interface access privileges
Conference
API resource access privileges
License Information
Third-Party Software
Open Source Software
Modifying Open Source Code
BSD
Software Version License Link
Cddl
NSS
Nsis
SAX
UPX GPL Lzma
Polycom DMA System Initial Configuration Summary
Add Required DNS Records for the Polycom DMA System
Additional DNS Records for H.323 Gatekeeper
Additional DNS Records for SIP Proxy
Verify That DNS Is Working for All Addresses
License the Polycom DMA System
Set Up Signaling
Set Up Security
Set Up MCUs
DMA Operations Guide Set Up MCUs
Set Up MCUs Polycom DMA System Initial Configuration Summary
Connect to Microsoft Active Directory
Test the System
Set Up Conference Templates
Test the System
How Certificates Work
Security Certificates Overview
PEM Pkcs #7
Forms of Certificates Accepted by the Polycom DMA System
How Certificates Are Used by the Polycom DMA System
Frequently Asked Questions
Certificate Settings
Column Description
Certificate Signing Request Dialog Box
Certificate Information Dialog Box
Field Description
Certificate Details Dialog Box
Add Certificates Dialog Box
Field Description
Section Description
Certificate Procedures
Go to Admin Local Cluster Certificates
Install a Certificate Authority’s Certificate
Actions list, select Add Certificates
Actions list, select Create Certificate Signing Request
Create a Certificate Signing Request in the DMA System
Install a Certificate in the DMA System
Actions list, select Add Certificates
Actions list, select Delete Certificate
Remove a Certificate from the DMA System
Security Settings
High security
Field Description Maximum security
Custom security
Https
Field Description
DMA system so that it trusts the CA
Go to Admin Local Cluster Security Settings
Consequences of Enabling Maximum Security Mode
On the Troubleshooting Utilities menu, Top is removed
DMA Operations Guide
Local Password
Login Policy Settings
Password Complexity
Field Description Password Management
Session
Field Description Account Lockout
Local User Account
Account Inactivity
Banner
Reset System Passwords
Reset System Passwords
Local Cluster Configuration
Network Settings
Server
Turn on Auto-negotiation or set Speed and Duplex
Field Description Shared Management
General System
Field Description Shared Signaling
Network Settings
Management Network Settings , except that under
Routing Configuration Dialog Box
Time Settings
FieldDescription Active License
Licenses
SIP Signaling
Signaling Settings
Field Description Activation Keys
Device Authentication
Dma1.polycom.com5223
Xmpp Signaling
SIP Settings
Signaling Settings Fields
Field Description Settings
Click Device authentication settings to go to
Click the Device authentication settings link to go to
Entry see Edit Guest Port Dialog Box on page 78 or
Xmpp Settings
Add Guest Port Dialog Box
Signaling is turned off on the Security Settings
Then Require certificate validation for TLS is turned
Edit Guest Port Dialog Box
Add Guest Prefix Dialog Box
Edit Guest Prefix Dialog Box
Logging Settings
Click Generate
Local Cluster Configuration Procedures
Add Licenses
Select Product Activation
Go to Admin Local Cluster Licenses
Configure Signaling
Go to Admin Local Cluster Signaling Settings
Under Unauthorized ports, click Add
Under Unauthorized prefixes, click Add
Configure Logging
Active Calls
Device Management
Information in the Active Calls list
Tab/Field/Column Description Call Info
Call Details Dialog Box
QoS
Tab/Field/Column Description Bandwidth
Call Events
Property Changes
Endpoints
Information in the Endpoints list
Column Description
Takes you to Reports Registration History and displays
Command Description
Names/Aliases in a Mixed H.323 and SIP Environment
Add Device Dialog Box
Add Device dialog box
Edit Device Dialog Box
Edit Devices Dialog Box
Edit Alias Dialog Box
Add Alias Dialog Box
Associate User Dialog Box
Site Statistics
Site Link Statistics
External Gatekeeper
Column Description External Gatekeeper
Add External Gatekeeper Dialog Box
Gatekeepers list
Apply the Resolve to external gatekeeper action
Authentication Mode
Column Description Postliminary
Edit External Gatekeeper Dialog Box
Debugging Dialog Box for Preliminaries/Postliminaries
Mode
External SIP Peer
Field Description External SIP Peer
Add External SIP Peer Dialog Box
Apply the Resolve to external SIP peer action, there is
Domain List
Template field
Field Description Postliminary
Use customized script
To header options
External Registration
Field Description Authentication
Device Authentication
Authentication
Edit External SIP Peer Dialog Box
To this peer server for resolution
Peer server to specific domains by adding
Rule action, such as Resolve to external address , is
118
SIP Peer Postliminary Output Format Options
Default To header for Microsoft. Equivalent to template
To Header Format Options
#orscheme##oruser#@#orhost#
Request-URI Header Format Options
Free Form Template Variables
Default Request-URI for Microsoft. Equivalent to template
Variable Description
Sipuser@host Sipuser@peerHostIp Displayname
To Header and Request-URI Header Examples
Original Template Result
Displayname
Edit Authentication Dialog Box
Add Authentication Dialog Box
Add Outbound Registration Dialog Box
Edit Outbound Registration Dialog Box
22Edit Outbound Registration dialog box
External SBC
Column Description External SBC
Add External SBC Dialog Box
Rule or the Dial endpoints by IP address dial rule both
Edit External SBC Dialog Box
25Edit External SBC dialog box
MCUs
MCU Management
DMA Operations Guide MCUs
See SVC Conferencing Support on
Information in the MCU list
Command Description
Unquarantine
Add MCU Dialog Box
Field Description External MCU
MCU
Profile. See Isdn Gateway Selection Process on
Direct dial-in prefixsession profile
PrefixdelimiterE.164 number
See Add Simplified Isdn Gateway Dialing Prefix
Media IP Addresses
Field Description Gateway Profiles
Postliminary
Edit MCU Dialog Box
Edit MCU dialog box
Direct dial-in prefixsession profile
Polycom, Inc 145
Edit Session Profile Dialog Box
Add Session Profile Dialog Box
Isdn Gateway Selection Process
148
Go to Network MCU MCUs
MCU Procedures
To edit an MCU
To delete an MCU
MCU Pools
7Information in the MCU Pools list
Edit MCU Pool Dialog Box
Add MCU Pool Dialog Box
Go to Network MCU MCU Pools
MCU Pool Procedures
MCU Pool Orders
11Information in the MCU Pool Orders list
Edit MCU Pool Order Dialog Box
Add MCU Pool Order Dialog Box
MCU Selection Process
MCU Availability and Reliability Tracking
+ 5 *1 / 1 + 5 = 5/6
+ 5 *1 / 1 + 5 =
+ 5 *5/6 / 1 + 5 = 31/36
Go to Network MCU MCU Pool Orders
MCU Pool Order Procedures
Microsoft Active Directory Integration
Integrations with Other Systems
164
Connection Status
Microsoft Active Directory
Active Directory Connection
Conference Room Errors Report report
Understanding Base DN on
Enterprise Chairperson and Conference Passcode Generation
Field Description Enterprise Conference Room ID Generation
To integrate with Active Directory
Active Directory Integration Procedure
170
Polycom, Inc 171
172
Use this Base DN To include the following
Understanding Base DN
Adding Passcodes for Enterprise Users
Polycom, Inc 175
About the System’s Directory Queries
When you click Update on the Microsoft Active Directory
User Search
Index used idxobjectCategory32561N
Group Search
Attribute Replication Search
Global Group Membership Search
Active Directory
Configurable Attribute Domain Search
Service Account Search
Domain Search
Microsoft Exchange Server Integration
Microsoft Exchange Server Integration
Microsoft Exchange Server
Exchange Server Integration Procedure
Go to Admin Integrations Microsoft Exchange Server
Resource Management System Integration
Resource Management System
Join Resource Management System Dialog Box
Resource Management System Integration Procedures
Juniper Networks SRC Integration
SRC
Juniper Networks SRC
Go to Admin Integrations Juniper Networks SRC
Juniper Networks SRC Integration Procedure
IpipAddress=192.168.70.228
192
Conference Settings
Conference Manager Configuration
Pool Orders on
Go to Admin Conference Manager Conference Settings
Two Types of Templates
Conference Templates
Standalone Templates
Templates Linked to RMX Profiles
Template Priority
About Conference IVR Services
About Cascading
Conference Templates List
Add Conference Template Dialog Box
Field Description Common Settings
RMX General Settings
Resource Management System Integration on
LPR
RMX Video Quality
RMX Gathering Settings
Telepresence mode is Yes
RMX Video Settings
Not available if Video switching or Same layout is
Not available if Presentation mode or Video switching
Select Layout Dialog Box on
RMX Audio Settings
RMX Conference IVR
RMX Skins
Cisco Codian
Field Description RMX Recording
FECC/DTMF
RMX General Settings
Field Description Common Settings
Edit Conference Template Dialog Box
4Edit Conference Template dialog box
212
Polycom, Inc 213
214
Not available if Video switching is on or Telepresence
216
Polycom, Inc 217
Field Description Cisco Codian
Select Layout Dialog Box
Go to Admin Conference Manager Conference Templates
Conference Templates Procedures
Shared Number Dialing
DMA Operations Guide Shared Number Dialing
Add Virtual Entry Queue Dialog Box
Add Direct Dial Virtual Entry Queue Dialog Box
Edit Direct Dial Virtual Entry Queue Dialog Box
Edit Virtual Entry Queue Dialog Box
DMA Operations Guide Shared Number Dialing 226
About Superclustering
Superclustering
228
DMAs
DMA Operations Guide DMAs
Following table describes the fields on
Join Supercluster Dialog Box
Go to Network DMAs
Supercluster Procedures
Actions list, click Join Supercluster
Actions list, select Remove from Supercluster
To remove a cluster from the supercluster
236
Call Server Configuration
About the Call Server Capabilities
Consequences of Enabling Maximum Security Mode on
External Gatekeeper on
Call Server Settings
Suggestions for Modifications on
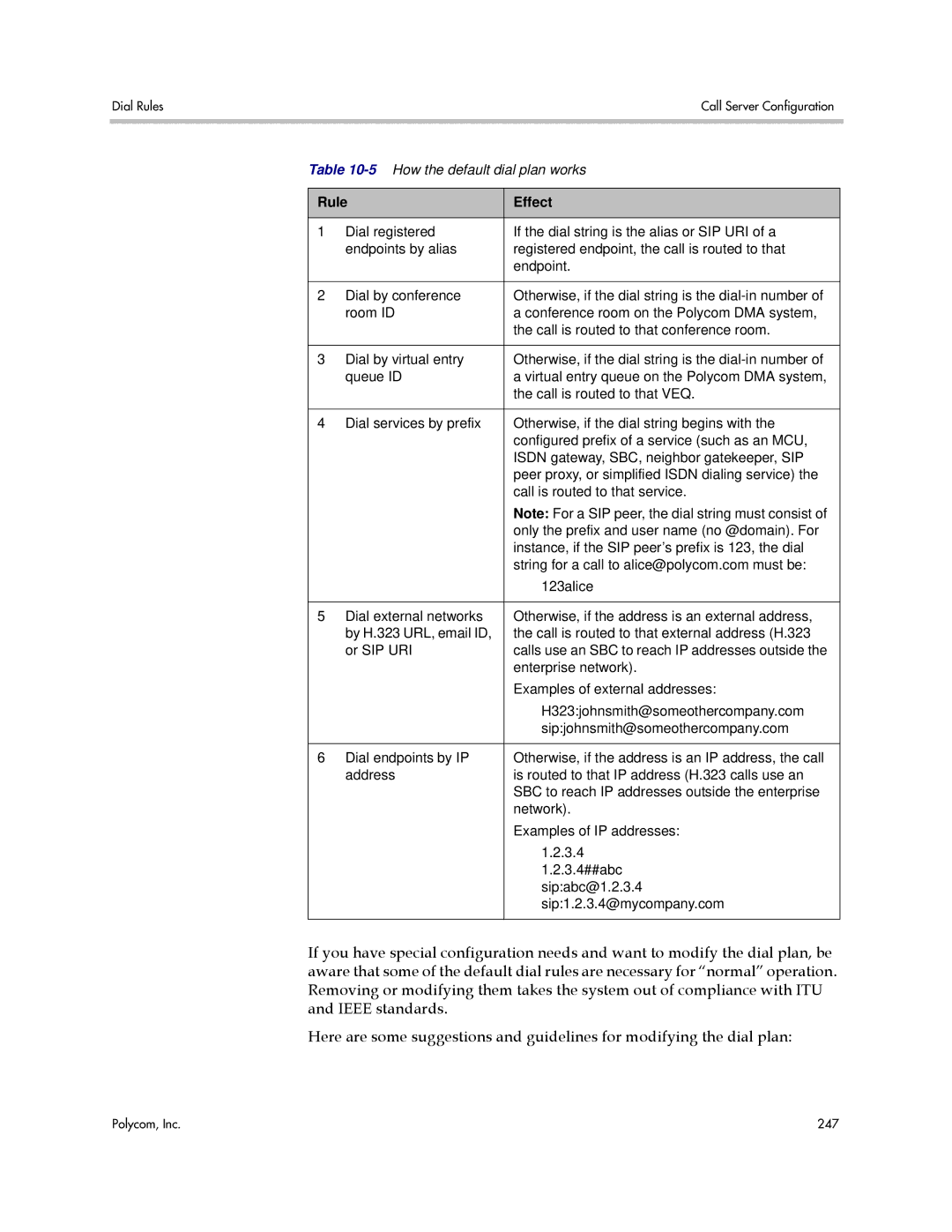
By alias dial rule see The Default Dial Plan
Answer
Larger than Timeout for call forwarding when no
Authorized domains list
Domains
Domain doesn’t match a Resolve to conference room
Dial Rules
3Fields in the Dial Rules lists
Sipsrbruce@10.47.7.9
Test Dial Rules Dialog Box
Default Dial Plan and Suggestions for Modifications
Rule Effect
248
Polycom, Inc 249
Sample Preliminary and Postliminary Scripts on
Add Dial Rule Dialog Box
Field Description Dial Rule
Preliminary
7Dial rule actions
Edit Dial Rule Dialog Box
9Dial rule actions
Variable Initial value
Preliminary/Postliminary Scripting
OUTPUTSIPHEADERSSome-Custom-Header
Ms-forking
OUTPUTSIPHEADERSUser-Agent =
Someone. Not a DMA
Dial Rule Action Output SIP Headers
Dialstring = sipxxx@10.33.120.58
Script Debugging Dialog Box for Preliminaries/Postliminaries
Add prefix 99 to the dial string 1234
Sample Preliminary and Postliminary Scripts
Substitute Domain SIP
User = Callersitecountrycode + Callersiteareacode + user
Site Based Numeric Nicknames
Hunt Groups
Hunt Group Members
Add Hunt Group Dialog Box
Edit Hunt Group Dialog Box
Field Description General Info
15Edit Hunt Group dialog box
Inbound Authentication
Device Authentication
On the Inbound Authentication tab, you can
Field Description Inbound Authentication
Shared Outbound Authentication
Shared Outbound Authentication
Add Device Authentication Dialog Box
External SIP Peer Dialog Box on page 114 . If there is
Field Description Device Authentication
Edit Device Authentication Dialog Box
Registration Policy
19Fields on the Registration Policy
Epdefinedincma
Registration Policy Scripting
EPISIPV4
Epversion
Sample Registration Policy Scripts
Script Debugging Dialog Box for Registration Policy Scripts
If EPH323DIALEDDIGITSALIAS0.length!= Return Noncompliant
Polycom, Inc 275
Prefix Service
MCU Dialog Box on
Add Simplified Isdn Gateway Dialing Prefix Dialog Box
Dialog Box on
Edit Simplified Isdn Gateway Dialing Prefix Dialog Box
Embedded DNS
Edit Vertical Service Code Dialog Box
Callservers.example.com
Following table describes the fields on the Embedded DNS
Callserver-paris.callservers.example.com
History Retention Settings
Records see Registration History Report on
Conference History on
About Site Topology
Site Topology
284
Sites
Field Description Site Info
Site Information Dialog Box
Device Types
Subnets
Field Description General Info General Settings
Bandwidth Settings
Add Site Dialog Box
Isdn Number Assignment
Field Description Territory Settings
From the Endpoints page see Edit Device Dialog Box
Isdn Outbound Dialing
Gateway Extension Dialing. Select this option if
Isdn Range Assignment for gateway extension dialing method
Isdn Range Assignment for did dialing method
Routing
SIP Routing
ALG
Edit Site Dialog Box
Gateway Extension Dialing . Select this option if
Field Description Isdn Number Assignment
Field Description Isdn Outbound Dialing
Polycom, Inc 295
296
Add Subnet Dialog Box
Edit Subnet Dialog Box
Add Site Link Dialog Box
Site Links
Edit Site Link Dialog Box
Add Site-to-Site Exclusion Wizard
Site-to-Site Exclusions
Go to Network Site Topology Site-to-Site Exclusions
Territories
Associated Sites pane
Add Territory Dialog Box
Column/Section Description
Territory Summary
Associated Sites
Edit Territory Dialog Box
FieldDescription Territory Info
Network Clouds
Field Description Cloud Info
Add Network Cloud Dialog Box
Site Link dialog box see Add Site Link Dialog Box on
Edit Network Cloud Dialog Box
Site Topology Configuration Procedures
Go to Network Site Topology Sites
Go to Network Site Topology Territories
About Site Topology on
310
Users and Groups
Role Description
User Roles Overview
Adding Users Overview
Users
Following table describes the parts of the Users list
Room of the user’s. See Edit Conference Room Dialog
CDR
Add User Dialog Box
Endpoints page see Associate User Dialog Box
Conference Settings on
Associated Endpoints
Select to open the Select Associated Endpoints
Conference Passcodes
Field Description Associated Roles
Edit User Dialog Box
Polycom, Inc 321
Field Description Conference Passcodes
Select Associated Endpoints Dialog Box
Conference Rooms Dialog Box
Pool Orders on
Add Conference Room Dialog Box
Conference Settings
See Conference Settings on
Conference Template Dialog Box on
Edit Conference Room Dialog Box
Call CDRs to this conference room
System after this date
Add Dial-out Participant Dialog Box
Edit Dial-out Participant Dialog Box
Users Procedures
Go to User Users
Conference Rooms Procedures
To edit one of a user’s conference rooms
To delete one of a user’s custom conference rooms
Endpoints on
Groups
MCU Pool Orders on
Import Enterprise Groups Dialog Box
See also Users on page 314 Groups on
Conference Templates on
Edit Group Dialog Box
Actions list, click Import Enterprise Groups
Enterprise Groups Procedures
Polycom, Inc 343
Login Sessions
Local Password on
Change Password Dialog Box
346
Management and Maintenance Overview
System Management Maintenance
Administrative Best Practices
Administrator Responsibilities
Auditor Responsibilities
Recommended Regular Maintenance
Auditor Best Practices
General system health and capacity checks
Microsoft Active Directory health
Dashboard
Call Server Active Calls Pane
Active Directory Integration Pane
Cluster Info Pane
Call Server Registrations Pane
Conference Manager MCUs Pane
Conference History Max Participants Pane
Conference Manager Usage Pane
Exchange Server Integration Pane
License Status Pane
Signaling Settings Pane
Resource Management System Integration Pane
Supercluster Status Pane
User Login History Pane
Territory Status Pane
Alert
Alerts
Hhmm GMT+/-HMM
No clusters assigned to list of territories
YYYY-MM-DD Hhmm GMT+/-HMM
Active Directory Connection section
364
Polycom, Inc 365
366
Cluster cluster The server certificate has expired
Cluster cluster One or more CA certificates have expired
Cluster cluster a private network error exists on server
Cluster cluster a management network error exists on server
Polycom, Inc 371
Server server CPU utilization 50% and 75%
Polycom, Inc 373
Cluster cluster Local users differ between servers
MCU MCUname has count warnings
No territories configured to host conference rooms
System Log Files
Actions list, click Download Active Logs
System Logs Procedures
To manually roll the system logs
Top
Troubleshooting Utilities
Ping
Traceroute
Backing Up and Restoring
Go to Maintenance Troubleshooting Utilities SAR
Stats
System may delete backups to free up disk space if necessary
3Information in the Backup and Restore list
Go to Maintenance Backup and Restore
Backup and Restore Procedures
Actions list, click Download Selected
To upload a backup file
Actions list, click Restore Selected
Polycom, Inc 387
Upgrading the Software
Following table describes the parts of the Software Upgrade
Go to Maintenance Software Upgrade
Basic Upgrade Procedures
Return to Maintenance Software Upgrade
To roll back an upgrade, restoring the previous version
Polycom, Inc 393
394
Incompatible Software Version Supercluster Upgrades
Factors to Consider for an Incremental Supercluster Upgrade
Simplified Supercluster Upgrade Complete Service Outage
398
Polycom, Inc 399
400
Polycom, Inc 401
Adding a Second Server
Complex Supercluster Upgrade Some Service Maintained
Expanding an Unpatched System
Expanding a Patched System
Replacing a Failed Server
Shutting Down and Restarting
Go to Maintenance Shutdown and Restart
Alert History
System Reports
Call History
Export History
Conference History
Conference Events
Associated Calls
Property Changes
Call Detail Records CDRs
Exporting CDR Data
VEQ
Call Record Layouts
Call CDR
Conference Room Dialog Box on
Conference Record Layouts
Value from the Conference room pass-through to
See Edit User Dialog Box on
Conference Room Dialog Box on
Registration History Report
Active Directory Integration Report
Registration History Procedures
All Domains
Auto-discover failed or is disabled could be
Selected on the Microsoft Active Directory Integration
Site could not be determined the system’s subnet
Groups with Partially Loaded or No Membership Information
Partially loaded or Unable to load see Error
Orphaned Users
Orphaned Groups and Users Procedures
Orphaned Groups and Users Report
Field Description Orphaned Groups
Conference Room Errors Report
12Information in the Conference Room Errors list
Exporting Conference Room Errors Data
Enterprise Passcode Errors Report
Information in the Enterprise Passcode Errors list
Network Usage Report
Exporting Enterprise Passcode Errors Data
Following table describes the fields in the records
Exporting Network Usage Data
14 Network Usage record layout
To download network usage data
DMA Operations Guide Network Usage Report 430
Snmp Overview
Polycom DMA System Snmp Support
Snmp Versions Supported
System MIB on
Snmp Settings
List of Available Snmp MIBs
Name Description
See Snmp Versions Supported on page 432 for a
Setting Description
Notification Agents
Notification Users
Snmp Versions Supported on
Add Notification User Dialog Box
3Add Notification User dialog box
Edit Notification User Dialog Box
Add Notification Agent Dialog Box
Edit Notification Agent Dialog Box
Go to Admin Local Cluster Snmp Settings
Snmp Procedures
Go to Admin Snmp Settings Click Download MIBs
CfgServer
Polycom DMA System MIB
CfgProdInfoSWExtVerPlatformVersion
CfgProdInfoSWExtVerApplicationVersion
Polycom DMA System MIB
444
Polycom, Inc 445
446
Polycom, Inc 447
448
Polycom, Inc 449
From SNMPv2-TC
DmaConformance
DmaConformanceGroups
TEXTUAL-CONVENTION, DisplayString, TruthValue, DateAndTime
Initial draft
Dma MODULE-IDENTITY
201109220000Z
Polycom, Inc
Dma.2.1.1.1 CfgProductInfo
Dma.2
Information about the DMA product
= cfgProdInfoSWExtendedVersion
Syntax GeneralString MAX-ACCESS read-only Status current
GeneralString
Read-only
An entry in cfgInterfacesTable
Not-accessible
= cfgNetwork
Syntax CfgInterfacesEntry
Polycom, Inc 455
= cfgCsSupercluster
Site topology configuration for the call server
= cfgCsSiteTopology
Configured territories
= cfgCsTerritoriesEntry Dma.2.1.3.1.1.2.1.3
= cfgCsIntDirSvcMSActiveDirectory Dma.2.1.3.1.2.1.1.3
= cfgCsIntCalMSExchange
Address of the Exchange server
= cfgCsIntegrations
Configurations for network integrations
Polycom, Inc 461
SIP signaling configuration for the cluster
Dma.2.2.1
= cfgCsSignaling
Dma.2.2
Current Description Contains status data for the DMA system
= stIdentity
Status current Description An entry in stVersionTable
Syntax DisplayString MAX-ACCESS read-only Status current
Dma.2.2.1.2.2 StVersionTable
Sequence of StVersionEntry
Server statuses
= stNetwork
Sequence of StNetClusterAffiliationEntry
An entry in stNetPrivateInterfaceTable
Syntax StNetPrivateInterfaceEntry MAX-ACCESS not-accessible
Dma.2.2.1.3.2 StNetPrivateInterfaceTable OBJECT-TYPE
Sequence of StNetPrivateInterfaceEntry
Polycom, Inc 469
Sequence of StNetManagementInterfaceEntry
= stNetManagementInterfaceEntry
= stNetSignalingInterfaceEntry Dma.2.2.1.3.4.1.3
Sequence of StNetSignalingInterfaceEntry
DisplayString
Sequence of StRsrcCPUUsageEntry
Memory usage information for the servers
Sequence of StRsrcMemoryUsageEntry
StRsrcMemUsageIndex Unsigned32 StRsrcMemUsageHostName
= stResources
= stRsrcMemoryUsageTable
StRsrcMemoryUsageEntry = Sequence
Swap
Sequence of StRsrcSwapSpaceEntry
Status current Description stRsrcSpaceTable index
Disk
Syntax StRsrcDiskSpaceEntry MAX-ACCESS not-accessible
= stRsrcSwapSpaceEntry
Sequence of StRsrcDiskSpaceEntry
An entry in stRsrcLogSpaceTable
Syntax StRsrcLogSpaceEntry MAX-ACCESS not-accessible
= stRsrcDiskSpaceEntry
Sequence of StRsrcLogSpaceEntry
Polycom, Inc 479
An entry in stMCUStatusTable
Syntax StMCUStatusEntry MAX-ACCESS not-accessible
Sequence of StMCUStatusEntry
= stMCUs
StMCUStIVRAvailable TruthValue
StMCUStServiceStatus Integer
= stMCUVideoPortUsageEntry Dma.2.2.2.1.3.1.3
Sequence of StMCUVideoPortUsageEntry
Sequence of StMCUVoicePortUsageEntry
484
Sequence of StMCUPCConnectionStatusEntry
= stMCUVoicePortUsageEntry
= stMCUsPerCluster
Sequence of StMCUPCReliabilityStatsEntry
StMCUPCConnStConnectionStatus Integer
= stMCUPCReliabilityStatsEntry
Sequence of StClustersEntry
Hundredths
Divided
Value
Dma.2.2.3.2.1.3 StClClusterStatus OBJECT-TYPE
Syntax StLicensesEntry MAX-ACCESS not-accessible
Sequence of StLicensesEntry
= stCallserver
Call server status shared across the supercluster
Sequence of StCsConfMgrTerritoriesEntry
Name of cluster performing AD caching
Failed5, outdated6, failedNoSuchEnterpriseUser7
Status of Active Directory caching
= stCsIntDirSvcMSActiveDirectory
True if Exchange integration is enabled
Syntax DateAndTime MAX-ACCESS read-only Status current
TruthValue
= stCsIntCalMSExchange
Status for site topology service integration
Number of territories provided by the CMA system
= stCsIntegrations
= stCsIntNetBWMgmtJuniperSRC
True if Juniper SRC integration is enabled
StCsConfMgrMCUsTable index
Sequence of StCsConfMgrMCUsEntry
= stCsConfMgrMCUs
Dma.2.2.4.2.1.2.1.1 StCsCMMCUIndex
One-minute intervals
Syntax Unsigned32 MAX-ACCESS read-only Status current
Dma.2.3.1.1.2 UseCHMaxPartsLast60MinutesTable OBJECT-TYPE
Sequence of UseCHMaxPartsLast60MinutesEntry
UseCHMaxPartsLast60MinutesEntry = Sequence
= useCHMaxPartsLast60MinutesTable
UseCHMaxParts24HrMaxAdHocCalls Unsigned32
Sequence of UseCHMaxPartsLast24HoursEntry
One-hour intervals
An entry in useCHMaxPartsLast24HoursTable
UseCHMaxParts24HrMaxPCOCalls Unsigned32
UseCHMaxParts180DaysTimestamp DateAndTime
Dma.2.3.1.1.6 UseCHMaxPartsLast180DaysTable OBJECT-TYPE
Syntax UseCHMaxPartsLast180DaysEntry
= useCHMaxPartsLast180DaysTable
= useCHMaxPartsLast180DaysEntry
Sequence of UseConfMgrUsageEntry
Dma.2.3.2.1.2 UseConfMgrUsageTable OBJECT-TYPE
= useCurrentConfsConfManagerUsage
Polycom, Inc 505
Sequence of UseDevRegistrationsEntry
= useDevRegistrations
Device registrations per cluster
= useDevRegistrationsEntry
Number of endpoints with an inactive registration status
= alActiveAlertsTable
Syntax AlActiveAlertsEntry MAX-ACCESS not-accessible
Polycom, Inc 509
Warn1, severe2, critical3
Text
= alActiveAlertsEntry
Dma.2.5 DmaNotifications OBJECT-IDENTITY Status current
NtfObjAlertID NtfObjAlertTimestamp NtfObjAlertCode
Accessible-for-notify
512
Polycom, Inc 513
514
Polycom, Inc 515
NtfObjAlertID NtfObjAlertTimestamp
Polycom, Inc 517
518
Polycom, Inc 519
520
Polycom, Inc 521
522
Polycom, Inc 523
524
Polycom, Inc 525
526
Polycom, Inc 527
CfgCallserver CfgCsSupercluster
DMA Conformance
CfgCsCluster CfgCsSignaling CfgCsSgnlH323
StVersionTable StVersionEntry StVerIndex
StNetSignalingInterfaceTable StNetSignalingInterfaceEntry
DmaConformanceStatus OBJECT-GROUP Objects DmaStatus
StIdentity StHardwareInfoTable
StRsrcDiskSpaceTable StRsrcDiskSpaceEntry StRsrcDiskIndex
StRsrcSwapSpaceTable StRsrcSwapSpaceEntry StRsrcSwapIndex
StCallserver StCsSupercluster
StClustersTable StClustersEntry
= dmaConformanceGroups
Description Conformance group for dmaStatus
534
1.4 DmaConformanceAlerts OBJECT-GROUP
Description Conformance group for dmaUsage
Description Conformance group for dmaAlerts
536
= dmaMonitoring1
Module POLYCOM-DMA-MIB MANDATORY-GROUPS
538
Index
540
Polycom, Inc Index
See MCU pool orders
543
Xmpp
545
Working in system Certificates 35 Xmpp signaling