May
Univerge Neax 2000 IPS
Liability Disclaimer
NEC Unified Solutions, Inc
Inaset
Chapter
OAI Application Software Development
Isdn Basic Rate Interface BRI
Univerge Neax 2000 IPS Documentation List
Overview of NEC
Introduction
Invention Age
Industrial Age
Electronic Age
Components
Information Age
Worldwide Leadership
Social Contributions
Communications
Global Resources
People
Innovation
Assets
Community
Education
Development ActivitiesDALLAS, Texas
NEC Unified Solutions, Inc
Areas
Major Product
Competitive Benefits and Advantages
Vertical Markets
Introduction
Introduction
Univerge Neax 2000 IPS
Station to Station Connection
Maintenance
Ccis Connection
Pstn
Various Installation Methods
Office Data Backup Enhancement
Built-in DRS Device Registration Server on MP
Reduced Hardware with IP based Architecture
Universal Slot
DC/DC Power Supply for
Extended Application Processor AP Port Capacity
Dual MP System
System Outline for Remote PIM
Univerge Neax IPS DML
Advantages of Remote PIM
Characteristics of the Univerge Neax IPS DM/IPS DML/IPS DMR
IPS System Capacity Single MP System Capacity Per PIM
Stand Alone System Capacity
PIM1 PIM2 PIM3 PIM4 PIM5 PIM6 PIM7
IP PAD
IPS System Capacity Single MP System cont’d Capacity Per PIM
2M-AMI
IPS System Capacity Dual MP System Capacity Per PIM
IPS System Capacity Dual MP System, Cont’d Capacity Per PIM
Capacity Per MC
IPS DM/IPS DML System Capacity
IP-PAD
8LC
Built-in Router Max card per Site Dtmf Sender
IP Remote Network Capacity
Total System Capacity Main plus Remote
Capacity
IPS DMR Capacity
DTI Isdn
IPS Pimmj As Remote PIM Capacity
Voice and Data Switching
System Architecture
Hardware Architecture
Fusion of RAM and ROM Programs
Hardware Design
Main Processor MP with Integrated Functionality
Application Processors
Unified Circuit Card
Integration
SN716 Attendant Console
Analog/Digital Telephones
PIM
Univerge Neax 2000 IPS System Configuration
Single MP System
Module and Installation Hardware
Dual MP System
Modules
Installation Hardware
Installation Hardware
Abbrev Description Quantity
Name Code Qty Remarks
Battery Backup
Internal Cabling
Cabling
External Cabling
Maintenance Administration Terminal MAT RS-232C
Built-in SMDR/MCI on MP
External Alarm Display
SMDR/PMS/Hotel Printer/MCI with AP00B MRC-C
Cable for AP00 Name Code Qty Remarks
IPS DM/IPS DML Modular Chassis MC
Univerge Neax IPS DM/IPS DML/IPS DMR System Configuration
Modular Chassis 2 Modular Chassis
IPS DMR Modular Chassis MC
Modular Chassis MC and Bracket
Modular Chassis MC Installation
System Power Supply and Cooling Fan
Software Architecture
System Packages
PKG IPS
Univ IPS DML IP SYS PKG
DM to Univ DM Upgrade Kit
Univ IPS DM IP SYS PKG-E
Univ IPS DM/DML Expansion Module 1E
Description Remarks
IP Remote PIM Packages
Univ IPS DMR SYS PKG-E
Univ IP Remote PIM-B IPS
Description Remarks Generic Program
Software Keys/Licenses
Key Keeper Parent Capacity Option
Capacity Option used w/Key Keeper
Processors
System Highlights
Main Processor MP
Name Code Remarks
Firmware Processor FP
PN-CP24-C PN-CP31-C PN-CP27-A
DAT
Application Processor AP Cards
Application Processor AP
AP Card
Function
Reliability and Availability
Reliability and Availability Chart Description Fit
Mean Time Between Failures Mtbf
Mtbf Mttr
Reliability Description Availability Fit
Reliability and Availability Chart
Fit
Years
Reliability Description Availability
Reliability Calculations
Mean Time To Repair Mttr
Availability Calculations
Reliability Calculation
Traffic Load
System Traffic
Busy Hour
Bhca Busy Hour Call Attempts
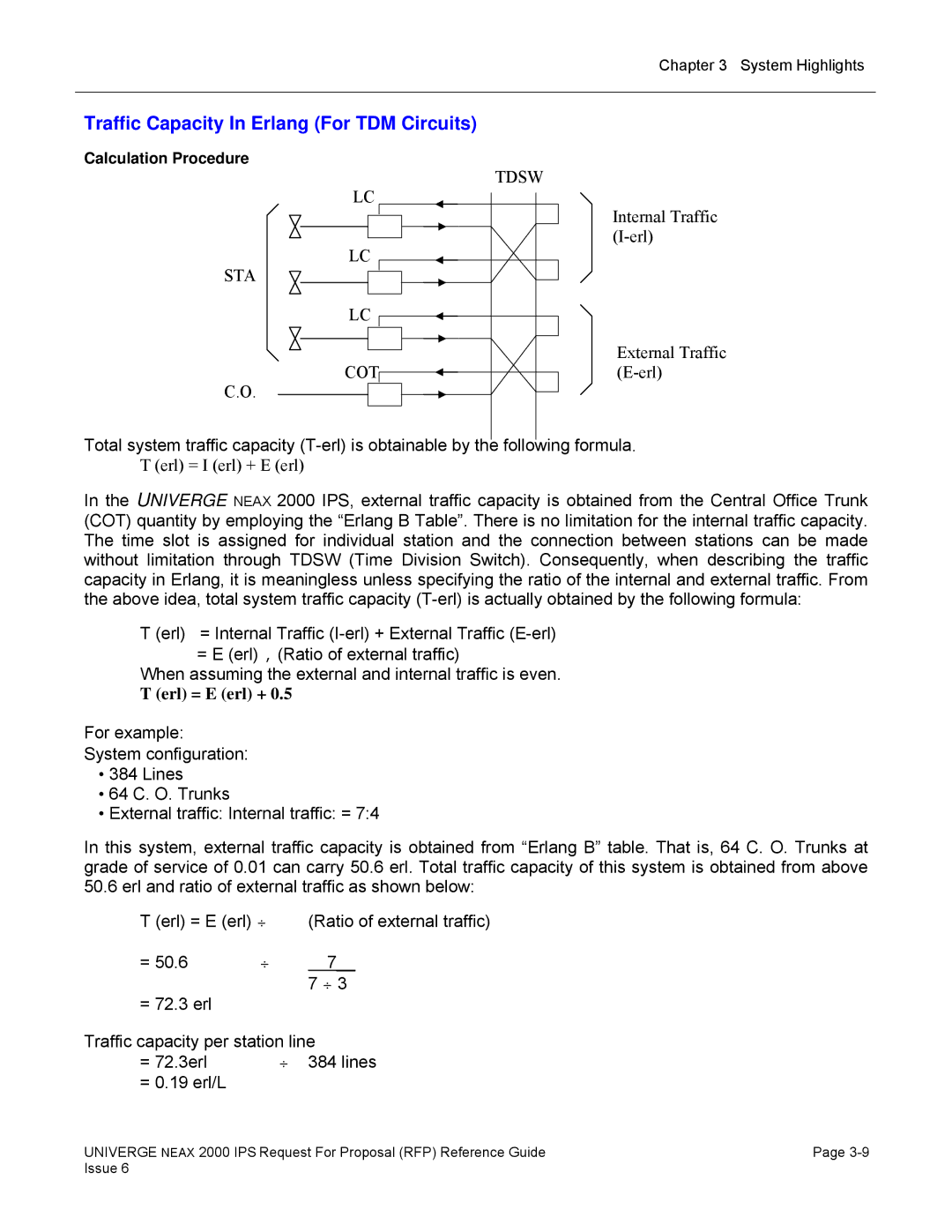
Traffic Capacity In Erlang For TDM Circuits
Calculation Procedure
Number of Trunks
Traffic Capacity per Line For TDM Circuits
Erlang B Table
Traffic Internal Call Distribution External Line Trunk
COT
PEG Count
Wireless PEG Count
Trunk PEG Count
UCD PEG Count
Ccis Point-to-Multipoint
Number of Voice Channels per IP Trunk
VoIP H.323
Payload size for Virtual IPT
IP PAD Calculation Number of extensions 100
IP PAD Calculation
Number of extensions 120 200 208 264 300 320 376 432
IP PAD Calculation
System Specifications
Line Conditions
Transmission Characteristics For TDM Circuits
Loop Resistance including Opposite End Resistance
Cable Length
Rotary Dial Signal
Rotary Dial Pulse and Dtmf Signaling
Dtmf Signal
Description Specifications Receiving Sending
Multi-frequency Compelled MFC R2 Signal
Ringing Signal
Audible Tones and Ringing Signal
Dimension and Weight
Audible Tones Frequency Interruption
System Specifications
Univerge Neax IPS DM/IPS DML/IPS DMR System Specifications
EMC
Open Industry Standards
FAX
IP Specifications
10BASE-T/100BASE-TX
LAN interface transmission modes Remarks
Hipaa Summary
System Compliance
Hipaa Compliance
Department of Defense Compliance
Page
Module/Installation Hardware
Equipment List
Equipment Name Function Name
Equipment Name Remarks
Common Control Cards
Circuit Cards
PN-CP15
PN-CP31
Ether
PN-PW00 Extpwr
Application Processor Cards
Application Processor Card Name and Function
Function Name Port Remarks
Application Processor Cards
Qsig
SPN-AP00B DBM-C AP
Line/Trunk LT Cards
Line/Trunk LT Cards
PN-8DLCL
SPN-2ILCA
Deskcon
PN-4DLCM
PAD-C
PAD-E
PZ-24IPLA
SPN-16VCTAA IP
PN-4COTB
PN-8COTQ
PN-4COTG
PN-2ODTA
PN-TNTA
PN-2DATA
SPN-IPTB-A
SPN-4VCTI-A
PN-RTA
SPN-4CSIA
Page
Terminal Line Up
Station Equipment
Dterm Series i Terminals
Dterm Series E Terminals
Inaset
Wireless Handset
Dterm IP Soft Phones
Dterm Extenders
Specification for Analog Terminals
Physical Features
Descriptions of the Dterm IP Terminals
Convergence Features
Call Handling Features
DTR-2DT-1 BK TEL DTR-2DT-1 WH TEL DTR-4D-1BK TEL
Descriptions of Terminals
DTR-16LD-1 BK TEL DTR-16LD-1 WH TEL
DCR-60-1 BK Console DCR-60-1 WH Console
Specification
Standard features
Cable Length Standard With AC Adapter
Terminal Options
Dterm Series E Soft keys
Standard features
Descriptions of Series E Multi-line Digital Terminals
Description of Series E Multi-line Digital Terminals
ADA-U
Dterm Series E Accessories & Adapters
HFU-U
APR-U
WMU-U
ACA-U
WMU-W
IPW-2U ELC
2DT
Dterm Series E Specifications
16D 32D Add-On
DSS
Loop Resistance and Distance Long Loop circuit built-in
Dterm Series E Line Conditions
Dterm Cordless Terminals
Dterm Cordless II DTR-4R-2 BK
Options
Options
Dterm Cordless Lite II DTH-4R-1 BK
Plantronics CT Cordless
Specifications
Additional Applications
Inaset Applications
Inaset Basic Network Capability
Inaset Terminal Line UP
PBX System Requirements
WM-RL Unit
Dterm PS III Options
Dterm PS III Wireless Handset
Features
Key Features and Benefits
Internet Link
Links with PC applications
Real Time Communication
Presence/Status
Application Collaboration
Voice Recording
One Key Operation
Voice Quality Alarm
Call Log Export
Line Display
One Touch Button in Compact Mode
Client PC specification
PB tone sending
Pause into Dialing string
Dterm SP30 Softphone Parts List
PBX Specification Must be peer to peer IP enabled
Software/Licenses/Accessories
Dterm Extenders
Service Conditions for Dterm Analog EXT
Page
Type of Trunks
Trunking
Type of Trunk Circuit Package
LT/AP
Trunk Parameters
Trunk Card Specifications
PN-AUCA
SPN-BRTC
PN-4RSTBA MF Receiver for T1 MF ANI
PN-8RSTG Dtmf Receiver
PN-4RSTC ID Number Receiver
PN-4RSTBA-911 MF Sender
IPS Trunking Capacity System Capacity
System Trunking Capacity
IPS DM/DML Trunk Capacity
Least Cost Routing LCR
Six Digit Least Cost Routing
Route Restriction Class RSC
Toll Restriction
Digit Toll Restriction
Priority Restriction Class
Page
Attendant Console SN716
Attendant Answering Position
SN716 Deskcon General Features
SN716 Deskcon Exclusive Features
Deskcon Exclusive Features
Face Layout of the SN716 Deskcon
Location Key or Lamp Full Basic Key/Lamp Number Designation
Functions and use of Keys and Lamp Indications
LDN
LCD
Interface ’ty Remarks Power Options
SN716 Specifications
Business Attendant System BAS
BAS Benefits
Business Attendant System Directory
Business Attendant System Speed Dials Pad
Business Attendant System Additional Features
Business Attendant System Ccis Network Information
Hardware Requirements
Business Application Environment
Page
System Administration
System Administration
Customer Administration Terminal CAT
Password Entry
Maintenance Administration Terminal MAT
Mach Script Editor
PBX Configuration Wizard
Traffic Management
MATWorX PC Requirements
Minimum Requirements Recommended
Self Diagnostic/System Messages
System Diagnostics
Remote Maintenance
Service Conditions
General Service Conditions
MP Program Download
MP Download Process
Program Changeover Service Conditions
Program Download Service Conditions
Required Hardware
Equipment Comments
MA4000 Management System
Business/Hotel/Data Feature List
Feature Descriptions
Business/Hotel/Data Feature List
Descriptions
Snmp
Business/Hotel/Data Feature Descriptions
Attendant Assisted Calling
Attendant Camp-on Full and Semi- automatic
Attendant Console SN716 Deskcon
Attendant Lamp Check
Authorization Code
Attendant Delay Announcement
Attendant Lockout
Attendant Overflow
Automatic Camp-on
Automatic Call Distribution ACD
Automatic Wake-up
Automatic Recall
Background Music
Back Up CPU
Brokers Call
Call Back
Call Forwarding
Call Park
Call Redirect
Call Pickup
Call Transfer
Caller ID Class
Camp-on
Class of Service
Centrex Compatibility
Check In / Check Out
Conference 32 Party
Conference Six/Ten Party
Group Call
Consecutive Speed Dialing
Diagnostics
Delayed Ringing
Data Line Security
Dial By Name
Direct Inward Termination DIT
Direct Inward System Access Disa
Direct Outward Dialing DOD
Direct Station Selection/Busy Lamp Field DSS/BLF Console
Distinctive Ringing
Do Not Disturb
Fax Arrival Indicator
Elapsed Call Timer
Dterm Assistant
DtermIP
Flexible Line Key Assignment
Feature Activation from Secondary Extension
Flexible Numbering Plan
Forced Account Code
Hands-free Answerback
Individual Attendant Access
Hands-free Dialing and Monitoring
Hold
Internal Zone Paging with Meet-Me
IP Enabled Dterm
Last Number Redial
Least Cost Routing 3/6 Digit
Message Center Interface MCI
Miscellaneous Trunk Access
Message Registration
Message Reminder
Night Service
Mobility Access
Modem over IP
MP Program Download FTP
Off-hook Alarm
No CID Call Routing
Off-Premises Extensions
Power Failure Transfer
Pooled Line Access
Optical Interface
Pad Lock
Automatic Idle Return
Remote Hold
Reserve Power
Remote PIM over IP
Resident System Program
Single Digit Feature Access Codes
Security Alarm
Save and Repeat
Set Relocation
Tenant Service
System Clock Setup by Station Dialing
Terminal Login via NAT
Tie Line Tandem Switching
Timed Reminder
Timed Queue Uniform Call Distribution UCD
Trunk Direct Appearances
Trunk Queuing Outgoing
Uniform Numbering Plan UNP -Voice and Data
Voice Mail Private Password
Variable Timing Parameters
Voice Guide
Voice Over IP H.323
Voice Mail Transfer
VoIP Log Collection
Whisper
Ccis Feature List
Ccis Features Descriptions
Call Forwarding Intercept Ccis
Centralized E911 Ccis
Flexible Numbering of Stations Ccis
Multiple Call Forwarding All Calls Ccis
Station-to-Station Calling Ccis
Isdn Feature List
Isdn Feature Descriptions
Event-Based Ccis
SIG Feature Descriptions
SIG Feature List
Wireless Feature List
Feature Adjunct Type Integrated Type Analog PBX
Table of Features by Configuration Type
Interface Wired for Wireless
Ccis Univerge Neax 2000 IPS
Wireless Feature Descriptions
Group Call 2Way Calling
This feature protects a call from being tapped
Page
System Input/Output I/O Interfaces
Station Message Detail Recording Smdr
2400 Extended Format
IMS Format
Smdr Terminal Interface
Smdr w/AP00
Combinations available at the same time
Combinations between Smdr and Smdr Output Format
Pattern D
ARP, IP, ICMP, UDP, TCP
Combinations for Local Office of Centralized Billing
Combinations for Center Office of Centralized Billing
System Capacity
Data Transmission Sequence for Ethernet Interface
Message Center Interface MCI
Hardware Required for Smdr
Description Qty Remarks
Hardware Required for MCI
VMS
Modem
Feature
Feature
Property Management System PMS
Type of Information
PMS Interface
Hardware Required for PMS
Description Qty Remarks
RS PRT-4S CA-A
System Outline
Open Application Interface
OpenWorX Attendant Statistics
OpenWorX Business Attendant System BAS
BAS Call Control Functionality
Brief Description of Call Control Function
Brief Definition of Queues
BAS Speed Dials Pad
BAS Directory
Did for Company Lookup
BAS Authorization and Account Code Dialing
BAS Offline Mode Pseudo Night Mode
BAS Overhead Paging
BAS Call Recording and Playback
BR Speed Dials Pad
OpenWorX Business Receptionist BR
BR Directory
BR Overhead Paging
BR Authorization and Account Code Dialing
OpenWorX Communications Portal
BR Attendant PC Minimum Hardware Requirements
Communications Portal Benefits
Communications Portal Functionality
OpenWorX Dialer
Dialer Database
Dialer Benefits
OpenWorX Message Reader MR
OpenWorX Location Status Information LSI
OpenWorX Short Text Messaging
MR Benefits
STM Benefits
OpenWorX Incoming Call Assistant ICA
ICA Functionality
ICA Benefits
OpenWorX Group Call Forward Control Gcfc
ICA Comparison of ICA and IPS Functionality
ICA ICA vs. Camp On
Gcfc Functionality
OpenWorX Personal Call Assistant PCA
PCA OpenWorX Desktop
PCA Limiting User Views
Desktop Directory
Personal Directory
PCA OpenWorX Inaset
OpenWorX Name Display
OAI Application Software Development
OpenWorX Multiple Ccis Node Configuration
BAS Ccis Network Information
Business Receptionist Ccis Network Information
Page
Automatic Call Distribution ACD with MIS
Automatic Call Distribution ACD
Basic ACD
Delay Announcement ACD
Basic ACD Features
Busy In/Busy Out ACD
Call Waiting Indication ACD
Immediate Overflow ACD
CallCenterWorX ACD 3.0 for Business
Priority Queuing ACD
Queue Size Control-ACD
CallCenterWorX ACD Features
Automatic Call Distribution with MIS
Business Turnkey Packages
CallCenterWorX MIS
Business Software Only Packages
CallCenterWorX ACD 3.0 for Business Turnkey Packages
CallCenterWorX MIS
Item ACD Capacities CallCenter WorX MIS
Business System Capacities
5GB
Bhca
Related Documents
PBX Requirements
ACD Terminals
PBX Requirements Remarks
Master Contact Center Solutions
Master
Contact Routing Q-Control
Announcements Q-Announce
Reports Q-Control
Agent Desktop Q-Desktop
Multi-Media Q-Email, Q-Chat, Q-Fax
Callbacks Q-Callback
Interactive Voice Response Q-IVR
Outbound Dialing Q-Outdial
QueWorX 4.0 Features
QueWorX 4.0 Licensed Applications
Auto Attendant
Scheduled Callbacks
Immediate Customer Callback
Internet Initiated Callbacks
Estimated Time to Answer ETA
Soft Phone
Screen Pop
Multilingual Announcements
Global Repeat Verification
Professional Services for QueWorX
Customized Announcements
Customizable Reports
Extended Enterprise IP Solution
VoIP Solutions
VoIP Solutions
Voice over IP VoIP
Equipment Name Function
Typical IP Gateway, Branch and Adapter configurations
IP Station
Peer-to-Peer Connections over Ccis Networking via IP
Peer-to Peer Connections between IP Enabled Dterm
Remote Connections of IP Stations
Connections to Legacy Stations and Trunks
Automatic Program Download for IP Enabled Dterm
8IPLA/24IPLA
Options Per Location
Service Conditions on System Registration
Service Conditions on Legacy Service Features
Service Conditions on Encryption in System Registration
Service Conditions on Vlan
MD5 is an algorithm defined in RFC 1321 from the Ietf
Local Connection Mode Remote Connection Mode
Service Conditions on Remote Connections
Operation mode for each IP terminal
Location number in each operation mode for each IP station
Example 1 When Sta logs in Location #1
Example 2 When Sta logs in Location #2
Service Conditions on Automatic Program Download
Required Equipment for IP Station
Ccis Networking via IP
SPN-32IPLAA IP PAD
SPN-16VCTAA IP PAD
Ccis Networking via IP Peer-to-Peer Connections Basis
Ccis Networking via IP Non Peer-to-Peer Connections Basis
Point-to-Multipoint Connection
IP Trunk Point-to-Multipoint Connection
IP Trunk Card Specifications
Service Conditions IP Ccis via IP Trunk cards
Required Equipment for IP Ccis via IP Trunk cards
Payload Period Maximum Voice Channels per IP Trunk
Connection
Features
Features
Service Conditions for H.323
Required Equipment for H.323
IP Trunk Specifications
Example of FAX and Modem over IP connection
FAX and Modem over IP
SPN-8IPLA IP PAD-B
SPN-8IPLA IP PAD-C
SPN-8IPLA IP PAD-A
SPN-32IPLA IP PAD-E
Opposite Office 2000 IPS
Required Equipment for FAX or Modem over IP
Opposite Office
Own
Required bandwidth for FAX Connection
Required bandwidth for Modem Connection
Connection Conditions Required Bandwidth One-way
Remote PIM over IP
Network Conditions and Payload
Requirement Remarks
Bandwidth Requirement
With G7.23.1 With G729a 8k Without Compression 3k/6.3k
Compression
Advantages
Required Hardware and Software
Host Site Equipment Name Remarks
Remote Site Equipment Name Remarks
XNote
List of Service Features Operation
Vendor Support for Open System Standards
Planning and Installation
Voice Messaging
Bandwidth requirements
Network Bandwidth
Network Consideration
Bandwidth utilization
Codec Filler Time Msec
Codec Total Bandwidth per transmit stream Msec
Device Registration Server DRS and Dhcp
Quality of Service QoS
Port Type Destination Default Port No Remarks
For Dterm IP
For Voice Control/Voice Packet
For H.323 IP Trunk
For Ccis Virtual IPT
IPT Ccis
PBX TCP
System Conditions/Limitations Peer-to-Peer IP
Limitations
Conditions
Common Channel Inter-Office Signaling Ccis
System Outline of a Ccis Connection
Ccis and Isdn
Digital and Analog Ccis
Digital Ccis
Analog Ccis
Voice Compression
Peer-to-Peer Connections
Common Channel Inter-Office Signaling Ccis
Ccis Networking via IP Non Peer-to-Peer
Service Conditions on Non Peer-to-Peer Connections
Centralized Billing
Local office/Tandem office
Center office
Common Channel Inter-Office Signaling Ccis
Centralized E911 Ccis
Look Ahead Routing
Call Set Up Times
Alternate Routing
Shared Trunk Facilities and Alternate Routing
Centralized System Maintenance and Administration
Centralized Maintenance Facility
Centralized Management Center
Centralized Call Accounting / Billing
Centralized Call Accounting/Billing Systems
Centralized Voice Processing / Messaging
Centralized Attendant Consoles
Ccis Centralized Voice Mail
Ccis Feature Name Neax 2400 Required
Ccis Feature Chart
Uniform Numbering Plans
YES
Ccis Feature Chart
System Capacity for Ccis with Digital Interface
System Capacity
System Capacity for Ccis with Analog Interface
System Capacity for Ccis Networking via IP
Required Equipment for Digital Ccis
Required Equipment
Required Equipment for Analog Ccis
Required Equipment for Ccis Networking via IP
Specifications Remarks
IP Specifications
PAD
24IPLA
Characteristics Channel
DTI Specifications
Page
PRI Services & Features
Integrated Services Data Network Isdn
Isdn Feature List
Isdn Primary Rate Interface
Call-By-Call Service Selection
Called Party Recognition Service Direct-In Termination DIT
CPN To Network-Present
CPN To Terminating User-Display
Did and DOD Addressing
Did Addressing
Isdn Terminal
AT&T
Page
Megacom 800 Service/800 Wats Ultra Wats
Megacom Access/WATS
Multiquest /900 Service
Subaddress-Present
Event Based Ccis
Trunk Provisioning Service Selection
Business Feature List
Business Feature List
Isdn Network Requirements for Layer One
Supported Network Services Trunk provisioned only
For 24DTI
Isdn PRI Specifications
For 30DTI
For 24PRT
BRT
DMS Selection 4ESS NET
Dedicated Access AT&T NTI MCI Sprint
NET IPS
DMS Provisioning 4ESS NET
AT&T NTI MCI Sprint
Voice Features DMS 4ESS NET
Dedicated Access NTI
AT&T MCI Sprint Selection DMS 4ESS NET IPS Switched Data
AT&T MCI Sprint Provisioning DMS 4ESS NET IPS Switched Data
AT&T MCI Sprint Virtual Private Network DMS 4ESS NET
Call by Call Service AT&T NTI Siemens Selection 5ESS
Services and Features LEC Carriers
Dedicated Access AT&T NTI Siemens
Virtual Private Network AT&T NTI DMS 4ESS NET
AT&T NTI Siemens
Voice Features AT&T NTI Siemens
Facility Management
Network Message Waiting
Ewsd Switched Data
Call By Call Service Selection
AT&T NTI Siemens 5ESS
Virtual Private Network AT&T NTI Siemens
Applications
Isdn Basic Rate Interface BRI
ONE SC03 Supports Four 2ILCA
System Requirements
Isdn PRI Required Equipment
Isdn Equipment List
Isdn BRI Required Equipment
Isdn Terminal Required Equipment
Capacity for ISDN-PRI
Documentation
System Capacity for ISDN-BRI
24DTI 24PRT
Page
Univerge Neax 2000 IPS Wireless Communication System WCS
Wireless System
Wired for Wireless
Analog PBX Interface
Ccis Interface
Wireless Roaming
Multi-Site Roaming
931a Roaming over IP Trunk
HLR
Wireless Definitions
Configuration Application Integrated Type
Wireless Short Text Message Notification OAI
Feature Matrix by Configuration Type
Features
2000 IPS Interface1 Interface2 Wired for Wireless
Adjunct Type Integrated Type
Feature Descriptions
Wireless
Wired for
Way Calling
Handover
Preset Dialing
Authorization
Out of Zone
Indication
Dterm PS
System Description
Lithium-Ion Battery
Dterm PS III Accessories
Battery Charger
Headsets
Zone Transceiver II ZT
Wireless Specifications
Zone Transceiver II Specifications
Integrated Adjunct Analog Adjunct Ccis
Equipment Description QTY Remarks
WCS Required Equipment
PN-4VCTI 4VCT
PN-IPTB IPT
Wireless LAN
Wireless LAN Handset
Wireless LAN Documentation
Hotel/Motel System
Hotel Feature List
PMS
Terminal Console
Hotel Console
Application Processor
Hotel/Motel Front Desk Terminal
Station Message Detail Recording Smdr
Executed Task Print Out
Hotel Printer
Automatic Wake-up
Direct Data Entry
Check In / Check Out
Do Not Disturb Console
Check
Do Not Disturb-Hotel/Motel
Do Not Disturb-System
Hotel/Motel Attendant Console
Hotel/Motel Front Desk Instrument
Maid Status
House Phone
Message Waiting
Message Registration
Voice Message Waiting System
Voice Message Waiting Individual
Property Management System PMS
Room Cutoff Console
Room Cutoff
Room Status
Single Digit Dialing
Items indicated are as follows
Specifications PMS/SMDR Interface Hotel Printer Interface
Hotel System Capacity
Description Capacity
SN716 Deskcon
Station Equipment
AIMWorX
Call Accounting
Multi-Site Centralized Operations
AIMWorX databases
Select Database Licensing Option Description
SQL Server licensing
Information you need before installing AIMWorX
Oracle database
Licensing
Configurations
Standalone
Call Record and User Capacity
Integrating AIMWorX modules
AIMWorX Manager
Corporate tier
Enterprise tier
1 SPE
Alarm Manager
Asset Manager
Auth Code Manager
Cable Manager
Bill Reconciler
Custom SPE Writer
Hospitality Links
Trouble Ticket
Additional Reference Material
Voice Mail SPE
Work Order
Voice Mail Integration
Voice Messaging Systems
Voice Messaging Systems
Description
MCI Service Conditions
System Architecture
NEAXMail AD-120
Level II Server Software License with Exchange
Voice Cards
Client Access Licenses CAL
Third Party Software
Platform Components
Mail Reader Text-to-Speech
Optional Software Feature Packages
Third Party Fax Server Integration
PBX Integration Software
2GB
Platform Specifications
NEAXMail AD-64
Level I/Level II Specifications Platform Level
Level I/Level II Platform Specifications
Level I Dell GX280 Level II Dell PE2800
40GB Sata 36GB Scsi
Additional Hardware Components
UPS Uninterruptible Power Supply
Optional Software
Optional ActiveFax Software
Unified Messaging
Hacker Prevention Features are as follows
Voice Messaging Systems
Voice Messaging Systems
Available Languages
Automated Attendant
Mailbox Manager
Audiotext
Voice Messaging Systems
Maintenance
Voice Messaging Systems
ViewMail
Visual Messaging
ViewCall Plus
NEAXMail IM-16 LX
Unified Messaging and Call Management
Full Digital Integration
Hospitality Feature Package
Basic Features
Enjoy the Benefits of Integrated Messaging
Additional Features
System Documentation
Niverge Neax 2000 IPS Features and Specification
Univerge Neax 2000 IPS Documentation List
Univerge Neax 2000 IPS Technical Manuals