R
Chapter 9: Configuration and Status
.
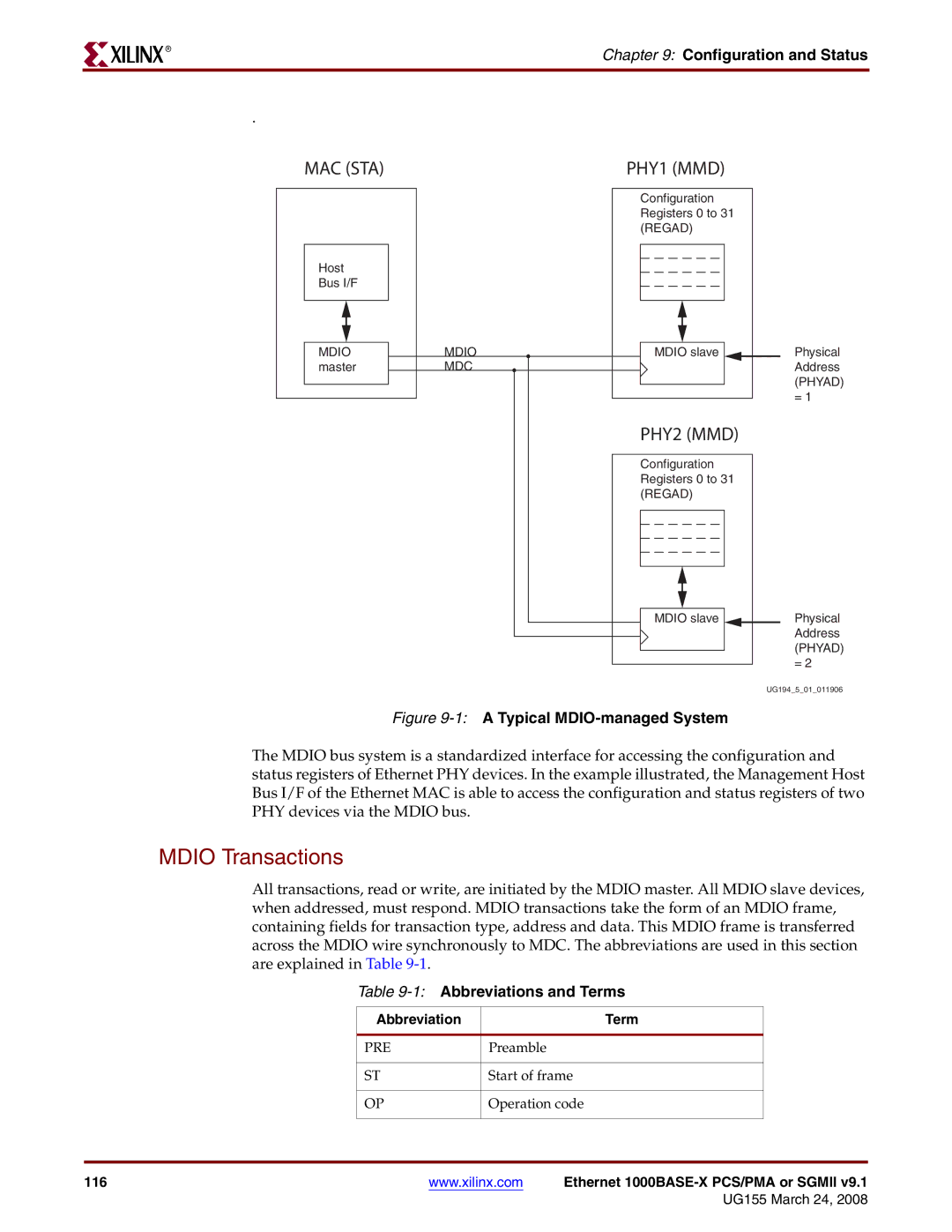
MAC (STA) | PHY1 (MMD) |
Host
Bus I/F
MDIO | MDIO |
master | MDC |
Configuration Registers 0 to 31 (REGAD)
MDIO slave ![]()
PHY2 (MMD)
Configuration Registers 0 to 31 (REGAD)
MDIO slave ![]()
Physical Address (PHYAD) = 1
Physical Address (PHYAD) = 2
UG194_5_01_011906
Figure 9-1: A Typical MDIO-managed System
The MDIO bus system is a standardized interface for accessing the configuration and status registers of Ethernet PHY devices. In the example illustrated, the Management Host Bus I/F of the Ethernet MAC is able to access the configuration and status registers of two PHY devices via the MDIO bus.
MDIO Transactions
All transactions, read or write, are initiated by the MDIO master. All MDIO slave devices, when addressed, must respond. MDIO transactions take the form of an MDIO frame, containing fields for transaction type, address and data. This MDIO frame is transferred across the MDIO wire synchronously to MDC. The abbreviations are used in this section are explained in Table
Table 9-1: Abbreviations and Terms
Abbreviation | Term |
|
|
PRE | Preamble |
|
|
ST | Start of frame |
|
|
OP | Operation code |
|
|
116 | www.xilinx.com | Ethernet |
|
| UG155 March 24, 2008 |