R
Chapter 5
Using the Client-side GMII Data Path
This chapter provides general guidelines for creating designs using
Designing with the
It is not within the scope of this document to define the Gigabit Media Independent Interface (GMII)— see clause 35 of the IEEE 802.3 specification for information about the GMII. Timing diagrams and descriptions are provided only as an informational guide.
GMII Transmission
This section includes figures that illustrate GMII transmission. In these figures the clock is not labeled. The source of this clock signal varies, depending on the options selected when the core is generated. For more information on clocking, see Chapters 6, 7 and 8.
Normal Frame Transmission
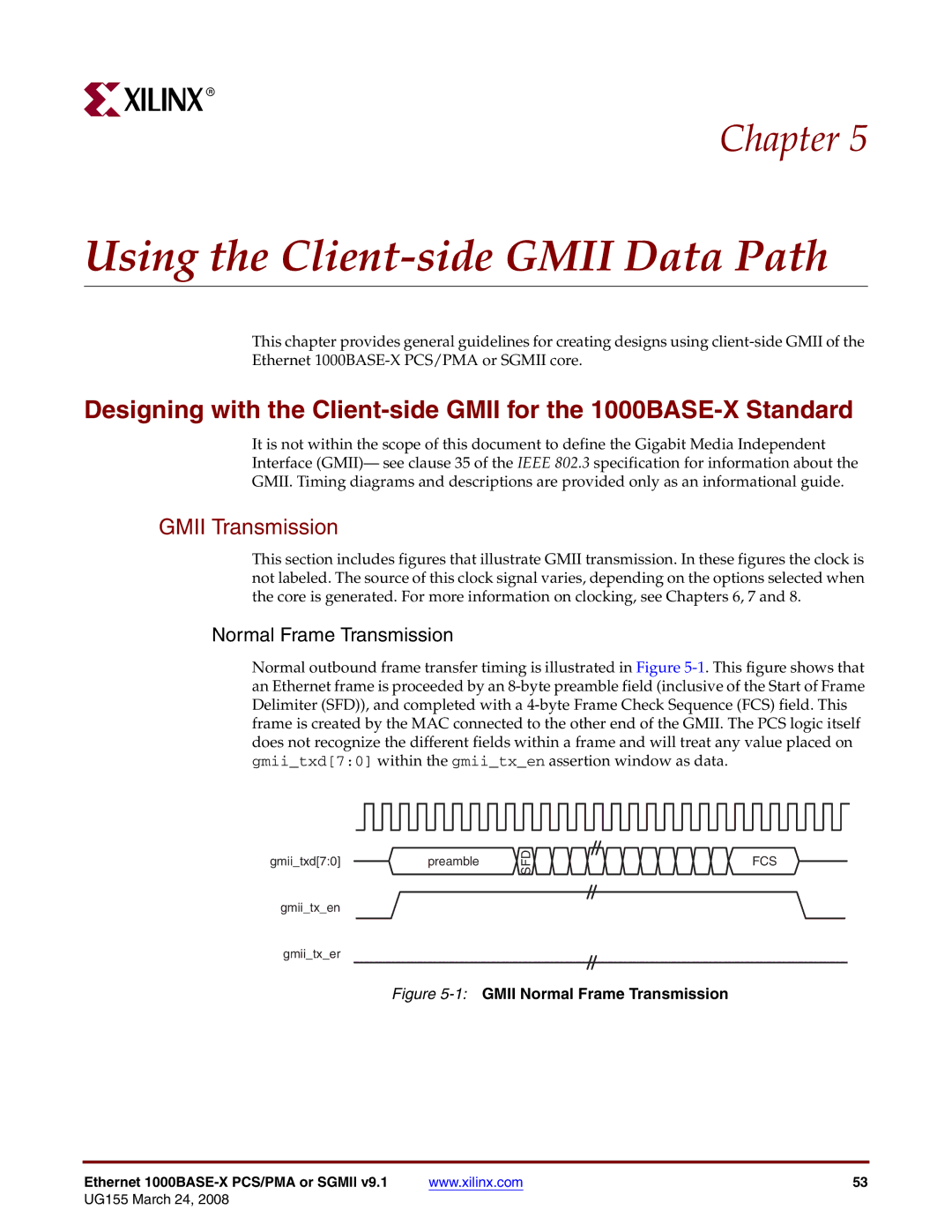
Normal outbound frame transfer timing is illustrated in Figure
gmii_txd[7:0]preamble
SFD![]()
FCS
gmii_tx_en
gmii_tx_er
Figure 5-1: GMII Normal Frame Transmission
Ethernet | www.xilinx.com | 53 |