R
Chapter 2: Core Architecture
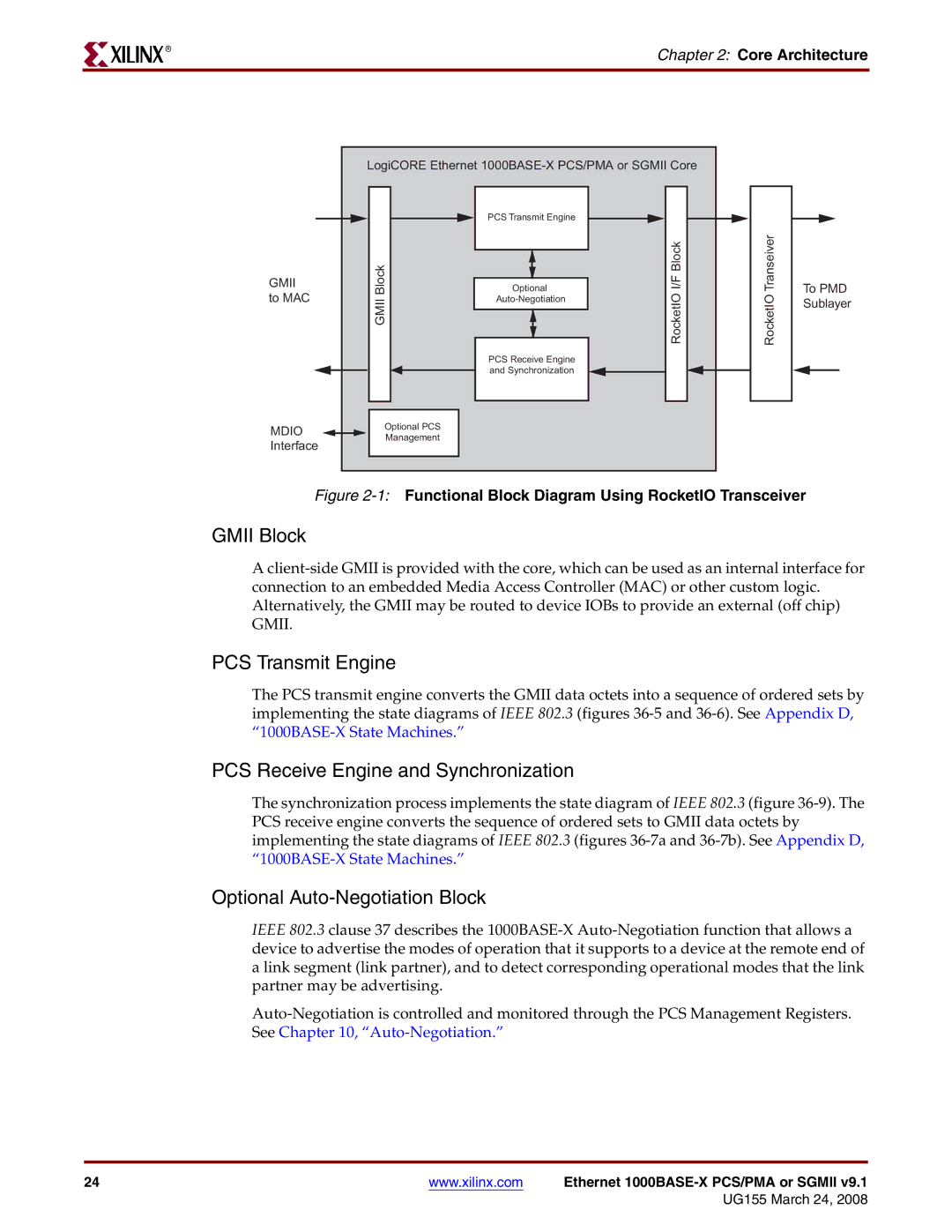
| LogiCORE Ethernet |
|
| |||
|
| PCS Transmit Engine |
|
|
| |
GMII | GMII Block | Optional | RocketIO I/F Block | RocketIO Transeiver | To PMD | |
to MAC | ||||||
Sublayer | ||||||
|
| |||||
|
|
| ||||
|
| PCS Receive Engine |
|
|
| |
|
| and Synchronization |
|
|
| |
MDIO |
| Optional PCS |
|
|
| |
| Management |
|
|
| ||
Interface |
|
|
| |||
|
|
|
| |||
| Figure | |||||
GMII Block
A
PCS Transmit Engine
The PCS transmit engine converts the GMII data octets into a sequence of ordered sets by implementing the state diagrams of IEEE 802.3 (figures
PCS Receive Engine and Synchronization
The synchronization process implements the state diagram of IEEE 802.3 (figure
Optional Auto-Negotiation Block
IEEE 802.3 clause 37 describes the
24 | www.xilinx.com | Ethernet |