R
Chapter 5: Using the Client-side GMII Data Path
gmii_tx_clk
IPAD
gmii_txd[0]
IPAD
gmii_tx_en
IPAD
gmii_tx_er
IPAD
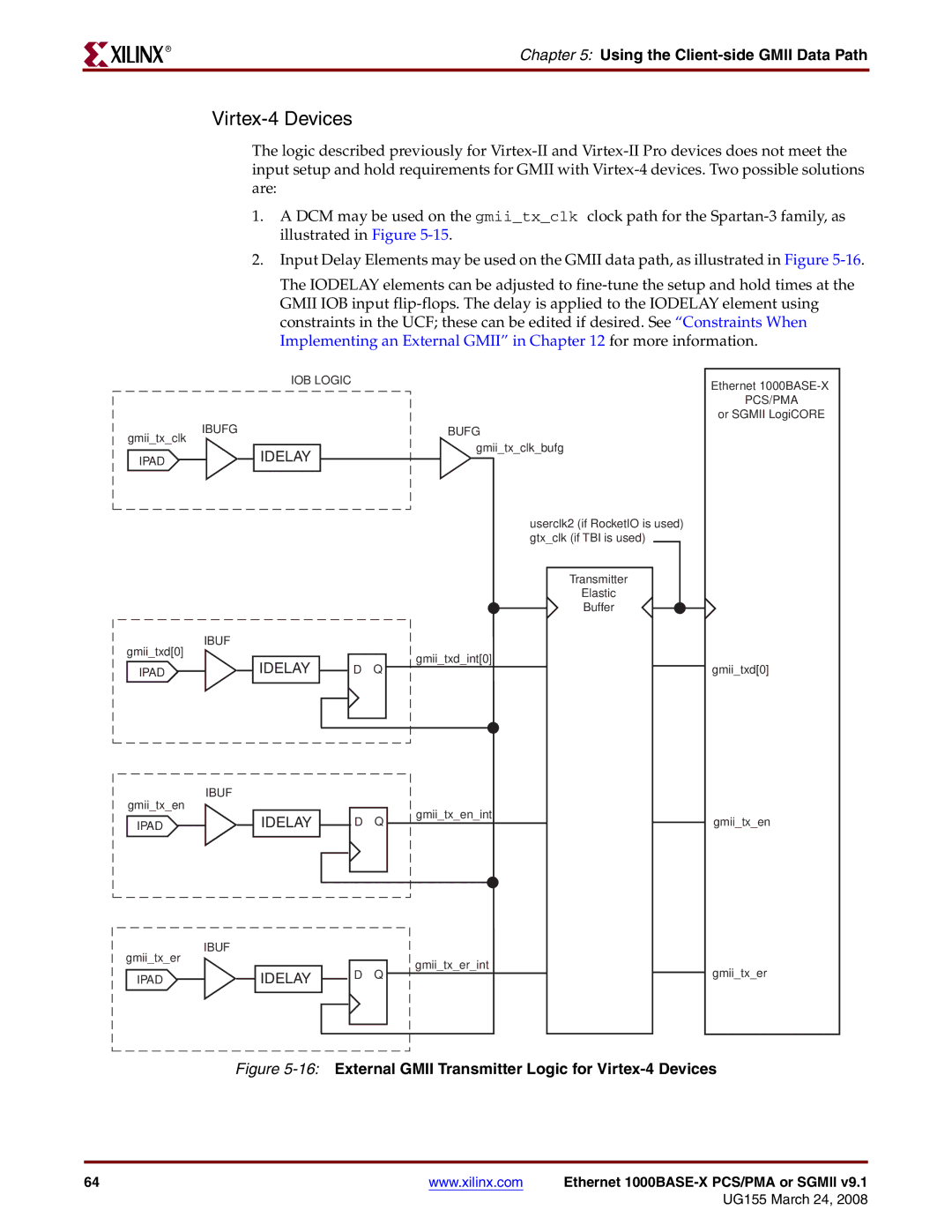
Virtex-4 Devices
The logic described previously for
1.A DCM may be used on the gmii_tx_clk clock path for the
2.Input Delay Elements may be used on the GMII data path, as illustrated in Figure
The IODELAY elements can be adjusted to
|
| IOB LOGIC | Ethernet | |
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
| PCS/PMA |
IBUFG |
|
|
| or SGMII LogiCORE |
|
|
| BUFG | |
|
|
|
| gmii_tx_clk_bufg |
|
| IDELAY |
| |
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
userclk2 (if RocketIO is used) gtx_clk (if TBI is used)
Transmitter
Elastic
Buffer
IBUF
IDELAY | D Q | gmii_txd_int[0] |
gmii_txd[0] |
IBUF
IDELAY | D Q | gmii_tx_en_int | gmii_tx_en |
|
IBUF
IDELAY | D Q | gmii_tx_er_int | gmii_tx_er |
|
Figure 5-16: External GMII Transmitter Logic for Virtex-4 Devices
64 | www.xilinx.com | Ethernet |
|
| UG155 March 24, 2008 |