R
Chapter 8: SGMII / Dynamic Standards Switching with RocketIO Transceivers
Closely Related Clock Sources
Case 1
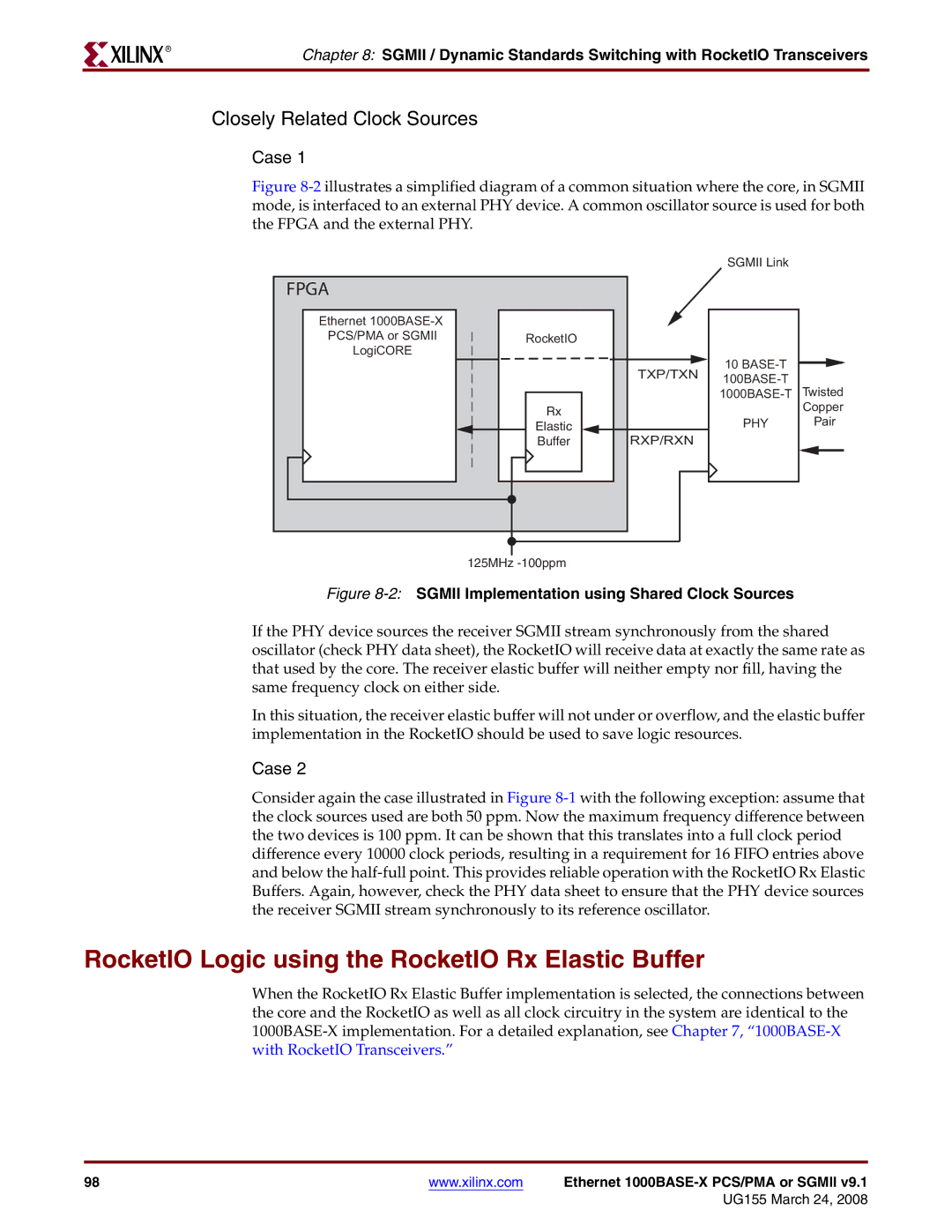
Figure 8-2 illustrates a simplified diagram of a common situation where the core, in SGMII mode, is interfaced to an external PHY device. A common oscillator source is used for both the FPGA and the external PHY.
SGMII Link
FPGA |
|
|
|
Ethernet |
|
|
|
PCS/PMA or SGMII | RocketIO |
|
|
LogiCORE |
|
| 10 |
|
| TXP/TXN | |
|
| ||
|
|
| |
| Rx |
| PHY |
| Elastic | RXP/RXN | |
| Buffer |
| |
| 125MHz |
|
|
Figure | |||
Twisted
Copper
Pair
If the PHY device sources the receiver SGMII stream synchronously from the shared oscillator (check PHY data sheet), the RocketIO will receive data at exactly the same rate as that used by the core. The receiver elastic buffer will neither empty nor fill, having the same frequency clock on either side.
In this situation, the receiver elastic buffer will not under or overflow, and the elastic buffer implementation in the RocketIO should be used to save logic resources.
Case 2
Consider again the case illustrated in Figure
RocketIO Logic using the RocketIO Rx Elastic Buffer
When the RocketIO Rx Elastic Buffer implementation is selected, the connections between the core and the RocketIO as well as all clock circuitry in the system are identical to the
98 | www.xilinx.com | Ethernet |
|
| UG155 March 24, 2008 |