Design Overview
R
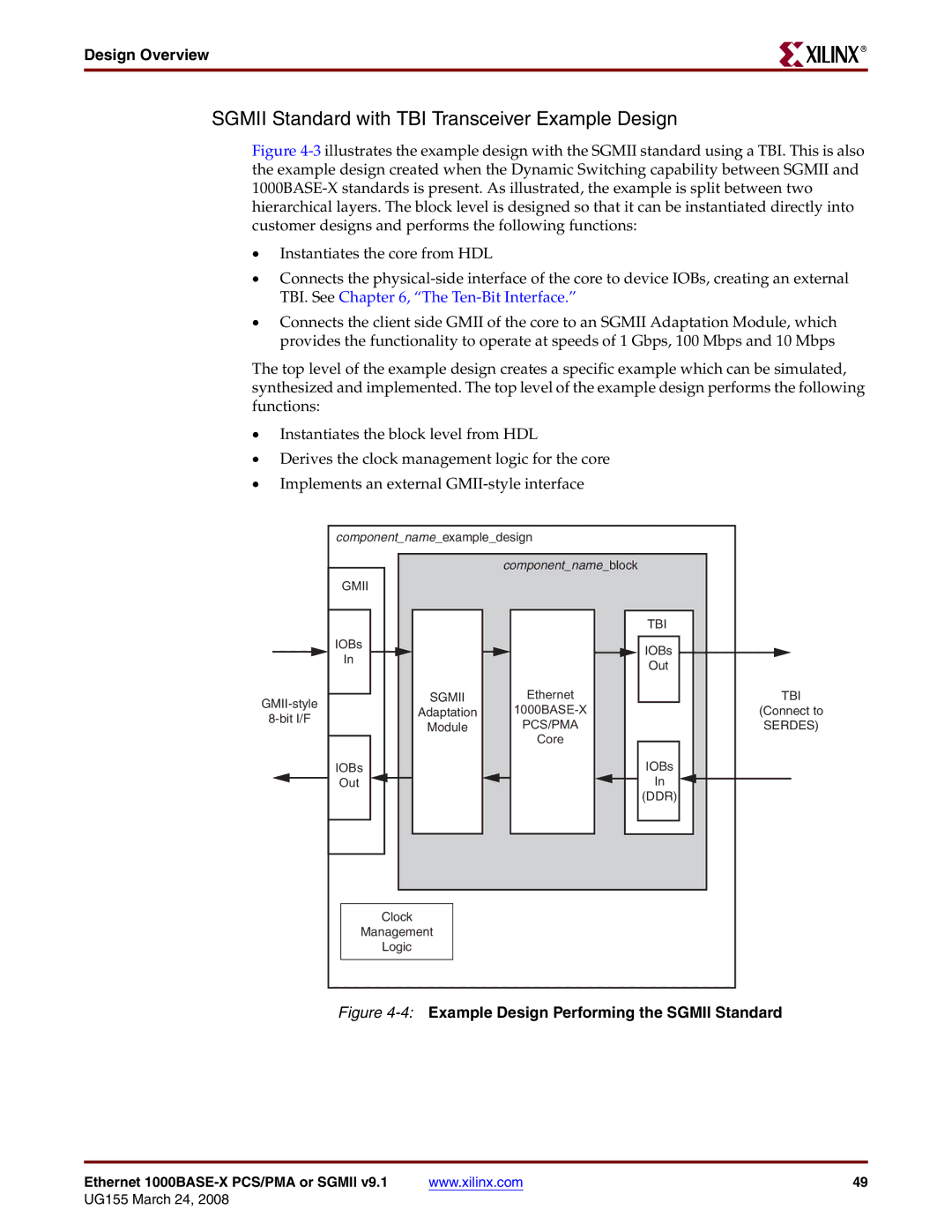
SGMII Standard with TBI Transceiver Example Design
Figure 4-3 illustrates the example design with the SGMII standard using a TBI. This is also the example design created when the Dynamic Switching capability between SGMII and 1000BASE-X standards is present. As illustrated, the example is split between two hierarchical layers. The block level is designed so that it can be instantiated directly into customer designs and performs the following functions:
•Instantiates the core from HDL
•Connects the physical-side interface of the core to device IOBs, creating an external TBI. See Chapter 6, “The Ten-Bit Interface.”
•Connects the client side GMII of the core to an SGMII Adaptation Module, which provides the functionality to operate at speeds of 1 Gbps, 100 Mbps and 10 Mbps
The top level of the example design creates a specific example which can be simulated, synthesized and implemented. The top level of the example design performs the following functions:
•Instantiates the block level from HDL
•Derives the clock management logic for the core
•Implements an external GMII-style interface
component_name_example_design |
| |||
|
| component_name_block |
| |
GMII |
|
|
| |
|
|
| TBI | |
IOBs |
|
| IOBs | |
In |
|
| ||
|
| Out | ||
|
|
| ||
SGMII | Ethernet | TBI | ||
Adaptation | (Connect to | |||
Module | PCS/PMA | SERDES) | ||
| ||||
|
| Core |
| |
IOBs |
|
| IOBs | |
Out |
|
| In | |
|
|
| (DDR) | |
Clock |
|
|
| |
Management |
|
| ||
Logic |
|
|
| |
Figure | ||||
Ethernet | www.xilinx.com | 49 | ||
UG155 March 24, 2008 |
|
|
| |