56
A Windows user account that is not stored in the PDC server’s LDAP directory can be used to access other services. For example, Mac OS X Server can authenticate users with accounts in the server’s local directory domain for the server’s Windows file service.
Mac OS X Server also authenticates users with accounts on other directory systems, such as an Open Directory master on another Mac OS X Server system, or Active Directory on a Windows server.
For complete information about the different kinds of directory domains, see Open Directory Administration.
Predefined User Accounts
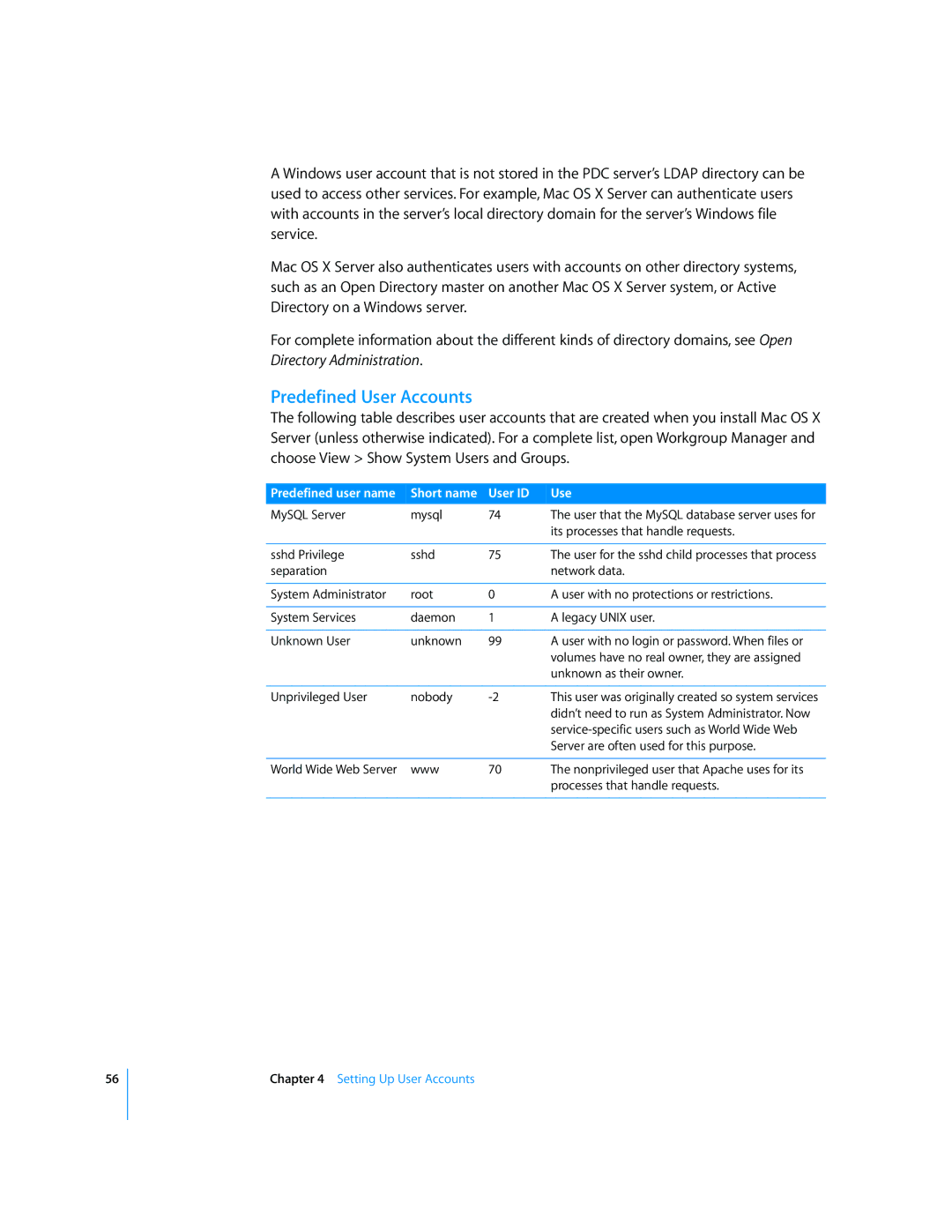
The following table describes user accounts that are created when you install Mac OS X Server (unless otherwise indicated). For a complete list, open Workgroup Manager and choose View > Show System Users and Groups.
Predefined user name | Short name | User ID | Use |
MySQL Server | mysql | 74 | The user that the MySQL database server uses for |
|
|
| its processes that handle requests. |
|
|
|
|
sshd Privilege | sshd | 75 | The user for the sshd child processes that process |
separation |
|
| network data. |
|
|
|
|
System Administrator | root | 0 | A user with no protections or restrictions. |
|
|
|
|
System Services | daemon | 1 | A legacy UNIX user. |
|
|
|
|
Unknown User | unknown | 99 | A user with no login or password. When files or |
|
|
| volumes have no real owner, they are assigned |
|
|
| unknown as their owner. |
|
|
|
|
Unprivileged User | nobody | This user was originally created so system services | |
|
|
| didn’t need to run as System Administrator. Now |
|
|
| |
|
|
| Server are often used for this purpose. |
|
|
|
|
World Wide Web Server | www | 70 | The nonprivileged user that Apache uses for its |
|
|
| processes that handle requests. |
|
|
|
|
Chapter 4 Setting Up User Accounts