Literature Number SPRU629 April
Important Notice
Read This First
Trademarks
Contents
Discusses operation of the video capture port
Video Capture Port
VCASTRT1, VCBSTRT1
VCASTOP1, VCBSTOP1
VCASTRT2, VCBSTRT2
VCASTOP2, VCBSTOP2
11.1
VDVSYNE2
General Purpose I/O Operation
Vcxo Interpolated Control Port
Figures
Xii
Figures Xiii
Video Port
Tables
Xvi
Tables Xvii
Overview
Topic
Video Port
SPRU629
VCLK1 VCLK2 VCTL1 VCTL2
VCTL3
Channel a
Channel B
Video Port Fifo
DMA Interface
Video Capture Fifo Configurations
Ysrca Cbsrca Crsrca Ysrcb Cbsrcb Crsrcb
Ysrca
Y/C Video Capture Fifo Configuration
Ysrca Cbsrca Crsrca
Video Display Fifo Configurations
Ydsta Cbdst Crdst
10-Bit Raw Video Display Fifo Configuration
Ydsta
Ydstb
10. Y/C Video Display Fifo Configuration
Video Port Registers
Video Capture Signal Mapping
Video Port Pin Mapping
Video Display Signal Mapping
Usage Raw Data Display Mode
Capture Mode BT.656 Raw Data
Data Bus 10-Bit 16-Bit 20-Bit Mode
Vdin Bus Usage for Capture Modes
Vdin Data Bus Usage for Capture Modes
Vdout Data Bus Usage for Display Modes
Vdout Data Bus Usage for Display Modes
Video Port
Peripheral Bus Reset
Reset Operation
Power-On Reset
Software Port Reset
Capture Channel Reset
Display Channel Reset
Interrupt Operation
DMA Operation
Capture DMA Event Generation
Capture DMA Event Generation Flow Diagram
Fifo ≥
Display DMA Event Generation
Display DMA Event Generation Flow Diagram
DMA Size and Threshold Restrictions
DMA Interface Operation
Clocks
Video Port Functionality Subsets
Video Port Functional Clocks
Data Bus Width
Video Capture Throughput
Video Port Throughput and Latency
Fifo Size
Y/C Video Capture Fifo Capacity
Bit Bit Dense 10-Bit
Bit Bit Dense 10/16-Bit 20-Bit Samples 5120 3840 2560 1280
Video Display Throughput
Raw Video Display Fifo Capacity
Acronym Register Name Section
Video Port Control Registers
Video Port Control Registers
Video Port Control Register Vpctl
Video Port Control Register Vpctl Field Descriptions
Bit
Value Description
None Clear
VCLK2P
None Reverse
None Activelow
Vpctl Bit
Video Port Operating Mode Selection
Operating Mode
Video Port Status Register Vpstat
Video Port Status Register Vpstat Field Descriptions
Video Port Interrupt Enable Register Vpie
Dcna
Serrb
Ccmpb
Lfda
Video Port Interrupt Status Register Vpis
Dcna Dcmp
Tick STC
Lfda Sfda VINTA2 VINTA1 Serra Ccmpa Covra
Vcount = Ystop
Vcbctl
Out of the port. The DMA complete interrupt can be used to
BT.656 or Y/C capture mode Lfda is set when long field
Vcactl
Video Capture Port
TSI Bit Cmode Bits Mode Description
Video Capture Mode Selection
Video Capture Mode Selection
BT.656 Video Capture Mode
1 BT.656 Capture Channels
2 BT.656 Timing Reference Codes
BT.656 Video Timing Reference Codes
Error Correction by Protection Bits
BT.656 Protection Bits
Line Information Bits Protection Bits
Received F, V, and H Bits
P 0 Bits
3 BT.656 Image Window and Capture
010 011 100 101
Video Capture Parameters
Common Video Source Parameters
4 BT.656 Data Sampling
5 BT.656 Fifo Packing
Bit BT.656 Fifo Packing
VDIN9-0 / VDIN19-10 Cb Cr 0 Y Cb 1 Y
Bit BT.656 Dense Fifo Packing
2 Y/C Timing Reference Codes
Y/C Video Capture Mode
1 Y/C Capture Channels
3 Y/C Image Window and Capture
4 Y/C Fifo Packing
Bit Y/C Fifo Packing
VDIN9-0 VDIN19-10 Little-Endian Packing Big-Endian Packing
Bit Y/C Dense Fifo Packing
BT.656 and Y/C Mode Field and Frame Operation
Capture Determination and Notification
Operation
BT.656 and Y/C Mode Capture Operation
VC xCTL Bit
Vertical Synchronization
VCxCTL Bit
VC xCTL Bit VMode
Vertical Counter Reset Point
Vertical Synchronization Programming
Vcount Operation Example EXC =
Horizontal Counter Reset Point
Horizontal Synchronization
Horizontal Synchronization Programming
VCxCTL Bit HMode
Hcount Operation Example EXC =
Field Identification
Field Identification Programming
Field Detect Method
EAV code
11.Field 1 Detection Timing
Short and Long Field Detect
10. Input Filter Mode Selection
Video Input Filtering
Input Filter Modes
Filter Operation
Chrominance Resampling Operation
Scaling Operation
13 /2 Scaled Co-Sited Filtering
EAV
Edge Pixel Replication
SAV
16. Capture Window Not Requiring Edge Pixel Replication
Xstart Xsize SAV
Vertical Ancillary Vanc Data Capture
Ancillary Data Capture
Horizontal Ancillary Hanc Data Capture
Raw Data Capture Mode
Raw Data Capture Notification
11. Raw Data Mode Capture Operation
Raw Data Fifo Packing
17 -Bit Raw Data Fifo Packing
19 -Bit Dense Raw Data Fifo Packing
21 -Bit Raw Data Fifo Packing
TSI Data Capture
TSI Capture Mode
TSI Capture Features
Vclkin Capen Pacstrt
TSI Capture Error Detection
Synchronizing the System Clock
PCR
Ctmode
Vcactl Bit
12. TSI Capture Mode Operation
TSI Data Capture Notification
Writing to the Fifo
Vclkin
TSI TSI Fifo
Perr
Capture Line Boundary Conditions
Reading from the Fifo
Ipcount = IMGHSIZE78 Vclkout
Fifo
Capturing Video in BT.656 or Y/C Mode
Handling Fifo Overrun in BT.656 or Y/C Mode
Capturing Video in Raw Data Mode
Capturing Data in TSI Capture Mode
Handling Fifo Overrun Condition in Raw Data Mode
Handling Fifo Overrun Condition in TSI Capture Mode
Video Capture Registers
13. Video Capture Control Registers
Video Capture Channel x Status Register VCASTAT, Vcbstat
BT.656 or Y/C Mode Raw Data Mode TSI Mode
Description Bit
Detected
Value BT.656 or Y/C Mode Raw Data Mode TSI Mode
Vcfld
Video Capture Channel a Control Register Vcactl
Block
Rdfe
FIELD1
FIELD2
Eavfid
FDL
V1EAV
V0EAV
Half
CON ‡
Description Raw Data Mode TSI Mode
VCXSTART/VCVBLNKP
Vcystart
SSE
Vcxstart
Vcvblnkp
Vcystop
Vcxstop
Field† Symval†
FFFh Last captured line Not used
VIF2 FSCL2
VINT2
VIF1
VINT1
VIF2
SPRU629
VCTHRLD2
VCTHRLD1
CAPEVTCT2
CAPEVTCT1
CON Frame CF2 CF1
Video Capture Channel B Control Register Vcbctl
Vrst Hrst Vcen PK10B Lfde Sfde Resmpl
F1C, F2C, and Frmc status bits, in VCBSTAT, are not
EAV or Not used VCTL1 active edge
CON‡
Capture field Not used
TSI Capture Control Register Tsictl
Enstc Tcken Sten Ctmode
Value BT.656, Y/C Mode TSI Mode Or Raw Data Mode
24. TSI Capture Control Register Tsictl Field Descriptions
BT.656, Y/C Mode TSI Mode Or Raw Data Mode
TSI Clock Initialization LSB Register Tsiclkinitl
Inpcr
Bit Field
Inpcre
TSI Clock Initialization MSB Register Tsiclkinitm
Inpcrm
TSI System Time Clock LSB Register Tsistclkl
42. TSI System Time Clock LSB Register Tsistclkl
Pcre
TSI System Time Clock MSB Register Tsistclkm
Pcre Pcrm
TSI System Time Clock Compare LSB Register Tsistcmpl
ATC
TSI System Time Clock Compare MSB Register Tsistcmpm
45. TSI System Time Clock Compare MSB Register Tsistcmpm
TSI System Time Clock Compare Mask LSB Register Tsistmskl
Atcm
TSI System Time Clock Compare Mask MSB Register Tsistmskm
TSI System Time Clock Ticks Interrupt Register Tsiticks
Tickct
Capture Mode Register BT.656 or Y/C Raw Data
Video Capture Fifo Registers
34. Video Capture Fifo Registers
35. Video Capture Fifo Registers Function
Video Display Port
Video Display Mode Selection
Video Display Mode Selection
Dmode Bits Mode Description
Image Timing
Ntsc Compatible Interlaced Display
Interlaced Blanking Intervals and Video Areas
Progressive Blanking Intervals and Video Area
Video Display Counters
Horizontal Blanking and Horizontal Sync Timing
Fpcount
Sync Signal Generation
Flcount
Vblnk
Vsync
External Sync Operation
Port Sync Operation
BT.656 Video Display Mode
Display Timing Reference Codes
BT.656 Frame Timing
Line Number
11.Digital Vertical F and V Transitions
Blanking Codes
3 BT.656 Image Display
4 BT.656 Fifo Unpacking
12 -Bit BT.656 Fifo Unpacking
13 -Bit BT.656 Fifo Unpacking
14. BT.656 Dense Fifo Unpacking
Y/C Video Display Mode
1 Y/C Display Timing Reference Codes
4 Y/C Fifo Unpacking
2 Y/C Blanking Codes
3 Y/C Image Display
16 -Bit Y/C Fifo Unpacking
17 -Bit Y/C Fifo Unpacking
18 -Bit Y/C Dense Fifo Unpacking
Output Filter Mode Selection
Video Output Filtering
Output Filter Modes
Vdctl Bit
19. Chrominance Resampling
20 x Co-Sited Scaling
23. Luma Edge Replication
Raw Data Display Mode
Ancillary Data Display
Horizontal Ancillary Hanc Data Display
Vertical Ancillary Vanc Data Display
Raw Mode RGB Output Support
Raw Data Fifo Unpacking
26 -Bit Raw Fifo Unpacking
28 -Bit Raw Fifo Unpacking
30 -Bit Raw 3/4 Fifo Unpacking
Video Display Field and Frame Operation
Display Determination and Notification
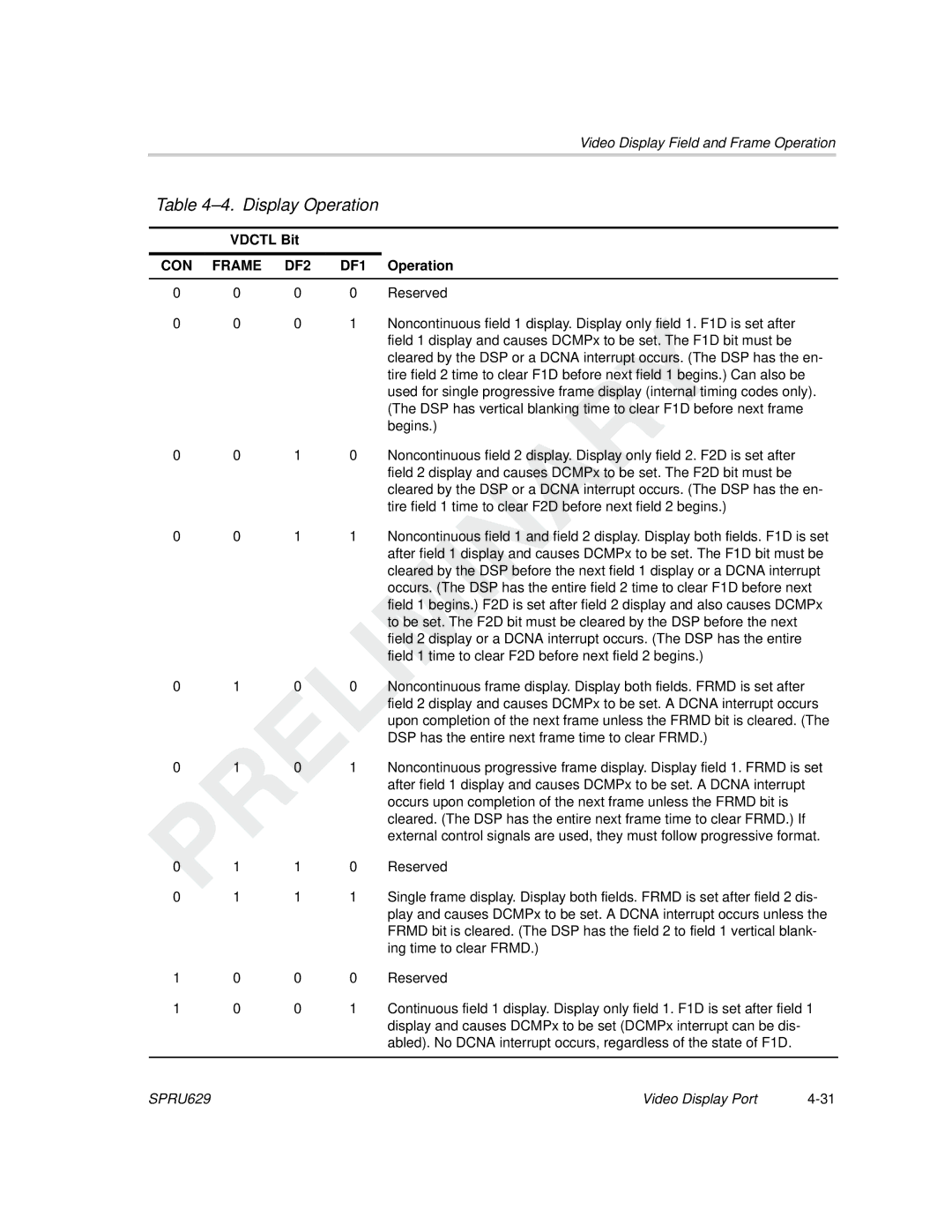
Display Operation
CON Frame DF2 DF1
Video Display Event Generation
Display Line Boundary Conditions
32. Display Line Boundary Example
Display Timing Examples
Interlaced BT.656 Timing Example
33. BT.656 Interlaced Display Horizontal Timing Example
SPRU629
34. BT.656 Interlaced Display Vertical Timing Example
Interlaced Raw Display Example
35. Raw Interlaced Display Horizontal Timing
SPRU629
36. Raw Interlaced Display Vertical Timing Example
3 Y/C Progressive Display Example
37. Y/C Progressive Display Horizontal Timing Example
SPRU629
38. Y/C Progressive Display Vertical Timing Example
Displaying Video in BT.656 or Y/C Mode
Displaying Video in BT.656 or Y/C Mode
Displaying Video in Raw Data Mode
Displaying Video in Raw Data Mode
Handling Underrun Condition of the Display Fifo
Video Display Registers
Video Display Control Registers
Video Display Status Register Vdstat
Video Display Status Register Vdstat Field Descriptions
Video Display Control Register Vdctl Field Descriptions
BT.656 and Y/C Mode Raw Data Mode
Video Display Control Register Vdctl
Disable Enable
Blkdis
FXS
Output
Value BT.656 and Y/C Mode Raw Data Mode
Rgbx
Blanking
Frmdis
Flddis
Frmwidth
Video Display Frame Size Register Vdfrmsz
Frmheight
Video Display Horizontal Blanking Register Vdhblnk
Hbdla
Hblnkstart
Delay
Hblnkstop
VBLNKYSTART1
VBLNKXSTART1
VBLNKYSTOP1
VBLNKXSTOP1
Field† Symval†
VBLNKYSTART2
VBLNKXSTART2
VBLNKYSTOP2
VBLNKXSTOP2
Video Display Field 1 Image Offset Register VDIMGOFF1
Negoff
IMGVOFF1
IMGHOFF1
IMGHSIZE1
Video Display Field 1 Image Size Register VDIMGSZ1
IMGVSIZE1
IMGHOFF2
Video Display Field 2 Image Offset Register VDIMGOFF2
IMGVOFF2
None
IMGHSIZE2
Video Display Field 2 Image Size Register VDIMGSZ2
IMGVSIZE2
FLD1XSTART
Video Display Field 1 Timing Register VDFLDT1
FLD1YSTART
FLD2XSTART
Video Display Field 2 Timing Register VDFLDT2
FLD2YSTART
Video Display Threshold Register Vdthrld
Incpix
VDTHRLD2
VDTHRLD1
Hsyncstart
Video Display Horizontal Synchronization Register Vdhsync
Hsyncstop
VSYNCYSTART1
VSYNCXSTART1
VSYNCYSTOP1
VSYNCXSTOP1
VSYNCYSTART2
VSYNCXSTART2
VSYNCYSTOP2
VSYNCXSTOP2
Video Display Counter Reload Register Vdreload
Vrld
Hrld
Crld
DISPEVT1
Video Display Display Event Register Vddispevt
DISPEVT2
Video Display Clipping Register Vdclip
Clipchigh
Clipyhigh Clipylow
Clipclow
Ydefval
Video Display Default Display Value Register Vddefval
Crdefval Cbdefval
Defval
Crdefval
Video Display Vertical Interrupt Register Vdvint
64. Video Display Vertical Interrupt Register Vdvint
Fbitclr
Video Display Field Bit Register Vdfbit
Fbitset
VBITCLR1
VBITSET1
Field† Symval†
VBITCLR2
VBITSET2
Field† Symval†
Register Field 525/60 Value 625/50 Value
Video Display Registers Recommended Values
34. Video Display Register Recommended Values
VDVSYNS2 VSYNCXSTART2
VDVSYNE2 VSYNCXSTOP2
Vdfbit Fbitclr Fbitset
VDVBIT1 VBITSET1
Video Display Fifo Registers
35. Video Display Fifo Registers
36. Video Display Fifo Registers Function
Register BT.656 or Y/C Raw Data
General Purpose I/O Operation
Gpio Registers
Gpio Registers
Video Port Registers
Video Port Peripheral Identification Register Vppid
Type
Class Revision
Class
Video Port Peripheral Control Register PCR
Soft Free
Peren
Soft
Stop
Comp
Video Port Pin Function Register Pfunc
Video Port Pin Function Register Pfunc Field Descriptions
PFUNC22
Normal
PFUNC20
PFUNC10
VDATA10TO19
PFUNC0
Video Port Pin Direction Register Pdir
Video Port Pin Direction Register Pdir Field Descriptions
PDIR22
VCTL3IN
PDIR21
VCTL2IN
VCTL2OUT
PDIR20
PDIR8
VDATA8TO9IN
VDATA8TO9OUT
PDIR4
Video Port Pin Data Input Register Pdin
PDIN20
PDIN12
PDIN7 PDIN6
Video Port Pin Data Input Register Pdin Field Descriptions
Video Port Pin Data Output Register Pdout
PDOUT20
Video Port Pin Data Out Register Pdout Field Descriptions
PDOUT21
Video Port Pin Data Set Register Pdset
PDSET20
Video Port Pin Data Set Register Pdset Field Descriptions
PDSET21
Video Port Pin Data Clear Register Pdclr
Video Port Pin Data Clear Register Pdclr
Video Port Pin Data Clear Register Pdclr Field Descriptions
Video Port Pin Interrupt Enable Register Pien
Video Port Pin Interrupt Enable Register Pien
PIEN21
PIEN20
Video Port Pin Interrupt Polarity Register Pipol
PIPOL21 PIPOL20 PIPOL19
PIPOL17 PIPOL16 PIPOL15
PIPOL13 PIPOL12
PIPOL22
VCTL3ACTHI
VCTL3ACTLO
PIPOL21
Video Port Pin Interrupt Status Register Pistat
PISTAT22
VCTL3INT
VCTL2INT
PISTAT20
Video Port Pin Interrupt Clear Register Piclr
PICLR4
PICLR20
PICLR22
PICLR21
Vcxo Interpolated Control Port
Overview
VIC Port Interface Signals
VIC Port Signal Direction Description
Interface
Operational Details
Example Values for Interpolation Rate
VIC Port Registers
Enabling VIC Port
VIC Port Registers
VIC Control Register Vicctl
VIC Control Register Vicctl Field Descriptions
GO bit can be written to at any time
Vicinbits
VIC Input Register Vicin
VIC Input Register Vicin Field Descriptions
Vicclkdiv
VIC Clock Divider Register Vicdiv
VIC Clock Divider Register Vicdiv Field Descriptions
Video Port Configuration Examples
Example 1 Noncontinuous Frame Capture for 525/60 Format
VCAIMGHSIZE2 * VCAIMGVSIZE2
Frame
VPVCASTOP1RMKVCAYSTOP1, VCAXSTOP1
VPVCASTRT1SSEENABLE, VCAXSTART1
Vpvcactlblkcapclear
SPRU629
Vcayedmafrmcnt
Edmaoptrmk Edmaoptprimedium
Example 2 Noncontinuous Frame Display for 525/60 Format
Vdhblnkstop Vdhblnkstart +
Define vertical blanking bitVDVBITn reg values
VDIMGHSIZE1 * VDIMGVSIZE1
Dmode
VPVDFRMSZRMKVDFRMHEIGHT, Vdfrmwidth
VPVDVBLKS2RMKVDVBLNKYSTART2, VDVBLNKXSTART2
VPVDVSYNE2RMKVDVSYNCYSTOP2, VDVSYNCXSTOP2
Vpvdstatfrmdclear
Vdyedmafrmcnt Vdyedmaelecnt
Example 2 Noncontinuous Frame Display for 525/60 Format
EDMAOPT2DSYES
Index
Index-2
Index-3
Pin data set register Pdset Pin direction register Pdir
Vcaevtct
Vdhblnk
Index-7
Vddefval Vddispevt
Index-9
Ydsta Ydstb