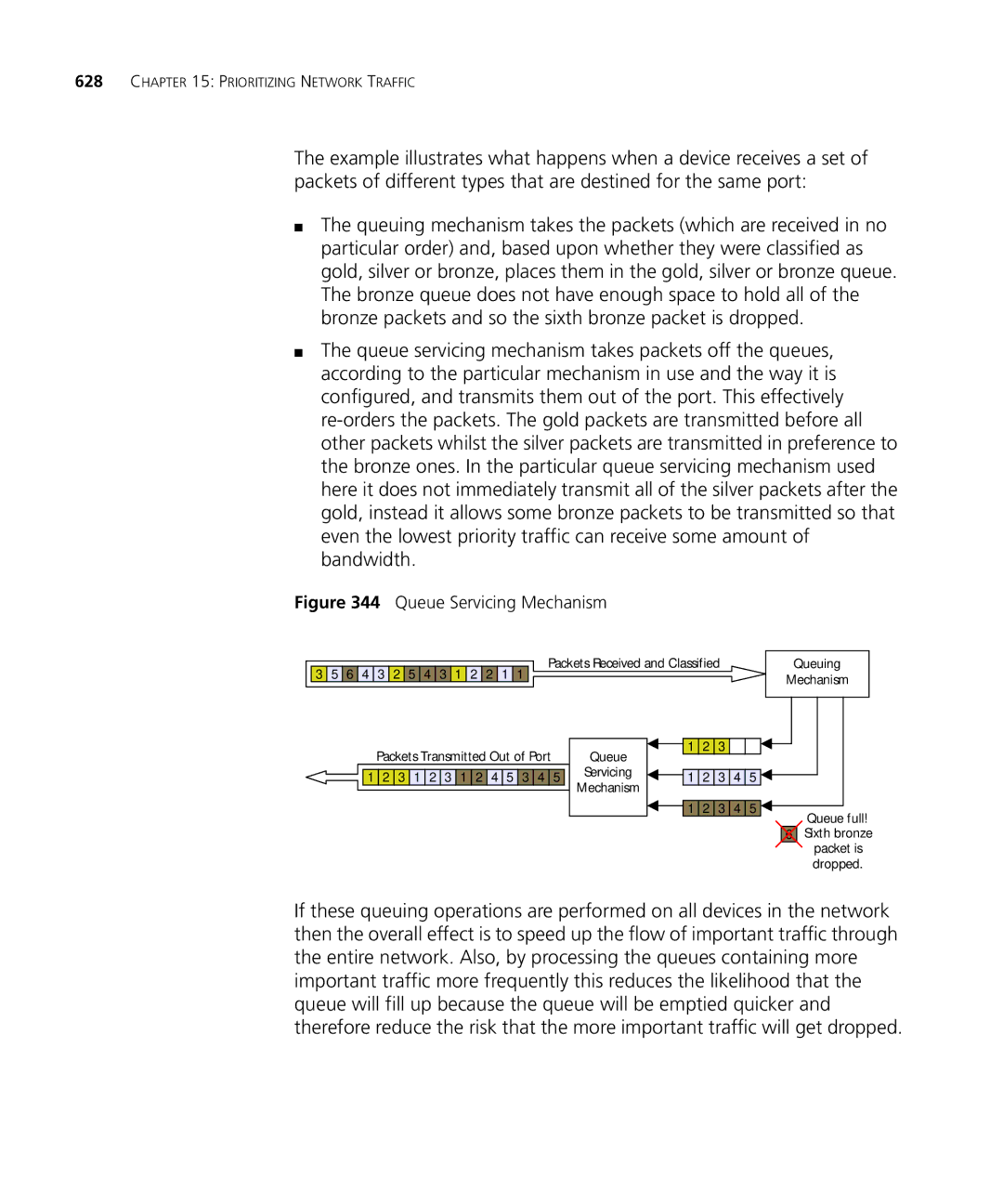
3Com Network Director User Guide
3C15500
3Com Corporation Campus Drive Marlborough MA USA
United States Government Legend
Page
Page
Contents
Product Activation
Main Window
Discovering the Network
Monitoring Logging VLANs
Other Clouds 103
110
124 Summary Pane 126
128
166 167 Clouds
143
158 Device Icons Pull-Right Menu for Devices 161
193
217
225 Files Associated with Saved Maps 226 Network Login
241
242 Properties Dialog Box for a Subnet 244
245
Overview
282
Showing Thresholds 289
290 Exporting a Graph Zooming into a Graph 291
300
321
343
325 Alerts
337
364 Attaching Alerts to Items 366 Configuring Alerts
369 Examples Viewing the Unresolved Events for a Subnet 370
371
378
383
No Graph Available for an Event 383
395 Mapping file format
400
What is Rmon 404
404 History Host 405
405 Matrix 406
425
471
455
458
Configuring Single Devices
Vlan Management
497
Useful Information and References 569
550
568
Configuring Access Rights 596 Configuring Trusted IP Hosts
Configuring the Device as a Radius Client
Reference C
584 Editing Device and Port Selections
648
635 Applications Step 636 Application Field Values 637
644 Prioritizing a Video Conferencing Application 645
652 DiffServ Codepoint Field
Servers That Cannot be Selected for Blocking 660
661
662
Overview Key Concepts 681 Multi-Site Networks
676
Agent Image Filenames
NBX Support
768 Useful Information and References 769 NBX system
770 NBX NetSet Key Considerations Troubleshooting
761 Monitoring a Phone Monitoring a Line Card 762
784 Device Backup Events
789 Specify Telnet Login Information Step 790
792 Restore Summary Report Setup Components
787 Specify Device Being Replaced Step 788
Configuration Source Type Step 793
793 Specify Source Backup Step 794
Why Errors can Occur during Restore and Setup 809
795
3C OM D Evice V IEW
About Device View 852 Management Support Matrix
Register Your Product to Gain Service Benefits
855
Page
Page
About this Guide
List conventions that are used throughout this guide
Text Conventions
Icon Description
Convention Description
Which can be accessed through the application
Pddtechpubscomments@3com.com
About this Guide
All its major features
Getting Started
Use Windows Explorer to browse the CD and access the files
Create a new network map
Start using 3Com Network Director with your 3Com devices
Displayed which enables you to
Discovery Type Step
Specify Subnets Step
Monitor Core Devices and Links Step
Community Strings Step
Coexistence with 3Com Network Director
Scheduled Discovery Step
Summary Step
Using saved Network Supervisor maps
Using saved 3Com Network Supervisor files
Device Warranty feature
Network Monitoring
Main Window
Network Discovery
Main Features
For more information, see Bulk Configuration on
For more information, see Upgrading Device Software on
Main Features
Getting Started
Describes how to activate 3Com Network Director
Customer support for 3Com Network Director for the duration
Relating to both this and other associated products
This chapter covers the following topics
This number when it is first installed
Process
Product Number the part number of your software, which
Starts with ‘3C’
About Dialog Before Registration
Wizard consists of two steps as follows
Activation Wizard License Key
If you prefer, you can register your product manually at
US, Canada and Latin America
Outside US, Canada and Latin America
Activating 3Com
Network Director
Where can I find the license key for 3Com Network Director?
What product number is right for me?
What if I lose my Activation Key after registration?
Why can’t I log in to the 3Com support web site?
Product Activation
Key Considerations
License Key Warning
Troubleshooting
Product Activation
Main Window
Director
To the main window
For a selected link the text displayed is
Following section describes the features of the main window
Describes the operations you can perform from this window
File Menu
Menu Item Hot Key Operation
Edit Menu
Menu Item Hot Key Operation
View Menu
See Deleting Items from the Map
Grouped Network View on
Background Images on
Device Menu
Management on page 491 for more
Device Setup
Monitoring Menu
Alerts/Events Menu
Rmon Menu
Tools Menu
Statistics group on page 417 for
User Guide on
Saved
Tree
Scheduled Tasks Menu Option
File New File Open Edit Add Device Edit Delete
General
Device Management
General Tab
Components
See Live Update on page 811 for more information
Internet
Discovery
Monitoring
Logging
Monitoring Tab
See Performance Reporting on page 385 for more information
Retry/Timeout
VLANs
Retry/Timeout Tab
Security Tab
Index Menu Option
Guide
Help About 3Com
Dialog box is displayed
You have a query about an aspect of 3Com Network Director
Number
Activation Key
Activation key
About Dialog Box License Number
About your network
Process and the steps you can take to overcome them
This chapter. This section explains the key concepts behind
Discovery process itself
Stages. The main concepts associated with these operations
Associated stages are outlined in this section as follows
Device Capability Detection
Purpose of each stage is described below
IP Ping
End Station Type Recognition
IP to MAC Resolution
Snmp Type Detection
NBX Phone Detection
DNS Name Resolution
Web Type Recognition
Device Sizing
Sizing stage
Spanning Tree stage
Remote Poll Stage broadcast ARP
Remote Poll Stage directed pings
Device Resolution Stage
Initial Endstation stage
Clouds Unknown Topology
Outstanding end station stage
Tree Building Stage
Clouds Unknown Topology
Edge Switch Unknown Topology
Other Clouds
Discovering the Network
Key Concepts
Scheduled
Discoveries
Welcome dialog box
File New
Tools Network Discovery with nothing selected
Tools Network Discovery with a discovered subnet selected
Tools Network Discovery with an undiscovered subnet selected
Undiscovered Subnet
Discovery Type Pane
This is the first pane of the wizard
Specify Subnets Pane
Adding subnets to the list
Add Subnet Dialog Box
Add Range Dialog Box
Choosing from a list of known subnets
Editing subnets in the list
Removing subnets from the list
Find Subnets List
Importing subnets from a file
Query Failure Dialog Box
Monitor Core Devices and Links Pane
Community Strings Pane
Community Strings Pane
NBX Voice Network Pane
NBX Call Processors Pane
NBX Call Processors Pane
Discovery Options Pane
Components
Scheduled Discovery Pane
Scheduled Discovery Pane
Options Dialog Box Discovery Tab
Summary Pane
Network Discovery Wizard Summary Pane
Network Discovery Progress Dialog Box
Network Discovery Progress Dialog Box Minimized
Network Discovery Summary dialog box
Network Discovery Summary Dialog Box
Components
Topology
Initial Map Creation
Directly From the Options dialog box
Subsequent Map Updates
Midnight?
Am is midnight and 1200 pm is midday
From the Discovery Wizard
Scheduled Discovery Pane
Discovering the Network
Network how do
Useful Information References
Some devices are the wrong type
There are clouds in my map
Discovering the Network
Key Considerations
Following devices
Discovery Section
Discovered
Discovery Report Errors and Warnings
Topology Section
Following devices returned invalid port information
Discovery Report Errors and Warnings
Discovering the Network
Discovery Report Errors and Warnings
Discovering the Network
Within 3Com Network Director
Following topics are covered in this chapter
3Com Network Director
Map
Icons Used in the Map
IconDescription
IconDescription
Example Tree
Components
Map Structure
Device Groups Example
Devices
Device Icons
Network Infrastructure Device Icons
Device Icon Description
Telephony Solution Icon Description
NBX Networked Telephony Solution Icons
Device Icon Description 3Com Wireless LAN Access Point
Pull-Right Menu for Devices
End Station Icons
Devices Pull-Right Menu Options
End Station Icon Description Standard end station
3Com Device View on page 475 for more information
Physical Links
Menu Item Operation
Annotation Type Graphical Description Representation
Unvalidated Links
Physical Link Annotations
Physical Links Menu Options
Spanning Tree Protocol Support
Pull-Right Menu for Physical Links
Layer-3 Connections
Attach Alerts Dialog Box on page 364 for more information
Pull-Right Menu for Layer-3 Connections
Layer-3 Connections Menu Options
Clouds and Submaps
Label Description
Pull-Right Menu for Clouds
Subnets
Undiscovered Subnets
Subnet Icon’s Name
Subnets Menu Options
View Filtered Events
Ungrouping Device Groups
Device Groups
Grouping Devices into a Device Group
Pull-Right Menu for Device Groups
Device Groups Menu Options
Tooltips
Tooltip
Map Item Information Displayed
Map Item Labels and Address Translation
Tooltip Displays
Label Type Label Source
Custom Name
Vendor Translation of MAC Addresses
Becomes
Working with the MAP
Translate MACs Option
Release the mouse button
Selecting Items in the Map and Tree
Selecting Multiple Map Items in the Currently Viewed Map
Selecting Multiple Items in the Tree
Selecting Multiple Map Items
Zoom
Selection and the Pull-Right Menu
Panning
Zoom out
Fit to
Toolbar Zoom Buttons
Button Action Zoom
Using the Zoom Rectangle
Navigating Between Submaps and the Top-Level Map
Currently Viewing Text Displayed in Title
Pull-Right Menu for Map Background
Title Bar Displays
Shortcut Symbols
Pull-Right Menu Options from the Map Background
Navigating Around the Map Using the Tree
Shortcut Icon
Viewing the VLANs on Your Network
Trace Path
Changing the Displayed Path
Trace Path Example
Using the Filtered Trace Path View
Button Action Explanation
Using The Trace Path Wizard
Trace Path Wizard
Finding Items on Your Network
This button launches the Find dialog box
Using Wildcards to Find Partial Matches
For example
Searching Within the Search Results
Wildcard Characters
Wildcard Matches
Option Description
Using the Find Dialog Box to Select Items for Operations
Finding Devices
Address address
Finding Links
Search by Option Description
Speed Duplex mode Spanning tree mode
Finding NBX Telephony Components
Search by Option Description
Comment field
Manual Layout of Map Items
Automatic Relayout of Maps
Manually Modifying the Map Contents
Adding Items to the Map
Add Map Item Dialog Box
Linking Items in the Map
Deleting Items from the Map
Login on
Keeping the Map Up-to-date
Working with the MAP
Default Map Location
Exporting Maps to Microsoft Visio
Export to Visio Dialog Box
Working with the MAP
Components
Following section provides some examples of how to perform
Common tasks with the map and tree
Network
Launch the Find dialog box by selecting Edit Find
Select 3Com Switch 4400 from the Device type list
Select Tools Reports to launch the capacity report
Search Results Table
Viewing Devices without Grouping by Subnets
Double-Clicking on a Router in the Tree
Focusing in on a Set of Devices in the Map
Zooming
Adjusting the Magnification
From Different Submaps
Locating the Two Devices
Map
Selecting Edit Add Link
Opening the Submap
Selecting Edit Add Map
Selecting Properties
NBX Network Telephony Solution
3Com Switch
3Com Wireless Access Points
Tree
Saved Map Files
Filename Contents
Files Associated with Saved Maps
FilenameContents
Network Login
Dialog box
Discovered
It allows you to
Items on the network map
Items on network
Items Supported by the Properties Dialog Box
See for more information
Structure Tabbed Pane
Selected item
Tab Title Contents
Description of the Tabs in the Properties Dialog Box
Tab Title Contents
Device Tree
Device Tree
Components
Tabs for a Node
Tabs for a Port
Tabs for an interface
Tabs for an Aggregated Link
Aggregated links on the device, as shown in Figure
Tabs Available for a Unit/Slot
Properties Dialog Box for a Supported Device Single Unit
Properties Dialog Box for an Unsupported Device
Properties Dialog Box for an End-Station
Phone tab
Properties Dialog for a Phone
Tabs available for a Subnet
For a Subnet
Tabs available for a subnet are shown in Table
Properties Dialog Box for a Device Group
Properties Dialog Box for a Cloud
For a Link
Properties Dialog Box for a Non-WAN Link
Tabs available for a link are shown in Table
Tabs Available for a Non-WAN Link
Tab Title
Tabs Available for a WAN Link
Tabs available for a WAN link are shown in Table
Connection
Tabs available for a Layer-3 Connection
Tabs available for a link to a subnet are shown in Table
Selection explanatory text is displayed, as shown in Figure
Properties Dialog Box for a Multiple Selection
No Common Information Across the Selection
Changing the Custom Name
Changing the Comments
Setting the IP Address for a Manually Added Device
Click OK to save your changes
Addresses Tab for a Manually Added Device
Setting the Port Numbers for a Manually Added Link
For a Device
Ports Tab for a Manually Added Link
Components
Security Tab for a Device
Community Strings Not Accepted
Monitoring tab of the Properties dialog box
Retry and timeout settings can be configured from within
Retry/Timeout tab of the Properties dialog box
How Do I View the Properties of a Specific Port on a Device?
4007
Examples
Properties for a Specific Port
Security Tab for Multiple Devices
How Do I Prevent the Discovery of End-Stations in a Subnet?
How Do I Restrict Monitoring to Snmp Traps for a Device?
There Is No Port Information For My Device
There Is No General Unit Information For My Device
Lot of Fields in the Properties Dialog Box Show Unknown
Key Considerations
Viewing Device Details
Monitor
When issues arise
Network using 3Com Network Director
Monitoring the Network
Map Item Color Key
Color Description
Monitoring State and the Grouped View
IP Ping Monitoring
Snmp MIB Data Retrieval
Service Polling
Snmp Trap Receipt
Monitoring Non-3Com Devices
Components
Poll Rates
Live Graph Display
Displaying Thresholds
Live Graphs Toolbar
Bi-State Monitors State Representation
Live Graphs Monitor Menu
Detailed Graph Dialog Box on
Live Graphs View Menu
Display thresholds Toggles the forcing of the display
Components
Viewing a Monitor’s Component Values
Detailed Graph
Showing Thresholds
Component Values Fields
Showing Plot Points
Exporting a Graph
Zooming into a Graph
Graph Save As... Dialog box
Zooming
After zooming
Configuration
Performed automatically from the Network Discovery Wizard
Disabling and Enabling Individual Monitors
Detailed Graph for Disabled Monitor
Monitoring Mode
Configuration
Poll Rate
Monitoring Tab of Tools Options Dialog Box
Monitoring Tab of Subnet’s Properties Dialog Box
Monitoring Tab of Device’s Properties Dialog Box
Specifying Monitoring Mode in the Discovery Wizard
Monitoring Pane of Network Discovery Wizard
Monitors event will be generated
Destination
Monitoring Tab of Tools Options Dialog Box
Monitoring the Network
Logging Tab of Tools Options Dialog Box
On the Core Devices
Network
Enabling Monitoring
Subnet Selection from Main Window Tree
Properties Dialog Box for a Subnet
Use Defaults Option in Tools Options Dialog Box
Close the Properties dialog box by clicking OK
Poll Rates in Tools Options Dialog Box
Minutes
Maintained
Monitor History
Maintain Monitor History Field Detail
Problems Starting Monitoring for a Device or Link
Monitoring the Network
Error Message Dialog Box
Monitoring the Network
Event LOG
Relevant and concise
Event Types
Monitor-Based Events
Snmp Trap-Based Events
Information Severity
Recurring Severity
High Severity Events
Critical Severity
Color Severity
Event Severity Colors
Event List Color Coding Key
Event Correlation
Recurring Event Handling
Event Suppression
Snmp Trap Filtering
Window
Viewing Unresolved Events for a Selection To view all
Events List
Events Window Main Window
Events List Column Headings
Column Heading Contents
Following table details the columns used in the Events list
File Menu Item Hot Key Operation
Events Toolbar
Events Menu
Event Menu
Edit Menu Item Hot Key Operation
View Menu Item Hot Key Operation
Event Menu Item Hot Key Operation
Status Bars
There are two status bars shown in the Events window
Navigating to Event Sources in the Map
Database Status Bar
Commenting on Events
Manually Resolving Events
Comment Dialog Box
Deleting Events
To stop an update while it is in progress select View Stop
Export as CSV Format Dialog Box
Wildcards Used in Find Operations
Wildcard Matches Example Example Matches
Events List Components
You may filter on any combination of the fields
Name Filter
This field filters for events that have a specific severity
Show only voice related events Filter
Severity Filter
Last number of days Filter
Resolved Filter
Deleted Events Filter
Description Filter
Comment Filter
Filter Status Bar
Events Window Filter Status Bar Details
Text Description
Event Tab
Event tab provides a description of the event
Graphs Tab
Events List Components
Trap Decode Tab
Disabling
Enabling Events
Disabled Events Dialog Box
Selecting Items
Selected Items dialog box
Advanced Settings Dialog Box
Controlling Global Smart Event Analysis
Smart Event Analysis will be ignored
Controlling Snmp Trap Filtering
Controlling Per-Event Advanced Settings
Launching the Threshold Settings Dialog Box
High and Warning Thresholds
Threshold Settings Dialog Box
Threshold Settings Dialog Box
Event System Configuration
Event LOG
Logging Tab
Event LOG
Ageing Dialog Box
Alerts System
Overview
Attach Alerts Dialog
Box
Attach Alerts Dialog Box
Configuring Alerts
Attaching Alerts to Items
Alert System Tokens
Token Replaced In Generated Alert By
Sample Pop-up Alert
Snmp Trap Alerts
Pop-up for a Device
View relevant events and assist in troubleshooting
Snmp Trap Alert Options
Examples
Filter Dialog Box 7 Days of High Severity
Select File Export as CSV
Filter Dialog Box Show
Events Window Updated
Event LOG
Problem
Clear the Enable event suppression check box
Close the global Advanced Settings dialog box by clicking OK
Server Farm Is Unreachable
Add Alert Dialog Box Pager Option
Set Up Alerts Dialog Box
Attach Alerts Dialog Box
Events List Update Was Stopped
Match the configured filter
No Events
Events list
Filter Has Excluded All Events
Events List Window Bottom Status Bar
Options Dialog Box Logging Tab
Performance Reporting
See how network usage changes over a period of time
Performance Reporting
Historical Report Example
Report Resolutions
Resolution Time span
Link monitors
Device Monitors
Data Source Usage
Monitor Sub-graphs Comments
Select Tools Options
\Program Files\3Com\3Com Network Director\logging
On a link
Requirements
Trend of Link Utilization
Daily Graph of Http Response Time
Links between switches/hubs
Filename, Switch1 MAC address, Switch2 MAC address
Links between a switch/hub and an end station/cloud
Filename, MAC address
Performance Reporting
Link Monitors
Monitor Data source
Disk Space Requirements
Monitored Monitored links Devices Disk space
Navigate to the data\com\coms\wsd\tns subdirectory
Troubleshooting Mapping file not updating
Changing the logging data directory
Missing data within RRD database files
Key Considerations
Performance Reporting
Rmon
Standard
Support provided by 3Com Network Director
Statistics
History
Following section describes the key concepts of Rmon
Host
HostTopN
Matrix
By 3Com Network Director
RMONView window
Menu bar
File menu
View menu
RMONView window
Options menu
Options Menu
Manual Upload Toggles Manual Upload on/off. If
See Map Item Labels and Address
Update menu
Update Menu
Toolbar
Window menu
Help Menu
Additional Features
Toolbar Buttons
There are three ways to control the display of rows
Table View
Table Control Dialog Box
Viewing Rmon Statistics data for a selected device
Graph View
Viewing data from the Rmon Statistics group
Rmon Statistics Option
Rmon Statistics Slot 5 36 Port 10/100 L2 Switch
Viewing Rmon statistics data for a selected link
Rmon Statistics Data for a Selected Link
Statistics View dialog box
Statistics View Dialog Box
Community String
View
Predefined Views
Predefined View Definition
Viewing data from the Rmon History group
Viewing Rmon History data for a selected device
Rmon History Data for a Specific Device
Viewing Rmon history data for a selected link
Viewing Single Link Lists
History View dialog box
History View Dialog Box
Update Rate
History Entries
Add, Delete
Rmon
Viewing data from the Rmon Host group
Viewing Rmon Host data for a selected device
Host Data for a Specific Device
Switch 4007 Selection of the Slot within the Chassis
Viewing Rmon host data for a selected link
Host View Dialog Box with the Vlan Interface Preselected
Select Vlan Dialog Box
Host View dialog box
Update Rate
Sort by
Error dialog box
Viewing data from the Rmon Matrix group
Viewing Rmon Matrix data for a selected device
3Com Switch
Rmon Matrix Data
Switch 4007 Separate Submenu
Viewing Rmon matrix data for a selected link
Matrix View Dialog Box
Host Submenu
Update Rate
Stations
Matrix Flow
Managing Rmon tables
Deletion of Rmon Tables
Interface Dialog Box
Components
Errors
This section describes some Rmon examples supported by 3Com
How do I graph utilization on a specific VLAN?
Rmon Support on individual 3Com devices
Rmon Limits on individual devices for table creation
Creating Reports
Feature Report Types
Feature Report Types Covered
Feature Report Types Covered
Open Windows Explorer Navigate to the following directory
Properties to use in your own command line scripts
Types are also available
Inventory Report
Capacity Report
Components
Creating Reports
Generate Report Tab
Reports Dialog Box
History Tab
History
CSV format used for exported reports is
Custom Report Types Dialog Box
Columns Step
Add/Edit Report Type Wizard Columns Step
Available Columns for Node Details
Column Description
Column Description
Available Columns for ‘Link Details
Name and Description Step
Add/Edit Report Type Wizard Name and Description Step
Report types
Further details
Assessing Network
Work out which 3Com devices to connect them to
Choose to Place chart As new sheet and click Finish
Creating Reports
Key Considerations
Creating Reports
Web Management launches your default web browser against a
Administration Menu contains integrated add-on 3Com device
Devices on your network for any applicable warranty
Device selected in the network map
Devices using 3Com Network Director
3Com Switch Manager
Switch Manager is the element manager of the Switch
Network Jack Configuration Manager
3Com Device View
Configuring Single Devices
Key Concepts
Properties General Tab
Security
Following two radio buttons are provided
Unit Information
Properties Unit Information Tab
Properties VLANs Tab
Properties VLANs Tab Vlan Routing
Devices as shown in Figure
Introduction Step
Contact Details Step
Partner/Reseller Details Step
Partner/Reseller Details step displays the following fields
Device Selection Step
Summary Step
What Data is Sent to the 3Com server
Device Warranty
Web Management
Device Warranty
Devices on your network
Web Interface
Select the device and right-click on it to launch the menu
Click OK to launch the Device Warranty wizard
View
Examples
Select the Tools Device Warranty menu option
Why are some registered devices missing from the email?
Configuring Single Devices
Configured on your
Configuring VLANs
Viewing the VLANs
On your network
Concepts About VLANs
Key Concepts
General Vlan
Network Setup Showing Three VLANs
Benefits of VLANs
Port-based VLANs
802.1Q VLANs
Ieee 802.1Q standard for VLANs aims to
Tagged and untagged Vlan membership
Example of VLANs Distributed Amongst More Than One Switch
Communication between VLANs
Key Concepts
Switches Connected by 802.1Q Tagged Links
Primary and Secondary IP interfaces
Protocol-based VLANs
Spanning Tree
3Com Network Director Vlan Concepts
Discovering VLANs in 3Com Network Director
For further information see Discovering the Network on
Vlan membership inference
Vlan equivalence
Vlan Matching by 3Com Network Director
Network Example
If the above network was additionally configured like this
Restrictions on Vlan support in 3Com Network Director
Show VLANs
Show VLANs
Filter View button
Interaction with Trace Path
Maps with no Vlan information
Vlan names
Identifier Description
Where
Show VLANs Toolbar Vlan Descriptions
Naming the Vlan
Find Dialog Box
Options Dialog Box
Listing Vlan Members
Options Dialog Box VLANs Tab
Vlan IDs
Vlan membership
VLAN-aware switches. See Vlan membership inference on
VLANs tab for VLAN-aware switches
Columns in the Ports in Vlan table are
Ports in Vlan table
Protocol Details button
Protocol Details Button
Vlan Routing button
Protocol Column
Vlan Routing Dialog Box
Components
VLANs tab for VLAN-unaware devices
VLANs Tab for VLAN-Unaware Devices
VLANs Tab
VLANs tab for a link
VLANs Tab for a Link
Vlan configuration report
Generate Report Dialog Box
Misconfigurations and Optimizations Report
Vlan Configuration Report Entry
Inconsistent Vlan IDs
Inconsistent Vlan configuration on link
Inconsistent Vlan naming
Changes Report
Create Vlan wizard
Launching the wizard
Entering the new Vlan name and ID
Modifying the list of selected switches and ports
Nearest Switch Port to the Non-Switch
Components
Untagged radio buttons
Add Ports by Type dialog box
Checking Vlan connectivity
Vlan Management
Finding a Layer 3 Switch for a Vlan
Configuring unsupported devices
Checking the Vlan limit
Manually Configuring a Vlan on Unsupported Devices
Adding an IP routing interface
Specify an IP Routing Interface
Components
Summary of changes to be made
Creating the new Vlan on the selected switches and ports
Device Summary Stage
Edit Port Vlan Membership wizard
Modifying the list of selected switches and ports
Adding Unconnected Ports
Modifying the VLANs on the selected switch ports
Untagged Vlan
Tagged VLANs
Tri-state Check Boxes
How the changes will be applied
Configuring unsupported devices
Final Wizard Stage
Applying the changes
Device History Report
Moving a port to another Vlan
Selecting the Link to the End Station on the Map
Vlan is an existing Vlan on your network Before
Network Before
Extending your VLANs to include new inter-switch links
After
Selecting the Link
Second Wizard Stage
Creating a new Voice Vlan for 3Com NBX systems
Useful Information References
Troubleshooting Incorrect Vlan membership inference
Incorrect topology if all subnets are not discovered at once
Network Topology Example
Network Topology Example
Switch Switch4400-6 Port 00-30-1e-c6-40-38
Changes report Vlan configuration consists
Vlan configuration and Display by Device Type
Device Type Vlan Display Vlan Configuration
Reference a
Reference B
Maximum number of VLANs by 3Com device
Maximum Number
Device Type VLANs
Reference C
Device Type
Same or different types, in a single operation
More of the 3Com devices in a network in a single operation
3Com devices on the network
Configuration
Templates
Selection
Configuration Editor Dialog Box
Configuration Summary Tree Features
Switch Device configuration template
Switch Port configuration template
Features
Feature Configuration Panels
Configuration Editor Dialog box
Loading and Saving Configuration Templates
Port Selection Editor
Editing Device and Port Selections
Bulk Configuration
Components
Loading and Saving Device and Port Selections
Schedule Configuration Dialog Box
Configuration Progress Dialog Box
Device Status Configuration Stage
Device Status Information
Account Parameter
Configuring User Accounts
User Account Parameters
Account Parameter
Bulk Configuration
Add User Account Dialog Box
Edit User Account Dialog Box
Configuring Access Rights
Configuring Trusted IP Hosts
Trusted IP Hosts Panel
Add Trusted IP Address Dialog Box
Add Trusted IP Address Dialog Box
Configuring the Device as a Radius Client
Radius Servers Panel
Parameter Restriction
Configuring System Information
Radius servers feature restrictions
Configuring Trap Destinations
Trap Destination Table Entries
Parameter Description
Configuring Spanning Tree
Add Trap Destination Dialog Box
Spanning Tree Panel
Spanning Tree Parameter Restrictions
Configuring Igmp
Configuring Broadcast Storm Control
Configuring Port Security
Broadcast Storm Control Panel
Continuous learning, automatic-learning, full security
Configuring Port Administration
Configuring Autonegotiation
Port Administration Panel
Autonegotiation Panel
Autonegotiation Parameter Restrictions
Configuring Lacp
Lacp Panel
Configuration feature of 3Com Network Director
This section provides some examples of how to use the Bulk
Examples
Schedule Configuration Dialog Box
Examples
Configuration Template Editor Radius Servers
Select the user-login security mode
Configuration Template Editor Port Security
Bulk Configuration
Bulk Configuration Feature Summary
Device Family Supported Features
Device Family
Key Considerations
Bulk Configuration
Over your network
Network traffic on the 3Com devices on your network
Dropped in times of congestion
Classification
Key Concepts
Network Topology
Key Concepts
Queue Servicing Mechanism
Classification Rules Service Level
Service Level DiffServ Codepoint
DiffServ Codepoints
Classification Rule Service Level
Manually set up classifiers, dropping, queuing and marking
DiffServ Codepoints and Service Levels
Configuration Type Step
Prioritize Network Traffic Wizard Configuration Type
NBX Step
NBX step
Servers Step
Applications Step
Prioritize Network Traffic Wizard Applications
Application Field Values
Agent Upgrades Required for Prioritization report
Finish Step and Progress
Prioritization Configuration Report
Network Prioritization Report
Configuration
Configuration Type Prioritizing NBX Voice Traffic Example
Prioritizing Network Traffic
Examples
Prioritizing Network Traffic
Examples
Prioritizing Network Traffic
Examples
Servers Restricting Access to Snmp Example
Examples
Prioritizing Network Traffic
Applications Restricting Access to Snmp Example
User Priority
User Priority
RFC Definitions
RFC Number Title
Classifier Type Classifier Value Description
Traffic
NBX Phone Traffic Classifier Rules
Service Level Queue Marking Value Queue Device 802.1p
3Com Network Director Service Levels
Service Levels Used by 3Com Network Director
Device Type Agent Version
Key Considerations
Resource Warning Content Explanation if appropriate
Key Considerations
Servers That Cannot Be Selected for Blocking
Key Considerations
Prioritizing Network Traffic
You can use the Agent Update feature to
Upgrade or downgrade the agent software on individual 3Com
Agent software available to you
Agent software you have available
Feature
Agent Update Wizard Introduction
Update Type Step
Agent Update Wizard Update Type
Agent Update Wizard Specify Devices and Agent Versions
Specify Devices and Agent Versions Step
Upgrading Device Software
Agent Update Wizard Change Version
Change Agent Version Step
Agent Update Wizard Scheduling
Scheduling Step
Summary Step
Agent Update Wizard Progress Dialog Box
Progress Dialog Box
Reports Agent Update Summary report
Agent Audit report
Agent evening. To do this
Problem Device
Agent Filename Format by Device Type
Device Family Agent Filename Format
Troubleshooting
Device Problems
Update
Co-existence With
Default location of 3Com Network Director is
TIMEOUT,/TIMEOUT
Upgrading Device Software
Monitor and manage multi-site networks
Local and Remote Sites
Issues with Managing a Multi-Site Network
Configurable Timeouts
Configurable Retries
Configurable Poll Rates for Active Monitoring
Configurable Monitoring Modes
Configurable Discovery Options
Configurable Monitor Thresholds
Default WAN cloud
Connecting Point-to-Point WAN Interfaces Together
Grouping Logically Connected WAN Interfaces Together
Using 3COM Network Director on a MULTI-SITE Network
Components
Manual Layout of WAN Topology and Rediscovery
Configuring WAN Link Monitors
Disabling Monitors on WAN Links
There is a three level hierarchy in this mechanism
Using 3COM Network Director on a MULTI-SITE Network
Specifying Retries and Timeout Periods at the Subnet Level
Retry/Timeout Tab
Specifying Retries and Timeout Periods at the Device Level
Using 3COM Network Director on a MULTI-SITE Network
Determining Appropriate Retry and Timeout Periods
Using 3COM Network Director on a MULTI-SITE Network
Retry and Timeout Defaults
Default Number Request Type Retries Default Timeout Period
Using 3COM Network Director on a MULTI-SITE Network
Configuration
Determining Monitoring Modes and Poll Rates
Configuration
Using 3COM Network Director on a MULTI-SITE Network
Configuration
Configuring Discovery Options in Multi-Site Networks
Configuring Discovery
Configuration
Using 3COM Network Director on a MULTI-SITE Network
Scheduling Discoveries in Multi-Site Networks
Using 3COM Network Director on a MULTI-SITE Network
Examples
Find Dialog Box Default WAN
Click Find
Examples
Adding a Cloud by Drag and Drop
Properties Dialog Box General Tab
Map Links Selected
Select one of the routers and the new cloud in the map
Map Router and New Cloud Selected
Map Router and New Cloud Linked
Properties Dialog Box Ports Tab
Map Showing Labelled Cloud
Map Showing Multiple Links
Finally, relayout the map by selecting View Relayout Map
Rediscovered Map
Examples
Default Retry and Timeout Settings
Discovery Type step select Specify subnets
Network Discovery Wizard
Add Subnet Dialog Box
Add Subnet Dialog Box Subnet Address and Mask
Add Range Start
Add Subnet Dialog Box Discover Custom Ranges Selected
Add Subnet Dialog Box End IP Address Edited
Add Subnet Dialog Box Use Defaults Option Unchecked
Add Subnet Dialog Box Retries and MS Timeouts
Network Discovery Wizard Subnet Added
Network Discovery Wizard Monitor Core Devices and Links
Click Next to move onto the NBX Call Processors step
Click Next to move onto the Discovery Options step
Network Discovery Wizard Use Defaults Unchecked
Network Discovery Wizard Discovery Options
Network Discovery Wizard Only IP Devices Checked
Find Dialog Box
Find Dialog Box Fields Populated
Map Zoomed to Search Results
Weekly Graphs 30 Minute Average
Smtp Response Time
Threshold Settings Dialog Box
WAN Interface Types
WAN Family ifType
Isdn
25lapb16 X25ple40 X25mlp121 X25huntGroup122
Key Considerations
Using 3COM Network Director on a MULTI-SITE Network
Solutions
Provides the following features
Topology The NBX Call Processors, line cards and phones are
Displayed on the 3Com Network Director network map
Icons
Shows the different types of icons and their meaning
NBX Map Icons
Device Type Icon Example
NBX Call Processor
Line Cards
NBX Phones and Attendant Consoles
NBX Applications
Discovering the NBX Voice Network
NBX Call Processors step displays the following settings
NBX Call Processors Step of the Network Discovery Wizard
Add NBX Call Processor/Modify NBX Call Processor
Add NBX Call Processor
Modify NBX Call Processor
Monitoring the NBX Call Processor
Monitoring a Phone
Selecting the Phones Associated with an NBX Call Processor
Monitoring a Line Card
Context Menu for the NBX Call Processor
Context Menu for the Phone or Line Card
Understanding Voice-related 3Com Network Director Events
Events related to the NBX Call Processor
Events related to phones
Events related to other links or devices on the network
Launching NetSet for a phone or line card
When my Phones
To be informed immediately when any of the phones become
Stop Working
Unavailable
Useful Information References
There is no NBX Call Processor associated with my phone
There is no NBX Call Processor associated with this device
Phone is not managed by the NBX Call Processor anymore
Display of end stations in the map has been disabled
Phone was added manually
NBX Support
Key Considerations
Why are there a lot of unconnected phones on the map?
Phone was removed from the network
Phone cannot be reached
How do I change the label of a phone or line card?
You can use Backup, Restore and Setup to
Save the software configuration of your 3Com devices
Device from which it originated or to a replacement device
Same type
Source device it is replacing
Backup feature is designed to help you store the software
Physical Configuration Devices
Wizard
Device Backup
Backup Type Step
Device Backup Wizard Backup Type
Specify Devices to Backup Step
Specify Telnet Login Information Step
Username and password may be left blank
Backup Identification Step
Device Backup Wizard Backup Identification
Scheduled Tasks
Summary Step and Progress
Reports Backup Summary Report
Backup Audit Report
Backup Audit report lists the following
No Backups Found Step
Device Restore Wizard No Backups Found
Specify Device Being Replaced Step
Specify Backup to Use Step
Device Restore Wizard Specify Backup To Use
Summary Step and Progress
Backing UP Device Configurations
Configuration Source Type Step
Specify Source Device Step
Specify Source Backup Step
Device Setup Wizard Specify Source Device
Specify Devices to Setup Step
Device Setup Wizard Specify Source Backup
Device Setup Wizard Specify Devices To Setup
Device Setup Wizard Summary
Backing UP Device Configurations
Scheduling a Device Backup Operation
Backup Identification Example
Scheduling Example
Examples
Specify Device Being Replaced Example
Specify Source Device Example
Backing UP Device Configurations
Shown in Backup, Restore and Setup on
Supported Parameters by Device Family
Device Family Supported Parameters
Backup File Content by Device Family
Device Family Content of Backup File Body Section
Install LOCATION\backups\lost
Key Considerations
Backing UP Device Configurations
Manages the download of these files
Advantage of the latest bug-fixes and device support
Existing devices
Latest 3Com Product News notifies you of new 3Com products
This section describes the keys concepts of Live Update
Live Update Setup
Connection Type Step
Use Custom Settings Step
Live Update Setup Wizard Use Custom Settings Step
Live Update Setup Wizard Summary Step
Click Finish to connect to the Internet
Box
Live Update Select File Groups
Status
Table consists of three columns as follows
Live Update Select File Groups Group Name
File Group Details
Download Progress
Live Update
Options Internet
Live Update
To view the report Select the Tools Reports menu option
Examples
File Group Details Example
Automatic Configuration Example
Click OK to validate the changes
Solution 2 Manual Configuration using the Options Dialog Box
Live Update
Proxy Settings are not Retrieved
Click OK to validate the settings
Key Considerations
Live Update
Versions
Device Type Minimum Agent Version
Vlan Configuration
Device Type Version
Setup are shown in Table
Agent Versions
Restrictions Backing Up and Restoring 3Com Devices
Backup, Restore and Setup
Appendix a Supported Devices
Shows the devices that are supported by the Agent Update
Agent Update Supported 3Com Devices and Minimum Agent
Restrictions Updating 3Com Agent Software
Agent Update
Appendix a Supported Devices
Rmon
Rmon Supported 3Com Devices
Supported Devices
Devices supported by Device View are listed below
Device View Supported Devices
Device View
Router Manager Supported Devices
Switch Manager Supported Devices
Device Warranty Supported Devices
Device Warranty
Compatibility issues with 3Com Network Director
On the Network Director map as Generic IP devices
3COM Device View
Management features that are available
Support Matrix
Management Support Matrix
PWR
Registration, Repair Services, and Service Request
Technical solutions written by 3Com support engineers
Support information
You will find support tools posted on the 3Com web site at
Diagnostic error messages
Details about recent configuration changes, if applicable
From 3Com or your reseller
Benefits, you must first register your product at
Telephone Technical Support and Repair
US and Canada Telephone Technical Support and Repair
System Requirements
Allow approximately 2Mb per device for data logging
Report Examples
Example
Discovery Report
Vlan configuration of the following devices could not be
Following devices have been configured into multiple
Segment configuration of the following devices could not be
Following devices stopped responding while 3Com Network
Appendix E Report Examples
Listings of the devices are provided as described
Device Learned On Learned By Multiple Ports Ports Learned On
Network Configuration
Network Configuration
Misconfigurations Optimizations Report
Misconfigurations and Optimizations Report
Appendix E Report Examples
Configure aggregated links using Lacp
Misconfiguration and Optimization Reports
Web Cache Redirection
Misconfigurations and Optimizations Report
Appendix E Report Examples
Misconfigurations and Optimizations Report
Appendix E Report Examples
Misconfigurations and Optimizations Report
Successful Configuration
Unsuccessful Configuration
Unable to Confirm Webcache Mode Changed
Unable to Determine Traffic Server Status
Unable to Restart Webcache Traffic Server
Cache Mode Not Changed
Traffic Server Restart Already Under Way
Limitations Webcache Redirection and VLANs
Redirection on the Cache Port
Webcache Software Releases
Restarting Webcache Traffic Server
3rd Party Devices
Report Section Combinations
Appendix E Report Examples
Where the fields are as follows
Adding Trap Decodes
RemedyRemedy Text/remedy
885
Appendix F Adding Trap Decodes
Translations
000102 3Com 3COM Corporation
889
Appendix G Adding MAC Address Vendor Translations
Integrating AN SSH Client
Locate the following file on your disk
MyClient -ip %1% -verbose
Index
Backup summary report
Broadcast storm control configuring
490
386
Page
Page
Internal 321
Examples
Deleted events
How backup files are discarded discarding backup files
Map 204 Links Finding 197
Page
Files 64
NBX
New
Page
Properties dialog box 229
786 Backup summary Changes 133
Page
Backup 783 Search
Support for Rmon 407 supported 3Com devices
Third party devices 142 threshold settings dialog box
Viewing VLANs 188 499 Visio
General concepts 500
Page
3COM END User Software License Agreement
Governing LAW