Page
Page
Page
Preface
Page
Table of Contents
Parameters
Troubleshooting
Keypad and Start Up
Appendix a Specifications Appendix B Accessories
Fault Code Information and Maintenance
Reference Table for the 7-segment LED Display of the Digital
Appendix D How to Use PLC Function
Appendix C How to Select the Right AC Motor Drive
Program Download Program Monitor Limit of PLC Ladder Diagram
Appendix E CANopen Function
This page intentionally left blank
Introduction
MODELVFD007E23A
Receiving and Inspection
Nameplate Information
Model Explanation
25-2HP/0.2-1.5kW Frame a
Series Number Explanation 007E23A 7T 7
Drive Frames and Appearances
Internal Structure
15HP/0.75-11kW Frame B&C
Introduction
RFI Jumper
Remove Instructions
Remove Fan Remove Extension Card
Remove Keypad
Remove Front Cover
Remove RST Terminal Cover Remove UVW Terminal Cover
Transportation
Preparation for Installation and Wiring Ambient Conditions
Operation
Storage
For VFD-E-P series heat sink system example
Frame B and C Mounting Clearances
Frame a Frame B and C
Introduction
Frame
Dimensions
Dimensions for VFD-E-P series H2 H1
This page intentionally left blank
Installation and Wiring
Wiring
MI1 MO1
MI1
MI5
+/B1
RL1 SL2
RL1 SL2 TL3
NPN mode with external power
SG+
Canl
Good
FUSE/NFB
External Wiring
Main Circuit Main Circuit Connection
Output terminals for main circuit U, V, W
Terminal Symbol
Mains power terminals R/L1, S/L2, T/L3
Explanation of Terminal Function
+/B1
Terminals +/B1, B2 for connecting brake resistor
Frame a Frame B Frame C
Main Circuit Terminals
Control Terminals
Circuit diagram for digital inputs NPN current 16mA
MI3
MI1
OFF
MI2
ACM
MO1
MCM
AVI
General
Analog inputs AVI, ACI, ACM
Digital outputs MO1, MCM
Terminals
This page intentionally left blank
Keypad
Keypad and Start Up
Operation Method
MI1-DCM
Trial Run
Frequency Source
Method Source
Check if the motor runs steadily
Parameters
Summary of Parameter Settings
Parameter Explanation Settings Factory Customer
Parameter Explanation Settings Factory Customer
Parameter Explanation Settings Factory Customer
Parameter Explanation Settings Factory Customer
AVI2
UP/DOWN
Operation mode indication
AFM
Group 4 Input Function Parameters
Parameter Explanation Settings Factory Customer
Parameter Explanation Settings Factory Customer
Parameter Explanation Settings Factory Customer
Setting
Parameter Explanation Settings
Group 5 Multi-Step Speeds Parameters Explanation Settings
Group 6 Protection Parameters Explanation Settings
Parameter Explanation Settings Factory Customer
Parameter Explanation Settings Factory Customer
FLA
Group 7 Motor Parameters Explanation Settings
Parameter Explanation Settings Factory
Group 8 Special Parameters Explanation Settings Factory
Parameter Explanation Settings Factory Customer
Parameter Explanation Settings Factory Customer
Parameter Explanation Settings Factory
AVI2
Group 11 Parameters for Extension Card
MO5/RA5
MO2/RA2
MO3/RA3
MO4/RA4
Setting
Parameters
Parameter Explanation Settings Factory Customer
Parameters
Multi-step Operation Applications Purpose Functions
Parameter Settings for Applications
DC Brake before Running Applications Purpose Functions
Overheat Warning Applications Purpose
Two-wire/three-wire Applications Purpose
Wire
Operation Command Applications Purpose
Parameters
Parameters
Parameters
115V/230V Series
Description of Parameter Settings
00.02 Parameter Reset
Group 0 User Parameters
Factory Setting
00.05
00.04
00.09
00.08
00.11 Reserved 00.12 50Hz Base Voltage Selection
00.09
00.08
00.10 Control Method
01.02
Group 1 Basic Parameters
01.00
01.01
01.07
01.04
01.05
01.06
01.11
01.08
01.09
01.10
01.14
01.13
01.13 01.14
01.15
01.18
01.17
01.23
01.20
01.21
01.22
01.29
01.26
01.27
01.28
01.40
01.34
01.38
01.39
Factory Setting
Settings First Master Frequency Command Only
115V/230V/460V Series
02.03
Method B Frame a Frame B & C
Method a Frame a Frame B & C
Parameters
Source Pr.02.01 is changed
OFF on
02.08
600Hz 50.0Hz 28 s 68 s Sec 34 s
02.15
02.11
02.12
Display Value Bit Function
02.16
Group 3 Output Function Parameters
Settings Function Description
03.02
Desired Frequency 2 Attained Unit Settings 00 to 600.0 Hz
03.04
03.06
03.05
03.08
AFM
03.12
03.11
Weights =Active =Off Bit Relay MO1
Example 2 Use of bias
04.00
04.02
Example 1 Standard application
Example 3 Use of bias and gain for use of full range
Example 5 Use of negative bias in noisy environment
04.14
04.11
04.12
04.13
04.21
04.17
04.18
04.20
RUN/STOP
FWD/STOP
FWD /STOP REV/STOP
REV / Stop
Application
Speed by programming the AC motor drive’s internal PLC
Function. There are 17 step speed frequencies including
Master Frequency and Jog Frequency to select for
Accel/Decel Inhibit Accel/Decel Time Selection Command
Function Description
Settings
Accel/Decel Time Selection
04.09
MI6=4 MI5=3 MI4=2 MI3=1
04.10
MI7
MI8
MI9
MI3 MI4 MI5 MI6
=OFF
ACI/AVI2
Weights
04.27
04.28
=OFF
05.03
05.00
05.01
05.02
Multi-speed via External Terminals
06.00
Group 6 Protection Parameters
06.02
06.01
06.05
Over-current stall prevention during operation
06.04
06.07
Factor %
Parameters
Parameters
07.02
Group 7 Motor Parameters
07.00
07.01
07.05
07.04
07.09
07.06
07.07
07.08
Resistor-divider
07.16
07.15
07.20
07.13
07.18
07.19
07.34
07.31
07.32
07.33
08.02
Group 8 Special Parameters
08.00
08.01
08.05
Revision June 2008, 04EE, SW--PW V1.11/CTL 105
08.10
08.07
08.08
08.09
08.16
08.12
08.13
08.14
AVR function disabled for stop
08.22
08.19
08.20
08.21
08.25
Status 2 unexpected power off, such as momentary power loss
Parameters
Group 9 Communication Parameters
RS-485 not for VFD*E*C models
09.03
Ascii mode
RTU mode
Data
STX
END
Start
Command message
5CH
6FH
F7H
FEH
1FH
EEH
Command message Address 01H Function 08H Data address 00H
D9H
A0H
4DH
Address 01H Function 03H Starting data address 21H 02H
Revision June 2008, 04EE, SW--PW V1.11/CTL 123
Overload2 oL2
Revision June 2008, 04EE, SW--PW V1.11/CTL 125
Ascii mode RTU mode
Communication program of PC
A1H
Exception Explanation Code
Void main Int OutportbPORT+MCR,0x08
RS485 BUS
09.07
130 Revision June 2008, 04EE, SW--PW V1.11/CTL
09.11
10.02
Group 10 PID Control
10.05
10.03
10.04
10.08
10.06
10.07
10.13
10.10
10.11
10.12
10.16
Revision June 2008, 04EE, SW--PW V1.11/CTL 137
138 Revision June 2008, 04EE, SW--PW V1.11/CTL
Revision June 2008, 04EE, SW--PW V1.11/CTL 139
Settings Function
Speed, and then accelerate to Master Frequency
Speed search function and synchronize with the motor
142 Revision June 2008, 04EE, SW--PW V1.11/CTL
When AC motor drive is in Stop mode and this function is
12.04
Group 12 Analog Input/Output Parameters for Extension Card
12.02
12.03
12.08
12.05
12.06
12.07
12.15
12.12
12.13
12.14
12.22
12.25
13.02
Group 13 PG function Parameters for Extension Card
CCW
13.01
13.09
13.04
13.05
13.06
PLC
Different Parameters for VFD*E*C Models
Revision June 2008, 04EE, SW--PW V1.11/CTL 153
03.09 Reserved 03.10
Revision June 2008, 04EE, SW--PW V1.11/CTL 155
Group 9 Communication Parameters Explanation Settings
Group 7 Motor Parameters Explanation Settings Factory
Revision June 2008, 04EE, SW--PW V1.11/CTL 157
158 Revision June 2008, 04EE, SW--PW V1.11/CTL
Over Current OC
Troubleshooting
Over Voltage OV
Ground Fault
Low Voltage Lv
Overload
Over Heat OH
Keypad Display is Abnormal
Phase Loss PHL
Motor cannot Run
Motor Speed cannot be Changed
Motor does not Run as Expected
Motor Stalls during Acceleration
Environmental Condition
Electromagnetic/Induction Noise
Affecting Other Machines
Over current
Fault Code Information
Common Problems and Solutions
Fault Fault Descriptions Corrective Actions Name
Low voltage
CC current clamp OV hardware error
GFF hardware error OC hardware error
Overheating
OV or LV Temperature sensor error
Fault Descriptions Corrective Actions Name
External Fault
Phase error
Phase Loss
Communication Error
Analog signal error
PID feedback signal error
Fault Fault Descriptions Corrective Actions Name
Periodic Inspection
Reset
Maintenance and Inspections
Daily Inspection
Voltage Maintenance Check Items Methods and Criterion
Change of copper plate
Keypad Maintenance Check Items Methods and Criterion
Main circuit Maintenance Check Items Methods and Criterion
One
Year
Daily
Page
Appendix a Specifications
Appendix a Specifications
Conditions
This page intentionally left blank
All Brake Resistors & Brake Units Used in AC Motor Drives
Appendix B Accessories
Appendix B Accessories
Motor
NFB
Dimensions and Weights for Brake Resistors
Order P/N BR500W030, BR500W100, BR1KW020, BR1KW075
Appendix B Accessories
Order P/N BR200W150, BR200W250
Phase Recommended Model No-fuse Breaker a
No-fuse Circuit Breaker Chart
JJN-6 JJS-6
Fuse Specification Chart
JJN-6
Impedance
AC Reactor AC Input Reactor Recommended Value
~5% impedance
AC Output Reactor Recommended Value
M1 reactor AC motor drive Motor
Applications
Line impedance will be small and the charge
AWG
Zero Phase Reactor RF220X00A
Diagram a
Diagram B
5 4 16 15 14 13 11 RC-01Terminal block
Remote Controller RC-01
Stop
Reset
PU06 Description of the Digital Keypad VFD-PU06
Explanation of Display Message
XX-XX
Operation Flow Chart
Descriptions
KPE-LE02 Description of the Digital Keypad KPE-LE02
Display Message
Display Message
Start
How to Operate the Digital Keypad
LED
EME-R3AA
Extension Card
Relay Card
EME-R2CA
Communication Card
Digital I/O Card
Analog I/O Card
EME-PG01
Speed Feedback Card
Mounting Method
Wiring and Settings
Switch
Setting MAC addresses
Step
Power Supply
LEDs Display
LonWorks Communication Module CME-LW01
Specifications
LED Indications Profibus Communication Module CME-PD01
Panel Appearance
VFD-E
Parameters Settings in VFD-E
Profibus Address
Can
CME-COP01 CANopen
Product Profile
Address Meaning
Pin Definition on CANopen Connection Port
Components
PRE-OPERATIONAL
LED Indicator Explanation & Troubleshooting
RUN LED
Stopped
LED OFF
Error LED
SP LED
LED on
DIN Rail MKE-DRA
Clamp TWO Hole Strap
MKE-DRB MKE-EP
Appendix B Accessories
This page intentionally left blank
Related Specification
Appendix C How to Select the Right AC Motor Drive
Capacity Formulas
When one AC motor drive operates one motor
When one AC motor drive operates more than one motor
⋅ IM ≤ the rated current of AC motor drive a
Selection Note
General Precaution
Parameter Settings Note
Standard motor
How to Choose a Suitable Motor
Pole-changing Dahlander motor
Special motors
Motor torque
Power Transmission Mechanism
This page intentionally left blank
CPU
Ladder Diagram Editor WPLSoft
PLC Overview Introduction
※ This function is not for VFD*E*C models
RS485
Start-up Steps for PLC Execution
MI7 MI8 MI9
Device Reference Table
MI1 MI2 MI3 MI4 MI5 MI6
MO2 MO3 MO4
WPLSoft Installation
EME-DR2CA
Program Input Program Download
Limit of PLC
Program Monitor
Appendix D How to Use PLC Function
Ladder Diagram Program Scan Chart of the PLC Ladder Diagram
Appendix D How to Use PLC Function
Andp
LDI
ORI
LDP
MPP
Edition of PLC Ladder Diagram
MPS
MRD
ORB ANB OUT TMR
Appendix D How to Use PLC Function
Example 1 the latching circuit for priority of stop
Example for Designing Basic Program
Example 3 the latching circuit of SET and RST commands
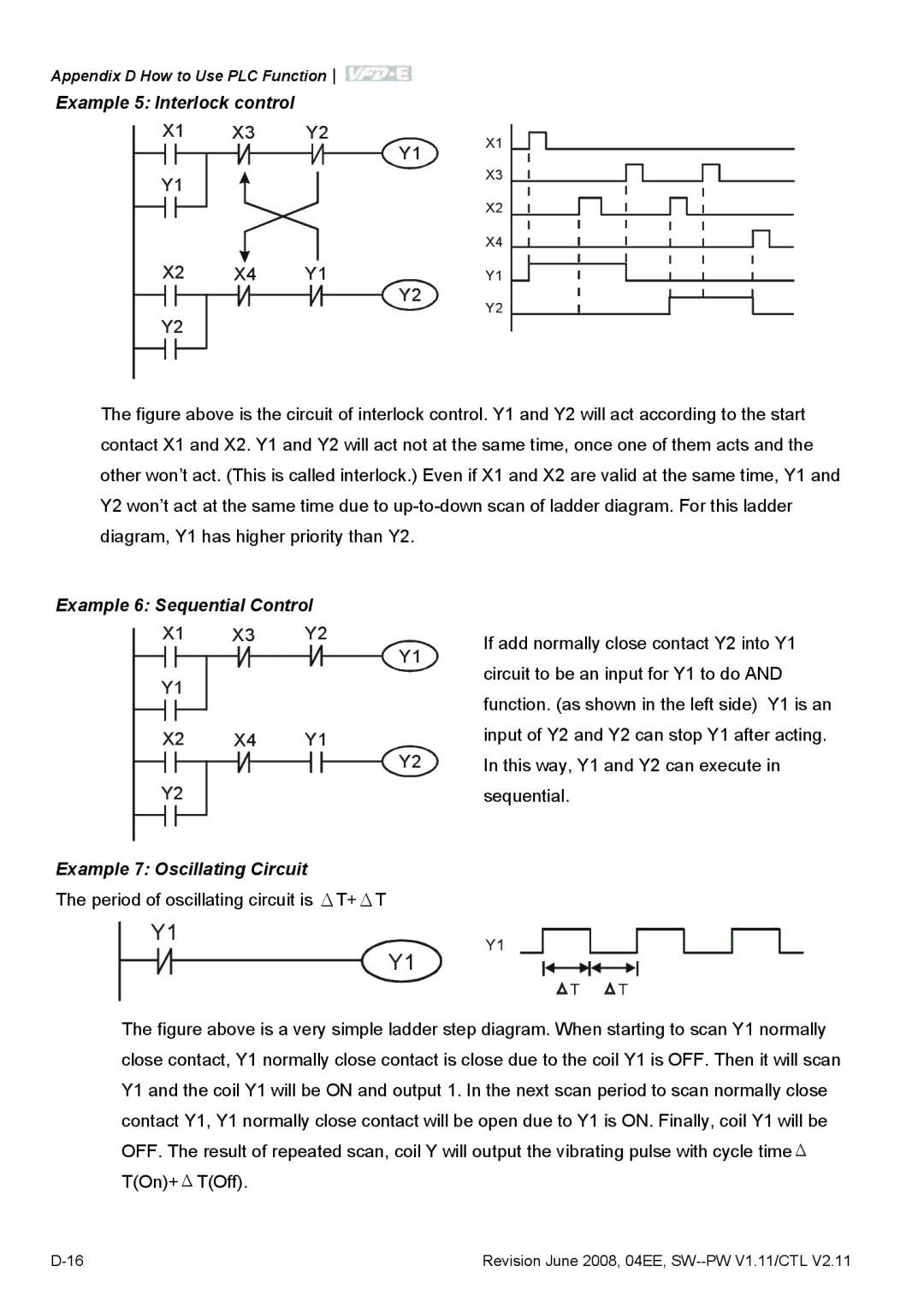
Example 6 Sequential Control
Example 8 Blinking Circuit
Seconds
Steps
PLC Devices Summary of DVP-PLC Device Number
„ The Function of Input/output Contacts
Devices Functions
Value, Constant K / H
Function of Auxiliary Relay
Function of Timer
Features and Functions of Counter
RST C0 CNT C0 K5 LD C0 OUT Y0
Register Types
Special Auxiliary Relays
Special Registers
Communication Addresses for Devices only for PLC2 mode
Commands Basic Commands
Function Code only for PLC2 mode
Rising-edge/falling-edge Detection Commands of Contact
Output Commands
Timer and Counters
Main Control Commands
Mnemonic Function
Rising-edge/falling-edge Output Commands
End Command
Explanation for the Commands
Mnemonic
LDI
ANI
ORI
ORB
ANB
Operand Function
ANI
MPP
MRD
True
INV
INV
False OFF
SET
T5 K1000
Device Status
RST
TMR
MC / MCR
CNT
C2 K100
MCR
LDF
LDP
OUT Y1
LDF
Andp
Andf
ORF
ORP
PLS
PLF
Description of the Application Commands
Type Bit Devices Word devices Program Steps
Explanation for the Application Commands
API
Mnemonic Operands Function
Zrst M0 M2 RST M2
RST M0 RST M1
S 2, S, D Zone Compare
Move
MOV
MOV K10 D0 MOV T0 D10
Mnemonic Operands
Bmov D10
ADD
Word devices Program Steps
Type
Type Bit Devices Word devices
Bit command B15 B31 B16b15
INC
Quotient Remainder
Decp D0
Incp D0
DEC
Decrement
ROL
ROR
D10
Special Application Commands for the AC Motor Drive
Appendix D How to Use PLC Function
M100
Wprp
WPR
S1, S2
S1, S2, S3, S4
Fpid
S1, S2, S3
Freq
Freqp
Plff
Error Code
Code Description Corrective Actions
This page intentionally left blank
Appendix E CANopen Function
DSP-XXX
Overview CANopen Protocol
Pre-Defined Connection Set
2 RJ-45 Pin Definition
NMT Network Management Object
CANopen Communication Protocol
After power is applied, it is auto in initialization state
Emerg
SDO Service Data Object
PDO SDO
PDO Process Data Object
Master transmits PDO data to Slave
Controller CANopen
Display Error Description Register Code Bit 0~7
Emcy Emergency Object
COB-ID Sync
Controller CANopen Error Display Description
Index Sub Definition Factory Size Unit Setting
Code Bit 0~7
Index Sub Definition Factory Size Unit Setting
Index Sub Definition Factory Size Unit Setting
How to Control by CANopen
Xxxxxxxx
Disable


![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() Y1 Y1
Y1 Y1![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() Y2 Y2
Y2 Y2![]() T
T ![]() T
T