ProSafe M4100 and M7100 Managed Switches
Trademarks
Support
Revision History
Table of Contents
LAGs
Ospf
ACLs
DiffServ
Security Management
Sntp
Switch Stacks
Snmp
Spanning Tree Protocol
Dvmrp
Index
Documentation Resources
Virtual LANs
VLANs
This chapter provides the following examples
Create Two VLANs
CLI Create Two Vlans
Web Interface Create Two Vlans
Select Switching Vlan Advanced Port Pvid Configuration
Assign Ports to VLAN2
CLI Assign Ports to VLAN2
Web Interface Assign Ports to VLAN2
Select Switching Vlan Basic Vlan Configuration
Create Three VLANs
CLI Create Three Vlans
Web Interface Create Three Vlans
ProSafe M4100 and M7100 Managed Switches
Assign Ports to VLAN3
CLI Assign Ports to VLAN3
Web Interface Assign Ports to VLAN3
Acceptable Frame Types list, select Admit All
Assign VLAN3 as the Default Vlan for Port 1/0/2
CLI Assign VLAN3 as the Default Vlan for Port 1/0/2
CLI Create a MAC-Based Vlan
Create a MAC-Based Vlan
Add port 1/0/23 to VLAN3
Select Switching Vlan Advanced Vlan Membership
Web Interface Assign a MAC-Based Vlan
Map MAC 00000A000002 to VLAN3
Add all the ports to VLAN3
ProSafe M4100 and M7100 Managed Switches
CLI Create a Protocol-Based Vlan
Create a Protocol-Based Vlan
MAC Address field, enter 00000A000002
Enable protocol Vlan group 1 and 2 on the interface
Web Interface Create a Protocol-Based Vlan
Create the protocol-based Vlan group vlanipx
Screen similar to the following displays
ProSafe M4100 and M7100 Managed Switches
CLI Create an IP Subnet-Based Vlan
Virtual VLANs Create an IP Subnet-Based Vlan
Create an IP subnet-based Vlan
Web Interface Create an IP Subnet-Based Vlan
Assign all the ports to Vlan
Subnet Mask field, enter
Voice VLANs
Vlan 1 to 4093 field, enter Click Add
CLI Configure Voice Vlan and Prioritize Voice Traffic
Create Vlan
Configure Voice Vlan globally
Configure Voice Vlan mode in the interface 1/0/2
Configure Vlan 10 as the matching criteria for the class
Include the ports 1/0/1 and 1/0/2 in Vlan
ProSafe M4100 and M7100 Managed Switches
ProSafe M4100 and M7100 Managed Switches
Select Switching Vlan Advanced Voice Vlan Configuration
Interface Mode list, select Vlan ID
Select QoS Advanced DiffServ Class Configuration
Select the 1/0/2 check box
Class Name field, enter ClassVoiceVLAN
Select QoS DiffServ Advanced Policy Configuration
Policy Name field, enter PolicyVoiceVLAN
Click the Policy PolicyVoiceVLAN
Set the Policy Name field as PolicyVoiceVLAN
Screen similar to the following displays Click Apply
Private VLANs
Private VLANs
Packet flow within a Private Vlan domain VLANs
Assign Private-VLAN Types Primary, Isolated, Community
CLI Assign Private-VLAN Type Primary, Isolated, Community
Assign Vlan 101 as an isolated Vlan
CLI Configure Private-VLAN Association
Configure Private-VLAN Association
Web Interface Configure Private-VLAN Association
CLI Configure Private-VLAN Port Mode Promiscuous, Host
Configure Private-VLAN Port Mode Promiscuous, Host
Configure port 1/0/1 to promiscuous port mode
Configure Private-VLAN Host Ports
CLI Configure Private-VLAN Host Ports
Web Interface Assign Private-VLAN Port Host Ports
CLI Map Private-VLAN Promiscuous Port
Map Private-VLAN Promiscuous Port
Web Interface Map Private-VLAN Promiscuous Port
Promiscuous Primary Vlan field, enter
LAGs
Link Aggregation Groups
Select Switching LAG LAG Configuration
Create Two LAGs
CLI Create Two LAGs
Web Interface Create Two LAGs
Add Ports to LAGs
CLI Add Ports to the LAGs
Web Interface Add Ports to LAGs
Enable Both LAGs
CLI Enable Both LAGs
Web Interface Enable Both LAGs
By default, the system enables link trap notification
Port Routing
This chapter provides the following sections
Port Routing Configuration
Layer 3 switch configured for port routing Port Routing
Enable Routing for the Switch
Enable Routing for Ports on the Switch
CLI Enable Routing for the Switch
Web Interface Enable Routing for the Switch
CLI Enable Routing for Ports on the Switch
Web Interface Enable Routing for Ports on the Switch
Routing Mode field, select Enable
IP Address field, enter Subnet Mask field, enter
IP Address field, enter Subnet Mask field, enter
Add a Default Route
CLI Add a Default Route
Web Interface Add a Default Route
Select Routing Routing Table Basic Route Configuration
Route Configuration screen displays
Route Type list, select DefaultRoute
Add a Static Route
CLI Add a Static Route
Web Interface Add a Static Route
Vlan Routing
Layer 3 switch configured for port routing
Web Interface Create Two VLANs
Select Switching Vlan Advanced Port Pvid Configuraton
Scroll down and select 1/0/1 and 1/0/2 check boxes
CLI Set Up Vlan Routing for the VLANs and the Switch
Set Up Vlan Routing for the VLANs and the Switch
Select Routing Vlan Vlan Routing
Click Add to save the settings
Routing Information Protocol
Routing for the Switch
Network with RIP on ports 1/0/2 and 1/0/3
Web Interface Enable Routing for the Ports
Routing for Ports
RIP for the Switch
Web Interface Enable RIP on the Switch
CLI Enable RIP on the Switch
RIP for Ports 1/0/2 and 1/0/3
CLI Enable RIP for Ports 1/0/2 and 1/0/3
Web Interface Enable RIP for Ports 1/0/2 and 1/0/3
ProSafe M4100 and M7100 Managed Switches
CLI Configure Vlan Routing with RIP Support
Vlan Routing with RIP
Enable RIP for the switch Route preference defaults to
Netgear Switch Config#ip routing
Web Interface Configure Vlan Routing with RIP Support
IP Address field, enter Network Mask field, enter
Network Mask field, enter
Ospf
Open Shortest Path First
CLI Configure an Inter-area Router
Inter-area Router
Assign IP addresses to ports
Web Interface Configure an Inter-area Router
Select Routing IP Advanced IP Interface Configuration
ProSafe M4100 and M7100 Managed Switches
RFC 1583 Compatibility field, select Disable
CLI Configure Ospf on a Border Router
Ospf on a Border Router
Web Interface Configure Ospf on a Border Router
Set disable 1583compatibility to prevent a routing loop
Enable IP routing on the switch
Select Routing IP Basic IP Configuration
IP Address field, enter Network Mask field, enter
Admin Mode field, select Enable
ProSafe M4100 and M7100 Managed Switches
Select Routing Ospf Advanced Interface Configuration
Router Priority 0 to 255 field, enter
Enable routing on the switch
CLI Configure Area 1 as a Stub Area on A1
Stub Areas
Configure area 0.0.0.1 as a stub area
Switch a injects a default route only to area
Enable Ospf area 0 on ports 2/0/11
Enable Ospf area 0.0.0.1 on 2/0/19
Web Interface Configure Area 1 as a Stub Area on A1
IP Address field, enter Network Mask field, enter
Select Routing Ospf Advanced Interface Configuration
CLI Configure Area 1 as a Stub Area on A2
Import Summary LSAs field, select Disable
Enable Ospf area 0.0.0.1 on the 1/0/15
Web Interface Configure Area 1 as a Stub Area on A2
Set the router ID to
IP Address field, enter Network Mask field, enter
ProSafe M4100 and M7100 Managed Switches
CLI Configure Area 1 as an nssa Area
Configure area 0.0.0.1 as an nssa area
Nssa Areas
Stop importing summary LSAs to area
Web Interface Configure Area 1 as an nssa Area on A1
Enable area 0.0.0.1 on port 2/0/19
IP Address field, enter Network Mask field, enter
Subnet Mask field, enter
CLI Configure Area 1 as an nssa Area on A2
Import Summary LSA’s field, select Disable
Enable Ospf area 0.0.0.1 on port 1/0/15
Configure the area 0.0.0.1 as an nssa area
Redistribute the RIP routes into the Ospf
Web Interface Configure Area 1 as an nssa Area on A2
Select Routing RIP Advanced Interface Configuration
Select Routing Ospf Advanced Nssa Area Configuration
Vlan Routing Ospf
ProSafe M4100 and M7100 Managed Switches
CLI Configure Vlan Routing Ospf
Specify the router ID and enable Ospf for the switch
Web Interface Configure Vlan Routing Ospf
Enable Ospf for the Vlan and physical router ports
IP Address field, enter Network Mask field, enter
ProSafe M4100 and M7100 Managed Switches
On A1, enable IPv6 unitcast routing on the switch
CLI Configure OSPFv3
OSPFv3
On A2, enable IPv6 unitcast routing on the switch
Enable OSPFv3, and assign 1.1.1.1 to router ID
Enable OSPFv3, and assign 2.2.2.2 as the router ID
Enable IPv6 unicast routing on the switch
Web Interface Configure OSPFv3
Select Routing IPv6 Basic IPv6 Global Configuration
Autonomous Flag field, select Disable
Click Add to save the settings Enable OSPFv3 on port 1/0/1
ProSafe M4100 and M7100 Managed Switches
Proxy ARP Examples
Proxy Address Resolution Protocol
CLI show ip interface
Web Interface Configure Proxy ARP on a Port
CLI ip proxy-arp
Vrrp
Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol
CLI Configure Vrrp on a Master Router
Enable Vrrp for the switch
Enable Vrrp on the port
Vrrp on a Master Router
Web Interface Configure Vrrp on a Master Router
Select Routing Vrrp Advanced Vrrp Configuration
Vrrp on a Backup Router
CLI Configure Vrrp on a Backup Router
Mode field, select Active Click Apply to save the settings
Primary IP Address field, enter
Web Interface Configure Vrrp on a Backup Router
Set the priority for the port. The default priority is
Priority 1 to 255, enter Primary IP Address field, enter
Status list, select Active
Click Add to save the settings
Access Control Lists
MAC ACLs
ACL Configuration
IP ACLs
CLI Set Up an IP ACL with Two Rules
Set Up an IP ACL with Two Rules
Apply the ACL to one or more interfaces
Web Interface Set Up an IP ACL with Two Rules
Select Security ACL IP ACL IP Extended Rules
ProSafe M4100 and M7100 Managed Switches
ProSafe M4100 and M7100 Managed Switches
One-Way Access Using a TCP Flag in an ACL
CLIConfigure One-Way Access Using a TCP Flag in an ACL
Configure the Switch
This is a two-step process
ProSafe M4100 and M7100 Managed Switches
Enter the following commands
Configure the GSM7352S
Create an ACL that permits all the IP packets
ProSafe M4100 and M7100 Managed Switches
Configuring the Switch
This is a two-part process
Create Vlan 30 with IP address 192.168.30.1/24
Select Routing Vlan Vlan Routing Wizard
IP Address field, enter Network Mask field, enter
Select Routing IP Basic IP Configuration
Select Routing Routing Table Basic Route Configuration
Select Security ACL Advanced IP ACL
ProSafe M4100 and M7100 Managed Switches
ProSafe M4100 and M7100 Managed Switches
ProSafe M4100 and M7100 Managed Switches
Configuring the GSM7342S Switch
Create Vlan 40 with IP address 192.168.40.1/24
IP Address field, enter Network Mask field, enter
Select Routing Routing Table Basic Route Configuration
ProSafe M4100 and M7100 Managed Switches
Use ACLs to Configure Isolated VLANs on a Layer 3 Switch
Using ACLs to isolate VLANs on a Layer 3 switch
Enter the following CLI commands
Create ACL 103 to permit all other traffic
IP Address field, enter Network Mask field, enter
IP Address field, enter
Select Security ACL Advanced IP ACL
Select Security ACL Advanced IP Extended Rules
Select Security ACL Advanced IP Extended Rules
Select Security ACL Advanced IP Extended Rules
Select Security ACL Advanced IP Binding Configuration
ProSafe M4100 and M7100 Managed Switches
Set up a MAC ACL with Two Rules
CLI Set up a MAC ACL with Two Rules
Web Interface Set up a MAC ACL with Two Rules
Select Security ACL MAC ACL
Select Security ACL MAC ACL MAC Rules
Select Security ACL MAC ACL MAC Binding Configuration
ACL Mirroring
CLI Configure ACL Mirroring
ACL mirroring
View the configuration
Web Interface Configure ACL Mirroring
Bind the ACL with interface 1/0/1
ProSafe M4100 and M7100 Managed Switches
ProSafe M4100 and M7100 Managed Switches
ProSafe M4100 and M7100 Managed Switches
ACL Redirect
CLI Redirect a Traffic Stream
Create an IP access control list with the name redirectHTTP
Web Interface Redirect a Traffic Stream
ProSafe M4100 and M7100 Managed Switches
Redirect Interface list, select 1/0/19
ProSafe M4100 and M7100 Managed Switches
Configure IPv6 ACLs
CLI Configure an IPv6 ACL
Create the access control list with the name ipv6-acl
Netgear Switch #show ipv6 access-lists
Web Interface Configure an IPv6 ACL
Select Security ACL Advanced IPv6 ACL
ProSafe M4100 and M7100 Managed Switches
Select Security ACL Advanced IP Binding Configuration
ProSafe M4100 and M7100 Managed Switches
Class of Service Queuing
CoS Queuing
CoS Queue Mapping
Trusted Ports
Untrusted Ports
CoS queue mapping uses trusted and untrusted ports
CoS Queue Configuration
Show classofservice Trust
CLI Show classofservice Trust
To use the CLI to show CoS trust mode, use these commands
Set classofservice Trust Mode
Web Interface Show classofservice Trust
CLI Set classofservice Trust Mode
Web Interface Set classofservice Trust Mode
Show classofservice IP-Precedence Mapping
CLI Show classofservice IP-Precedence Mapping
Web Interface Show classofservice ip-precedence Mapping
Global Trust Mode list, select trust dot1p
IP precedence to queue mapping of the interface is displayed
Set CoS Trust Mode for an Interface
Scheduler Type list, select Weighted
Configure Traffic Shaping
CLI Set CoS Trust Mode for an Interface
Web Interface Set CoS Trust Mode for an Interface
Interface Trust Mode list, select trust dot1p
Web Interface Configure Traffic Shaping
CLI Configure traffic-shape
Interface Shaping Rate 0 to 100 field, enter
Click Apply to save the settings
Differentiated Services
DiffServ
This chapter provides the following examples DiffServ on
Auto VoIP on
Class B subnet with differentiated services
DiffServ
CLI Configure DiffServ
Ensure that the DiffServ operation is enabled for the switch
Netgear Switch Config policy-map#exit
Web Interface Configure DiffServ
Class Name field, enter financedept
Source IP Address field, enter Source Mask field, enter
Class Name field, enter marketingdept
Source IP Address field, enter Source Mask field, enter
Class Name field, enter developmentdept
Policy Selector field, enter internetaccess
Member Class list, select marketingdept
Member Class list, select testdept
Member Class list, select developmentdept
ProSafe M4100 and M7100 Managed Switches
ProSafe M4100 and M7100 Managed Switches
ProSafe M4100 and M7100 Managed Switches
Policy In list, select internetaccess
Select QoS CoS Advanced Interface Queue Configuration
ProSafe M4100 and M7100 Managed Switches
ProSafe M4100 and M7100 Managed Switches
ProSafe M4100 and M7100 Managed Switches
CLI Configure DiffServ for VoIP
DiffServ for VoIP
Attach the defined policy to an inbound service interface
Select QoS DiffServ Advanced DiffServ Configuration
Web Interface Diffserv for VoIP
Click classvoip
Click classef
Screen similar to the following displays
Select QoS DiffServ Advanced Service Configuration
Auto VoIP
CLI Configure Auto VoIP
Auto VoIP
View the auto VoIP information
Web Interface Configure Auto-VoIP
DiffServ for IPv6
DiffServ for IPv6
CLI Configure DiffServ for IPv6
Define matching criteria as protocol ICMPv6
Create the policy policyicmpv6
Associate the previously created class classicmpv6
Select QoS DiffServ Advanced IPv6 Class Configuration
Web Interface Configure DiffServ for IPv6
Class Name field, enter classicmpv6
ProSafe M4100 and M7100 Managed Switches
Policy Name field, enter policyicmpv6
ProSafe M4100 and M7100 Managed Switches
Policy Name list, select policyicmpv6
Select the Interface 1/0/1, 1/0/2, and 1/0/3 check boxes
Screen similar to the following displays Click Apply
Color Conform Policy
CLI Configure a Color Conform Policy
Create classes classvlan and classcolor
Web Interface Configure a Color Conform Policy
Apply this policy to port 1/0/13
ProSafe M4100 and M7100 Managed Switches
Select QoS DiffServ Advanced Class Configuration
Class Name field, enter classcolor
Policy Name field, enter policyvlan
Member Class field, enter classvlan
Committed Rates field, enter
Committed Burst Size field, enter
For Conform Action, select the Send radio button
Policy Name list, select policyvlan
Igmp Snooping and Querier
Igmp
CLI Enable Igmp Snooping
Web Interface Enable Igmp Snooping
Following example shows how to enable Igmp snooping
Igmp Snooping
CLI Show igmpsnooping
Show mac-address-table igmpsnooping
Web Interface Show igmpsnooping
CLI Configure the Switch with an External Multicast Router
External Multicast Router
CLI Show mac-address-table igmpsnooping
Web Interface Show mac-address-table igmpsnooping
Multicast Router Using Vlan
CLI Configure the Switch with a Multicast Router Using Vlan
Multicast Router field, select Enable
Igmp Querier
Enable Igmp Querier
CLI Enable Igmp Querier
Web Interface Enable Igmp Querier
Querier IP Address field, enter
To see the Igmp querier status, use the following command
Show Igmp Querier Status
CLI Show Igmp Querier Status
Web Interface Show Igmp Querier Status
MVR Multicast Vlan Registration
Configure MVR in Compatible Mode
MVR switch GSM7212P in this case
CLI Configure MVR in Compatible Mode
Configure multicast Vlan on the source port
Configure the receive ports
Create MVlan, VLAN1, VLAN2, and VLAN3
ProSafe M4100 and M7100 Managed Switches
Web Interface Configure MVR in Compatible Mode
Show mvr status
ProSafe M4100 and M7100 Managed Switches
ProSafe M4100 and M7100 Managed Switches
ProSafe M4100 and M7100 Managed Switches
CLI Configure MVR in Dynamic Mode
Configure MVR in Dynamic Mode
Configure MVR in dynamic mode
Configure the receive ports
Web Interface Configure MVR in Dynamic Mode
Show the MVR status
ProSafe M4100 and M7100 Managed Switches
ProSafe M4100 and M7100 Managed Switches
ProSafe M4100 and M7100 Managed Switches
Security Management
Port Security
Set the Dynamic and Static Limit on Port 1/0/1
CLI Set the Dynamic and Static Limit on Port 1/0/1
Click Apply to save the settings
Create a Static Address
Select the Convert Dynamic Address to Static check box
Protected Ports
CLI Create a Static Address
Web Interface Create a Static Address
Static MAC Address field, enter
Create one Vlan 192 including PC 1 and PC
Protected ports
Enable IP routing and configure a default route
Enable a protected port on 1/0/23 and 1/0/24
Create one Vlan 202 connected to the Internet
Create a Dhcp pool to allocated IP addresses to PCs
ProSafe M4100 and M7100 Managed Switches
IP Address field, enter Network Mask field, enter
IP Address field, enter Network Mask field, enter
Next Hop IP Address field, enter
CLI Authenticating dot1x Users by a Radius Server
802.1x Port Security
Web Interface Authenticating dot1x Users by a Radius Server
Select Routing Basic IP Configuration
Select Routing Advanced IP Interface Configuration
IP Address field, enter Subnet Mask field, enter
Control Mode list, select Force Authorized
Message Authenticator field, select Enable
Accounting Mode field, select Enable Click Apply
Server Address field, enter
Accounting Server Address field, enter
Create a Guest Vlan
Guest Vlan
Enable dot1x and Radius on the switch
CLI Create a Guest Vlan
Enable the guest Vlan on ports 1/0/1 and 1/0/24
Web Interface Create a Guest Vlan
Click Apply to save settings Enable dot1x on the switch
ProSafe M4100 and M7100 Managed Switches
Assign VLANs Using Radius
Radius Server IP Address field, enter
CLI Assign Vlans Using Radius
Netgear Switch #network protocol none
Enable dot1x authentication on the switch
Use the Radius as the authenticator
Set the Radius server IP address
Set the NAS-IP address for the Radius server
Show the dot1x detail for 1/0/5
Web Interface Assign Vlans Using Radius
Assign the IP address for the Web Management Interface
IP Address field, enter Subnet Mask field, enter
Control Mode list, select Force Authorized
Dynamic ARP Inspection
Enable Dhcp snooping globally
CLI Configure Dynamic ARP Inspection
Enable Dhcp snooping in a Vlan
Web Interface Configure Dynamic ARP Inspection
Enable ARP inspection in Vlan
Select Security Control Dhcp Snooping Global Configuration
View the Dhcp Snooping Binding table
ProSafe M4100 and M7100 Managed Switches
ProSafe M4100 and M7100 Managed Switches
ProSafe M4100 and M7100 Managed Switches
CLI Configure Static Mapping
Configure the rule to allow the static client
Static Mapping
Create an ARP ACL
Configure ARP ACL used for Vlan
Web Interface Configure Static Mapping
ACL Name list, select ArpFilter
Dhcp Snooping
Click Apply Screen similar to the following displays
CLI Configure Dhcp Snooping
Dhcp Snooping
Web Interface Configure Dhcp Snooping
ProSafe M4100 and M7100 Managed Switches
CLI Enter Static Binding into the Binding Database
Enter Static Binding into the Binding Database
Enter the Dhcp snooping static binding
Select Security Control Dhcp Snooping Binding Configuration
Maximum Rate of Dhcp Messages
CLI Configure the Maximum Rate of Dhcp Messages
Web Interface Configure the Maximum Rate of Dhcp Messages
View the rate configured
Control the maximum rate of Dhcp messages
IP Source Guard
IP Source Guard
Enable IP Source Guard in interface 1/0/2
ProSafe M4100 and M7100 Managed Switches
ProSafe M4100 and M7100 Managed Switches
Select the Interface 1/0/2 check box
MAC Address field, enter
Simple Network Time Protocol
Show Sntp CLI Only
Show sntp
Show sntp client
Show sntp server
Configure Sntp
CLI Configure Sntp
Web Interface Configure Sntp
Set the Time Zone CLI Only
Set the Named Sntp Server
Web Interface Set the Named Sntp Server
CLI Set the Named Sntp Server
Address field, enter time-f.netgear.com
DNS Server field, enter
Tools
Traceroute
CLI Traceroute
Select Maintenance Troubleshooting Traceroute
Web Interface Traceroute
Configuration Scripting
This section provides the following examples Script on
Script
Script list and script delete
Create a Configuration Script
Script apply running-config.scr
Upload a Configuration Script
Create a Pre-Login Banner CLI Only
Pre-Login Banner
Transfer the file from the PC to the switch using Tftp
CLI Specify the Source Mirrored Ports and Destination Probe
Port Mirroring
Select Monitoring Mirroring Port Mirroring
Dual Image
Session Mode field, select Enable Click Apply
Destination Port field, enter 1/0/3
CLI Download a Backup Image and Make It Active
Web Interface Download a Backup Image and Make It Active
Select Maintenance File Management Dual Image Configuration
Server Address Type list, select IPv4
Remote File Name, enter gsm73xxse-r8v0m0b3.stk
Outbound Telnet
This section, the following examples are provided
CLI show network
CLI show telnet
Select Security Access Telnet
Web Interface Configure Telnet
CLI transport output telnet
CLI Configure the session-limit and session-timeout
Web Interface Configure the Session Timeout
Maximum number of sessions field, enter
Syslog
Log Files Syslog
Configure the syslog
Show Logging
CLI Show Logging
Web Interface Show Logging
Select Monitoring Logs Console Log
Select Monitoring Logs Command Log
Select Monitoring Logs Buffer Logs
Show Logging Buffered
CLI Show Logging Buffered
Show Logging Traplogs
Web Interface Show Logging Buffered
CLI Show Logging Traplogs
Web Interface Show Logging Trap Logs
Show Logging Hosts
CLI Show Logging Hosts
CLI Configure Logging for the Port
Configure Logging for a Port
Web Interface Show Logging Hosts
Web Interface Configure Logging for the Port
Severity Filter list, select Alert
Email Alerting
For Position Only FPO
Netgear Switch Config#logging traps
Switch Stacks
Switch Stack Management and Connectivity
Stack Master and Stack Members
Stack Master
Stack Members
Stack Member Numbers
Compatible Switch Models
Install and Power-up a Stack
Stack Member Priority Values
Switch Firmware
Install a Switch Stack
Migrate Configuration with a Firmware Upgrade
Upgrade the Firmware
Code Mismatch
Configure a Stacking Port as an Ethernet Port
Continue with the boot of operational code
Copy Master Firmware to a Stack Member Web Interface
Copy Master Firmware to Unit list, select
On Switch A, Configure the Stack Port and Reboot
CLI Configure a Stacking Port as an Ethernet Port
After Switch a reboots
Web Interface Configure a Stacking Port as an Ethernet Port
On Switch B, Configure the stack port and reboot
After Switch B reboots
Configured Stack Mode list, select Ethernet
ProSafe M4100 and M7100 Managed Switches
CLI Stack Switches Using 10G Fiber
Stack Switches Using 10G Fiber
On Switch A, show the port information
Web Interface Stack Switches Using 10G Fiber
Reboot Switch B
On Switch A, you see the following
Select System Stacking Advanced Stack Port Configuration
Add Switches to an Operating Stack
Configured Stack Mode list, select Stack
Reboot Unit No. list, select Click Apply
Add, Remove, or Replace a Stack Member
Remove a Switch from the Stack
Switch Stack Configuration Files
Replace a Stack Member
Preconfigure a Switch
Switch Stack Master Scenarios
Preconfigured Switches Compared to Stack Configuration
Renumber Stack Members
CLI Renumber Stack Members
Web Interface Renumber Stack Members
Now the unit ID of the stacking member is
CLI Move the Stack Master to a Different Unit
Move the Stack Master to a Different Unit
Web Interface Move the Stack Master to a Different Unit
CLI Add a New Community
Add a New Community
Snmp V3 on SFlow on
Enable Snmp Trap
CLI Enable Snmp Trap
This example shows how to send Snmp trap to the Snmp server
Web Interface Add a New Community
Web Interface Enable Snmp Trap
Snmp
CLI Configure Snmp
Web Interface Configure Snmp
Confirm Password field, enter
Click Apply to save the settings Configure the Snmp V3 user
SFlow
Encryption Key field, enter
SFlow
Configure the sFlow receiver IP address
View the sampling port configurations
Select the 1 check box
ProSafe M4100 and M7100 Managed Switches
View the polling port configurations
CLI Configure Time-Based Sampling of Counters with sFlow
Time-Based Sampling of Counters with sFlow
Select System Management DNS DNS Configuration
Specify Two DNS Servers
Domain Name System
CLI Specify Two DNS Servers
Select System Management DNS Host Configuration
Manually Add a Host Name and an IP Address
CLI Manually Add a Host Name and an IP Address
Web Interface Manually Add a Host Name and an IP Address
IP Address field, enter
CLI Configure a Dhcp Server in Dynamic Mode
Configure a Dhcp Server in Dynamic Mode
Dhcp Server
Web Interface Configure a Dhcp Server in Dynamic Mode
Select System Services Dhcp Server Dhcp Pool Configuration
Configure a Dhcp Reservation
CLI Configure a Dhcp Reservation
Web Interface Configure a Dhcp Reservation
ProSafe M4100 and M7100 Managed Switches
DHCPv6 Server
DHCPv6 stateful IPv6 address assignment DHCPv6 Server
CLI Configure DHCPv6
Enable IPv6 routing
Create a DHCPv6 pool and enable Dhcp service
Enable DHCPv6 service on port 1/0/9
Web Interface Configure an Inter-area Router
Select Routing IPv6 Advanced Interface Configuration
ProSafe M4100 and M7100 Managed Switches
ProSafe M4100 and M7100 Managed Switches
Prefix field, enter 000100011540144f0000004daad0
CLI Configure Stateless DNS Server
Configure Stateless DHCPv6 Server
Enable IPv6 Dhcp server on interface 2/0/21
Web Interface Configure Stateless DHCPv6 Server
Select System Services Dhcp Server DHCPv6 Pool Configuration
ProSafe M4100 and M7100 Managed Switches
Double VLANs
Double VLANs and Private Vlan Groups
This chapter includes the following examples
Web Interface Enable a Double Vlan
CLI Enable a Double Vlan
Create static Vlan
ProSafe M4100 and M7100 Managed Switches
ProSafe M4100 and M7100 Managed Switches
Private Vlan Groups
Create a private group in isolated mode
Create a private group in community mode
CLI Create a Private Vlan Group
Web Interface Create a Private Vlan Group
Add 1/0/16 and 1/0/7 to the private group
Acceptable Frame Type list, select Admit All
ProSafe M4100 and M7100 Managed Switches
ProSafe M4100 and M7100 Managed Switches
CLI Configure Classic STP 802.1d
Configure Classic STP 802.1d
Spanning Tree Protocol
Web Interface Configure Classic STP 802.1d
Configure Rapid STP 802.1w
CLI Configure Rapid STP 802.1w
Web Interface Configure Rapid STP 802.1w
Select Switching STP CST Port Configuration
Configure Multiple STP 802.1s
CLI Configure Multiple STP 802.1s
Web Interface Configure Multiple STP 802.1s
ProSafe M4100 and M7100 Managed Switches
In4 tuennel between two switches Tunnel
Tunnel
Configure Switch GSM7328S1
CLI Create a Tunnel
Configure Switch GSM7328S2
Web Interface Create a Tunnel
Source Address field, enter Destination Address field, enter
Click Apply Assign an IPv6 address to the tunnel
Configure Switch GSM7328S2
IP Address field, enter Subnet Mask field, enter
ProSafe M4100 and M7100 Managed Switches
Create an IPv6 Routing Interface
IPv6 Interface Configuration
CLI Create an IPv6 Routing Interface
Assign an IPv6 address to interface 1/0/1
Select Routing IPv6 Advanced Prefix Configuration
Web Interface Create an IPv6 Routing Interface
Create an IPv6 Network Interface
CLI Configure the IPv6 Network Interface
Web Interface Configure the IPv6 Network Interface
IPv6 Prefix/Prefix Length field, enter 200111/64
EUI64 field, select False Click Add
CLI Create an IPv6 Routing Vlan
Create an IPv6 Routing Vlan
IPv6 Gateway field, enter
Netgear Switch Config#ipv6 forwarding
Web Interface Create an IPv6 Vlan Routing Interface
Select Routing IPv6 Advanced Interface Configuration
ProSafe M4100 and M7100 Managed Switches
CLI Configure DHCPv6 mode on routing interface
Configure DHCPv6 Mode on the Routing Interface
Enable DHCPv6 on the interface 1/0/23
Web Interface Configure DHCPv6 mode on routing interface
Show the ipv6 address assigned from 1/0/23
ProSafe M4100 and M7100 Managed Switches
Protocol-Independent-Multicast
PIM-Dense Mode PIM-DM PIM-Sparse Mode PIM-SM
PIM-SMon
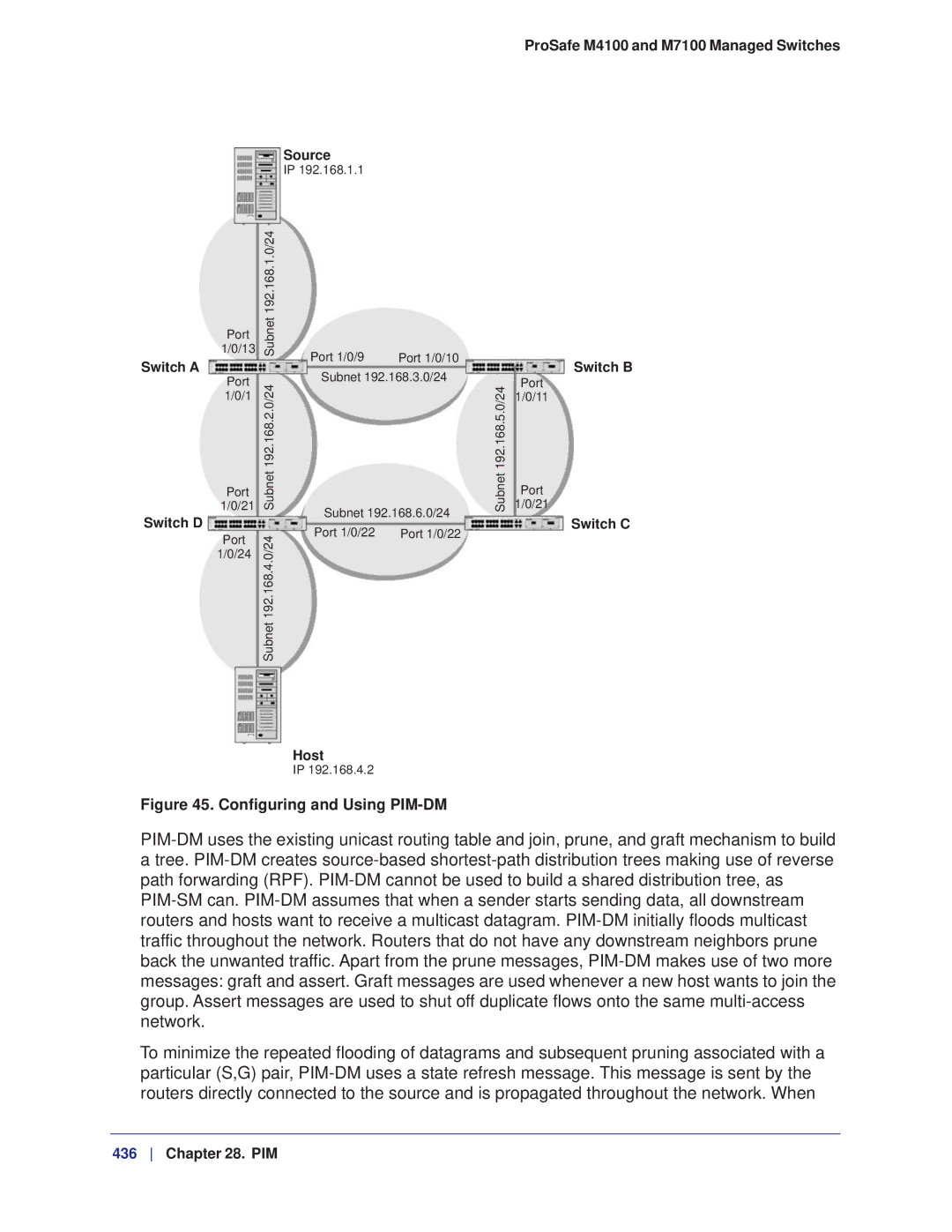
Configuring and Using PIM-DM
CLI Configure PIM-DM
PIM-DM on Switch a
Enable pimdm on the switch
Enable IP multicast forwarding on the switch
PIM-DM on Switch B
Enable PIM-DM on the interface
PIM-DM on Switch D
PIM-DM on Switch C
Enable Igmp on the switch
Enable Igmp on 1/0/24
PIM-DM builds the multicast routes table on each switch
Web Interface Configure PIM-DM
IP Address field, enter Subnet Mask field, enter
Select Routing RIP Advanced Interface Configuration
ProSafe M4100 and M7100 Managed Switches
ProSafe M4100 and M7100 Managed Switches
PIM-DM on Switch B
Select Routing RIP Advanced Interface Configuration
Select Routing Multicast PIM Global Configuration
PIM-DM on Switch C
IP Address field, enter Subnet Mask field, enter
Select Routing RIP Advanced Interface Configuration
Select Routing Multicast PIM Global Configuration
PIM-DM on Switch D
IP Address field, enter Subnet Mask field, enter
IP Address field, enter Subnet Mask field, enter
ProSafe M4100 and M7100 Managed Switches
Select Routing Multicast PIM Interface Configuration
Select Routing Multicast Igmp Interface Configuration
ProSafe M4100 and M7100 Managed Switches
PIM-SM
CLI Configure PIM-SM
PIM-SM on Switch a
Enable PIM-SM on the switch
Enable RIP to build a unicast IP routing table
PIM-SM on Switch B
Netgear Switch#configure
PIM-SM on Switch C
PIM-SM on Switch D
Web Interface Configure PIM-SM
Pimsm
IP Address field, enter Subnet Mask field, enter
IP Address field, enter Subnet Mask field, enter
Select Routing RIP Advanced Interface Configuration
ProSafe M4100 and M7100 Managed Switches
PIM-SM on Switch B
IP Address field, enter Subnet Mask field, enter
Select Routing Multicast Global Configuration
Select Routing Multicast PIM Interface Configuration
Click Add Set up the BSR candidate configuration
Group Mask field, enter
PIM-SM on Switch C
IP address, enter Subnet Mask field, enter
Select Routing Multicast Global Configuration
Select Routing Multicast PIM Interface Configuration
Click Add BSR Candidate Configuration
Select Routing Multicast PIM BSR Candidate Configuration
PIM-SM on Switch D
IP Address field, enter Subnet Mask field, enter
Select Routing RIP Advanced Interface Configuration
Select Routing Multicast Global Configuration
Select Routing Multicast PIM Interface Configuration
Click Add Set up BSR Candidate configuration
Select Routing Multicast Igmp Interface Configuration
ProSafe M4100 and M7100 Managed Switches
Dhcp L2 Relay
Dhcp L2 Relay and L3 Relay
This chapter includes the following sections
CLI Enable Dhcp L2 Relay
Enable the Dhcp L2 relay on the switch
Enable the Option 82 Circuit ID field
Enable the Option 82 Remote ID field
Web Interface Enable Dhcp L2 Relay
Enable Dhcp L2 relay on port 1/0/5
Enable Dhcp L2 relay on port 1/0/6
Trust packets with option 82 received on port 1/0/6
ProSafe M4100 and M7100 Managed Switches
Remote ID String field, enter rmtid
82 Option Trust Mode field, select Enable
CLI Configure a Dhcp Server
Configure the Dhcp Server Switch
Dhcp L3 Relay
Web Interface Configure a Dhcp Server
Create a Dhcp pool
Select System Services Dhcp Server Dhcp Server Configuration
IP Range From field, enter IP Range To field, enter
Select System Services Dhcp Server Dhcp Pool Configuration
CLI Configure a Dhcp L3 Relay
Configure a Dhcp L3 Switch
Create a routing interface and enable RIP on it
Web Interface Configure a Dhcp L3 Relay
Create a routing interface connecting to the client
Subnet Mask field, enter
IP Address Configuration Method field, enter Manual
Select Routing RIP Advanced Route Redistribution
Redistribute Mode field, select Enable
UDP Port field, enter dhcp Click Add to save the settings
Configure MLD on MLD Snooping on
Multicast Listener Discovery
CLI Configure MLD
Configure MLD
MLD on Switch a
MLD on Switch B
Enable OSPFv3 to build a unicast route table
Enable IPV6 MLD on the switch
Enable IPV6 PIM-DM on the switch
Web Interface Configure MLD
Enable MLD on interface 1/0/24
Select Routing IPv6 Advanced Interface Configuration
ProSafe M4100 and M7100 Managed Switches
Select Routing OSPFv3 Advanced Interface Configuration
Select Routing IPv6 Multicast IPv6 PIM Global Configuration
MLD on Switch B
Select Routing IPv6 Advanced Interface Configuration
ProSafe M4100 and M7100 Managed Switches
Select Routing OSPFv3 Advanced Interface Configuration
Select Routing IPv6 Multicast IPv6PIM Global Configuration
Select Routing IPv6 Multicast MLD Global Configuration
MLD Snooping
CLI Configure MLD Snooping
Enable MLD snooping on Vlan
Web Interface Configure MLD Snooping
ProSafe M4100 and M7100 Managed Switches
ProSafe M4100 and M7100 Managed Switches
Dvmrp
Distance Vector Multicast Routing Protocol
Dvrmp on Switch a
CLI Configure Dvmrp
Create routing interfaces 1/0/1, 1/0/13, and 1/0/21
Enable Dvmrp protocol on the switch
255
Enable Dvmrp mode on interfaceS 1/0/13 and 1/0/20
Dvrmp on Switch B
Create routing ports 1/0/13 and 1/0/20
192.168.2.1
Dvrmp on Switch C
Enable IP Dvmrp protocol on the switch
Enable Dvmrp mode on interfaces 1/0/3, 1/0/11, and 1/0/24
Enable Igmp protocol on the switch
Enable Igmp mode on the interface 1/0/24
Web Interface Configure Dvmrp
Dvmrp on Switch a
Routing Mode field, select Enable
Select Routing Multicast Dvmrp Interface Configuration
Dvmrp on Switch B
IP Address field, enter Subnet Mask field, enter
Select Routing Multicast Dvmrp Interface Configuration
Dvmrp on Switch C
IP Address field, enter Subnet Mask field, enter
Select Routing Multicast Dvmrp Global Configuration
Click Apply to save the settings Enable Igmp on the switch
Select Enable in the Interface Mode field
Select Routing Multicast Igmp Global Configuration
ProSafe M4100 and M7100 Managed Switches
Captive Portal
Captive Portal Configuration
Enable Captive Portal
CLI Enable Captive Portal
Enable captive portal on the switch
Web Interface Enable Captive Portal
Enable captive portal instance
Enable captive portal instance 1 on port 1/0/1
Select Security Control Captive Portal CP Configuration
Client Access, Authentication, and Control
Local Authorization, Create Users and Groups
Block a Captive Portal Instance
CLI Block a Captive Portal Instance
Web Interface Block a Captive Portal Instance
CLI Create Users and Groups
Web Interface Create Users and Groups
Remote Authorization Radius User Configuration
Group field, select Click Add
CLI Configure Radius as the Verification Mode
Web Interface Configure Radius as the Verification Mode
Default-RADIUS-Server
SSL Certificates
ISCSI
Shows an example of iSCSI implementation
CLI Enable iSCSI Awareness with Vlan Priority Tag
Enable iSCSI Awareness with Vlan Priority Tag
Web Interface Enable iSCSI Awareness with Vlan Priority Tag
Enable iSCSI Awareness with Dscp
CLI Enable iSCSI Awareness with Dscp
Web Interface Enable iSCSI Awareness with Dscp
Select Switching iSCSI Basic
Set the iSCSI Target Port
CLI Set iSCSI Target Port
Web Interface Set iSCSI Target Port
IP Address, enter
CLI Show iSCSI Sessions
Show iSCSI Sessions
Web Interface Show iSCSI Sessions
ProSafe M4100 and M7100 Managed Switches
Index
Numerics
Index
SFlow 373, 374