J2-Super Series
Safety Instructions
To prevent electric shock, note the following
Additional instructions
HC-SFS81
Wiring
COM
Usage
RA EMG 24VDC
For Maximum Safety
Maintenance, inspection and parts replacement
Low voltage directive
Configuration
EMC directive
Machine directive
Grounding
Power supply
Wiring
Auxiliary equipment and options
Use UL/C-UL standard-compliant products
Memo
Contents Functions and Configuration
Operation
Servo Configuration Software
12.1
11.1
11.2
12.2
13.3
13.1
13.2
13.4
15-16
15-11
15-14
15-18
Page
Memo
Functions and Configuration
Introduction
Function block diagram of this servo is shown below
Function block diagram
Stop
System configuration
Operation using external input signals
Operation using external input signals and communication
External I/O signals Servo amplifier axis
Operation using communication
Functions and Configuration
3 I/O devices
Servo amplifier standard specifications
Phase pulse Dog cradle type
Other functions Structure Ambient Temperature
Weight
Humidity
Function list
Model code definition Rating plate
Model
Combination with servo motor
Structure 1.6.1 Part names MR-J2S-100CL or less
MR-J2S-200CL MR-J2S-350CL
Output analog monitor data Encoder connector CN2
Backup Battery holder
MR-J2S-500CL
Name plate Main circuit terminal block TE1
MR-J2S-700CL
Brake option and servo motor
For MR-J2S-500CL
For MR-J2S-700CL
Cables
For 3-phase 200V to 230VAC or 1-phase 230VAC
No-fuse breaker
Magnetic contactor Section Manual pulse generator
Magnetic contactor
For 1-phase 100V to 120VAC
FR-BAL
SETUP151E
MRZJW3
Servo configuration software
Command device Junction terminal Servo amplifier Block
Installation
Installation
Control box 10mm 0.4 in. or more 40mm Or more
Others
Installation of two or more servo amplifiers
Keep out foreign materials
Cable stress
Signals and Wiring
Signals and Wiring
Standard connection example
Signals and Wiring
Internal connection diagram of servo amplifier
CN1A OPC
I/O signals Connectors and signal arrangements
Signal arrangement
DOG COM SON CN2 MDR MRR
Signal devices explanations O devices
Input devices
DOG
ST2
OFF
Proportional type
DI3 DI2 DI1 DI0
Proportion control
Than the rated by the analog torque limit TLA
Stop/Restart Turn it on again to make a restart
Multiplication Parameter No.1 setting
Temporary
Is ignored
Output devices
MBR
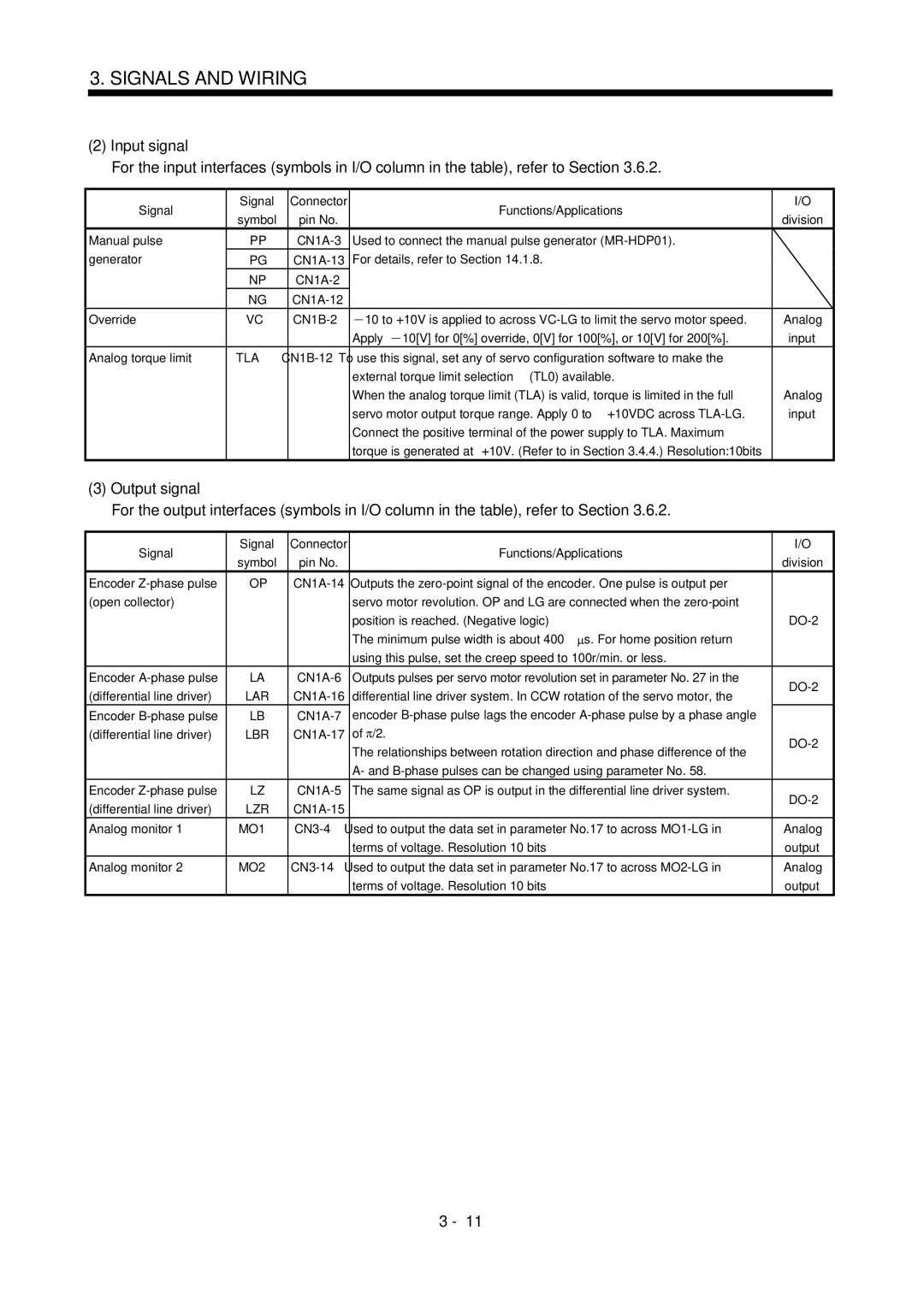
Input signal
Output signal
Communication
Refer to for the communication function
3ms or less
Movement complete
OFF
Override selection OVR
Override
Override VC
Used to make the override VC valid or invalid
Internal torque limits 1
Torque limit
Analog torque limit TLA
Parameter No Parameter No
External torque limit offset parameter No.26
TL2
Parameter No TLA
Overcurrent, overload 1 or overload
Regenerative alarm
Instantaneous power failure
Incremental system
OPC MR-HDP01 Ppnp
Interfaces 3.6.1 Common line
CN1A CN1B 24VDC VDD COM
TXD L
Digital input interface DI-1
Detailed description of the interfaces
Digital output interface DO-1
Output pulse
Lamp load
Encoder pulse output DO-2 Open collector system Interface
COM 24VDC VDD VDD-COM
Analog output
Analog input
Input impedance 10 to 12k
Source input interface
Nfbmc
For 3-phase 200 to 230VAC power supply
EMG SON VDD COM ALM
For 1-phase 100 to 120VAC or 1-phase 230VAC power supply
Terminals
11, L Control circuit power supply Phase 200 to 230VAC
50/60Hz Phase 100 to 120VAC
Refer to Sections 14.1.2 and 14.1.3 for details
Forced stop
Power-on sequence Power-on procedure
Timing chart
VDD COM EMG
Connection diagram
HC-UF13 B to 73 B
HC-MF053 B to 73 B
HA-FF053 B to 63 B
HC-SF121 B to 301 B
3 I/O terminals HC-KFS HC-MFS HC-UFS3000r/min series
Earth
HC-SFS HC-RFS HC-UFS2000 r/min series
MDR MRR BAT
Setting
COM MBR 24VDC
Coasting Servo motor speed Min 60ms Base circuit
Alarm occurrence
Both main and control circuit power supplies off
CN1A CN1B
JST
Servo amplifier terminal block TE2 wiring method
NH1 Nichifu
CRIMPFOX-UD6
N6L TDK
Instructions for the 3M connector
Torque screwdriver
Nakamura Seisakusho
Before starting operation, check the following
Operation
Machine
Machine conditions
CDV
Function selection Absolute position detection system
Startup procedure
Program end
Home position return
ZRT
Program operation mode What is program operation mode?
Command list
Programming language
Tripi
Trip
ITP
TIM
For
Lpos
Times
TIM Dwell command time 100 ms MOV Absolute move command 2000
Details of programming languages
200 ms MOV Absolute move command
500 r/min STC
Incremental move command
Continuous move command Mova Movia
Absolute continuous move command
Incremental continuous move command
Outon
Mova Absolute continuous move command STM m
OUT1 OFF
OUT2 is turned off in 100ms
300 MOV Absolute move command 1000 10STM
OUT1 is turned off in 200ms
OUT3 is turned off in 500ms
Tripi Incremental trip point 300
Trip Absolute trip point 250
Outof
OUT2 OFF
Tripi Absolute trip point 300
300 Movi Incremental move command
MOV cannot be used with Tripi
Program output 3 OUT 3 is turned OFF
TIM Dwell command time 200 ms SPN
Movi Incremental move command 500 r/min
OUT1
PI1 OFF
Interrupt positioning command ITP
ITP Interrupt positioning command 200
Count
Count
Trip Trip point 500
Waiting for PI1 to be turned on by SYNC1 a
Step repeat command end
Step repeat command for Next
Step repeat command end For
Next
Times
Position latch Lpos
Current position latch is set
Movi R1
Movi R2
CCW rotation with
Basic setting of signals and parameters
Parameter
Position data Initial value 100 1000
100 ms MOV Absolute move command 2500
Program operation timing chart Operation conditions
100 ms MOV Absolute move command 5000
SPN Speed Motor speed 1000 r/min STC
Servo motor rotation direction
Manual operation mode
Jog operation Setting
ST1ON ST2ON CCW
PED OFF
10 m
Manual pulse generator operation Setting
Manual pulse generator multiplication
100 m
Parameter No.1 setting valid Time Times
Length of the proximity dog
Manual home position return types
Since the machine part collides with
Home position return parameter
Instructions
Dog type home position return
Signals, parameters
Set the input signals, parameters and program as follows
Length of proximity dog
Adjustment
Count type home position return
Set the input signals and parameters as follows
Movement over the moving distance
Data setting type home position return
Return is selected
Is obtained to output home position return
Stopper type home position return
Completion ZP
Signals, parameter
Set the input signals and parameter as follows
Set the input signals and parameters as indicated below
Dog type rear end reference home position return
Count type front end reference home position return
Phase signal position
Dog cradle type home position return
Home position return automatic return function
Software limit cannot be used with these functions
Restrictions
Specifications
Absolute position detection system
Structure
Outline of absolute position detection data communication
Servo amplifier Program No. selection DI0 to DI3, etc
Parameter setting
CON1
Selection of programs
Serial communication operation
Positioning operation in accordance with programs
Multidrop system
Group designation
Group setting example
Station
Group setting instructions
MOV
Incremental value command system
Commands
Mova
Program example
Parameters
List
Item list
TLO
SIC
FFC
TL1
LPF
NH1
NH2
PG2B
Command system, regenerative brake option selection 0000
Detail list
Multiplication factor Function Column
85Hz
Refer to Chapter
High
CMX CDV PED
MOD Analog monitor output
Communication conditions, and clear the alarm history
Monitor 2 MO2. Refer to Section
Status display on servo amplifier display
19 *BLK Basic parameters 20 *OP2 22 *OP4
No time-out check Time-out check period setting
Setting s
Operation can be performed for the parameters marked
65535
999 to
Used to set the offset voltage to analog override 999
Pulses/rev Set value
DCT
ZTT
Parameter error
Setting
OP9 Function selection
Connector pins
OPA Function selection a 0000
Used to selection the machine resonance suppression filter
0000 Don’t change this value by any means
Machine resonance suppression filter 0000
Used to set the machine resonance suppression filter
Low-pass filter/adaptive vibration suppression control 0000
Changing is valid. Made valid when auto tuning is invalid
63 LPF Expansion parameters 64 GD2B 65 PG2B 66 VG2B
Control. Refer to Chapter
Gain changing selection 0000
68 *CDP
CDS
BIN HEX
0001 0209 060A 1918 030B 0504 0102 0000 0005 120E
Reduction ratio n Servo motor resolution Pt Pulse/rev
Guideline for setting the electronic gear is
Machine specifications Ballscrew lead Pb 10 0.39 mmin
Machine specifications Pulley diameter r 160 6.30 mmin
Changing the status display screen
Pattern acceleration/deceleration
Change the following digits of parameter No.17
Contents of a setting
Alarm history clear
Changing the stop pattern using a limit switch
Software limit
Memo
System configuration Components
Servo Configuration Software
MR-CPCATCBL3M
For use of RS-422 Up to 32 axes may be multidropped
Configuration diagram
For use of RS-232C
CN3 CN2
Closing of the station setting window
Station setting
Station number setting
Click the Close button to close the window
Parameter value write a
Parameters
Parameter value verify b
Parameter value batch-write d
Parameter default value indication g
Parameter value batch-read c
Parameter change list display e
Simple Program 6.5.1 Program data
How to open the setting screen
Explanation of Program Data window
Explanation of Program Edit window
Servo Configuration Software
Explanation of Indirect Addressing window
Indirect addressing
Limited number of time to write to EEP-ROM is 100,000
Servo Configuration Software
When using the device setting, preset 000E in parameter No
Device assignment method
Screen explanation
Servo Configuration Software
Servo Configuration Software
Point
Servo motor start c, d
Servo motor speed setting a
Acceleration/deceleration time constant setting b
Servo motor stop e
Positioning operation
Temporary stop of servo motor f
Moving distance setting c
Servo motor start d, e
Positioning operation window closing g
Click Start to perform motor-less operation
Click Close to close the window
Signal ON/OFF setting a, b
Output signal do forced output
Do forced output window closing c
Program test operation
Program of the MR-J2S-CL can be test-operated
Closing the Program Test window b
Displaying the program a
Click the OK button to close the Program Test window
Alarm history clear a
Alarm history
Alarm history display
Closing of alarm history window b
Memo
Display flowchart
Display and Operation
Display transition
Status display
DOW
Display examples
Following table lists display examples
Status display list
Following table lists the servo statuses that may be shown
Diagnosis mode 7.3.1 Display transition
Down
Diagnosis mode list
Display and Operation
Alarm mode
Alarm mode list
Indicates no occurrence of an alarm
Display and Operation
Parameter mode
Parameter mode transition
Operation example Parameter of 5 or less digits
Signed 5-digit parameter
Display definition
External I/O signal display
Segments of the seven-segment LEDs correspond to the pins
CN1A CN1B CN1B
Press UP twice Press SET for more than 2 seconds
Mode change
How to use the buttons is explained below
Termination of jog operation
How to use the keys is explained below
To terminate the motor-less operation, switch power off
Termination of motor-less operation
Memo
General Gain Adjustment
Gain adjustment mode explanation
You can automatically set the optimum gains
Adjustment sequence and mode usage
Adjustment using servo configuration software
Executing gain search under to-and-fro
Position control gain
Auto tuning Auto tuning mode
Speed control gain
PG1,VG1
Auto tuning mode operation
Block diagram of real-time auto tuning is shown below
PG2,VG2,VIC
Adjustment procedure by auto tuning
Response level setting in auto tuning mode
Adjustment by manual mode
Manual mode 1 simple manual adjustment
Operation of manual mode
Adjustment procedure
For position control
General Gain Adjustment
Adjustment description
Interpolation mode
Adjustment procedure
PG2
Auto tuning selection
100Hz 105Hz 130Hz 160Hz 200Hz 240Hz 300Hz
Memo
Special Adjustment Functions
Machine resonance suppression filter Function
Parameter No Notch frequency
Deep 40dB 14dB 8dB Shallow 4dB
Adaptive vibration suppression control Function
Low-pass filter Function
Set the operation of the low-pass filter parameter No
Gain changing function
Applications
GD2B
Gain changing condition parameter No
Parameters No , 34 to
Gain changing selection parameter No
Gain changing time constant parameter No
Setting
This operation will be described by way of setting examples
When you choose changing by external input
Gain changing operation
Gain changing selection 0003
When you choose changing by droop pulses
Speed integral compensation 250 Changing ratio
Gain changing condition Pulse
Memo
Life
Inspection
Inspection
Years
Memo
Trouble at start-up
Troubleshooting
Position control mode Troubleshooting
Make operation instable
When alarm or warning has occurred
Alarms and warning list
MR-J2S- CL
MR-J2S
Option
Reexamine acceleration
Option, change regenerative brake
Capacity of built-in regenerative
Review environment so that ambient
AL.50 Overload Load exceeded
Servo motor locked Input terminals U, V, W
Serial Communication cable fault Repair or change the cable
Remedies for warnings
Memo
TE1 TE2
Outline Dimension Drawings
TE1
MR-J2S-70CL MR-J2S-100CL
PE terminal Fan air orientation Servo amplifier Weight
Mounting hole Unit 1305.12 2007.87 1184.65 Terminal layout
Mounting hole 1807.09 1606.23
Soldered type
Connectors Servo amplifier side 3M
Insulation displacement type
Threaded type
Communication cable connector JAE
DE-C1-J6-S6 34.5 24.99 #4-40
Memo
Overload protection characteristics
Characteristics
MR-J2S-10CL to MR-J2S-100CL MR-J2S-200CL to MR-J2S-350CL
HC-MFS23 HC-UFS23 HC-KFS43
HC-KFS053
HC-MFS053 HC-UFS13 HC-KFS23
HC-MFS43 HC-UFS43 MR-J2S-60CL HC-SFS52 HC-SFS53 HC-KFS73
Temperature distribution in enclosure
Heat dissipation area for enclosed servo amplifier
Mmin
Dynamic brake characteristics
There is internal relay delay time of about 30ms
Mm/minin/min
HC-SFS3000r/min series
HC-KFS series
HC-SFS1000r/min series
HC-MFS series
MR-JCCBL M-H MR-JHSCBL M-H MR-ENCBL M-H
Encoder cable flexing life
MR-J2S-500CL MR-J2S-700CL
MR-JCCBL M-L MR-JHSCBL M-L
Attenuated to approx a in 0.5 to 1ms
MR-J2S-10CL 20CL 30A
MR-J2S-40CL 60CL 30A
MR-J2S-70CL 100CL 54A
Memo
100 300 500
Options and Auxiliary Equipment
Selection of the regenerative brake option
130 300 500
1047
Servo amplifier Inverse efficiency% Capacitor chargingJ
Connection of the regenerative brake option
Set parameter No.2 according to the open to be used
For the MR-RB50 install the cooling fan as shown
Mounting method
For the MR-RB50 MR-RB51 install the cooling fan as shown
MR-RB32 MR-RB30 MR-RB31
Outline drawing
MR-RB032 MR-RB12
119
MR-RB50
12.3
FR-BU-15K
Brake unit
Selection
16.5 MR-J2S-500CL FR-BU-30K
Brake unit FR-BU
Outside dimensions
Unit mmin
FR-RC15
Resistor unit FR-BR
FR-RC30
FR-RC
FR-BAL VDD COM EMG ALM SON
RDY
RA2 EM1 OFF
Outside dimensions of the power return converters Unit mmin
Mounting hole machining dimensions
Cables and connectors Cable make-up
HC-KFS
MR-JHSCBL M-L
MR-JCCBL M-L
MR-JCCBL M-H
JAE
MR-TB20
MR-J2CN1
MR-J2TBL
MR-J2CN3TM
131.2
Standard flexing life Long flexing life
16.4
164.0
MR-JCCBL10M-L MR-JCCBL10M-H MR-JCCBL30M-L MR-JCCBL50M-H
MR-JCCBL2M-L MR-JCCBL5M-L MR-JCCBL2M-H MR-JCCBL5M-H
MRR MDR BAT
MR-JHSCBL M-L
SHD
MR-ENCBL50M-H
Model MR-CPCATCBL3M
Connection diagram
Communication cable
MR-CPCATCBL3M
Terminal labels
How to use the junction terminal block
Junction terminal block MR-TB20
MR-J2TBL05M
LSP LSN ALM
Junction terminal block cable MR-J2TBL M Model MR-J2TBL M
DI0 PED ST1
B10
CN3A CN3B CN3C
Maintenance junction card MR-J2CN3TM Usage
MR-J2HBUS CN3B CN3A CN3C
VDD COM EM1
Bus cable MR-J2HBUS
MR-J2HBUS05M MR-J2HBUS1M MR-J2HBUS5M
Terminal arrangement
When using the MR-DP60, set 1 4 in parameter No
External digital display MR-DP60
Start bit Date bit
Outline dimension drawing
Mounting
Manual pulse generator MR-HDP01 Specifications
VDD CN1B OPC CN1A
Battery MR-BAT, A6BAT
Auxiliary equipment
Recommended wires Wires for power supply wiring
Recommended wires
MR-J2S-10CL MR-J2S-20CL MR-J2S-40CL AWG14 a 25 AWG16 a
Recommended crimping terminals
Wires for cables
Wires for option cables
AMP
MR-J2S-20CL
Power factor improving reactors
No-fuse breakers, fuses, magnetic contactors
MR-J2S-40CL 20CL1
Surge absorbers
Relays
Following relays should be used with the interfaces
Noise reduction techniques
Noises produced by servo amplifier
Noise reduction products
10 to 100MHz 100 to 500MHz 150
Ex A.2003
Outline drawing
Outline drawing Unit mm Unit FR-BLFMR-J2S-350CL or more
NV-SW
Leakage current breaker Selection method
NFB
Selection example
HC-MFS73
Combination with the servo amplifier
EMC filter
NFB Line Load
R3.25
HF3040-TM HF-3050A-TM
HF3040A-TM 260 210 155 140 125
HF3050A-TM 290 240 100
WA2WYA2SEBK2KΩ Japan Resistor make
Memo
Wire as shown below
Configuration 15.1.1 RS-422 configuration Outline
Cable connection diagram
Communication Functions
15.1.2 RS-232C configuration Outline
Single axis of servo amplifier is operated
Description
Communication specifications 15.2.1 Communication overview
MSB
Serial communication selection
Serial communication response delay time
Serial communication baudrate
Protocol station number selection
Protocol
Transmission of data from the controller to the servo
Data length depends on the command
Recovery of communication status by time-out
Data frames
Ascii codes are used
For example, 61H is transmitted in hexadecimal for group a
Checksum
Error codes
SOH
Time-out operation
Retry operation
Data item Value Description
Communication procedure example
Initialization
STX ETX
Parameter Command
Command and data No. list
Read commands Status display Command
External I/O signals Command
Alarm history Command
Current alarm Command 02
General-purpose register Dx value Command 6E
Current position latch data Command 6C
General-purpose register Rx value Command 6D
Group setting Command 1F
Current alarm Command
Write commands Status display Command
External I/O signal Command
General-purpose register Rx value Command B9
Data for test operation mode Command 92 A0
External input signal disable Command
Operation mode selection Command 8B
Group setting Command 9F
Detailed explanations of commands 15.12.1 Data processing
Processing the read data
Writing the processed data
Status display data clear
Command Data No
Status display Status display data read
1EA5
Command Data No Data No. definition
Parameter Parameter read
Parameter write
Command Data No Set data
00 to See below
Reply ON/OFF statuses of the input pins are sent back
External input pin status read
CN1B-18
External output pin status read
CN1A-14
Ready RD Limiting torque TLC Trouble ALM
Read of the statuses of output devices
Device ON/OFF
See below
Enable
Disable/enable of I/O devices DIO
Signal Status
Input devices DI
Input devices ON/OFF test operation
See below
Cancel the test operation mode
Test operation mode Instructions for test operation mode
1EA5 Choose the test operation mode
Enable the disabled input devices
LSN and ST2 Stop Turns on SON LSP and LSN
Forward rotation start Turns on SON
LSN and ST1 Reverse rotation start Turns on SON
Servo-on Turns on SON LSP LSN Stroke end OFF
Communication Functions
External output signal ON/OFF
Output signal pin ON/OFF output signal do forced output
Choosing do forced output in test operation mode
Command Data No Setting data
Alarm occurrence time read
Alarm history Alarm No. read
For example, 0032 means A.32 and 00FF A. no alarm
Erase the alarm history Send command 82 and data No
Read of the status display at alarm occurrence
Current alarm Current alarm read
Current alarm clear
Transmission
Send command 6C and data No to be read
Current position latch data
Reply
General-purpose register General-purpose register Rx read
General-purpose register Dx read
General-purpose register Rx write
General-purpose register Dx write
Reply Slave station sends back the group setting requested
Group setting write
Group setting read
Servo amplifier group designation
Software version
Reply Slave station returns the software version requested
Appendix
App 1. Status indication block diagram
App
Appendix
For CN1B
Revisions
Manual number is given on the bottom left of the back cover
Model Code