Appendix A
Mitigating ARP Spoofing Attacks Using Packet Content ACL
Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) is the standard method for finding a host's hardware address (MAC address) when only its IP address is known. This protocol is vulnerable because it can spoof the IP and MAC information in the ARP packets to attack a LAN (known as ARP spoofing). This document is intended to introduce ARP protocol, ARP spoofing attacks, and the counter measure brought by
•How Address Resolution Protocol works
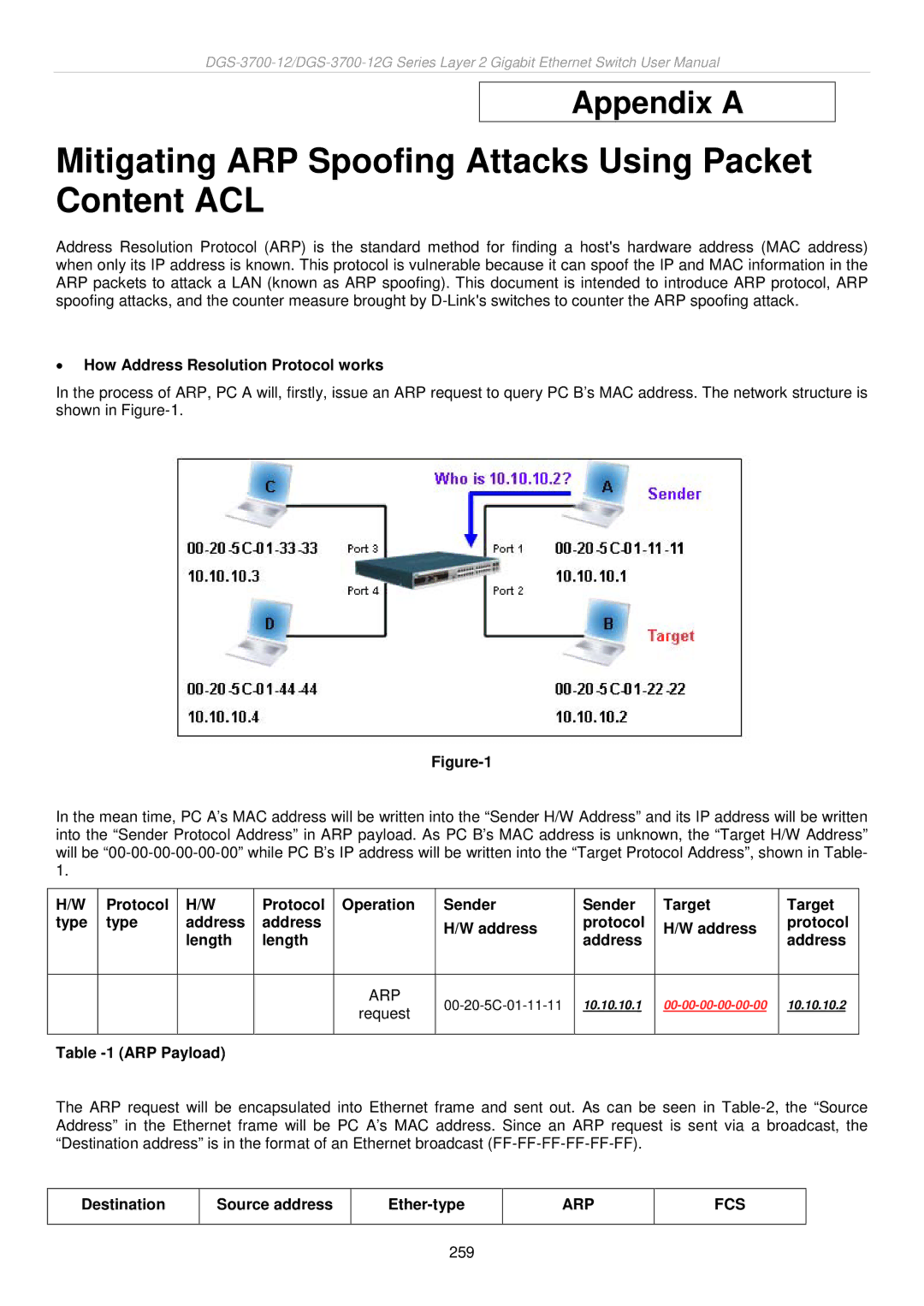
In the process of ARP, PC A will, firstly, issue an ARP request to query PC B’s MAC address. The network structure is shown in
In the mean time, PC A’s MAC address will be written into the “Sender H/W Address” and its IP address will be written into the “Sender Protocol Address” in ARP payload. As PC B’s MAC address is unknown, the “Target H/W Address” will be
H/W | Protocol | H/W | Protocol | Operation | Sender | Sender | Target | Target |
type | type | address | address |
| H/W address | protocol | H/W address | protocol |
|
| length | length |
| address | address | ||
|
|
|
|
| ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ARP | 10.10.10.1 | 10.10.10.2 | ||
|
|
|
| request | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Table |
|
|
|
|
|
| ||
The ARP request will be encapsulated into Ethernet frame and sent out. As can be seen in
Destination
Source address
ARP
FCS
259