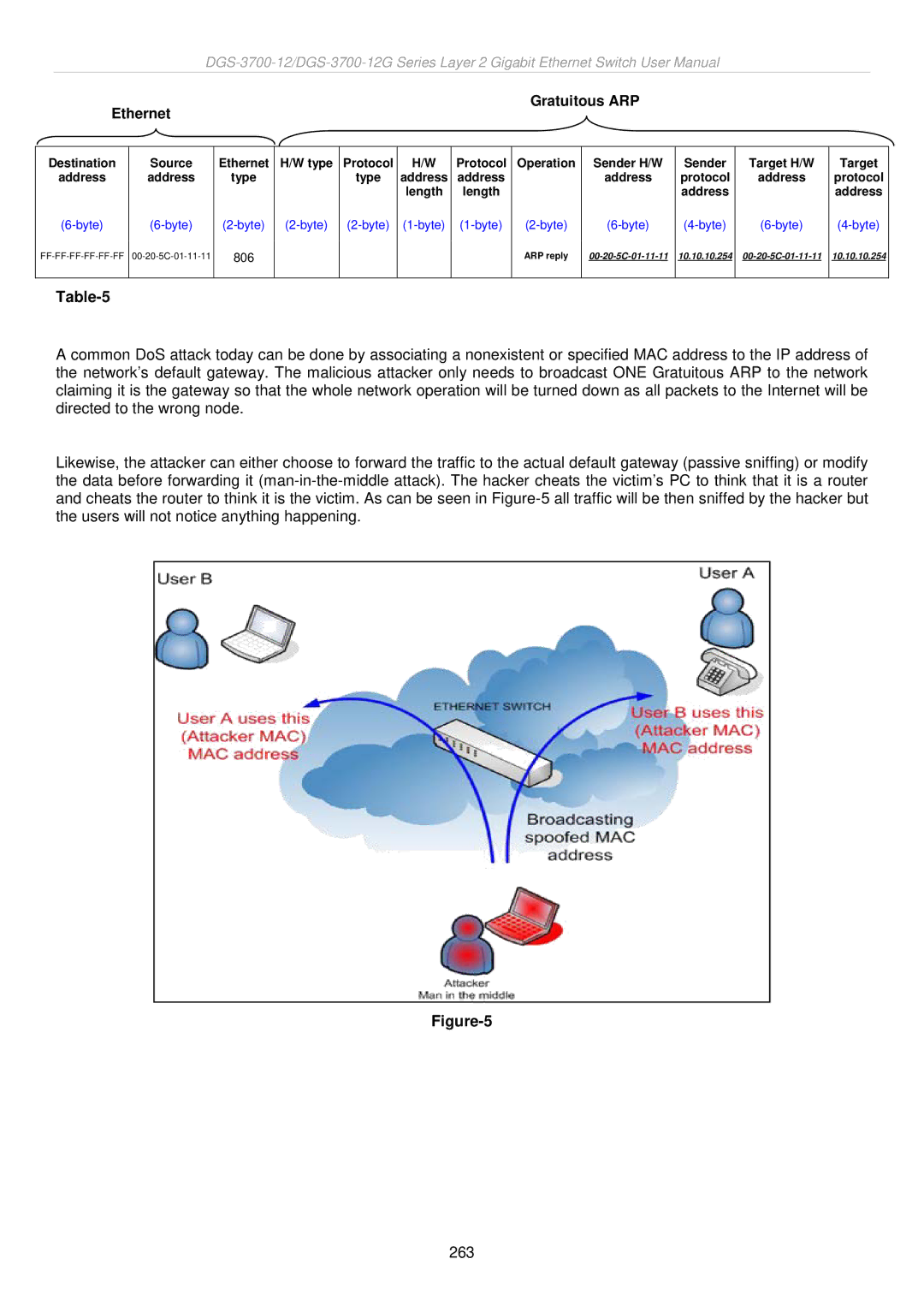
Ethernet
Gratuitous ARP
Destination | Source |
address | address |
Ethernet | H/W type | Protocol | H/W | Protocol | Operation |
type |
| type | address | address |
|
|
|
| length | length |
|
806 |
|
|
|
| ARP reply |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Sender H/W | Sender | Target H/W | Target |
address | protocol | address | protocol |
| address |
| address |
10.10.10.254 | 10.10.10.254 | ||
|
|
|
|
A common DoS attack today can be done by associating a nonexistent or specified MAC address to the IP address of the network’s default gateway. The malicious attacker only needs to broadcast ONE Gratuitous ARP to the network claiming it is the gateway so that the whole network operation will be turned down as all packets to the Internet will be directed to the wrong node.
Likewise, the attacker can either choose to forward the traffic to the actual default gateway (passive sniffing) or modify the data before forwarding it
263