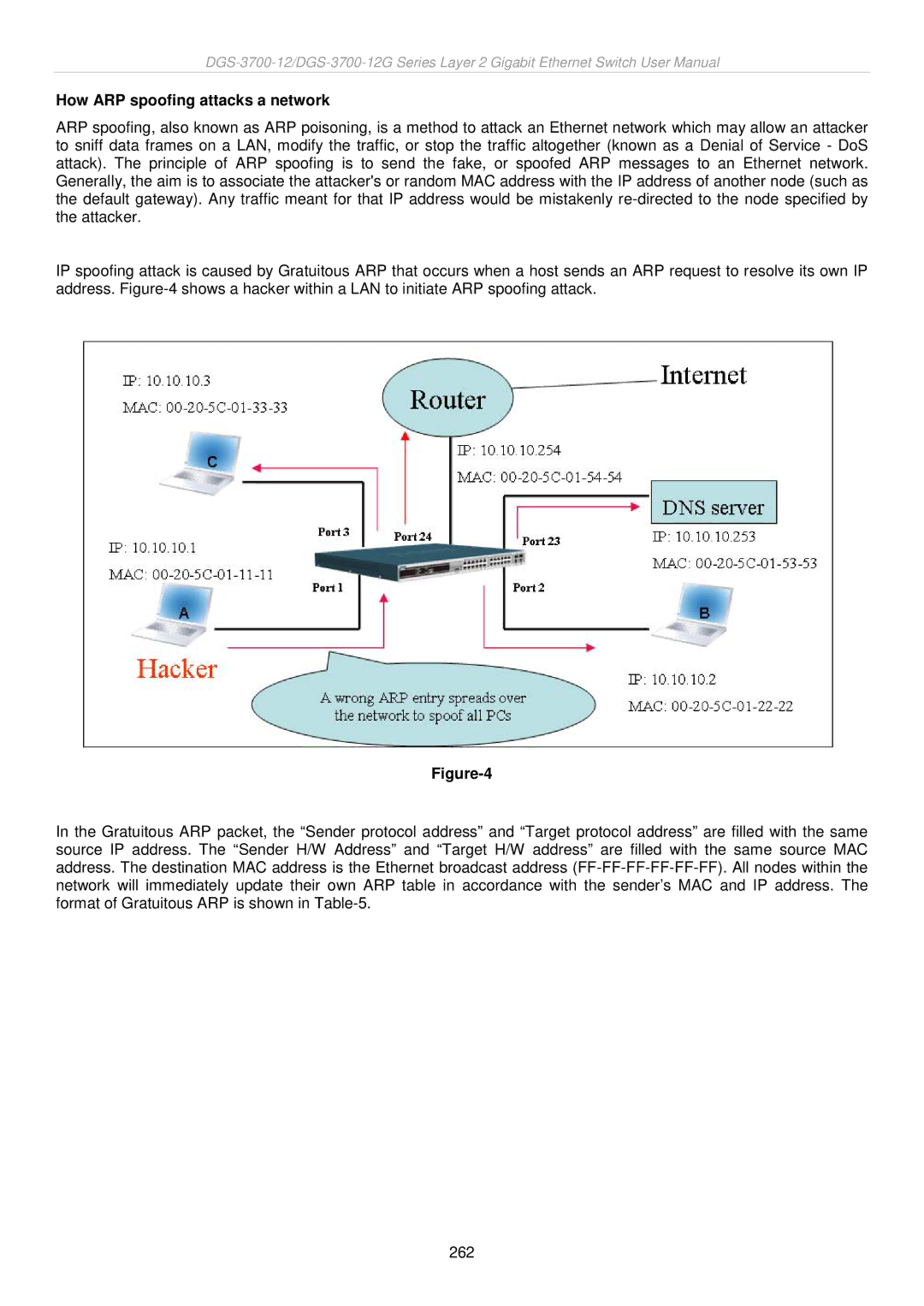
How ARP spoofing attacks a network
ARP spoofing, also known as ARP poisoning, is a method to attack an Ethernet network which may allow an attacker to sniff data frames on a LAN, modify the traffic, or stop the traffic altogether (known as a Denial of Service - DoS attack). The principle of ARP spoofing is to send the fake, or spoofed ARP messages to an Ethernet network. Generally, the aim is to associate the attacker's or random MAC address with the IP address of another node (such as the default gateway). Any traffic meant for that IP address would be mistakenly
IP spoofing attack is caused by Gratuitous ARP that occurs when a host sends an ARP request to resolve its own IP address.
In the Gratuitous ARP packet, the “Sender protocol address” and “Target protocol address” are filled with the same source IP address. The “Sender H/W Address” and “Target H/W address” are filled with the same source MAC address. The destination MAC address is the Ethernet broadcast address
262