Table 8 (Continued). Discrete Input Terminal Assignment Selections and Descriptions.
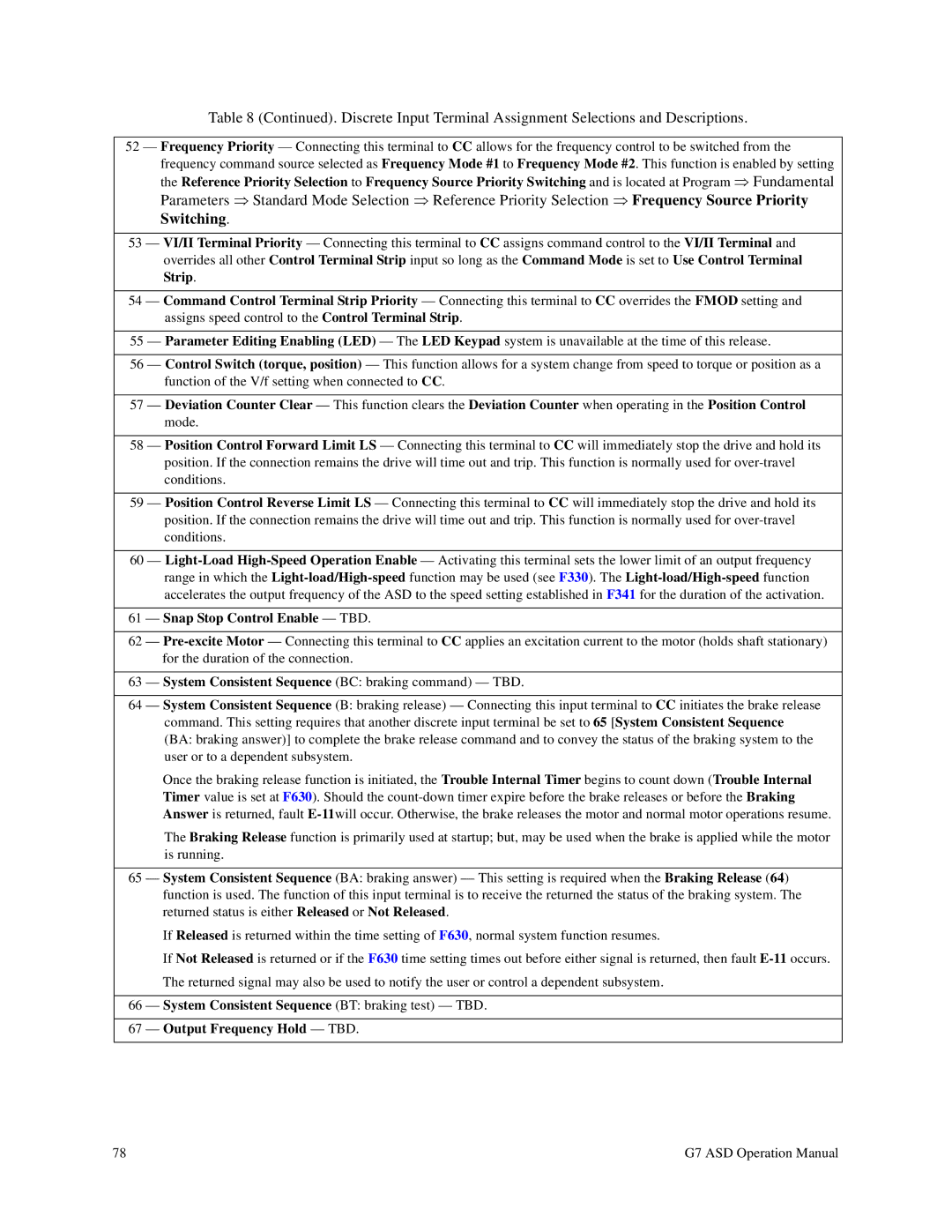
52 — Frequency Priority — Connecting this terminal to CC allows for the frequency control to be switched from the frequency command source selected as Frequency Mode #1 to Frequency Mode #2. This function is enabled by setting
the Reference Priority Selection to Frequency Source Priority Switching and is located at Program ⇒ Fundamental
Parameters ⇒ Standard Mode Selection ⇒ Reference Priority Selection ⇒ Frequency Source Priority
Switching.
53 — VI/II Terminal Priority — Connecting this terminal to CC assigns command control to the VI/II Terminal and overrides all other Control Terminal Strip input so long as the Command Mode is set to Use Control Terminal
Strip.
54 — Command Control Terminal Strip Priority — Connecting this terminal to CC overrides the FMOD setting and assigns speed control to the Control Terminal Strip.
55 — Parameter Editing Enabling (LED) — The LED Keypad system is unavailable at the time of this release.
56 — Control Switch (torque, position) — This function allows for a system change from speed to torque or position as a function of the V/f setting when connected to CC.
57 — Deviation Counter Clear — This function clears the Deviation Counter when operating in the Position Control
mode.
58 — Position Control Forward Limit LS — Connecting this terminal to CC will immediately stop the drive and hold its position. If the connection remains the drive will time out and trip. This function is normally used for
59 — Position Control Reverse Limit LS — Connecting this terminal to CC will immediately stop the drive and hold its position. If the connection remains the drive will time out and trip. This function is normally used for
60 —
61 — Snap Stop Control Enable — TBD.
62 —
63 — System Consistent Sequence (BC: braking command) — TBD.
64 — System Consistent Sequence (B: braking release) — Connecting this input terminal to CC initiates the brake release
command. This setting requires that another discrete input terminal be set to 65 [System Consistent Sequence (BA: braking answer)] to complete the brake release command and to convey the status of the braking system to the user or to a dependent subsystem.
Once the braking release function is initiated, the Trouble Internal Timer begins to count down (Trouble Internal Timer value is set at F630). Should the
The Braking Release function is primarily used at startup; but, may be used when the brake is applied while the motor is running.
65 — System Consistent Sequence (BA: braking answer) — This setting is required when the Braking Release (64) function is used. The function of this input terminal is to receive the returned the status of the braking system. The returned status is either Released or Not Released.
If Released is returned within the time setting of F630, normal system function resumes.
If Not Released is returned or if the F630 time setting times out before either signal is returned, then fault
The returned signal may also be used to notify the user or control a dependent subsystem.
66 — System Consistent Sequence (BT: braking test) — TBD.
67 — Output Frequency Hold — TBD.
78 | G7 ASD Operation Manual |