Xerox WorkCentre C226 User Guide
Warranty
Trademark information
Table of contents Introduction
Xerox WorkCentre C226 User Guide
Before Using the Product
Managing the Machine
Peripheral Devices
Before Making Copies
Basic Procedure for Making Copies
Convenient Copy Functions
Machine Maintenance for Copying
Basic Printing Procedures
Setting the Printer Driver Properties
Xerox WorkCentre C226 User Guide Vii
Printer Configuration Settings
Web Pages in the Printer
Printing from the Operation Panel
Key Operator Programs
Troubleshooting
Appendix
Sending an Image
Condition Setting Screen of Scanner Mode
Scanning Settings
Specifications
Before Using the FAX Feature
Transmission Using F-Codes
Basic Operations
Advanced Transmission Methods
Xii Xerox WorkCentre C226 User Guide
Xerox WorkCentre C226 User Guide Xiii
Convenient Methods of Use
Programming
Xiv Xerox WorkCentre C226 User Guide
Safety Notes
Operator Accessible Areas
Maintenance
Cleaning Your Product
Electrical Supply
Operational Safety Information
Do These
Disconnect Device
Xerox WorkCentre C226 User Guide Xvii
Maintenance Information
Ozone Safety Information
For Consumables
Do Not Do These
Xerox WorkCentre C226 User Guide Xix
Product Safety Certification
Radio Frequency Emissions
FAX Send Header Requirements
CE Mark
Data Coupler Information
Xerox WorkCentre C226 User Guide Xxi
Xxii Xerox WorkCentre C226 User Guide
Canada
Europe
Xerox WorkCentre C226 User Guide Xxiii
USA Energy Star
Canada Environmental Choice
Europe Energy
Xxiv Xerox WorkCentre C226 User Guide
Xerox WorkCentre C226 User Guide Xxv
Other countries
Xxvi Xerox WorkCentre C226 User Guide
Before Using the Product
Installation Requirements
General Information
If the machine has been placed on a stand/1-Tray Unit
Installation Requirements
Moving this machine
If the machine is to be left unused for a long time
Introduction
Introduction
Original and paper sizes
Meaning of R in original and paper size indications
Main Features
Main Features
Auto power shut-off mode
Energy saving features
Preheat mode
Part Names and Functions
Exterior
Part Names and Functions
Operation panel
Stand/1-Tray
Unit
Tray Unit
Duplex Bypass/ See Inverter Unit and exit tray
Interior
Part names and functions of peripheral devices
Other optional equipment
Ready indicator Data indicator
Operation panel
Start key
Settings key
Start key Clear ALL key
Using the touch panel
Touch panel
Beep tone
Selection of function
Copier feature
Auditing Mode
Paper Empty in the job status display
Account counter is enabled only for the colour copy mode
Using the machine when the auditing mode is enabled
Auditing Mode
When the copy job is finished, press the key ACC.#-C key
Ready To Copy Please See Your Key Operator For Assistance
Managing the Machine
Loading Paper
Loading paper in Paper Tray
Loading Paper
Changing the paper size in Paper Tray
Loading paper in the Bypass Tray
General Information
When loading paper in the Bypass Tray or closing
Tray, close the paper cover as shown
Setting envelopes or postcards
Printing onto envelopes or postcards
Loading postcards
Loading envelopes
Fusing unit pressure adjusting levers
Printing onto envelopes
Loading paper in the stand/1-Tray Unit/3-Tray Unit
Upper tray / middle tray / lower tray
Specifications stand/1-Tray Unit/3-Tray Unit
Loading paper in the Duplex Module/2-Tray Unit
Upper tray
Middle and lower paper trays
Specifications Duplex Module/2-Tray Unit
Specifications for paper trays
Tray No
Paper in AB system Paper in inch system
More information on plain paper
More information on special media that can be used
Paper tray selection screen will appear
Setting the paper type except the Bypass Tray
Paper that can be used for automatic two-sided printing
Setting the paper size when an extra size is loaded
Touch the OK key to complete the setting
Setting the paper type and paper size in the Bypass Tray
Heavy Paper1 106g/m2 200g/m2
Custom Settings
Clock adjust
Total count
Display contrast
Tray settings
Receive mode
Fax data forward
Keyboard select
Detailed descriptions for program settings start on
Operation procedure common to all custom settings
More information on setting procedures
About the settings
Total count
Clock adjust
Tray settings
Display contrast
List print
Replacing the Toner Cartridges
Toner
Replacing the Toner Cartridges
Remove the protective material from the new toner cartridge
General Information
Storing Supplies
Proper storage
Storing Supplies
Supply and Consumables
Misfeed Removal
Misfeed Removal Guidance
Misfeed in the paper feed area
Misfeed in Tray
Misfeed Removal
Misfeed in the Bypass Tray
Misfeed in the transport area, fusing area, and exit area
Transport area
Upper exit tray
Fusing area
Models without the Duplex Bypass/Inverter Unit
Misfeed Removal
Misfeed in the stand/1-Tray Unit
Misfeed in the 3-Tray Unit
General Information
Misfeed in the upper or lower tray
Problem Check Solution or cause
Troubleshooting
Problem Check Solution or cause
Problem Check Solution or cause
Peripheral Devices
Saddle Stitch Finisher
Part names and functions
Saddle Stitch Finisher
Using the Saddle Stitch Finisher
Remove the empty staple box
Staple cartridge replacement and staple jam removal
Staple cartridge replacement
General Information
Staple jam removal
Remove the staple box
Saddle Stitch Finisher
Push the Saddle Stitch Finisher back against the main unit
Misfeed in the Saddle Stitch Finisher
Open the top cover
General Information
Saddle Stitch Finisher
Troubleshooting Saddle Stitch Finisher problems
Check the list below before calling for service
Problem Check Solution or cause
Stapling position quick reference guide for duplex output
Top binding
Relation between print image and saddle stitch
High Capacity Feeder
Part name
Loading paper in the High Capacity Feeder
Top cover
Misfeed in the High Capacity Feeder
High Capacity Feeder
General Information
High Capacity Feeder
General Information Xerox WorkCentre C226 User Guide
Before Making Copies
Part Names and Functions The Dadf
Touch Panel main screen of copy mode
Copier Operation
Acceptable originals
Dadf
Setting Originals
Size and weight of acceptable originals
When using the Dadf
Adjust the original guides to the size of the originals
How to place the original
When using the document glass
Setting Originals
Original size detection function
Operator programs
Standard original setting orientation
Example
Selecting the Original Size
Automatic copy image rotation rotation copying
Using the Dadf Using the document glass
Selecting the Original Size
Storing, Deleting, and Using Original Sizes
Storing or deleting an original size
Touch the Original tab Touch the Custom Size key
Touch the STORE/DELETE key
Storing, Deleting, and Using Original Sizes
Enter X and then touch the key to enter Y. a width
64 to 432 mm can be entered in X, and a length
To 297 mm can be entered in Y
Using a Stored Original Size
Touch the OK key Stored original size is called up
Basic Procedure for Making Copies
Normal Copying
Copying from the Dadf
Sided copies of 1-sided originals
A4 Plain B4 Recycled A3 Plain
Normal Copying
Copy mode output restrictions
Normal Copying
Copy output sort and group
About the offset function
Automatic two-sided copying from the Dadf
Touch Offset Touch OK
Selecting the output tray
Turning on the offset function
Following two-sided modes can be
Selected
Copying from the document glass
Set an original on the document glass pages 2-4 to
How to place the original
Normal Copying
Automatic two-sided copying from the document glass
Example TEXT/PRTD.PHOTO key is selected
Exposure Adjustments
Exposure Adjustments
Original type Contents of the original
Normally this setting is selected. When
Exposure is automatically adjusted to
Obtain the best image quality. When a
Making a copy of a copy
Reduction/Enlargement/Zoom
Automatic selection auto image
Reduction/Enlargement/Zoom
Manual selection
100
Menu
To return the ratio to 100%
XY Zoom
Touch the X key
64%
Special Papers
Special Papers
Colour adjustment menu
Convenient Copy Functions
Special Modes
Special Modes
Inserts key
Touch the Special Modes tab
Common operation procedure for using the special functions
Screen
To set the margin shift function
Margin shift
Touch the key for the desired special mode. Example
About the steps that follow
Touch the Margin Shift key on the Special Modes screen
Set the shift amount as needed and touch the lower OK key
Erase
Screen to indicate that the function is turned on
Dual page copy
When copying book originals
Touch the Dual page Copy key on the Special Modes screen
Centring
This function can be used to reduce a larger sized origi
Nal image and centre it on a copy of smaller paper size
As well as centre a smaller original onto a larger sized
Transparency film with insert sheets
Insert sheets must be the same size A4 or A4R
2 x 11 or 8-1/2 x 11R as the transpar
Ency film
Auto
Covers
Copying onto a cover
Not copying onto a cover
Touch the Covers key on the Special Modes screen
Select cover placement
See pages 2-13through
Touch the key to switch to the second Special Modes screen
Reverse
Originals with large black areas which use a large amount
Consumption
Colour Adjustments Menu
Colour Adjustments Menu
Key to weaken the colour
RGB Adjust
Select a colour from R RED, G GREEN, and B Blue
Sharpness
Suppress background
Colour balance
About the steps that follow
Brightness
Brightness setting screen will appear
Adjust the brightness
Intensity
Intensity setting screen will appear
Adjust the intensity
Single Produces copies with a selected single colour
Image Edit Menu
Image Edit Menu
Single colour
Select the desired colour
Mirror image
Touch the Mirror Image key on the Image Edit menu screen
Photo Repeat
See pages 2-21through
Multi shot
Touch the Multi Shot key on the Image Edit menu screen
On the copy
A3 11 x 17 Full-bleed
Lines are added around the borders of the images
Touch the A3 FULL-BLEED key on the Image Edit menu screen
Multi-page enlargement
Overlap of sections of image
Inch system
About the steps that follow
Pamphlet copy
Pamphlet copy icon , etc. will also appear
Upper left corner of the screen to indicate that the func
Tion is turned on
When using the Dadf
When using the document glass
Job Program Memory
Job Program Memory
Storing a job program
Number of copies cannot be stored
Recalling a job program
Make all copier selections to be stored
Deleting a stored job program
Played in to exit the job program mode
CEL key is touched, the screen in will return but
Program will not be deleted. If no other programs are
To be deleted, touch the Exit key on the screen dis
Interrupting a Copy Run
Interrupting a Copy Run
Copier Operation
Machine Maintenance for Copying
Removing an Original Misfeed
Removing a misfed original from the Dadf
Removing an Original Misfeed
Check location B
Check location C
User Maintenance for copying
User Maintenance for copying
Cleaning the Original Scanning Area
Printed Photo
Problem Check Solution or cause
Basic Printing Procedures
Setting the Printer Drivers
Change the settings using the printer properties
Windows 95 / 98 / Me
Printer Operation
Selecting a Color Mode setting
Windows NT4.0 / 2000 / XP / Server
Using the Help file to view explanations of the settings
Setting the Printer Drivers
Opening Help in Windows
Click Help to display
Printing in black and white
Setting the Printer Drivers
Printer Operation
Automatic switching between colour and black and white
Printer Operation
Setting the Printer Drivers
Printing in colour
Setting the Printer Drivers
Printing using optional peripheral equipment
Setting the Printer Drivers
Printer Operation
Selecting Printing Functions
Setting the Printer Driver Properties
Selecting Printing Functions
Frequently used settings
Colour mode display
Copies
Collate
Up Pamphlet
Document Style
Tiled Pamphlet
User Settings
Up Printing
Border
Save
Configure settings for staple or punch finishing
Auto Job Control review
Finishing
Binding Edge
Staple
Staple sort mode
Saddle stitch function
Stapling positions
Top left
Hole punching only if a Hole Punch Module is installed
Offset mode
Punch
No Offset
Retention Normal Print
Hold After Print
Hold Before Print
Proof Print
Notify Job End
Defaults
PIN 5-digit identification number
User Name
Default Job ID
Account Number
Paper settings
Job Name
Always Use This ID
Paper Size
Custom
Correct Wrong
Fit To Paper Size
Fit To
Paper Selection
Paper Source
Paper Type
Tray Status
Advanced settings
PCL5c
Transparency Inserts
Image Quality
Resolution Settings
Select 300 dpi or 600 dpi Default setting 600 dpi
Graphics Mode
Margin Shift
PostScript
Compress Options
Job Compression
Bitmap Compression
See the explanation for Overlays on
Watermark settings
Text
Size
Angle
Edit Fonts
Color settings
Original Type
Table of document type previews
Preview of document type
This shows a preview of the document type selected
Color Mode
Use this item to adjust the brightness and contrast
Print Priority
All Text to Black
Image
Contrast
Color Balance
Saturation
Red Strength
Printer Configuration Through the Network
Environment required for accessing Web pages
Accessing Web pages and displaying help
Web Pages in the Printer
Printer Configuration Through the Network
Destination
Items and outline of menu frame of Web pages
System Information Image Send Management
Device Setup
Password
Sender
Network Scanning
Network Setup
Printer Configuration Settings
Making Configuration Settings
Paper Select Condition Settings
Making Configuration Settings
Default settings
Default paper size
Default output tray
Copies
PCL settings
Default paper type
PCL symbol set setting
PCL font settings
Printing from the Operation Panel
Hold Job List
Hold Job List
Key Operator Programs
Key operator program list
Initialize and/or store settings
Key operator program list
Program name
Auto colour calibration
Procedure for using key operator programs
Touch the Printer Settings key
Procedure for using key operator programs
Key operator program menu
Level
Default settings
Description of Setting Programs
Printer settings
Interface settings
Network settings
Timeout
IP address setting
Enable TCP/IP
Colour adjustments
Enable EtherTalk
Enable NetBEUI
Reset the NIC
Initialize and/or store settings
Restore factory defaults
Store current configuration
Restore configuration
Troubleshooting
Degrees with Respect to paper
Paper type Keys
Checking the IP address
Touch the Printer Test page key
Screen and printing begins. To cancel printing, touch
Cancel key
Appendix
Disabling of notice page printing
Print Area
Print area of this product is shown below
Print Area
PCL symbol set
Symbol set
Printer Operation Xerox WorkCentre C226 User Guide
Options required to use the network scanner function
Network Scanner Operation
About the Network Scanner Function
About the Network Scanner Function
Accessing Web Pages
Web
About the Web
About the Web
Basic Settings for Network Scanning
Enable scanner delivery methods Enable Scanner Delivery to
Enabling user authentication Advanced Setup
Network Scanning Setup screen
Mail Server and DNS Server Settings
Basic Settings for Network Scanning
Smtp Setup Description
DNS Setup Description
Description
Setting Up Destination Information
Setting Up Destination Information
Storing destinations for Scan to E-mail
Drop down list
Check box for Frequently-Used
Storing destinations for Scan to FTP
Description
Storing Groups Scan to E-mail
Editing and deleting programmed transmission destinations
Storing Sender Information Scan to E-mail
Storing a Custom Directory
Storing a Custom Directory
Editing and deleting programmed senders information
Condition Setting Screen of Scanner Mode
Protecting Information Programmed in the Web Page Passwords
Condition setting screen
Protecting Information Programmed in the Web Page Passwords
Display
Mode and fax mode
Key
Address directory screen
Mail Destination Management
Key Index keys
Switching keys
Search key
Basic Transmission Method
Sending an Image
Basic Transmission Method
Up to 20 senders can be stored using the Web page.
When transmitting by Scan to E-mail
Touch the one-touch key for the desired destination
About pressing the Start key in the following procedure
Using the Dadf
Perform steps 1 through 9 of Basic Transmission Method on
Destination Input Methods
Destination address manual entry
Touch the E-MAIL Address key
Enter the e-mail address
Select the file type and the compression mode
Select where you put the destination
Destination Input Methods
Scanning in colour
Destination address entry with global address search
Enter a keyword for search
Touch the Search key
Select the destination type
You will return to the condition setting screen
Scanning and Transmitting a Two-sided Original
Scanning and Transmitting a Two-sided Original
Touch the Manual key
Scanning Settings
Manually Setting the Scanning Size
Manually Setting the Scanning Size
Touching the inner OK key in the step above returns
You to step
Selected size appears in the top half of the Original key
Change the exposure
When Auto is selected in step
Selecting the Exposure
Selecting the Resolution
Change the resolution
Selecting the Resolution
When Manual is selected in step
Touch the desired resolution key
Selecting the File Format
File format settings for colour scanning
File format settings for black and white scanning
Selecting the File Format
Remove the checkmark from the Programmed checkbox
Touch the OK key You will return to the initial screen
Cancelling an E-Mail/FTP Transmission
Touch the Direct Address key
Storing, Editing, and Deleting from the Touch Panel
Storing One-Touch Keys Only Addresses for Scan to E-mail
Storing One-Touch Keys Only Addresses for Scan to E-mail
Touch the Individual key
Touch the Name key
Touch the Initial key
Enter the e-mail address of the destination
Touch the Index key
Touch an index key
Check the file format and the compression mode
Settings for colour scanning
Compression mode LOW/MEDIUM*/HIGH
Settings for black and white scanning
Touch the one-touch key you wish to edit or delete
Editing and Deleting One-Touch Keys
Touching the Exit key returns you to the screen of on
Editing and Deleting One-Touch Keys
Steps 3 through
Following steps are for deleting a one-touch key
Touch the Delete key
Programming a Group Key
Programming a Group Key
Editing and Deleting Group Keys
Touch the group key you wish to edit or delete
Editing and Deleting Group Keys
Through
Following steps are for deleting a group key
If you wish to delete another group key, repeat steps 3, 6,
Touch the Sender Name key
Storing Sender Information
Touch the Store key
Editing and Deleting Sender Information
Editing and Deleting Sender Information
Edit or delete the sender
When touched, the letter entry screen appears
Storing a Group Index
Touch the Sending Address List Scanner key
Printing Programmed Information
Printing Programmed Information
To cancel printing, touch the Cancel key
Image cannot be scanned
Moiré stripe pattern appears on the scanned image
Scanned image is fuzzy or has smudges
Scanned image is clipped
Transmission takes a long time
Received image data cannot be opened
Recipient does not receive transmitted data
If a Transmission Error Occurs
Error Code Table
Resolution STANDARD, HIGHER, Highest
Error Code Description of the Error
Checking the IP Address
Checking the IP Address
Important Points When Using Scan to E-Mail
Approx KB Tiff High G4 format Jpeg Medium compression
Key Operator Programs
Using the Key Operator Programs
Setting Programs
Setting Programs
Network scanner settings
Initial resolution setting
Default display settings
Number of direct address keys displayed setting
Scan complete sound setting
Default sender set
Compression mode at broadcasting
Initial file format setting
Maximum size of e-mail attachments
Scanner mode timeout after last scan
Default exposure settings
Disable of address direct entry
Specifications
TCP/IP, UDP/IP
Scanning margins
Scanning margins
Network Scanner Operation Xerox WorkCentre C226 User Guide
To Use this Product Correctly as a Fax Device
Line connection
For United Kingdom
For Australia
Important Safety Information
Fax power switch
Settings and programming
Lithium battery
Before Using the FAX Feature
Points to Check and Program After Installation
Make sure the fax power switch is turned on
Make sure the correct date and time have been set
Connecting an Extension Phone
Connecting an Extension Phone
Look at the Operation Panel
Look at the Operation Panel
Fax Mode Condition Settings Screen
Start
Mode
Condition settings screen
Fax Mode Condition Settings Screen
Modes
Settings
Address directory screen alphabetically ordered
Originals that Can Be Faxed
Original sizes
Scanning area of original
Automatic reduction of faxed document
Using the Dadf
Using the Document Glass
Loading a Document
Loading a Document
Checking the Size of a Loaded Original
Original key. Check the key to make
Sure that the original size has been correctly
Detected
Sizes that can be selected are displayed
Touch the desired original size key
Change the resolution
Selecting Resolution and Exposure Settings
Selecting the Resolution
Resolution settings
Selecting Resolution and Exposure Settings
Standard
Ultra fine
Exposure, touch Key. To return to auto
Selecting the Exposure
Change the exposure
Exposure settings
Convenient Dialing Methods
One-touch dialing
Group dialing
On-hook dialing
Basic Procedure for Sending Faxes
Basic Operations
Sending a Fax
Sending a Fax
Entering a Pause
If needed, adjust the resolution setting see
If needed, adjust the exposure setting see
Using the Dadf
Using the document glass
Directory screen
Refer to page 5-9 for information on using the address
Continue from of Basic Procedure for Sending Faxes
Faxing a Two-Sided Original
Quick On-line
Storing transmission jobs memory transmission
Side are booklets, and two-sided originals
That are bound at the top are tablets
Image rotation
If a transmission error occurs
If the receiving party is busy
Priority Transmission of a Stored Job
Cancelling a Fax Transmission
Cancelling On-Hook Dialing
Cancelling a Fax Transmission
Press the JOB Status key Touch the FAX JOB key
Receiving Faxes
Receiving a Fax
Number of rings
Machine will ring* and reception will automatically begin
Advanced Transmission Methods
If received data cannot be printed
Using Broadcast Transmission
Using Broadcast Transmission
Dial Ann ot b e om itted
Dial
Can be omitted
Check the destinations
Setting Up a Timer Transmission
Transmission and Reception Using the Polling Function
Polling memory
Transmission and Reception Using the Polling Function
Polling
Using the Polling Function
Polling key is highlighted and the polling icon appears
Manual Polling
Touch the Special Modes key
Using Polling Memory
Touch the Data Store key
Printing document data in the Public Box
Touch the Print Data key
Touch the Public BOX key Message screen appears
Deleting document data from the Public Box
Touch the Delete Data key
Restricting polling access polling security
Own Number Sending
Example of fax page printed out by the receiving machine
11/JUN/2004/FRI
Faxing a Divided Original Dual Page Scan
Position of senders information
Faxing a Divided Original Dual Page Scan
Outside scanned data
Press the Clear ALL key
Programming Frequently Used Operations
Selecting Dual Page Scan
Using a Program
Programming Frequently Used Operations
Transfer instruction
Using the Transfer Function
Program the fax number of the transfer destination
Press the Custom Settings key Touch the FAX Data Forward key
Transferring received data
Transmission Between Machines Supporting F-codes
Transmission Using F-Codes
Transmission Between Machines Supporting F-codes
This machine
Condition Settings Sub Address
Code Polling Memory
Creating a Memory Box for F-Code Transmission
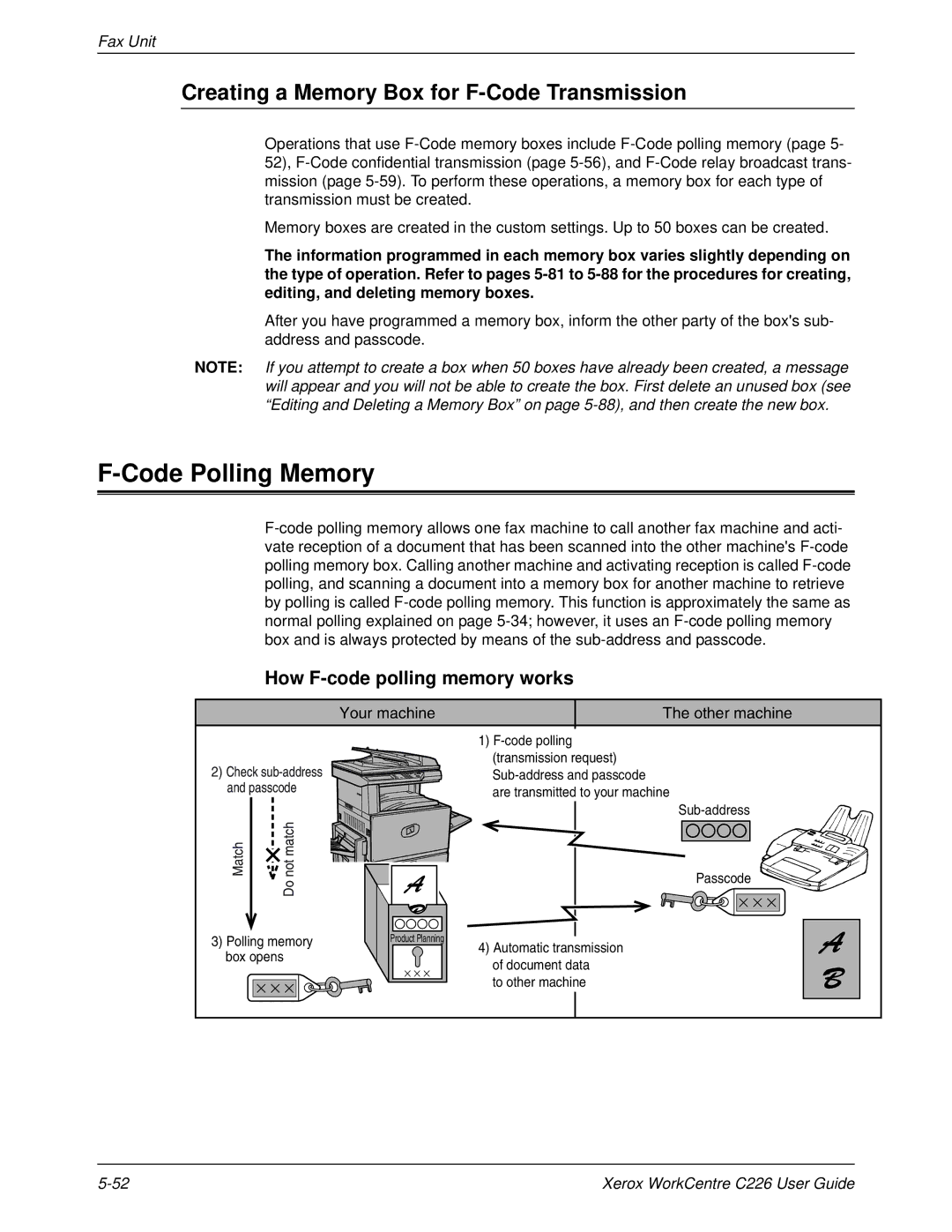
How F-code polling memory works
Your machine Other machine
Using F-Code Polling Memory
Scanning a document into an F-code polling memory box
Code Polling Memory
As the scanning destination
Procedure for F-Code Polling
Checking and clearing document data in a memory box
Corpo.Tps Xerox Group
Code Confidential Transmission
Code Confidential Transmission
Code Confidential Transmission
Press Start to Print DATA. appears
If the print PIN is not correct, the message PIN is not
Relay machine your machine
Code Relay Broadcast Transmission
Code Relay Broadcast Transmission
Using the F-Code Relay Broadcast Function
Your machine is the relay machine
Using an Extension Phone
Using the F-Code Relay Request Function
Using an Extension Phone
Convenient Methods of Use
FAX key
Sending a Fax after Talking Manual Transmission
Send key
Press the Custom Settings key Touch the Receive Mode key
Using an Extension Phone to Receive a Fax
Changing the reception mode to Manual Reception
When the extension phone is in Fax mode
Reception mode is set to Manual Reception
Reception begins when the other party begins transmis- sion
Receiving a Fax After Talking Manual Reception
Using an Extension Phone
Programming
Storing, Editing, and Deleting Auto Dial Keys and Programs
Storing, Editing, and Deleting Auto Dial Keys and Programs
Storing One-Touch Keys
Corporation Fax No Mode
Use the numeric keys to enter the fax number
Passcode max digits
Transmission speed
International correspondence mode
Selections are NONE, Mode 1, Mode 2, and Mode
Editing and Deleting One-Touch Keys
Touch the one-touch key that you wish to edit or delete
If you cannot edit or delete a one-touch key
Storing a Group Key
Address Review Opqrst Uvwxyz ABC Group
Editing and Deleting Group Keys
Touch the group key that you wish to edit or delete
Deleting a group key
If you wish to delete another group key, repeat steps 2, 5,
Storing a Program
Touch the Program Name key
Touch the Settings key
Special Modes
Editing and Deleting Programs
Touch the program you wish to edit or delete
Programming, Editing, and Deleting F-Code Memory Boxes
Programming, Editing, and Deleting F-Code Memory Boxes
Programming an F-Code Memory Box
Sub-address/passcode entry screen appears
Use the numeric keys to enter a passcode max digits
Setting for F-Code Polling Memory Boxes Polling Times
Next Exit
Touching the Exit key returns you to the screen
Setting for F-Code Relay Broadcast Memory Boxes Recipient
Use the numeric keys to enter a 4-digit number
123456/987654
Editing and Deleting a Memory Box
Touch the Sending Address List FAX key
Touch the key of the list you wish to print
Entering Characters
Entering alphabetical characters
Example Xerox äÄ Touch the X key
Touch the e key, r key, o key, and x key
Touch the ä key
Entering Characters
Touch the Space key
SharpXerox ä
Entering numbers and symbols
Screen 1/2 Screen 2/2
Fax Unit
When a Transaction Report Is Printed
When a Transaction Report Is Printed
Information appearing in the TYPE/NOTE column
Explanation
Port F-code communication
Rect sub-address or other reason
When an Alarm Sounds and a Warning Message Is Displayed
Message screen Alarm Meaning of message Action Page/Guide
Viewing the Communication Activity Report
Received fax cannot Add the indicated Loading Paper on
When an Alarm Sounds and a Warning Message Is Displayed
Self-diagnosis func Turn off the power
Manual reception was Try manual recep
Open Cated cover
100 Xerox WorkCentre C226 User Guide
Problems and Solutions
Problem Check Solution
Problems and Solutions
Problem Check Solution
Fax Unit 102 Xerox WorkCentre C226 User Guide
Symbols / Numerics
Index
Index
Index
Index
Index
Index
Index
Fax 5-14,5-15
Index
PCL 3-47,3-67

![]() x
x