Network Topologies
Infrastructure Wireless LAN for Roaming Wireless PCs
The Basic Service Set (BSS) defines the communications domain for each access point and its associated wireless clients. The BSS ID is a 48‐bit binary number based on the access point’s wireless MAC address, and is set automatically and transparently as clients associate with the access point. The BSS ID is used in frames sent between the access point and its clients to identify traffic in the service area.
The BSS ID is only set by the access point, never by its clients. The clients only need to set the Service Set Identifier (SSID) that identifies the service set provided by one or more access points. The SSID can be manually configured by the clients, can be detected in an access point’s beacon, or can be obtained by querying for the identity of the nearest access point. For clients that do not need to roam, set the SSID for the wireless card to that used by the access point to which you want to connect.
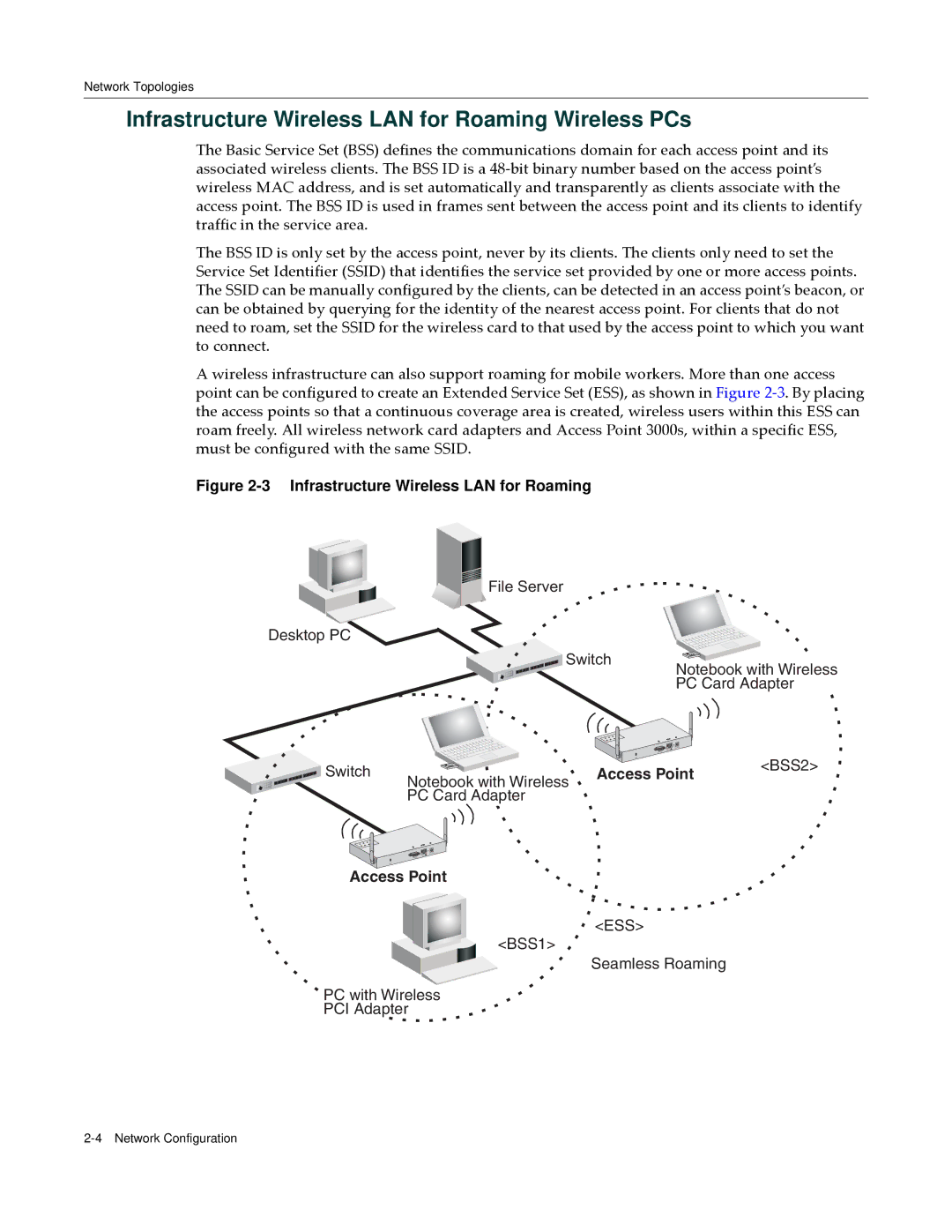
A wireless infrastructure can also support roaming for mobile workers. More than one access point can be configured to create an Extended Service Set (ESS), as shown in Figure 2‐3. By placing the access points so that a continuous coverage area is created, wireless users within this ESS can roam freely. All wireless network card adapters and Access Point 3000s, within a specific ESS, must be configured with the same SSID.
Figure 2-3 Infrastructure Wireless LAN for Roaming
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() File Server
File Server
Desktop PC
| Switch | Notebook with Wireless | ||
|
|
| ||
|
|
| PC Card Adapter | |
Switch | Notebook with Wireless | Access Point | <BSS2> | |
| ||||
|
|
|
| |
| PC Card Adapter |
|
|
|
Access Point
<ESS>
<BSS1>
Seamless Roaming
PC with Wireless
PCI Adapter