Section 1 |
| |
|
|
|
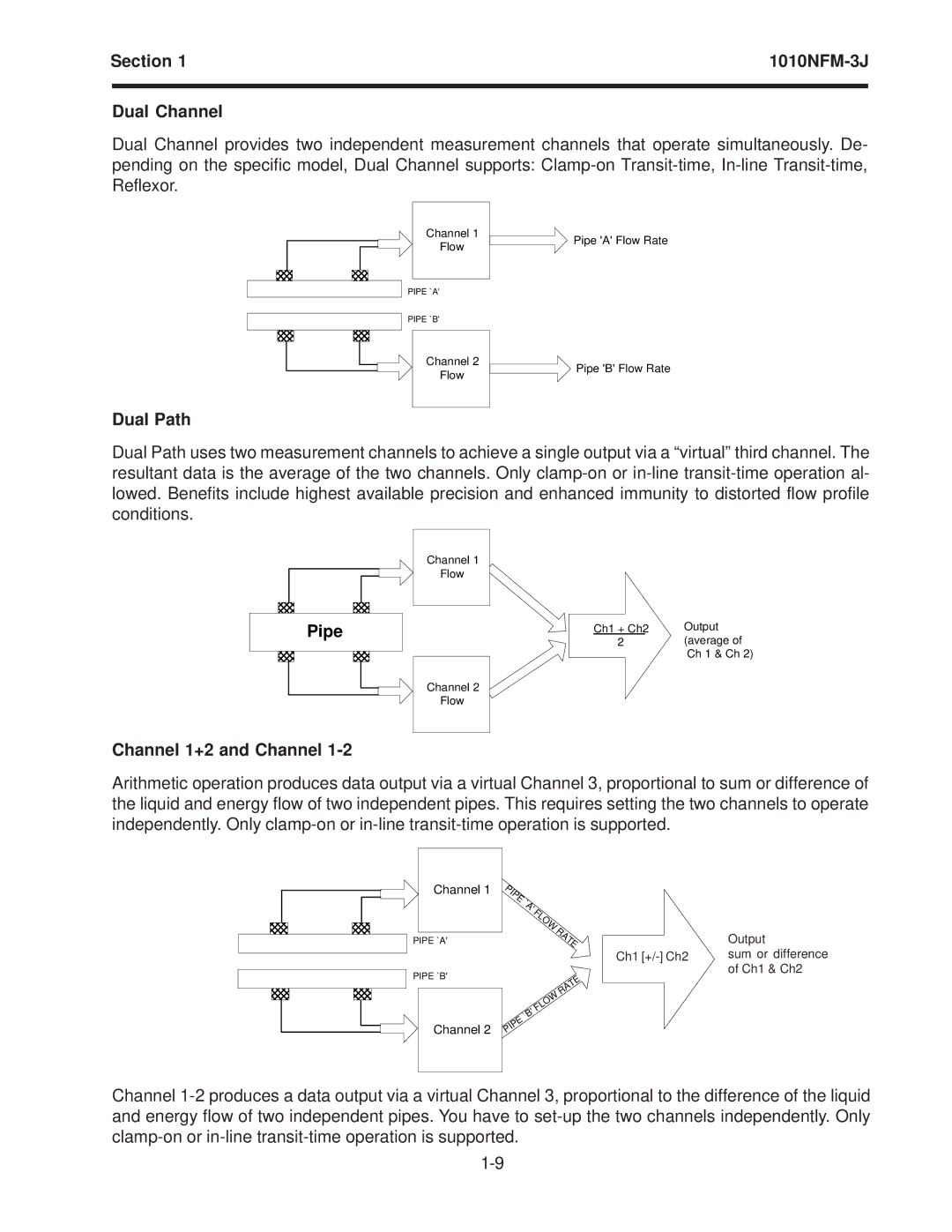
Dual Channel
Dual Channel provides two independent measurement channels that operate simultaneously. De- pending on the specific model, Dual Channel supports:
Channel 1 | Pipe 'A' Flow Rate | |
Flow | ||
| ||
|
|
PIPE `A'
PIPE `B'
Channel 2 | Pipe 'B' Flow Rate | |
Flow | ||
| ||
|
|
Dual Path
Dual Path uses two measurement channels to achieve a single output via a “virtual” third channel. The resultant data is the average of the two channels. Only
Channel 1
Flow
Pipe
Channel 2
Flow
Ch1 + Ch2 | Output |
2(average of Ch 1 & Ch 2)
Channel 1+2 and Channel 1-2
Arithmetic operation produces data output via a virtual Channel 3, proportional to sum or difference of the liquid and energy flow of two independent pipes. This requires setting the two channels to operate independently. Only
Channel 1
PIPE `A'
PIPE `B'
Channel 2
P |
|
|
|
|
I |
|
|
|
|
P |
|
|
|
|
E |
|
|
|
|
` |
|
|
| |
A |
|
|
| |
| ' |
|
|
|
| F |
|
| |
|
| L |
|
|
|
| O |
| |
|
| W |
| |
|
|
| R |
|
|
|
| A | Output |
|
|
| E | |
|
|
| T |
|
|
|
| Ch1 | sum or difference |
|
|
|
| of Ch1 & Ch2 |
|
|
| E |
|
|
|
| T |
|
|
|
| A |
|
|
|
| R |
|
|
|
| W |
|
|
| O |
| |
|
| L |
|
|
| F |
|
| |
| ' |
|
|
|
B |
|
|
| |
` |
|
|
|
|
E |
|
|
|
|
IP |
|
|
|
|
P |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Channel