Text Part Number OL-23826-09
Americas Headquarters
Copyright 2011-2013, Cisco Systems, Inc
Iii
N T E N T S
Related Documents Standards MIBs
Standards MIBs
Searching and Filtering Output of show and more Commands
Vii
Split-Horizon8-6
Viii
Restrictions
Manually Configuring an IP SLA CFM Probe or Jitter Operation
Restrictions
Overview
Xii
Setting up Manual Preemption for Vlan Load Balancing
Xiii
Configuring Mpls VPNs
19-6
Xiv
Verifying Local Switching
Xvi
Verifying the Synchronous Ethernet configuration
Xvii
Cisco IOS IP SLA
Xviii
Marking
Xix
Technical Assistance
Xxi
Configuring Hsrp
Xxii
Configuring Link Layer Discovery Protocol
Xxiii
How to Configure Bert
32-2
Xxiv
Xxv
Configuring IPv6 Duplicate Address Detection
Troubleshooting Tips
Xxvii
BFD
Xxviii
Verifying Layer 2 Tunneling
Xxix
Configuring Unspecified Bit Rate
Xxx
Creating IPv6 VRFs on PE Routers
Xxxi
Technical Assistance
Xxxii
Finding Feature Information
Xxxiii
Igmp
Xxxiv
IPv6 Multicast Groups
Xxxv
Span Traffic
Xxxvi
About This Guide
Document Revision History
Document Number Date Change Summary
Xxxviii
Xxxix
OL-23826-09
Xli
Xlii
Xliii
Xliv
Xlv
Xlvi
Audience
Objectives
Organization
Xlvii
Xlviii
Mpls OAM
Xlix
SLA
Chapter Description
Conventions
Convention Description
Boldface font
To access the related documentation on Cisco.com, go to
Related Documentation
Release Notes
Lii
Cisco ASR 901 Router Overview
Performance Features
Features
Introduction
This section contains the following topics
Management Options
Manageability Features
Quality of Service and Class of Service Features
Security Features
Layer 3 Features
Layer 3 VPN Services
Monitoring Features
OL-23826-09
Finding Feature Information
Contents
Licensing
Licenses Supported on Cisco ASR 901 Router
Feature Overview
Following licenses are supported
License Sl.No Chassis PID License PID Description
Licensing Licenses Supported on Cisco ASR 901 Router
Features Supported
Feature Based License
License Features
License Types
Port Based/Mode License
Port or Interface Behavior
1588BC License
Port Number Port Type Chassis PID License Required
Example When Port Based License is Installed
Example When Port Based License is not Installed
Port Based License
Router# show ip interface brief
Example When 10gigUpgrade License is not Installed
10gigUpgrade License
Routerconfig# interface gig 0/0
Router# show interface Ten0/1
Example When Flexi License is not Installed
Example When 10gigUpgrade License is Installed
Following is a sample output from the show license command
Flexi License
Example When 1588BC License is not Installed
Example When Flexi License is Installed
Example When 1588BC License is Installed
Following example shows how to install the 1588BC license
Routerconfig-ptp-clk#no ptp clock boundary domain
Use the license clear command to remove the 1588BC license
Removing the 1588BC License
Router# license clear 1588BC
Enable License install Copy tftp flash Show flash
Installing the License
License install license-file-name
Generating the License
Command Purpose
Changing the License
Example
Router# license install ?
Return Materials Authorization License Process
Example RMA Process
Router# copy tftp flash
To verify the new license, use the show license command
Where to Go Next
MIBs
Standards
RFCs
Standard
Description Link
Technical Assistance
Feature Name Releases Feature Information
Feature Information for Licensing
OL-23826-09
First-Time Configuration
Setup Mode
Before Starting Your Router
Configuring Global Parameters
Using Setup Mode
Enter a hostname for the router this example uses
Completing the Configuration
Configuring the Hostname and Password
Password prompt appears. Enter your password
Verifying the Cisco IOS Software Version
Exit back to global configuration mode
Verifying the Hostname and Password
Router# configure terminal
Router# show config
Managing and Monitoring Network Management Features
This section contains the following procedures
Network Management Features for the ASR
Enables privileged Exec mode
Configuring Snmp Support
Enter your password if prompted
Enters global configuration mode
String-Community string is the password to access the Snmp
Form of this command removes the specified community string
Protocol
View view-name-Optional Previously defined view. The view
Notification-type -snmp authentication -Enables RFC
Command
Envmon voltage shutdown supply fan temperature -When
Temperature
Snmp-server host command
Command Purpose
Exits global configuration mode
Configuring Remote Network Management
Enable Configure terminal
Interface loopback number
Command or Action Purpose
Zero-Touch Deployment
Zero-touch Deployment
Image Download
Network ip-address subnet-mask
Configuring a Dhcp Server
Specifies to exclude IP address of the Dhcp server
Ip dhcp
Creating a Bootstrap Configuration
Configuring a Tftp Server
Enabling a Tftp Server on the Edge Router
Configuring the Cisco Configuration Engine
Example Configuring Snmp Support
Configuration Examples
Example Configuring Remote Network Management
Example Configuring a Dhcp Server
Example Zero-touch Deployment
Additional References
Related Documents
Related Topic Document Title
MIBs
Network Management Features for the ASR
Understanding Command Modes
Using the Command-Line Interface
User Exec Log
Entered. Use a password
Exit, or logout
Use the interface
Line console
Understanding the Help System
Ctrl-Z or enter end
Help
Understanding no and default Forms of Commands
Understanding Abbreviated Commands
Understanding CLI Error Messages
Router# show conf
Changing the Command History Buffer Size
Using Command History
Error Message Meaning How to Get Help
Range is from 0 to
Recalling Commands
Using Editing Features
Disabling the Command History Feature
Enabling and Disabling Editing Features
Capability Keystroke1 Purpose
Editing Commands through Keystrokes
Press Ctrl-Y
Backspace key
Press Ctrl-V or Esc Q
Editing Command Lines that Wrap
Return and Space bar
Press Ctrl-L or Ctrl-R
Accessing the CLI
Command begin include exclude regular-expression
Router# show interfaces include protocol
Saving Configuration Changes
Software Upgrade
Selecting a Cisco IOS Image
Upgrading the Cisco IOS image
Copy the IOS Image from the Tftp server
If the right steps are not followed properly
Router# show file system
Verify the Cisco IOS upgrade
Save the configuration and reload the router
Verify the Cisco IOS image in the file system
Router# verify flashasr901-universalk9-mz.151-2.SNG
Router# show version
Auto Upgrading the MCU
Manually Upgrading the Rommon
Auto Upgrade of Rommon
Rommon AUTOUPGRADEROMMON=TRUE False
Router# upgrade rom-monitor internal
Configuring the Interface
Configuring Gigabit Ethernet Interfaces
To configure the GE interface, complete the following steps
Enters enable mode
Setting the Speed and Duplex Mode
Cdp enable
Gigabitethernet 0/1
Enabling the Interface
Modifying MTU Size on the Interface
Mtu bytes
Verifying the MTU Size
No mtu or default mtu command
Complete the following steps to configure MAC Flap control
Configuring MAC FLap Control
MAC Flap Control
Restrictions and Limitations
Restrictions
Configuring a Combo Port
Mac-flap-ctrl on per-mac mac-movement
Time-interval
Exits interface configuration mode and enters
Configures the media type
Auto-select-Specifies dynamic selection
Physical connection
Verifying the Media Type
Router# show interface gigabitethernet 0/1
Router# show interface gigabitethernet 0/7
Configuring Ethernet Virtual Connections
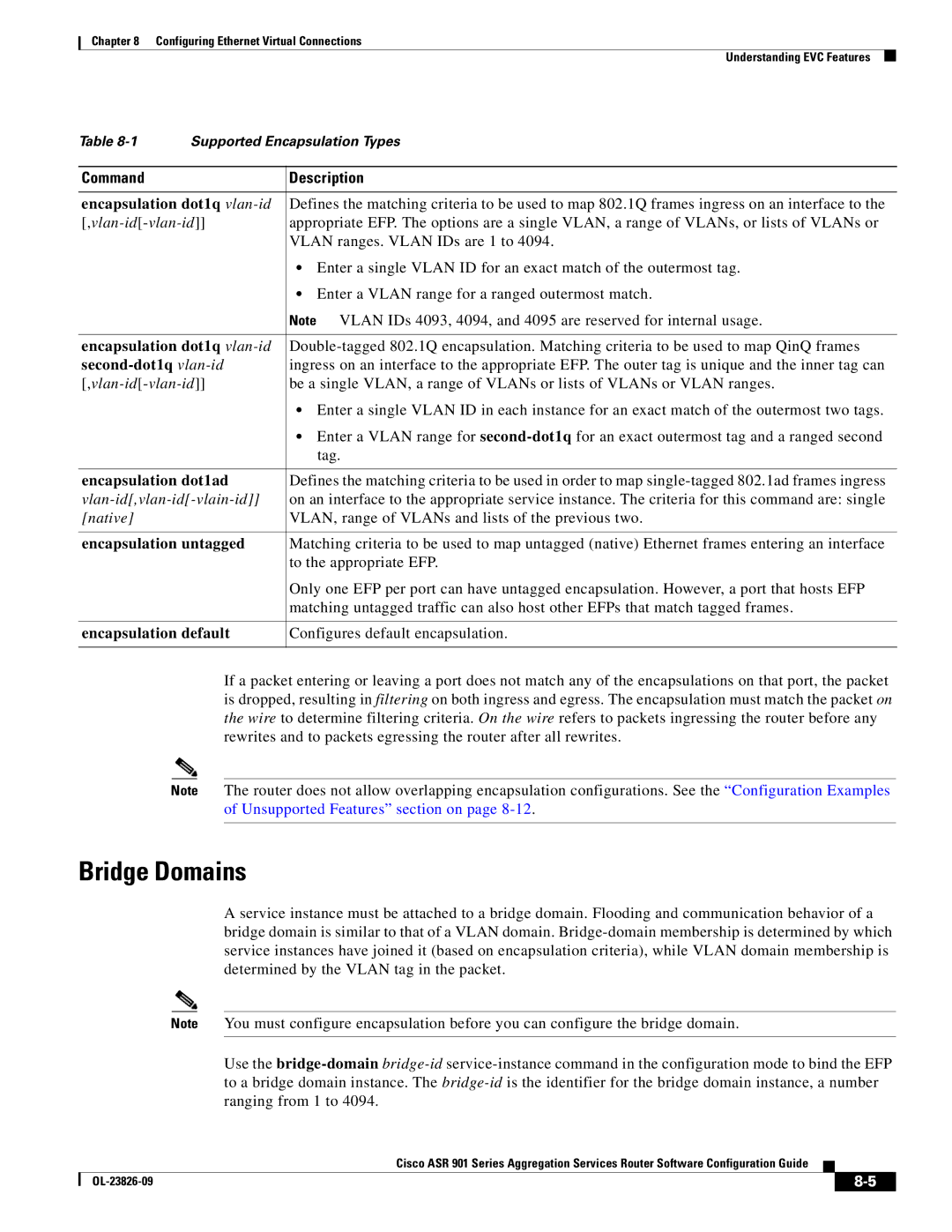
Supported EVC Features
Understanding EVC Features
Service Instances and EFPs
Ethernet Virtual Connections
Encapsulation
Configures default encapsulation
Bridge Domains
To the appropriate EFP
Dhcp Client on Switch Virtual Interface
Split-Horizon
Rewrite Operations
Configuring EFPs
Default EVC Configuration
Configuration Guidelines
Creating Service Instances
Default
Service instance number ethernet name
Show ethernet service instance
Copy running-config startup-config
Example Configuring a Service Instance
Configuration Examples of Supported Features
Example Encapsulation Using a Vlan Range
Example Bridge Domains and Vlan Encapsulation
Router config-if-srv#rewrite ingress pop 1 symmetric
Router config-if-srv#rewrite ingress tag pop 1 symmetric
Example Rewrite
Example Split Horizon
Configuration Examples of Unsupported Features
Example Filtering
Example Overlapping Encapsulation
How to Configure EVC Default Encapsulation
Configuring EVC Default Encapsulation with Bridge-Domain
Interface type number
Configuring EVC Default Encapsulation with Xconnect
Configures the default service instance
An identifier
Verifying EVC Default Encapsulation with Bridge-Domain
Verifying EVC Default Encapsulation with Xconnect
Configuring Other Features on EFPs
Configuration Examples for EVC Default Encapsulation
Example Configuring EVC Default Encapsulation with Xconnect
MAC Address Forwarding, Learning and Aging on EFPs
EFPs and EtherChannels
Interface type slot/port
No mac-address-table learning vlan vlan-id
Routerconfig# no mac-address-table learning vlan
End Return to privileged Exec mode
Addresses learned on a particular VLAN/BD
Router# show mac-address-table
802.1Q Tunneling QinQ
Configuring Ieee 802.1Q Tunneling using EFPs
Router# show mac-address-table interface 0/9
Router# show mac-address-table interface port-channel
1shows the tag structures of the double-tagged packets
You can use EFPs to configure 802.1Q tunneling in two ways
Configuration Examples
Configuration Example
Cisco ASR 901 router supports pop 2 configuration
Routed QinQ
Bridge Domain Routing
Example Configuring Bridge-Domain Routing
Configuring Dhcp Client on SVI
How to Configure Dhcp Client on SVI
Configures the Vlan interface and enters interface
Interface type-number
Verifying Dhcp Client on SVI
Configuration Example for Dhcp Client on SVI
EFPs and Mstp
EFPs and Switchport MAC Addresses
Monitoring EVC
Command Description
Sample Configuration with Switchport to EVC Mapping
Configuration Example
Line vty 0 4 login
Additional References
Supported EVC Features
OL-23826-09
Configuring EtherChannels
EtherChannel Feature Overview
Understanding How EtherChannels Work
EtherChannel Configuration Overview
Understanding How EtherChannels Are Configured
Understanding Manual EtherChannel Configuration
Understanding Ieee 802.3ad Lacp EtherChannel Configuration
Passive mode Active mode
Passive mode
Active mode Passive mode
Router a Router B Result
EtherChannel Configuration Guidelines and Restrictions
Understanding Port-Channel Interfaces
Understanding Load Balancing
Configuring Channel Groups
Configuring Etherchannels
Configuration examples for Lacp system priority
Configuring the Lacp System Priority and System ID
Lacp rate fast normal End
Configuring the Lacp Transmit Rate
Configuring EtherChannel Load Balancing
Configuration Examples
Verifying the Lacp Transmit Rate
Enable Configure terminal Interface port-channel number
Modifying MTU Size on Port-Channel
Verifying the MTU Size on Port-Channel
Restrictions for EVC EtherChannel
EVC On Port-Channel
Verifying the Configuration
Configuring EVC on Port-Channel
Router# show ethernet service evc id evc-idinterface
Router# show ethernet service instance interface
Problem Solution
Troubleshooting
Contents
Configuring Ethernet OAM
Understanding Ethernet CFM
Configuring Ethernet CFM
IP SLA Support for CFM
10-2
Ethernet CFM Configuration Restrictions and Guidelines
Default Ethernet CFM Configuration
Configuring the CFM Domain
Configure terminal Enter global configuration mode
10-4
We do not recommend configuring a large number
Second, 10 seconds, 1 minute and 10 minutes. The default
Is 2 to 255 the default is
Optional Configure the maximum number of MEPs
10-6
Example for Basic CFM configuration
Restrictions
Configuring Multi-UNI CFM MEPs in the Same VPN
Exit
10-7
10-8
Cfm mep domain domain-name mpid identifier
Alias alias-short-ma-name icc icc-code meg-id
Number ma-number vlan-id vlan-id vpn-id vpn-id
10-9
10-10
10-11
10-12
Configuring Ethernet CFM Crosscheck
Continuity-check static rmep
Configuring Static Remote MEP
Static
10-13
Configuring a Port MEP
Service ma-name ma-number vpn-id port
10-14
10-15
Configuring Snmp Traps
Ethernet echo mpid identifier domain domain-name
Configuring IP SLA CFM Operation
Ethernet jitter mpid identifier domain domain-name
10-16
Allowed by the protocol being used the default is 66 bytes
Repeats. The range is from 1 to 604800 seconds the default
Seconds to keep the operation in memory when it is not
Seconds. The default is 0 seconds
10-18
Configuring CFM over EFP with Cross Connect
Show the configured IP SLA operation
10-19
10-20
Configuring CFM over EFP Interface with Cross Connect
10-21
Example for untagged Encapsulation
10-22
Example for single tag Encapsulation
10-23
Configuring CFM with EVC Default Encapsulation
Cfm mep domain domain-name mpid mpid-value
10-24
10-25
Verifying CFM with EVC Default Encapsulation
Example Configuring CFM with EVC Default Encapsulation
Configuring Y.1731 Fault Management
Default Y.1731 Configuration
10-26
10-27
Configuring ETH-AIS
Show ethernet cfm error
Configuring ETH-LCK
Show ethernet cfm smep interface interface-id
Ethernet cfm lck link-status global
10-29
Managing and Displaying Ethernet CFM Information
10-31
10-32
Understanding the Ethernet OAM Protocol
Following OAM features are defined by Ieee 802.3ah
OAM Features
Benefits of Ethernet OAM
10-33
10-34
Link Monitoring
Setting Up and Configuring Ethernet OAM
This section includes the following topics
10-35
Restrictions and Guidelines
Default Ethernet OAM Configuration
Enabling Ethernet OAM on an Interface
Ethernet oam
Ethernet oam max-rate oampdus min-rate seconds
Ms mode active passive timeout seconds
Show ethernet oam status interface interface-id
10-37
Configuring Ethernet OAM Link Monitoring
Enabling Ethernet OAM Remote Loopback
10-38
10-39
Threshold high high-frames none low
Ethernet oam link-monitor frame-period
Ethernet oam link-monitor frame-seconds
10-40
Ethernet oam link-monitor receive-crc threshold
Configuring Ethernet OAM Remote Failure Indications
No ethernet link-monitor on
10-41
Dying-gasp link-fault action
Configuring Ethernet OAM Templates
Error-disable-interface
Ethernet oam remote-failure critical-event
10-43
Low-seconds window milliseconds
Threshold high high-seconds none low
Ethernet oam link-monitor high threshold action
Source-template template-name
Show ethernet oam discovery interface interface-id
Displaying Ethernet OAM Protocol Information
Show ethernet oam statistics interface interface-id
Show ethernet oam summary
Verifying Information Oampdu and Fault Statistics
Verifying Ethernet OAM Configuration
Verifying an OAM Session
Verifying OAM Discovery Status
10-47
Verifying Link Monitoring Configuration and Status
Verifying Status of the Remote OAM Client
Understanding E-LMI
10-48
Active
Default E-LMI Configuration
Configuring E-LMI
Restrictions
10-49
10-50
Enabling E-LMI
Understanding Ethernet Loopback
Configuring Ethernet Loopback
Displaying E-LMI Information
10-51
10-52
Enabling Ethernet Loopback
10-53
10-54
10-55
10-56
Configuring Y.1564 to Generate Ethernet Traffic
10-57
Internal Mode
Routerconfig# ip sla
Configuring IP SLA for Traffic Generation
Specify the SLA ID to start the IP SLA session
10-58
10-59
Measurement-type direction -Specifies the statistics
10-60
10-61
Example Two-Way Measurement
10-62
ITU-T Y.1731 Performance Monitoring
Prerequisites for ITU-T Y.1731 Performance Monitoring
11-1
Restrictions for ITU-T Y.1731 Performance Monitoring
Information About ITU-T Y.1731 Performance Monitoring
11-2
Frame Delay and Frame-Delay Variation
Two-way Delay Measurement
11-3
On-Demand and Concurrent Operations
Frame Loss Ratio
Single-ended ETH-SLM
11-4
Benefits of ITU-T Y.1731 Performance Monitoring
How to Configure ITU-T Y.1731 Performance Monitoring
Supported interfaces
11-5
Configuring Two-Way Delay Measurement
Max-delaymilliseconds Owner owner-id
11-6
Mac-address target-address -Specifies
Mac-address source-address -Specifies
11-7
11-8
Boundary ,...,boundary -Lists upper
Configuring Single-Ended Synthetic Loss Measurement
Enable Configure terminal Asr901-platf-multi-nni-cfm
11-9
11-10
Mac-addresstarget-address-Specifies
Mac-addresssource-address-Specifies
11-11
Enters IP SLA configuration mode
Exits IP SLA Y.1731 loss configuration mode
Exits IP SLA configuration mode and enters global
Owner-id-Specified the name of the Snmp
Number-of-measurements -Optional When
Threshold-type average
Number-of-measurements argument. The range is
Threshold-type consecutive
Scheduling IP SLAs Operations
Threshold-type immediate -Optional When a
Prerequisites
Threshold-value upper-threshold
Specifies an IP SLAs operation group number
Individual IP SLAs operation
Range of operation numbers to be scheduled for a
Multi-operation scheduler
Router# show ip sla configuration
11-16
Router-1#show running interface gigabitethernet0/0
11-17
Example Verifying Ethernet CFM Performance Monitoring
Router# show ethernet cfm pm session summary
Router# show ethernet cfm pm session detail
Example Verifying History for IP SLAs Operations
11-18
Router# show ip sla history interval-statistics
11-19
Configuring Direct On-Demand Operation on a Sender MEP
11-20
Configuring Referenced On-Demand Operation on a Sender MEP
11-21
Example On-Demand Operation in Direct Mode
Example On-Demand Operation in Referenced Mode
11-22
Router# ip sla on-demand ethernet slm 2002 duration
Ieee 802.1ag ITU-T Y.1731 MEF
Releases, and feature sets, use Cisco MIB Locator found at
Following URL
11-23
11-24
11-25
Feature Name Releases Feature Information
11-26
Understanding Resilient Ethernet Protocol REP
Configuring Resilient Ethernet Protocol
Overview
12-1
REP Open Segments
12-2
No-neighbor Topology
12-3
Fast Convergence
Link Integrity
Vlan Load Balancing VLB
12-4
Neighbor Offset Numbers in a Segment
12-5
12-6
REP Ports
Default REP Configuration
Configuring Resilient Ethernet Protocol REP
REP Configuration Guidelines
12-7
12-8
12-9
Configuring the REP Administrative Vlan
12-10
Configuring REP Interfaces
Service instance instance-id
Routerconfig# interface Gigabitethernet0/1
Enter the physical Layer 2 interface or port channel ID.
Port-channel range is 1 to
12-12
12-13
Verifies the REP interface configuration
File
12-14
12-15
Configuring REP as Dual Edge No-Neighbor Port
12-16
Rep segment segment-id edge no-neighbor
Primary preferred
12-17
Cisco ASR 901 Dual Rep Edge No-Neighbor Topology Example
76001
12-18
12-19
76002
12-20
Setting up Manual Preemption for Vlan Load Balancing
12-21
Configuring Snmp Traps for REP
Trap-rate command
Monitoring REP
12-22
12-23
Configuring the REP Administrative Vlan Example
Configuration Examples for REP
Configuring a REP Interface Example
This section contains the following examples
Configuring Snmp Traps for REP Example
Setting up the Preemption for Vlan Load Balancing Example
Monitoring the REP Configuration Example
12-25
12-26
Cisco ASR 901 Topology Example
12-27
ASR2
12-28
12-29
12-30
Configuring MST on EVC Bridge Domain
Overview of MST and STP
13-1
Overview of MST on EVC Bridge Domain
Restrictions and Guidelines
13-2
MST0
13-3
13-4
Configuring MST on EVC Bridge Domain
Specifies the gigabit ethernet interface to configure
Slot/port-Specifies the location of the interface
13-5
Configuration Example for MST on EVC Bridge Domain
Verification
13-6
Router# show spanning-tree vlan
13-7
This example shows MST on port channels
13-8
Router# show spanning-tree mst
13-9
Troubleshooting Tips
13-10
14-1
Configuring Multiprotocol Label Switching
14-2
Configuring EoMPLS
Understanding EoMPLS
15-1
15-2
Configuring EoMPLS
15-3
EoMPLS Configuration Example
Configuration Commands
Configuring Pseudowire Redundancy
Specifies an interface to configure
Configures encapsulation type for the service instance
Port Based EoMPLS
Configure terminal Enters global configuration mode Example
Show mpls l2t vc id
15-5
15-6
Routerconfig# xconnect Encapsulation mpls
Configuring Mpls VPNs
Understanding Mpls VPNs
16-1
Configuration Examples for Mpls VPN
Configuring Mpls VPNs
PE1 Configuration
16-2
16-3
Configuring Mpls VPNs Configuration Examples for Mpls VPN
16-4
16-5
Provider Configuration
PE2 Configuration
Interface details
16-6
16-7
Ospf and BGP details
16-8
Loop Back details
16-9
16-10
Understanding Mpls OAM
Configuring Mpls OAM
LSP Ping
17-1
LSP Ping over Pseudowire
Configuring Mpls OAM
LSP Traceroute
17-2
Using LSP Traceroute for LDP IPv4 FEC
Using LSP Ping for LDP IPv4 FEC
Using LSP Ping for Pseudowire
Ping mpls ipv4
Displaying AToM Vccv capabilities
Using LSP Traceroute over Pseudowire
Show mpls l2transport binding vcid
Vc-id-value
Changing Default Hashing Algorithm for Ecmp
Configuring Routing Protocols
Asr901-ecmp-hash-config global-type
18-1
18-2
Configuring BFD
Understanding BFD
19-1
Configuring BFD for Ospf
BFD Configuration Guidelines and Restrictions
Configuring BFD for Ospf on One of More Interfaces
Enables BFD for Ospf on the interface
Creates a configuration for an Ospf process
Configuring BFD for Ospf on All Interfaces
Specifies the BFD session parameters
Process
Configuring BFD for IS-IS
Configuring BFD for BGP
Configuring BFD for IS-IS on a Single Interface
19-4
19-5
Configuring BFD for IS-IS for All Interfaces
19-6
Configuring BFD for Static Routes
BFD with Ospf on All Interfaces
Configuration Examples for BFD
BFD with Ospf on Individual Interfaces
19-7
BFD with IS-IS on All Interfaces
BFD with BGP
BFD with IS-IS on Individual Interfaces
19-8
19-9
BFD with Static Routes
19-10
Configuring T1/E1 Controllers
Configuring the Card Type
20-1
Configuring E1 Controllers
Subslot
20-2
20-3
Channel-group channel-no timeslots timeslot-list 64 command
20-4
Configuring T1 Controllers
Troubleshooting Controllers
Troubleshooting E1 Controllers
20-5
Payload loopback mode of the framer. The framer re-clocks
Troubleshooting T1 Controllers
Receiver
Incoming traffic
Path to the receiver path
20-7
Local line
20-8
21-1
Configuring Pseudowire
Understanding Pseudowires
Structure-Agnostic TDM over Packet
21-2
Transportation of Service Using Ethernet over Mpls
Hot Standby Pseudowire Support for ATM/IMA
Limitations
21-3
Configuring Pseudowire Classes
Configuring Pseudowire
Xconnect ip pw-class pseudowire-class
Cem group-number
21-5
Class cem cem-class-name
Configuring CEM Classes
Cem group-number Cem class cem-class-name
Xconnect ip-addressencapsulation mpls
21-7
Enable Configure terminal Interface cemslot/port
Configuring a Backup Peer
Specifies the CEM class name
Xconnect peer-loopback-ip-addressencapsulation mpls
Configuring Structure-Agnostic TDM over Packet
Xconnect ip-addressencapsulation mpls Exit
21-9
21-10
30.30.30.2 255.255.255.255
Pseudowire-classpseudowire-class-name
Configuring a SAToP Pseudowire with UDP Encapsulation
Xconnect peer-router-id vcid pseudowire-class name
Udp port local-udp-port remote remote-udp-port
21-12
Exits the configuration mode
Values for SAToP pseudowires using UDP are from
Remote peer
Exits the CEM interface
Cem-groupgroup-number timeslots timeslot
Enable Configure terminal Controller e1 t1 slot/port
Exit Interface CEMslot/port
Xconnect ip-addressencapsulation mpls Exit End
Exits configuration mode
Configuring a CESoPSN Pseudowire with UDP Encapsulation
Defines a CEM channel
Recommend that you build a route from the xconnect address
Exits pseudowire-class configuration mode
Udp port local localudpport remote remoteudpport
21-16
21-17
21-18
QoS for CESoPSN over UDP and SAToP over UDP
Although the symmetric keyword appears to be optional, you
Service instance instance-number
21-19
Xconnect ip-addressencapsulation
Selects an E1 or T1 controller
Configuring L2VPN Pseudowire Redundancy
Creates a CEM interface and assigns it a CEM group number
21-20
21-21
Example Pseudowire Redundancy
Configuring ATM/IMA Pseudowire Redundancy in PVC Mode
Backup peer peer-router-ip-addr vcid
Interface interface-name
21-23
Or more virtual circuits VCs
Configuring ATM/IMA Pseudowire Redundancy in PVP Mode
Vpi-ATM network virtual path identifier VPI of the VC to
Multiplex on the permanent virtual path
Configuring ATM/IMA Pseudowire Redundancy in Port Mode
Transport over Mpls AToM static pseudowire
21-25
Peer-router-ip-addr-IP address of the remote peer router
Verifying Hot Standby Pseudowire Support for ATM/IMA
21-26
Router# show mpls l2transport vc
21-27
TDM Local Switching
21-28
Configuring TDM Local Switching on a T1/E1 Mode
Configuration Example for Local Switching
Verifying Local Switching
21-29
21-30
ATM/IMA
Configuration Examples for Pseudowire
Example TDM over Mpls Configuration-Example
21-31
21-32
21-33
Asrb
Following configuration uses CESoSPN with UDP encapsulation
Example CESoPSN with UDP
21-34
21-35
Example Ethernet over Mpls
21-36
21-37
Feature Information for Configuring Pseudowire
21-38
Configuring Clocking
Restrictions
22-1
22-2
Configuring Network Clock for Cisco ASR 901 Router
22-3
Configuring Network Clock in Global Configuration Mode
22-4
22-5
Example for GPS interface
22-6
Configuring Network Clock in Interface Configuration Mode
Synchronization Status Message
Understanding SSM and Esmc
Ethernet Synchronization Messaging Channel
Clock Selection Algorithm
QL-disabled mode
Configuring Esmc in Global Configuration Mode
Esmc behavior for Port Channels
Esmc behavior for STP Blocked Ports
22-9
Configuring Esmc in Interface Configuration Mode
Verifying Esmc Configuration
Show esmc
22-10
Show network-clock synchronization
Managing Synchronization
22-11
Router#show esmc interface gigabitEthernet 0/10
22-12
Synchronization Example
Verifying the Synchronous Ethernet configuration
Configuring Synchronous Ethernet for Copper Ports
Configures synchronous ethernet copper port as slave
Configures synchronous ethernet copper port as master
22-14
22-15
Synchronization detail RP command to confirm
Troubleshooting Tips
Shown in this example
22-16
22-17
Troubleshooting Esmc Configuration
22-18
Configuring PTP for the Cisco ASR 901 Router
Configuring PTP Ordinary Clock
Setting System Time to Current Time
Configuring Master Ordinary Clock
22-19
22-20
Priority1 priority-value Priority2 priority-value
22-21
Configuring Slave Ordinary Clock
22-22
Clock source source-address
22-23
22-24
Configuring PTP in Unicast Negotiation Mode
Configuring PTP in Unicast Mode
Port Name
Port Role
Configured with this command
Configures Cisco ASR 901 router on unicast
PTP Boundary Clock
Negotiation mode. The following options can be
Configuring PTP Boundary Clock
Clock-port port-namemaster
22-27
22-28
Verifying PTP modes
Exits clock port configuration mode
Ordinary Clock
22-29
Boundary Clock
Router# show ptp clock dataset default
22-30
Router# show ptp clock dataset time-properties domain
Verifying PTP Configuration on the 1588V2 Slave
22-31
Router# show ptp clock runn dom
Typical configuration on a 1588V2 master is
Verifying PTP Configuration on the 1588V2 Master
22-32
Router# show ptp clock running domain
22-33
Configuring a Hybrid Ordinary Clock
PTP Hybrid Clock
22-34
To work in hybrid mode. Enables the hybrid clock such
Hybrid-Optional Enables the PTP boundary clock
That the output of the clock is transmitted to the remote
Slaves
22-36
22-37
Configuring a Hybrid Boundary Clock
Router# show running-config section ptp
Verifying Hybrid modes
22-38
SSM and PTP Interaction
22-39
Router#show platform ptp channelstatus
PTP Redundancy
ClockClass Mapping
Telecom Profiles
22-40
Clock source source-address priority
Configuring Telecom Profile in Slave Ordinary Clock
End
22-41
22-42
22-43
Configuring Telecom Profile in Master Ordinary Clock
Timing packets with a PTP slave devices
Verifying Telecom profile
22-44
Router#show ptp port running detail
Router#show ptp clock running domain
22-45
Static Unicast Mode
Setting the TimeProperties
ASR901 Negotiation Mechanism
22-46
22-47
Configuring ToD on 1588V2 Slave
22-48
Configuring Ipsla Path Discovery
Cisco IOS IP SLA
23-1
23-2
Configuration Parameters
23-3
Example for Ipsla Path Discovery
This example shows the LPD parameter values configured
23-4
Router#show ip sla mpls-lsp-monitor neighbors
23-5
Two-Way Active Measurement Protocol
23-6
Configuring Twamp
Enable Configure terminal Ip sla server twamp
Configuring the Twamp Server
Port port-number
23-7
Configuration Examples for Twamp
Configuring the Twamp Reflector
Configures the switch as a Twamp responder, and enter Twamp
23-8
Example Configuring the Router as an IP SLA Twamp Reflector
Example Configuring the Router as an IP SLA Twamp server
Routerconfig# ip sla server twamp
Routerconfig# ip sla responder twamp
23-10
24-1
Configuring QoS
24-2
Understanding QoS
Default QoS for Traffic from External Ethernet Ports
Default QoS for Traffic from Internal Ports
24-3
24-4
Modular QoS CLI
Input and Output Policies
Input Policy Maps
24-5
Access Control Lists
Output Policy Maps
24-6
24-7
Classification
Match Command
Class Maps
24-8
Classification Based on IP Precedence
Classification Based on Layer 2 CoS
Classification Based on IP Dscp
24-9
This display shows the available classification options
Classification Comparisons
Per-hop Decimal Precedence CoS
24-10
Classification Based on QoS Groups
Traffic Type Per-hop Decimal Precedence CoS
24-11
24-12
Classification Based on Vlan IDs
24-13
Table Maps
24-14
Policing
Individual Policing
Gigabitethernet port
24-15
24-16
Unconditional Priority Policing
Routerconfig# policy-map policy1
Configuration Example
Egress Policing
24-17
Routerconfig# policy-map Example
Marking
24-18
Congestion Management and Scheduling
Traffic Shaping
24-19
Routerconfig# policy-map out-policy-parent
Routerconfig# policy-map out-policy
Routerconfig-pmap-c#service-policy out-policy
24-20
This is an example of a parent-child configuration
Class-Based Weighted Fair Queuing
Routerconfig# policy-map parent
24-21
24-22
Routerconfig-pmap-c#bandwidth remaining percent
24-23
Priority Queuing
Ingress and Egress QoS Functions
Routerconfig# policy-map pmapbckbone
Ingress QoS Functions
24-24
QoS Limitations
Configuring Quality of Service QoS
Egress QoS Functions
24-25
General QoS Limitations
Statistics Limitations
24-26
Classification Limitations
Propagation Limitations
GigabitEthernet
Value
24-28
Marking Limitations
Precedence Prec-transmit Qos-group
Congestion Management Limitations
Queuing Limitations
Rate Limiting Limitations
Policing with
ACL-based QoS Restrictions
Shaping Limitations
24-30
QoS for MPLS/IP over Mlppp
Improving Feature Scalability
Tcam with QoS
QoS for CPU Generated Traffic
24-32
QoS Configuration Guidelines
24-33
Sample QoS Configuration
Enter the password
Configuring Classification
Creating a Class Map for Classifying Network Traffic
24-34
24-35
24-36
Attaching the Policy Map to an Interface
24-37
Attaching Policy Map to Cross Connect EVC
24-38
Configuring Marking
24-39
Creating a Class Map for Marking Network Traffic
Set cos
Traffic Attributes Network Layer Protocol
Set dscp
Set qos-group
Specify an EVC
Configuring Mpls Exp Bit Marking using a Pseudowire
Specify an encapsulation type for the EVC
24-41
Configuring Low Latency Queueing LLQ
Configuring Congestion Management
Use the policy-mapcommand to define a policy map
24-42
Configuring Multiple Priority Queueing
Policy-map interface commands to verify your configuration
24-43
24-44
Use the exit command to exit class map configuration
Configuring Class-Based Weighted Fair Queuing Cbfq
Use the exit command to exit the policy map configuration
24-45
Amount of bandwidth
Weighted Random Early Detection Wred
This step is optional
24-46
No random-detect discard-class-based
Configuring Shaping
No random-detect discard-class value
24-47
24-48
Configuring the Secondary-Level Child Policy Map
Configuring Ethernet Trusted Mode
Creating IP Extended ACLs
24-49
Class-map match-all match-any
Using Class Maps to Define a Traffic Class
Class-map-name
24-50
Ip precedence ip-precedence-list
Match cos cos-list ip dscp dscp-list
Qos-group value vlan vlan-list
Show class-map
Match access-group name access-group-name
Creating a Named Access List
Permit source source-wildcard any log
Class-mapclass-map-name
24-53
What to do Next
Tcam with ACL
Router# show ip access-lists tcam1
24-54
Router# show run int gig 0/1
Router# show access-lists tes456
Verifying Named Access List
24-55
Router# show policy-map interface gigabitethernet 0/0
Configuration Example for Named Access List
Router# show running-config
24-56
Class-map match-any test
24-57
24-58
24-59
24-60
24-61
Cisco IP-SLAs
QoS Treatment for Performance-Monitoring Protocols
QoS Treatment for IP-SLA Probes
QoS Marking for CPU-Generated Traffic
24-63
QoS Queuing for CPU-Generated Traffic
To enter QoS class-map configuration mode
Configuring Class-map for Matching Mpls EXP Bits
Extending QoS for Mlppp
Class in the policy map
Configuring Class-map for Matching IP Dscp Value
Match ip dscp dscp-value...dscp-value
24-65
Dscp-value-The Dscp value used to identify a Dscp value
This configuration packets with IP Dscp of value af11 are
24-66
Match ip dscp
24-67
Configuring a Policy-map
Bandwidth percent bandwidth-percent Exit
Class class-default
Exampleclass
24-68
Bits defined by the policy map
Value in the type of service ToS byte
Dscp-value-The Dscp value used to identify a Dscp
24-69
Attaching the Policy-map to Mlppp Interface
Enable Configure terminal Interface multilink group-number
Ip address address subnet mask
24-70
24-71
24-72
Re-marking IP Dscp Values of CPU Generated Traffic
Generated traffic
Re-marking Mpls EXP Values of CPU Generated Traffic
Are 0 to
24-73
Class and enters QoS class-map configuration mode
Configuring a Policy-map to Match on CS5 and EXP4
Bandwidth percent bandwidth-percent Set ip dscp dscp-value
Class-map-name-The name used for class map
As a match criterion
Value in the type of service ToS byte
Cs-value-The Class SelectorCS value
Class-map-name-Name of the class for the class map
Configuring Class-map for Matching Mpls EXP Bits
Exits QoS policy-map class configuration mode
24-76
Configuring a Policy-map
Configuring Class-map for Matching IP Dscp Value
Following example shows a configuration of a policy-map
24-77
Configuring a Policy-map to Match on CS5 and EXP
Attaching the Policy-map to Mlppp Interface
24-78
24-79
Verifying Mpls over Mlppp Configuration
24-80
24-81
Troubleshooting Tips
24-82
24-83
Example Tcam troubleshooting related error
Routerconfig-if-srv#service-policy input policy2
24-84
Entries used 256/256 no free entries available
Routerconfig-if-srv#no service-policy input policy1
We now have enough free entries to configure policy2
Entries used 195/256 after unconfiguring policy1
24-85
24-86
Entries used 220/256 after configuring policy2
24-87
Related Topic Document Title
24-88
Feature Information for Configuring QoS
25-1
Configuring Mlppp
Prerequisites
Mlppp Optimization Features
Distributed Multilink Point-to-Point Protocol Offload
Mpls label protocol ldp
Multiclass Mlppp
Mpls over Mlppp
25-3
25-4
Mpls Label imposition LER Mpls Label switching LSR
Mpls over Mlppp on Core Links
Mpls over Mlppp on CE to PE Links
25-5
Configuring the Card Type, E1 and T1 Controllers
Configuring Mlppp Backhaul
Configuring a Multilink Backhaul Interface
Creating a Multilink Bundle
Example configures an IP address and subnet mask
Configuring Mrru
Example creates a multilink bundle
25-7
Configuring PFC and Acfc
Remote apply, pfc local request, and pfc remote apply
25-8
25-9
Requests. The syntax is as follows
Configuration requests
Acfc option are not accepted
25-10
Enabling Multilink and Identifying the Multilink Interface
Keepalive period retries
25-11
25-12
Ppp multilink group group-number
Mlppp Offload
Ppp multilink idle-link Ppp multilink queue depth
25-13
Configuring Additional Mlppp Settings
Configuring Mpls over the Mlppp on a Serial Interface
Ppp multilink Ppp multilink group group-number Exit
25-14
25-15
Number, and enters the interface configuration mode
Configuring Mpls over Mlppp for Ospf
25-16
Interface multilink group-number
25-17
25-18
Configuration Examples for Mpls over Mlppp
25-19
Verifying Mpls over Mlppp Configuration
Router# ping mpls ipv4 6.6.6.6/32
Router# show mpls ldp bindings 6.6.6.6
25-20
25-21
25-22
Feature Information for Mlppp
Understanding Obfl
Onboard Failure Logging
Retrieval of the Obfl message
Recording Obfl Messages
Configuring Obfl
Verifying Obfl Configuration
26-2
Clilog summary
26-3
26-4
27-1
Information About Hsrp and Vrrp
Text Authentication
Overview of Hsrp and Vrrp
Preemption
Configuring Hsrp
How to Configure Hsrp
Complete the following steps to configure Hsrp
Standby group-numberauthentication text string
27-4
Example Configuring Hsrp Active Router
Configuration Examples for Hsrp
Example Configuring Hsrp Backup Router
27-5
Example Hsrp Text Authentication
How to Configure Vrrp
Configuring Vrrp
Interface type number Ip ip-address mask
Vrrp group-numberauthentication text string
Vrrp group-numberpriority level
27-7
Example Configuring a Vrrp Master Router
Configuration Examples for Vrrp
Example Configuring a Vrrp Backup Router
27-8
27-9
Example Vrrp Text Authentication
27-10
27-11
Feature Information for Hsrp and Vrrp
27-12
28-1
Configuring Link Layer Discovery Protocol
Configuring Lldp
How to Configure Lldp
Restrictions for Lldp
Overview of Lldp
28-3
Example Configuring Hold Time
Configuration Example for Lldp
Verifying Lldp
Example Enabling Lldp Globally
Example Configuring Delay Time
Example Configuring Intervals
28-5
28-6
28-7
28-8
Feature Information for Lldp
29-1
Configuring Multihop Bidirectional Forwarding Detection
Configuring Multihop BFD Template
How to Configure Multihop BFD
Restrictions for Multihop BFD
Information About Multihop BFD
29-3
Configuring a Multihop BFD Map
Configuration Examples for Multihop BFD
Example Configuring Multihop BFD
Configuration for Router a
29-5
Configuration for Router B
Interface Fast Ethernet 0/1
Interface Fast Ethernet 6/0
29-6
29-7
Feature Information for Multihop BFD
29-8
Bit Error Rate Testing
Prerequisites
30-1
How to Configure Bert
Bert Pattern Description
30-2
Performing Bert on a T1/E1 Line
Enable Configure terminal Controller t1 e1 slot/port
Terminating Bert on a T1/E1 Controller
30-3
Verifying Bert on a T1/E1 Controller
Routerconfig-controller# no bert pattern
No bert pattern pattern interval time
30-4
30-5
Following is a sample configuration of the Bert feature
30-6
Feature Information for Bit Error Rate Testing
30-7
30-8
31-1
Microwave ACM Signaling and EEM Integration
31-2
IGP Metric Adjustment
QoS Policy Adjustment
Benefits
Link Removal
Configuring Connectivity Fault Management
Bridge-domainbridge-domain-id
31-4
31-5
31-6
31-7
Configuring EEP Applet Using CLIs
31-8
Exits applet configuration mode
Configuring Event Handler
An EEM applet is triggered
31-9
31-10
Example Configuring EEP Applet
Example Configuring CFM
Following is a sample configuration of CFM
31-11
Action 104 set n $ringnodes
31-12
31-13
31-14
Action 442 cli command isis metric $dlc
Example Configuring Event Handler
Following is a sample configuration of Event Handler
31-15
CFM Support for Microwave Adaptive
Cisco ASR 901 Router Commands
Bandwidth Transport Integration with Microwave ACM
31-16
31-17
31-18
32-1
IPv6 Support on the Cisco ASR 901 Router
32-2
Prerequisites for IPv6 Support on the Cisco ASR 901 Router
Overview of IPv6
Benefits
IPv6 Address Formats
32-3
IPv6 Addressing and Discovery
Static Configuration
IPv6 Address Type Preferred Format Compressed Format
32-4
Stateless Autoconfiguration
ICMPv6
32-5
IPv6 Neighbor Discovery
IPv6 Duplicate Address Detection
IPv4 and IPv6 Dual-Stack on an Interface
32-6
Bidirectional Forwarding Detection for IPv6
Routing Protocols
IS-IS Enhancements for IPv6
OSPFv3 for IPv6
Configuring IPv6 Addressing and Enabling IPv6 Routing
QoS for IPv6
32-8
32-9
Global configuration mode
Configuring a Static IPv6 Route
Enables the forwarding of IPv6 unicast datagrams
Enables Cisco Express Forwarding CEF globally on
Administrative-multicast-distance -Optional
Enabling Stateless Auto-Configuration
Ipv6 address autoconfig
32-11
Ipv6 enable or
Implementing IPv6 on Vlan Interfaces
32-12
32-13
Implementing IPv6 Addressing on Loopback Interfaces
Configuring ICMPv6 Rate Limiting
Enable Configure terminal Ipv6 icmp error-interval interval
32-14
Configuring IPv6 Duplicate Address Detection
Ipv6 nd dad attempts value
32-15
32-16
Configuring IPv6 Neighbor Discovery
32-17
Configuring IPv6 and IPv4 Dual-Stack on the Same Vlan
Configures an IPv4 address on the interface
Configuring OSPFv3 for IPv6
Configures IPv6 address on the interface
Enables IPv6 address on the interface
Enable Configure terminal Router isis area-tag
Configuring IS-IS for IPv6
Net network-entity-tag
Ipv6 router isis area-name
32-20
32-21
Configuring Multiprotocol-BGP for IPv6
Configuring BFD for IPv6
Specifying a Static BFDv6 Neighbor
32-22
Associating an IPv6 Static Route with a BFDv6 Neighbor
Interface-number -SVI name
32-23
32-24
32-25
Configuring BFDv6 and OSPFv3
32-26
Configuring BFDv6 for BGP
Exec mode
Exits global configuration mode and enters privileged
Implementing QoS for IPv6
Verifying IPv6 Addressing Routing
Verifying a Static IPv6 Route
32-28
Router# show ipv6 route
Verifying IPv6 Implementation on Vlan Interfaces
Verifying a Stateless Auto-Configuration
32-29
Router# show ipv6 interface loopback
Verifying IPv6 Implementation on Loopback Interfaces
Verifying ICMPv6 Configuration
32-30
Router# show ipv6 interface loopback0
Router# show ipv6 traffic
32-31
32-32
Verifying IPv6 Duplicate Address Detection Configuration
Verifying IPv6 and IPv4 Dual-Stack Configuration
Verifying IPv6 Neighbor Discovery Configuration
32-33
Router# show ipv6 neighbors detail
As shown in the example
Verifying OSPFv3 for IPv6 Configuration
32-34
Router# show ipv6 ospf
Verifying Multiprotocol-BGP for IPv6 Configuration
Verifying IS-IS for IPv6 Configuration
32-35
Router# show isis ipv6 rib
BGP
32-36
Verifying BFD for IPv6 Configuration
32-37
Router# show bfd neighbors
32-38
Verifying BFDv6 and OSPFv3 Configuration
32-39
Verifying BFDv6 for BGP Configuration
Example IPv6 Addressing on Vlan Interfaces
Example Configuring IPv6 Duplicate Address Detection
Example IPv6 Addressing on Loopback Interfaces
Example Customizing ICMPv6
Example Enabling IPv6 Stateless Address Autoconfiguration
Example Configuring IPv6 Neighborhood Discovery
Example Configuring the IPv4 and IPv6 Dual-Stack
Example Configuring IPv6 Static Routing
Example Configuring OSPFv3 for IPv6
Example Configuring BFD and Static Routing for IPv6
Example Configuring BFD and OSPFv3 for IPv6
Following is a sample configuration of OSPFv3 for IPv6
Example Configuring IS-IS for IPv6
Following is a sample configuration of IS-IS for IPv6
32-43
32-44
Example Configuring Multiprotocol-BGP for IPv6
32-45
Example Configuring BFD and Multiprotocol-BGP for IPv6
Debug Commands Show Commands Platform Hardware Commands
No ipv6 nd suppress-ra command to enable
Route advertisement messages. Also, define a
Valid prefix pool for IPv6
32-47
32-48
32-49
32-50
Chapter of the IPv6 Configuration Guide provide
BGP for IPv6 chapter of the IPv6 Configuration Guide
Aggregation Services Router Software Configuration Guide
32-51
32-52
33-1
Labeled BGP Support
Overview of Labeled BGP Support
How to Configure Labeled BGP Support
VPN/VRF over RFC
33-2
Configuration Example for Labeled Support
Send-label option
33-3
33-4
Verifying Labeled BGP Support
Router# show bgp ipv4 unicast labels
Labels
Vpnv4 all label
33-5
Vpnv4 vrf LTE12 label
Router# show ip cef vrf LTE12 113.22.12.0 internal
33-6
RFC-3107
Carrying Label Information in BGP-4
33-7
33-8
Feature Information for Labeled BGP Support
34-1
Mpls Traffic Engineering Fast Reroute Link Protection
34-2
BFD-triggered Fast Reroute
R2 R3
34-3
Fast Reroute
Link Protection
34-4
Enabling Mpls TE-FRR on an SVI Interface
Enables Mpls TE tunnel signaling on the specified interface
Enabling Mpls TE-FRR for EoMPLS on a Global Interface
Mpls traffic-eng tunnels
34-6
Pseudowire-class pw-class-name
Enabling Mpls TE-FRR for EoMPLS on an Interface
Xconnect peer-ip-address vc-id pw-classpw-class-name
34-7
34-8
34-9
Enabling Mpls TE-FRR for IS-IS
34-10
34-11
Configuring Primary One-hop Auto-Tunnels
34-12
34-13
Configuring Backup Auto-Tunnels
34-14
Mpls ldp discovery targeted-hello accept command
Enabling BFD Triggered FRR on an SVI Interface
Ip rsvp signalling hello bfd
Messages from all neighbors
34-15
Enable Configure terminal Ip rsvp signalling hello bfd
Configuration mode
Enabling BFD Triggered FRR on a Router
34-16
Verification Examples
Verifying Mpls TE-FRR Configuration
34-17
Router# show mpls traffic-eng tunnels brief
Router# show mpls traffic-eng tunnels backup
Use the following command to verify the reservation detail
34-18
Router# show mpls traffic-eng fast-reroute database
Verifying Primary One-hop Auto-Tunnels
Verifying Backup Auto-Tunnels
34-19
Router# show ip rsvp fast-reroute
34-20
Verifying BFD Triggered FRR Configuration
Database
34-21
Router# show ip rsvp hello
34-22
Router# show ip rsvp interface detail
34-23
Router# show ip rsvp hello bfd nbr
Router# show ip rsvp hello bfd nbr detail
Example Configuring Primary One-hop Auto-Tunnels
Example Configuring Mpls TE-FRR
Example Configuring Backup Auto-Tunnels
Example Configuring BFD Triggered FRR
34-25
Mpls TE FRR
34-26
34-27
34-28
35-1
Layer 2 Control Protocol Peering, Forwarding, and Tunneling
Layer 2 Control Protocol Forwarding
Layer 2 Control Protocol Tunneling
35-2
35-3
Default Action Configuration Option
Configuring Layer 2 Peering
L2protocol peer protocol
35-4
35-5
Configuring Layer 2 Forwarding
Routerconfig-if# service instance Ethernet
Routerconfig-if# l2proto-forward tagged Cdp
Protocol-Specifies the protocol to be forwarded
35-6
35-7
Configuring Layer 2 Tunneling
35-8
L2protocol tunnel protocol Bridge-domain bridge-id
Verifying Layer 2 Forwarding
Verifying Layer 2 Peering
Verifying Layer 2 Tunneling
35-9
Example Configuring Layer 2 Forwarding
Example Configuring Layer 2 Peering
Following is a sample configuration of layer 2 peering
35-10
35-11
Example Configuring Layer 2 Tunneling
35-12
Router
35-13
35-14
Commands Cisco IOS LAN Switching Commands
35-15
Following command was introduced l2proto-forward
35-16
36-1
Configuring Inverse Muliplexing over ATM
36-2
How to Configure IMA
Ima-groupima-group-number
Configuring ATM IMA on T1/E1 Interface
Interface ATMslot-number/IMAima-group-number
No ip address Atm bandwidth dynamic No atm ilmi-keepalive
Configuring ATM IMA over Mpls
Configuring the T1/E1 Controller
36-4
Clock source internal
Configuring an ATM IMA Interface
Ima-groupgroup-number
36-5
Disables the Ilmi keepalive parameters
Configuring ATM over Mpls Pseudowire Interface
You can configure ATM over Mpls in the following modes
36-6
Configuring an N-to-1 VCC Cell Mode
Configuring a Port Mode Pseudowire
Configures the ATM interface
36-7
Enable Configure terminal Interface ATMslot/IMAgroup-number
Configuring an N-to-1 vPC Cell Mode
Xconnect ip-addressport-numberencapsulation mpls one-to-one
36-8
36-9
ATM AAL5 SDU VCC Transport
Sets the encapsulation type to AAL5. AAL5 is the default
Verifying IMA Configurations
L2transport encapsulation for the VCC mode
36-10
Configuring Constant Bit Rate
How to Configure ATM Class of Service
Enters the global configuration mode
36-11
Configuring Unspecified Bit Rate
Mode
36-12
ATM class of service with the rate equal to the bandwidth
Configuring Unspecified Bit Rate Plus
IMA links and the bandwidth of each link
Ubr+ pcr-rate mcr-rate
Circuit and specifies the bandwidth
Configures the UBR+ QoS class for an ATM permanent virtual
Pcr-rate-Peak cell rate in Kbps
Mcr-rate-Peak cell rate in Mbps
Example Configuring a Port Mode Pseudowire
Configuration Examples
Example Creating an IMA Interface
36-15
Example Configuring an N-to-1 VPC Cell Mode
Example Configuring an N-to-1 VCC Cell Mode
Example Configuring CBR
Example Configuring UBR
Example Configuring UBR Plus
Configuring Marking Mpls Experimental Bits
Example Configuring VBR for Real Time Traffic
Example Configuring VBR for Non-Real Time Traffic
Applying the Policy-map
Applying a Policy map on PVC and PVP
36-18
Sets the PVC encapsulation type to AAL0
Disables the Ilmi trap parameters
Attaches a policy map to the input interface
36-19
36-20
Applying a Policy map on ATM IMA Interface
Table-maptable-map-name
Creating a Table-map
36-21
Interface ATM slot/IMA group-number
Creating a Policy-map for SVI Interface
Default copy
Map from from-value to to-value
36-22
Applying a Service Policy on SVI Interface
Mpls ip Service-policy output policy-map-name
36-23
36-24
36-25
36-26
Feature Information for Inverse Multiplexing over ATM
37-1
IPv6 over Mpls 6PE and 6VPE
37-2
Benefits of 6PE and 6VPE
IPv6 on Provider Edge Routers
37-3
Components of MPLS-based 6VPE Network
IPv6 on VPN Provider Edge Routers
IPv6 router on the customer
PE equipment, connected to CEs and entry
37-5
Supported Features
Configuring 6PE
How to Configure IPv6 over Mpls 6PE and 6VPE
Scalability Numbers
Interface Numbers
Address-family ipv6
Exit-address-family
37-7
37-8
Configuring 6VPE
Setting up IPv6 Connectivity from PE to CE Routers
37-9
VRF table for an IPv6 address
Setting up MP-BGP Peering to the Neighboring PE
Vrf-name-Optional a specific VRF table for an IPv6
37-10
Enable the exchange of information with a BGP neighbor
Places the router in address family configuration mode for
Address prefixes
Extended-Specifies that only extended communities will be
37-12
Setting up MPLS/IPv4 Connectivity with LDP
37-13
Creating IPv6 VRFs on PE Routers
Sessions that use standard IPv4 address prefixes
To configure dual-stack VRF, complete the following steps
37-14
Address-family ipv4
37-15
Verifying IPv6 over Mpls 6PE and 6VPE Configuration
Router# show bgp vpnv6 unicast all
Router# show ipv6 protocols vrf vpe1
Router# show ipv6 cef vrf cisco1
37-16
37-17
Router# show ipv6 route vrf
Router# show mpls forwarding-table vrf vpe1
Following is a sample configuration of 6PE
Example Configuring 6PE
37-18
Router# show bgp ipv6 200133/64
Example Configuring 6VPE
Following is a sample configuration of 6VPE
37-19
37-20
37-21
Feature Information for IPv6 over Mpls 6PE and 6VPE
37-22
38-1
Storm Control
38-2
Configuring Storm Control
38-3
38-4
Verifying Storm Control
Errdisable recovery cause
Configuring Error Disable Recovery
38-5
Storm-control
Seconds-Specifies the time to recover from a specified
Monitoring Error Disable Recovery
Error-disable cause
Cause
Configuration Example for Storm Control
38-7
Router# debug platform hardware ether SC
38-8
38-9
Feature Information for Storm Control
38-10
39-1
Remote Loop-Free Alternate Fast Reroute
39-2
Remote LFA-FRR Link Protection
39-3
Benefits of Remote LFA-FRR
Pseudowire Redundancy over FRR
Avoiding Traffic Drops
39-4
Conditions for Switchover
CESoPSN, SAToP, and ATM/IMA
39-5
39-6
Configuring Remote LFA-FRR for IS-IS
Specifies an IP address for the specified interface
Switch Virtual Interface SVI
39-7
Ip router isis
39-8
39-9
Configuring Remote LFA-FRR for Ospf
Enables the Ospf routing protocol and enters the router
39-10
Router ospf
Configuring Remote LFA-FRR for Ethernet and TDM Pseudowires
Enables Mpls LDP synchronization on interfaces for an Ospf
39-11
Accept-Configures the router to respond to requests for
Configuring Remote LFA-FRR on a Global Interface
Targeted hello messages from all neighbors
39-12
39-13
Configuring Remote LFA-FRR on a GigabitEthernet Interface
39-14
Configuring Remote LFA-FRR on an SVI Interface
39-15
Configuring Remote LFA-FRR on IS-IS
39-16
Passive-interfaceinterface-type interface-number
39-17
39-18
Disables sending routing updates on an interface
Configuring LFA-FRR for EoMPLS
Backup peer peer-ip-address vc-id
39-19
Enables automatic negotiation
Removes an IP address or disables IP processing
39-20
Negotiation auto
39-21
Configuring LFA-FRR for ATM/IMA
39-22
Backup peer peer-ip-address
Configuring LFA-FRR for CESoPSN
Exit Interface CEM slot/port No ip address
39-23
39-24
Configuring LFA-FRR for SAToP
Exit Interface CEM slot/port
39-25
39-26
39-27
Verification Examples for Remote LFA-FRR
39-28
Verifying Remote LFA-FRR Configuration
Router# show ip ospf fast-reroute remote-lfa tunnels
Router# show ip cef 171.1.1.0 internal
39-29
Router# show ip ospf rib
Router# show isis fast-reroute remote-lfa tunnels
39-30
Router# show isis rib
Router# show mpls l2transport vc 1 detail
39-31
Router# show mpls l2transport vc 3001 detail
39-32
Verifying Remote LFA-FRR Configuration on ATM/IMA
Verifying Remote LFA-FRR Configuration on IS-IS
39-33
Router# show mpls l2 vc 90 detail
Verifying Remote LFA-FRR Configuration on CESoPSN
39-34
Router# show mpls l2 vc 111 detail
Configuration Examples for Remote LFA-FRR
Verifying Remote LFA-FRR Configuration on SAToP
39-35
Example Configuring Remote LFA-FRR for Ospf
Example Configuring Remote LFA-FRR for IS-IS
Example Configuring Remote LFA-FRR Globally
39-36
Example Configuring EoMPLS Pseudowire Redundancy over FRR
Example Configuring Remote LFA-FRR on an SVI Interface
Example Configuring LFA-FRR on ATM/IMA
39-37
Example Configuring LFA-FRR on CESoPSN
Example Configuring LFA-FRR on SAToP
39-38
39-39
39-40
Reroute,
40-1
Digital Optical Monitoring
Enters transceiver type configuration mode
How to Enable Transceiver Monitoring
Routerconfig# transceiver type all
40-2
Examples
Show interfaces transceiver command
Example Displaying Transceiver Information
40-3
Example Displaying Detailed Transceiver Information
40-4
Router# show interfaces transceiver detail
40-5
Example Displaying List of Supported Transceivers
40-6
Example Displaying Threshold Tables
40-7
40-8
Example Displaying Threshold Violations
Example When Transceiver Monitoring is Disabled
40-9
Router# show interfaces transceiver threshold violations
40-10
Example Displaying SPF Details
SCP6G44-C1-BMH
40-11
40-12
SFF-8472
40-13
Feature Information for Digital Optical Monitoring
40-14
41-1
IPv4 Multicast
41-2
PIM SSM for IPv4
Supported Protocols
Source Specific Multicast
Protocol Independent Multicast
IGMPv2
IGMPv1
IGMPv3
41-4
PIM SSM Mapping
Ip igmp static ssm-map command
Reverse Path Forwarding
Static SSM Mapping
Enables multicast routing
Configuring IPv4 Multicast
Enabling IPv4 Multicast Routing
Ip pim sparse-mode Asr901-multicast source
Enable Configure terminal Ip pim ssm default
Configuring PIM SSM
Ip pim sparse-mode Ip igmp version
41-7
Configuring PIM SSM Mapping
Ip igmp ssm-map static access-list source-address
41-8
Verifying IPv4 Multicast Routing
Verifying PIM SSM
41-9
41-10
Verifying PIM SSM Mapping
Router# show ip mroute
Router# show ip igmp ssm-mapping
Show ip igmp groups group-address
Configuration Examples for IPv4 Multicast
Show ip igmp groups interface-type interface-number
Show ip igmp groups interface-type detail
Example Configuring PIM SSM Mapping
Example Configuring PIM SSM
Example IPv4 Multicast Routing
41-12
Example Configuring Rendezvous Point
41-13
Router# debug ip igmp
41-14
41-15
41-16
Feature Information for IPv4 Multicast
41-17
IGMPv2,
41-18
42-1
IPv6 Multicast
42-2
IPv6 Multicast Routing Implementation
IPv6 Multicast Groups
Multicast Listener Discovery Protocol for IPv6
42-3
42-4
Protocol Independent Multicast
PIM Source Specific Multicast
PIM-Sparse Mode
Source Specific Multicast Mapping for IPv6
42-5
Enabling IPv6 Multicast Routing
Configuring IPv6 Multicast
Rendezvous Point
42-6
Enable Configure terminal No ipv6 mfib
Disabling IPv6 Multicast Forwarding
42-7
Disabling MLD Device-Side Processing
Disables IPv6 multicast forwarding on the router
No ipv6 mld router
42-8
Configuring MLD Protocol on an Interface
42-9
No ipv6 mld router
42-10
Configuring a Rendezvous Point
Configuring PIM SSM Options
Enable Configure terminal Ipv6 pim
42-11
Disables PIM on the specified interface
Configuring IPv6 SSM Mapping
Disabling PIM SSM Multicast on an Interface
No ipv6 pim
Verifying IPv6 Multicast
Configure terminal Ipv6 mld vrf vrf-namessm-map enable
No ipv6 mld vrf vrf-namessm-map query dns
42-13
Router# show ipv6 mld interface gigabitethernet 0/1
42-14
Router# show ipv6 mld traffic
Router# show ipv6 pim interface
42-15
Router# show ipv6 mld groups summary
Router# show ipv6 pim neighbor count
Router# show ipv6 pim neighbor
42-16
Router# show ipv6 mroute
Router# show ipv6 pim topology
Router# show ipv6 pim topology route-count
42-17
Router# show ipv6 pim group-map FF0EE0111
Router# show ipv6 pim range-list
42-18
Router# show ipv6 pim traffic
Router# show ipv6 pim join-prune statistic
42-19
Following example
Router# show ipv6 mfib status
42-20
Router# show ipv6 mfib summary
Router# show ipv6 mfib interface
Example Configuring IPv6 SSM Mapping
Configuration Examples for IPv6 Multicast
Example Enabling IPv6 Multicast Routing
42-21
42-22
Command Name Description
42-23
Feature Information for IPv6 Multicast
Chapter of the IP Multicast PIM Configuration Guide
42-24
42-25
Chapter of the IP Multicast LSM Configuration Guide
42-26
Configuring Switched Port Analyzer
Span Limitations and Configuration Guidelines
43-1
Understanding Span
Following sections describe Span
43-2
Span Session
Source Interface
43-3
Destination Interface
Configuring Span
Traffic Types
Span Traffic
43-5
Removing Sources or Destination from a Span Session
Enable Configure terminal No monitor session sessionnumber
Configuration Examples for Span
Clears existing Span configuration for a session
Verifying Local Span
Rspan Vlan
43-7
43-8
43-9
Feature Information for Switched Port Analyzer
43-10
IN-1
See BSC
IN-2
IN-3
IN-4
IN-5
IN-6
See MSC
IN-7
IN-8
IN-9
IN-10