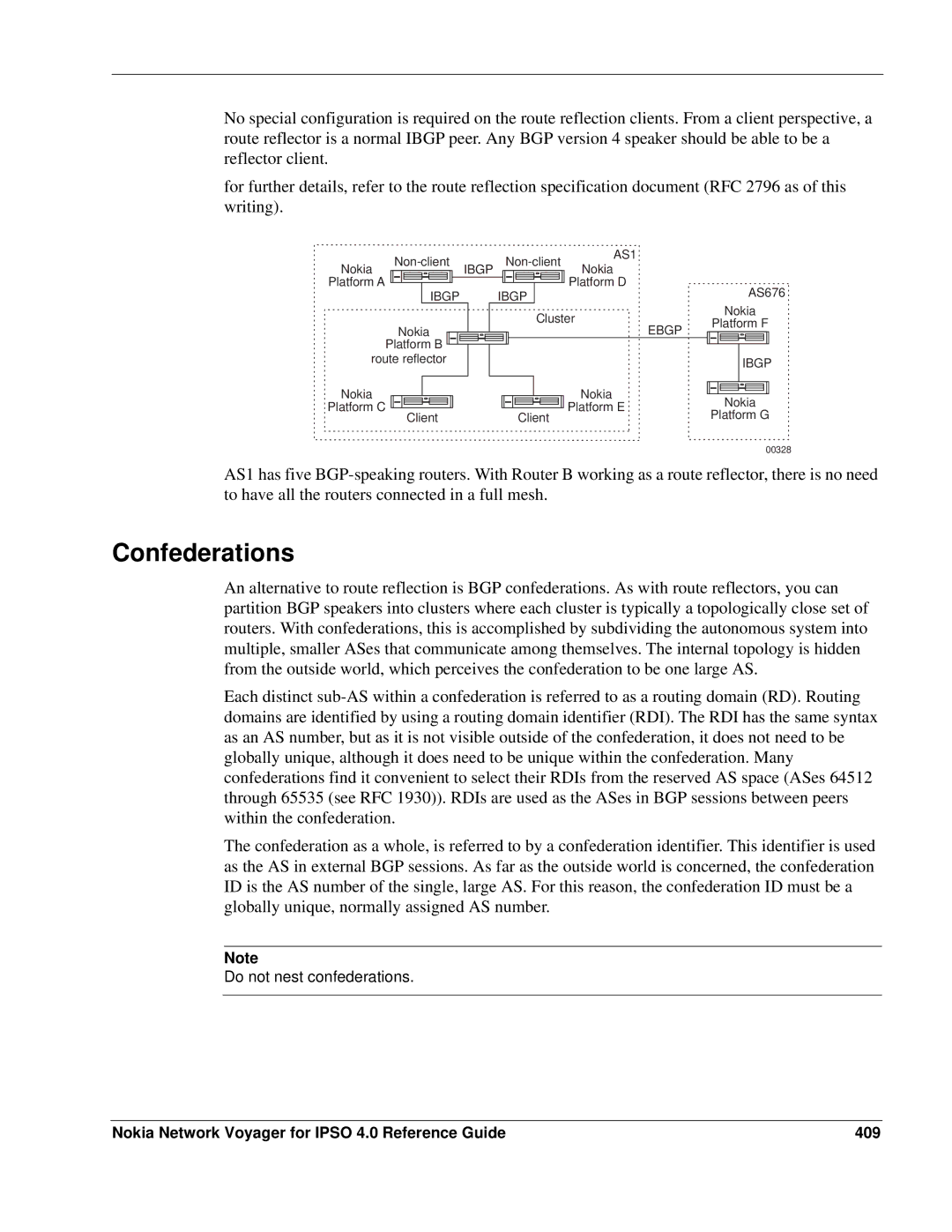
No special configuration is required on the route reflection clients. From a client perspective, a route reflector is a normal IBGP peer. Any BGP version 4 speaker should be able to be a reflector client.
for further details, refer to the route reflection specification document (RFC 2796 as of this writing).
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| AS1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||
Nokia |
|
|
| IBGP |
|
| Nokia |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||||
Platform A |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Platform D |
|
|
|
|
| AS676 | |
|
|
|
|
| IBGP | IBGP |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Cluster |
|
|
| Nokia | ||||||
|
| Nokia |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| EBGP | Platform F | |||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||||||
Platform B |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||||||
route reflector |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| IBGP | |||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||
Nokia |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Nokia |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
Platform C |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Platform E |
|
|
| Nokia | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||||||
|
|
|
| Client |
|
| Client |
|
|
|
| Platform G | |||||||||||||||
00328
AS1 has five
Confederations
An alternative to route reflection is BGP confederations. As with route reflectors, you can partition BGP speakers into clusters where each cluster is typically a topologically close set of routers. With confederations, this is accomplished by subdividing the autonomous system into multiple, smaller ASes that communicate among themselves. The internal topology is hidden from the outside world, which perceives the confederation to be one large AS.
Each distinct
The confederation as a whole, is referred to by a confederation identifier. This identifier is used as the AS in external BGP sessions. As far as the outside world is concerned, the confederation ID is the AS number of the single, large AS. For this reason, the confederation ID must be a globally unique, normally assigned AS number.
Note
Do not nest confederations.
Nokia Network Voyager for IPSO 4.0 Reference Guide | 409 |