MGC Manager
Catalog No. DOC2066F Version
Page
Page
Table of Contents
Monitoring On Going Conferences
Operations Performed During On Going Conferences
Meeting Rooms and Entry Queues
IVR and Entry Queue Services
Table of Contents
VoicePlus Overview
About the MGC Manager User’s Guide VoicePlus Edition
VoicePlus Main Features
Security features
System Requirements
VoicePlus Commands Shortcut Keys
Prerequisites
Command Shortcut Key Function
Ctrl + N
Ctrl + O
Ctrl + C
Ctrl + R
Ctrl + T
Ctrl + M
Ctrl + U
User’s Guide Conventions
F10
F11
F12
VoicePlus Overview
Audio Look & Feel
To set the MGC Manager to Audio Look & Feel
Audio Only Conferences
Default Reservation Templates
Reservation Templates
Reservations in Database Window
Display the Reservations Database window
MGC Manager User’s Guide VoicePlus Edition
Connecting to an On Going Conference
Undefined Dial-in Isdn Participants
Undefined Dial-in H.323 Participants
VoicePlus Overview
About Conferences
Conference Scheduling Methods
On Going Conferences
Attended and Unattended Conferences
Reservations
Unattended Conference
Conference Types
Participants Queue
IVR and Entry Queue Services
MCU Configuration and Audio Only Conferences
Participant Roles
Dial-in Participant
Participant Connection to Conference
Dial-out Participant
Direct Dial-In Access
Network
Entry Queue Access
Dial-in connection via Entry Queue with Numeric ID
IVR Access
Conference Access for Dial-out Participants
Standard with IVR Service Meeting Room with IVR Service
Defining New On Going Audio Conferences
To define an On Going Audio Only Conference
MGC Manager User’s Guide VoicePlus Edition
General Properties
Field/Option Description
MCU
Entry Queue
Number, or any other required information
Properties and is also saved to the CDR file as part
Settings Parameters
General Settings Basic
Encryption
Undefined dial-in participants can connect only if
General Settings Advanced
Between the VTX 1000 and the conference is
Through the WebCommander
Media Settings Basic
Unit
Participants
To add participants to a conference
Conference Properties Participants
Click the Add Participant button
Click the Delete Participant button
Defined as well as undefined participants
To list participants from the database
To add participants from the User Template file
To enable recording for an On Going Conference
Recording
Completing the Conference Definition
Resolving Scheduling Conflicts
Connection Type Conflict Criteria
Participants Scheduling Conflicts Table
To resolve the scheduling conflicts for participants
Participants Scheduling Conflicts table, select an action
Listing On Going Conferences
To view the On Going Conferences
Scheduling a New Reservation
To schedule a new Reservation
Define the following parameters
Conference Properties Settings dialog box appears
Conference Properties Meet Me Per Conf dialog box appears
Defining Recurrent Reservations
To define the recurrence parameters for the reservation
Reservation Recurrence Settings
End After number of Occurrences Specify
To view the Reservations list in the Browser pane
Listing Reservations
Displaying the List of Reservations in the Status Pane
To define the End of Conference Reminder
End of Conference Reminder
Conference End Time Alert dialog box opens
Defining Participant Properties
To define a new participant
Participant Properties Identification dialog box opens
ISDN/PSTN/T1-CAS Participant Definition
10 ISDN/PSTN/T1-CAS Properties and Identification Dialog Box
9SalesExtp345p222p
Audio at connection time is set to 5. One movement
VIP
Optional Click the Advanced tab
Abbreviated Taken from Service. These options
International Network Specific Subscriber
AGC
IP H.323 and SIP Participant Definition
SIP Only
Only
Defaults and loaded to the MGC Manager
VIP, to distinguish participants who require special
IP Participant Properties Advanced dialog box opens
Auto Gain Control AGC mechanism regulates
Participant for a Reservation template in the User
Simple Dial-in Using the IP Card Address
Dialing-in from an H.323 Endpoint
Advanced Dial-in
H.323 Participant Advanced Dial-in
Listing Participants
Monitoring On Going Conferences
General Monitoring
To view On Going Conferences in the Status pane
Listing On Going Conferences in the Status Pane
Click the On Going Conferences icon
Column Name Description
Operator Conference the name
General Conference and Participant Monitoring
Monitoring On Going Conferences
Conference Indicators
Column Icon Indication Description Name
Participant Indicators
Participant or a chairperson
Also displayed in the Status pane. The possible statuses
Resources currently installed
ISDN/T1
Audio Indicates whether the participants audio is connected
Information is cleared when the participant begins to speak
These statuses are primarily used in attended conferences
Participant’s Audio Status
Expand the On Going Conferences list
Monitor Filter
Participant Monitoring Filter dialog box opens
5Monitored Participant Statuses
Filtering Option Description
Automatic Monitoring of Conferences
Secure Conference Mode
To toggle between automatic and manual monitoring
Icon Indication Description
Audio Tones
Noisy Line Detection Mechanism and Automatic Muting
Participants Queue
Conference Level Monitoring
To view the parameters of an On Going Conference
Conference Properties General dialog box opens
Conference Properties Scheduler dialog box opens
Conference Properties Ongoing State dialog box opens
You can view the following parameters
Field/Option Description
Participant Level Monitoring
Monitoring ISDN/Telephone Participants
Participants Properties Identification dialog box opens
Isdn Participant Properties Identification
Participant Properties Connection Info1 dialog box opens
Isdn Network Service configuration
Participant Properties Connection Info2 dialog box opens
Attending
Participant Properties Resource Details dialog box opens
Resource Details
Net Resources
Participant Properties Disconnection Cause dialog box opens
Participant Hang Up The participant
To monitor the status of VoIP participant
Checking the Status of VoIP Participants
Participant’s Properties Identification dialog box appears
Click the Connection Info1 tab
Name Indicates the participant’s name User Defined
14 VoIP Participant Properties Connection Info1
Click the Connection Info2 tab
15 VoIP Participant Properties Connection Info2
Participant Properties H245 tab opens
16 VoIP Participant Properties H245
H.323 Participant Properties Disconnection Cause tab opens
Video
Operations Performed During On Going Conferences
Attended Conferences
Management Functions Overview
Unattended Conferences
Participant Level Operations
Participant and Conference Level Operations
Conference Level Operations
Operations Performed During On Going Conferences
Making Dial-Out Connections
Participant Level Operations
To establish a dial-out connection
Changing Participant Connection Types Dial-In/Dial-Out
To toggle between Connection Types
Disconnecting Participants from Conferences
To disconnect a participant
To delete a participant
Naming Undefined Dial-in Participants
To name a Meet Me dial-in participant
Right-click the participant icon, and then click Properties
Changing the Disconnected Participant’s Properties
To move participants using the right-click menu
Moving a Participant from one Conference to Another
Designating an Exclusive Speaker
Changing Participant’s Status to Conference Chairperson
To change a participant’s status to conference chairperson
To revert the chairperson’s status to regular participant
Designating a VIP Participant
To designate a participant as a VIP
Adjusting Participant’s Broadcasting and Listening Volume
To revert the VIP status to regular participant
Muting and Unmuting Participant’s Audio
Using the participant right-click menu
To mute/un-mute participant’s audio
From the Participant Properties dialog box
Participants Properties Connection Info2 dialog box opens
Enabling/Disabling Auto Gain Control AGC
Modifying the Participant’s User Defined Properties
Conference Level Operations
Adding New Participants to a Conference
Using the Conference right-click menu
Participant Properties dialog box opens
From the Conference toolbar
From the Conference Properties dialog box
Conference Properties Participants dialog box opens
MGC Manager User’s Guide VoicePlus Edition
Operations Performed During On Going Conferences
MGC Manager User’s Guide VoicePlus Edition
To activate the Mute Meet Me Parties feature
Muting Dial-In Participants Upon Connection
To cancel the Mute Meet Me Parties feature
Adding Remarks During an On Going Conference
Click Update Remark
To enter and save a remark during an On Going Conference
Locking and Unlocking a Conference
Using the Conference toolbar
To lock and unlock an On Going Conference
From the Conference Properties dialog box
Operations Performed During On Going Conferences
Managing Question-and-Answer Sessions
Controlling Q&A Queues with the Toolbar
Q&A toolbar contains the following buttons
Function Button Description
MGC Manager User’s Guide VoicePlus Edition
Operations Performed During On Going Conferences
Changing Participant’s Position in Q&A Queue
To change the participant’s position in the Q&A queue
Ending Participant Questions
Removing Participants from the Q&A Queue
To remove a participant from the Q&A queue
Managing Voting Sessions
To end the Q&A session and clear the queue
Conducting a Voting Session
To manage a voting session conference
Command buttons let you select optional operations
Click Start Voting
Choices
Voting Results Parameters
Viewing and Saving Voting Results
To view voting results
To save the voting results file
Placing a Conference On Hold
To view the voting results file
To place an On Going Conference On Hold
MGC Manager User’s Guide VoicePlus Edition
Modifying Conference General Parameters
To modify the conference general parameters
To manually extend an On Going Conference
Changing the Conference Duration
Open the Conference Properties dialog box
Ending a Conference before its Scheduled Termination Time
To manually terminate a conference manually
To reschedule a conference reservation
Rescheduling Conference Reservations
Reservation Properties dialog box opens
Deleting Recurring Reservations
To delete a single recurring reservation
Using the Reservations right-click menu
Using the Recurrent Reservation right-click menu
To delete all recurring reservations
Printing Conference Data
To print details of a single conference
MGC Manager User’s Guide VoicePlus Edition
Operations Performed During On Going Conferences
To print details of all On Going Conferences or Reservations
Managing Conferences Using Dtmf Codes
Dtmf Guidelines
Secure conference
New voting session
Enable Roll Call
Service Dtmf Codes dialog box. The same
Override Mute All But Me
Unmute and Return to Conference
Using Dtmf Codes in Cascading Conferences
Modifying Conference and Chairperson Passwords
User Action IVR Message
Dialing Out to Invite Participants Invite Session
Request Dtmf Help Menu
To invite participants to join the conference
Chairperson Initiated Blast Dial-out
Roll Call
Managing Secure Mode Conferences
Roll Call Guidelines
Operation Default Description
Code
Operations Performed During On Going Conferences
Meeting Rooms and Entry Queues
Meeting Rooms
Entry Queues
MGC Manager User’s Guide VoicePlus Edition
Defining a New Audio Only Meeting Room
To define a new Meeting Room
Click the Settings tab
Click the Meet Me Per Conf tab
Plus
Click the plus
To define Meet Me ISDN/T1-CAS Services
Option Description
To assign the H.323 Service Prefix to the conference
Field/Option Parameter
To view the Meeting Rooms list in the Browser pane
Listing Meeting Rooms
To view the Meeting Rooms list in the Status pane
Meeting Rooms and Entry Queues
Defining a New Audio Only Entry Queue
To define a new Audio Only Entry Queue
Entry Queue Properties dialog box opens
To automatically assign the Numeric ID
Ad Hoc Conferencing and External
Enabling Encryption for Entry Queues
To manually assign Dial-in numbers to the Entry Queue
Listing Entry Queues
Dialing in to an Entry Queue
To view the list of Entry Queues in the Browser pane
To view the list of Entry Queues in the Status pane
Participant
MGC Manager User’s Guide VoicePlus Edition
Meeting Rooms and Entry Queues
IVR and Entry Queue Services
Conference Access
Directly
Operations Performed Using IVR Services
IVR/Entry Queue Stages
Dtmf Enabled Action Permission
Using Roll Call
Using SilenceIT
Conference On Hold
Admittance during a Roll Call
No Other Participants Indication
Enabling SilenceIT
Hardware
IVR Requirements
Audio File Conversion
Defining IVR Software Module Properties
Expand the MCU Configuration tree
To define the IVR Properties
To download Audio Message files
Message Message Type Description Category
Conference when performing various operations, such as
Roll Call option is enabled for a conference
Been detected as noisy and has
MGC Manager User’s Guide VoicePlus Edition
Defining a New IVR Message Service
Setting IVR Message Services
To define a new IVR Message Service
IVR Service Properties Global
To determine if the system should request
MGC Manager User’s Guide VoicePlus Edition
IVR Service Properties Welcome Message
Select the appropriate audio files and options
Click Next Conference Password dialog box opens
IVR Service Properties Conference Password
Field/Option Description
Message Type Message Description
To end and cannot be extended
Anytime
Participant Menu
IVR Service Properties Operator Assistance
Click Next Roll Call dialog box opens
From the drop-down list, select the appropriate audio file
Roll Call Description Message
Roll Call Description Message
SilenceIT Description Message
Noise detection level and return to the conference
MGC Manager User’s Guide VoicePlus Edition
Listing IVR Message Services
To list the IVR Message Services
Setting an IVR Message Service as Default
To select the default IVR Service
Modifying IVR Message Service Properties
To modify the properties of an IVR Service
Assigning IVR Services to Conferences
To assign an IVR Service to an Audio Only conference
Defining a New Entry Queue Message Service
To set the new Entry Queue Message Service
Entry Queue Message Service dialog box opens
IVR
Option Description
12 IVR Properties Welcome Message
13 Entry Queue Properties Conference ID
ID or password
14 IVR Properties Operator Assistance Messages
Assigning Entry Queue Services to an Entry Queue
Connecting to a Conference from an Entry Queue
Viewing the Audio Messages Status
To view the status of the audio messages
Messages Occupancy pane shows
Printing IVR/DTMF Codes
Expand the IVR Message Services tree
To print the list of Dtmf codes
IVR and Entry Queue Services
Default IVR Prompts and Messages
Message Type Message Text File Name
PINRQST.ACA
NEWINVLD.ACA
SELFMUTE.ACA
LDRHP1A.ACA
PRTCHP.ACA
INVITHP.ACA
NAMERCRD.ACA
SLNRTMUT.ACA
IVR and Entry Queue Services
Attended Conferencing
Attended Conferencing
Requirements for an Attended Conference
Entity Description
Wait for operator
Assistance
Defining an Operator Conference
To define an On Going Operator conference
Conference Properties Settings dialog box opens
Conference Properties Participants dialog box opens
Attended Conferencing
Setting the Entry Queue to Attended Mode
Setting the Conference Connection to Attended Mode
Participants Queue Management
To display the Participants Queue window
Listing Participants in the Participants Queue Window
Column Description
From the conference to the Participants Queue or
Participant Queue Filter Toolbar
Participants Queue Toolbar
Button Function Description
Using Participants Queue Filters
To define Participants Queue filters in the Database
Click the Participants Queue Filter button
Participants Queue Filter dialog box opens
Participant Status in Participants Queue
Dial-In Numbers
Field/Option Description
Filter Name
Field/Option Description Actions
Public Filter Name
To modify a filter
To use filters
To delete a filter
Attended Participants Dialog Box
To move a participant to the Operator conference
Field/Option Description Attended Participant
Field/Option Description
Operator
Conferences
Ongoing meetings + 12h reservations
All Ongoing Meetings + 12h + MRs
Actions
VIP + Requested Help + Time Participants
Automatically moved to the Operator conference for
Move To Home Conf
To connect a participant to his/her destination conference
To move a participant to the Home conference
MGC Manager User’s Guide VoicePlus Edition
To place a participant On Hold
To join a conference as operator
To end the Join state of the operator
Selecting the Participants to Manage
Browser, Status, and Monitor pane, On Going Conference list
MGC Manager User’s Guide VoicePlus Edition
Performing Operations using the Right-Click Menu
Moving a Participant to the Operator Conference
Moving a Participant to the Home Conference
Using the To Home Conference option in the right-click menu
Using the Move option in the right-click menu
Placing a Participant On Hold
To place a participant on Hold in the Operator conference
MGC Manager User’s Guide VoicePlus Edition
Performing Operations Using the Participants Queue Toolbar
Button Operation
Performing Operations Using Shortcut Keys
Moving a Participant Interactively
Moving Multiple Participants to the Home Conference
To drag and drop a participant to the Operator conference
To drag and drop a participant to the Home conference
Using the Participants Queue toolbar
Attended Conferencing
Recording
System Setup
Recording
Recording System Setup Procedures
Conferencing MCU Setup
ReadiRecorder to
ReadiRecorder
Setting up Recording for Conferences
Defining a Recording Link
To define a new recording link
Isdn
Alias and Recording Service Name The H.323
URL ID
Defining Recording Functions in IVR Service
To define recording functions for an IVR Service
Default service
Enabling Recording for a Conference
To enable recording for a conference
Conference Properties Recording dialog box opens
Recording
Recording with MCU Version
To enable recording
Conference Properties- Participants dialog box opens
Recording
From the Conferencing Service
Recording and Playback Using Prairie Systems
From Prairie Systems
Defining a Recording Port Participant
To define a dial-out recording port
MGC Manager User’s Guide VoicePlus Edition
Participant Properties Advanced dialog box opens
To record a conference
To stop recording
To initiate a playback of a Prairie recording
Modifying System.cfg
SysConfig system.cfg dialog box opens
To modify the ReadiRecorder system.cfg
Audio Plus
External DB
General
Recording
Conferencing MCU system.cfg flags
Immediately, that is
Recording
Appendix a Glossary
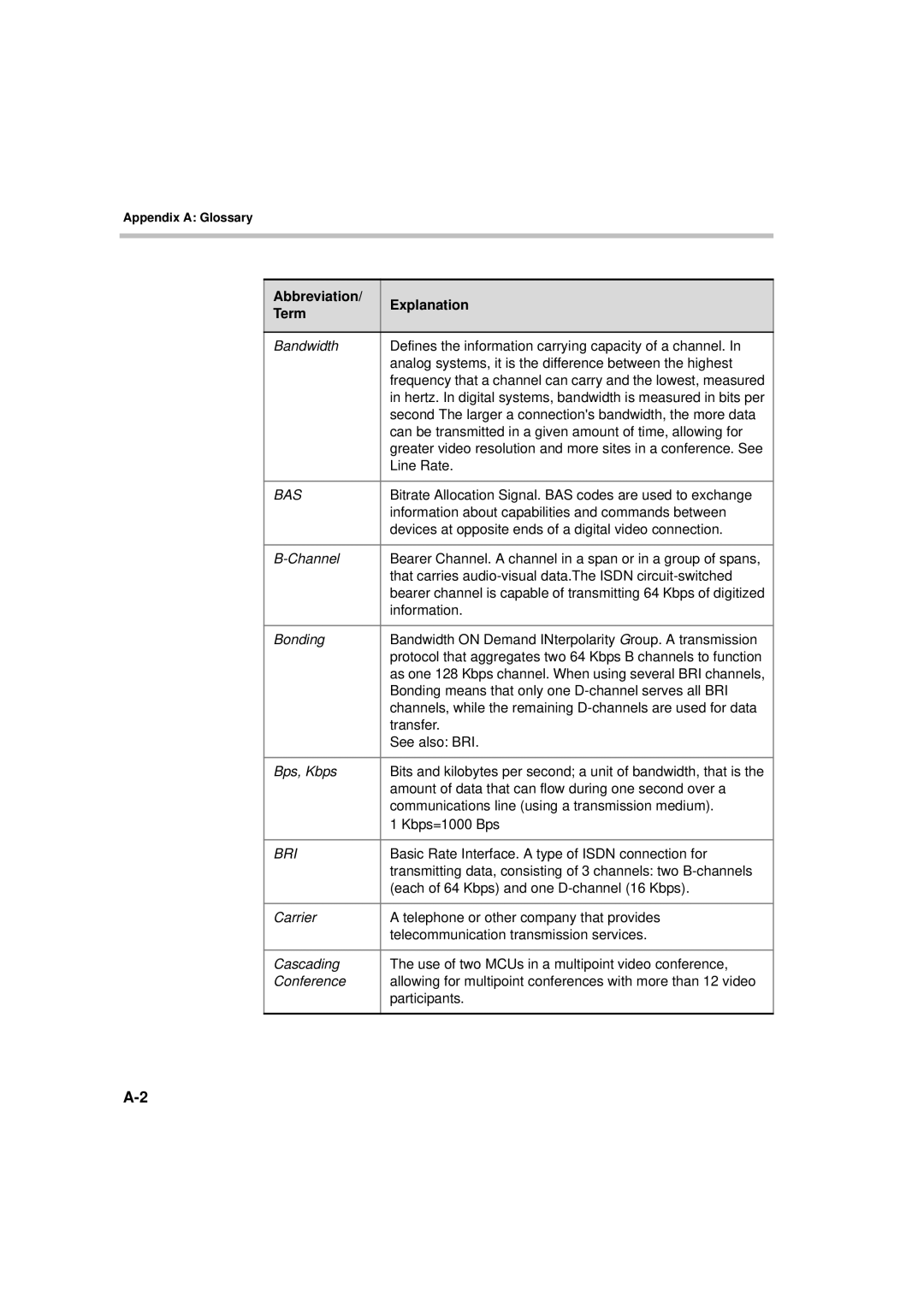
Abbreviation Explanation Term
BAS
CAS
Procedures and describes network maintenance functions
LAN
Pots
WAN
Appendix a Glossary