IBM
Page
IBM
Ninth Edition November
Research Triangle Park NC USA
Contents
Part 2. Understanding, Conguring, and Using Base Services
Conguration Process Config Talk 6 and Commands
Conguring and Monitoring the Config Process
Protocol Qcong Set Time Unpatch Update
Boot Config Process
Conguring Boot Config
Using the Event Logging System ELS
Operating/Monitoring Process Gwcon Talk 5
Messaging Monitr Talk 2 Process
145
Conguring and Monitoring the Event Logging System ELS
Part 3. Understanding, Conguring and Operating Interfaces
Conguring and Monitoring Performance
Getting Started with Network Interfaces
Conguring Ieee 802.5 Token-Ring Network Interfaces
Using the Ethernet Network Interface
Conguring and Monitoring the Ethernet Network Interface
Overview of LAN Emulation
Conguring and Monitoring ATM
Using LAN Emulation Clients
Using the X.25 Network Interface
Conguring and Monitoring LAN Emulation Clients
Conguring Serial Line Interfaces
XTP Conguring Commands 375 Add Change 378
Conguring and Monitoring the X.25 Network Interface
327
Conguring and Monitoring XTP
Using Frame Relay Interfaces
387
Conguring and Monitoring Frame Relay Interfaces
405
Using Point-to-Point Protocol Interfaces
Conguring and Monitoring Point-to-Point Protocol Interfaces
Using the Multilink PPP Protocol
Using Sdlc Interfaces
Conguring and Monitoring Multilink PPP Protocol MP
Conguring Sdlc Relay
Using Binary Synchronous Relay Brly
Using the V.25bis Network Interface
Conguring and Monitoring BSC Relay
Conguring and Monitoring the V.25bis Network Interface
Using the V.34 Network Interface
Using the Isdn Interface
Conguring and Monitoring the V.34 Network Interface
Conguring and Monitoring the Isdn Interface
Conguring and Monitoring Dial Circuits
Appendix A. Quick Conguration Reference
Appendix B. X.25 National Personalities
Appendix C. Making a Router Load File from Multiple Disks
Readers Comments Ð Wed Like to Hear from You
Figures
Xix
Xx MRS V3.2 Software Users Guide
Tables
Xxi
Xxii MRS V3.2 Software Users Guide
Xxiii
Xxiv MRS V3.2 Software Users Guide
Resulting from this authorization
For online versions of this book, you are authorized to
All other copies of the documentation
Exclusion may not apply to you
Xxvi MRS V3.2 Software Users Guide
Trademarks
Xxviii MRS V3.2 Software Users Guide
Preface
Who Should Read This Manual
About the Software
Xxix
Conventions Used in This Manual
IBM 2210 Nways Multiprotocol Router Publications
Separately from the device as part of the software order
Ctrl-P
Safety SD21-0030
Operations and Network Management SC30-3681
SC30-3992
SC30-3680
Planning and Installation GA27-4068
GC30-3867
Summary of Changes
Moved into the Using and Conguring Featuresbook
Editorial Changes
Clarications and corrections
Part 1. Understanding and Using the Software
MRS V3.2 Software Users Guide
Accessing the Software Using Local and Remote Consoles
Getting Started
Before You Begin
Migrating to the Current Release
Local Consoles
Remote Login Names and Passwords
Remote Consoles
Logging In Remotely or Locally
Telnet Connections
Reloading or Restarting the Router
Exiting the Router
Discussing the User Interface System
Understanding the First-Level User Interface
Quick Conguration Process
System Security
Same as the Opcon process
Automatically starts Cong-Only and then enters Quick Cong
Using the Software
Entering Commands
Connecting to a Process
Status
Identifying Prompts
Getting Help
Exiting a Lower Level Environment
Getting Back to Opcon
Some Conguration Suggestions
Creating a First Conguration
Basing a Conguration on an Existing Conguration
Basing on an Existing Conguration
Accessing the Second-Level Processes
Permanently Updating a Conguration
Temporarily Updating a Conguration
Accessing the Conguration Process, Config Talk
Entering the Config Process
Restarting or Reloading the Router
Are you sure you want to restart the router? Yes or No yes
Accessing the Operating/Monitoring Process, Gwcon Talk
Accessing the Third-Level Processes
Entering the Gwcon Command Process
Accessing the Network Interface Conguration Process
Config list devices
Following example adds a dial circuit interface
Following example adds a dial-in circuit
Following example adds a dial-out circuit
Architecture
Accessing the Network Interface Console Process
Network Architecture Supported Interfaces
Accessing Feature Conguration and Operating Processes
Accessing Protocol Conguration and Operating Processes
Accessing the Feature Processes
Entering a Protocol Conguration Process
Config protocol IP
+configuration
Entering a Protocol Operating Process
+ protocol
Command History for Gwcon and Config Command Line
Repeating a Command in the Command History
Enter
Ctrl-Bfor Backward, and the current line is replaced with
Repeating a Series of Commands in the Command History
Starting a Repeat Sequence As Commands Are Entered
Example
Starting a Repeat Sequence After All Commands Are Entered
Enter the following commands in Gwcon
MRS V3.2 Software Users Guide
Opcon Process
MRS V3.2 Software Users Guide
Using Opcon
Accessing the Opcon Process
Opcon Commands
Breakpoint
Divert
Syntax Breakpoint
Syntax Divert
Flush
Halt
Intercept
Logout
Memory
Pause EasyStart only
Memory Example
Syntax pause Example
Memory
Reload
Restart
Status
Stop EasyStart only
TTY1 or TTY2
Two dashes
Comments
Talk
Telnet
Syntax Talk
Example talk
Three clients outbound from the router
Syntax Telnet
Ip-address terminal-type
Display
Not connected to a host
Send ayt
Part 2. Understanding, Conguring, and Using Base Services
MRS V3.2 Software Users Guide
Conguration Process Config Talk 6 and Commands
What is CONFIG?
Using EasyStart
Using the Config Talk 6 Process
Configclear all
Configclear device
Cong-Only Mode
Automatic Entry Into Cong-Only Mode
Manual Entry Into Cong-Only Mode
Boot to Cong-Only mode
Quick Conguration
Automatic Entry Into Quick Cong Mode
Manual Entry Into Quick Cong Mode
Exiting from Quick Cong Mode
Conguring User Access
Technical Support Access
Conguring Spare Interfaces
Add a dial circuit using the add device command
Commands
Access the Gwcon process by entering talk
Restrictions for Spare Interfaces
Activate them on the network using the activate command
IPv6
OSI/DECnet
Resetting Interfaces
Restrictions for Resetting Interfaces
Talk 6 Confignet 1 PPP Config
Configprotocol ipx
Talk 5 +reset
DNA
Using the Config Talk 6 Process
Conguring and Monitoring the Config Process
Entering and Exiting Config
Config Commands
Enter the Opcon talk command and the PID for Config
Config Commands
Address-name
Network-dial-address
Network-subdial-address
Ppp-user
Password
Allow inbound access
Default value no
Default value
Default value none
Net-Route Mask
Hostname
Time-Allotted
Conguring Features
Disable user
Example with ECP encryption
Tunnel tunnel-name
Set shared secret
Shared Secret
Tunnel-Server endpoint address
Enter password
Enter password again
Do you want to add Technical Support access?
Enter permission
Boot
Syntax Boot
Change
Device dial-circuit
Enter current password
Enter new password
Enter new password again
Syntax Change pppuser Encryption-key Parameters Password
Clear
Tunnel-prole
Syntax Clear
Wrs WAN Restoral feature
Command
Default value is ªdisabledº
Ip IP
Delete
Example clear els
Syntax Delete
Isdn-address address-name
Disable
Enable
Enable Console-login Interface Modem-control
Modem-control carrier-wait or ring-wait service1 or service2
Environment Commands
Environment Command Summary
Environment
Syntax Environment
Event
Feature
Syntax Feature
Feature# or feature-short-name
List
Tunnel-prole Users V25-bis-address V34-address
Devices device or devicerange
Conguration
Displays conguration information about the router
Isdn-address
Displays the current Isdn address congurations
Patches
Pppusers
Call callback
Dial dialback
Encr encryption
Tunnel Name
Network
Patch
Networkinterface#
Syntax Patch
Ip-default-ttl #ofpackets
Valid Values 0 to Default Value Ospf-import-rate rate
Bgp-subnets new value
Dls-ignore-lfs new value
Performance
Protocol
Qcong
Set
Syntax Qcong
Baud-rate
Conguration command
Interface#
# of seconds
Global-buffers max#
Inactivity-timer #ofmin
Logging disposition setting
Only to increase it
Prompt-leveluser-dened-name
Additional functions as described in Table
Set prompt
Time
Receive-buffers interface# max#
Spare-interfaces n
Syntax Time
Update
Valid values -720 to Default value
Unpatch
Offset minutes
Config Commands
Config Commands
Boot Config Process
What is Boot CONFIG?
Conguring Booting
Using a Device as a Boot Server
How the Bootp Forwarding Process Works
Device as a Bootp Client
Using the Boot Config Process
Device as a Bootp Relay Agent
Enabling/Disabling Bootp Forwarding
Conguring a Bootp Server
IP Config enable bootp IP Config disable bootp
Using the Trivial File Transfer Protocol Tftp
IP Config add BOOTP-SERVER IP address of server
Accessing Conguration Files From a Remote Host or Router
Filename Denitions for IBD
Example 1 test.cfg
IBD Considerations When Transferring a File
Validating the Conguration Load
Conventions for File Name Extensions
Type of File Filename Extension
Tftp Server, Boot and Dump Directories
Loading an Image at a Specic Time
Conguring Dumping
Dump Files
Installing Software/Code
Status
Talk
Boot config list boot-entries
Enter exit
Using the Boot Config Process
Conguring Boot Config
Entering and Exiting Boot Config
Boot Config Commands
Boot Config Commands
Boot-entry
Add
Syntax Add
Address
Add Boot Entry Parameters
Bp-device
Loads/name
Changeaddress Boot-entry Bp-device Dump-entry
Dump-entry
Add dump-entry
File name ? c\dump\gertrude.dmp
Change address
Change bp-device Change which entry 1?
Change dump-entry
Copy
Removes the specied interface as a Bootp device
Ibd or lename
Address #
Disabledumping Unique-naming
Describe
Describeloadname
Loadname
Erase
Unique-naming
Syntax Erase
Loadname or bank-number
Addresses
Boot-entries
Displays the boot le conguration
Dump-entries
List bp-device
Load
Syntax Load Local Remote
Local loadname
List view
Store
Timedload
Deactivate
Example 1. Deactivate time activated load
Example 1. Load image source is a remote host
Example 2. Load image source is the IBD
Syntax Tftp Get Put
Local lename
Remote Host
Host lename
Console display is the same as the Tftp get command
Local lename?
Remote Host?
Host lename?
MRS V3.2 Software Users Guide
Boot Options
Description of Boot Methods
Boot Method Description
111
Bootp Using a Console Terminal
Unsuccessful Bootp
* indicates that the load image has nished loading
Booting from a Tftp host server using a console terminal
Boot Options Available
Accessing the Boot Options
Boot Option Prompts
Boot Options
Option Name Description
Boot Option Prompts
Prompt Description
Ethernet Prompts
Token Ring Prompts
BC Boot in Cong-only Mode
If you enter IBD, you see the following
To reload the current conguration, pressEnter
BM Boot using console queries
If you enter Ethernet, you see the following
If you enter Ethernet, you see the following
BN Boot, But Do Not Run, Using Console Queries
BP Boot using Bootp
Dump using stored conguration
Diag Execute IBM Extended Diagnostic Program
DM Dump using Console Queries
UB Display Tftp Boot Conguration
This option is used only by your service representative
UC Display Hardware Conguration
UG Go execute at address in RAM
LC Load Conguration Memory
If you enter Token Ring, you will see the following
If you enter WAN, you see the following
ZB ZModem Boot
CC Clear Conguration Memory
ZC ZModem conguration memory load
Enter y and the console displays the message
Conguring
MRS V3.2 Software Users Guide
Operating/Monitoring Process Gwcon Talk 5 and Commands
What is GWCON?
Gwcon Commands
Entering and Exiting Gwcon
Syntax boot Example
Gwcon Command Summary
Activate
Gwcon Process
Buffer
Syntax Buffer
Network# or rangeofnetwork#
Interface
Conguration
Bytes Alloc
Interface# or rangeofinterface#
Syntax Conguration
Configuration
MAC/Data Link
Type of MAC/Data link congured for the interface
Hardware
Testing
Disabled
State Current state of the network interface
Available
Disableinterface#
Not Present
HW Mismatch
Error
Syntax Error
Input Errors
Input Discards
Fault
Interface
Log
Physical installed memory
Syntax Log
Syntax memory Example
Total routing memory
Reserve
Never Alloc
Perm Alloc
Temp Alloc
X.25 interface by entering the X.25 operating commands
For the following network and link-layer interfaces
Bisync BSC
Ethernet
Queue
Queue
Reset
Statistics
Test
Uptime
Bytes Trans
Number of bytes transmitted at the MAC layer
Syntax Uptime
Gwcon Process
What is Messaging MONITR?
Commands Affecting Messaging
Messaging Monitr Talk 2 Process
Entering and Exiting the Messaging Monitr Process
Messaging Monitr
Using the Event Logging System ELS
What is ELS?
ELS is a subprocess that you access from the Opcon process
147
Using ELS
Entering and Exiting the ELS Conguration Environment
Event Logging Concepts
Causes of Events
Interpreting a Message
Subsystem
Event Number
Logging Level
Packet Completion Codes Error Codes
Message Text
Logging Levels
Logging Level Type
Using ELS
To delete a group, use the delete command
Groups
ELS displays network information as follows
See ªUsing ELS Message Bufferingº on
Managing ELS Message Rotation
Following message is displayed
Using ELS to Troubleshoot a Problem
Conguring ELS So Event Messages Are Sent In Snmp Traps
ELS Example
Display subsystem srt all Display subsystem br all
Talk
Using and Conguring ELS Remote Logging
Syslog Facility and Level
Remote Workstation Conguration
Using ELS
Conguring the 2210 for Remote Logging
Syslog.conf Conguration File
ELS configset remote source-ip-addr
ELS configset remote remote-ip-addr
ELS configset remote local-id ** IBM/2210
ELS configset remote no-msgs-in-buffer
Remote Logging Output
Conguring Subsystems and Events for Remote Logging
Sample Contents from Syslog News Info File
Msg
Output from Talk
Additional Considerations
ELS Messages Containing IP Addresses
Using ELS Message Buffering
Duplicate Logging
Recurring Sequence Numbers in Syslog Output Files
None
Using ELS
MRS V3.2 Software Users Guide
Accessing the ELS Conguration Environment
ELS Conguration Commands
ELS Conguration Command Summary
Conguring and Monitoring the Event Logging System ELS
ELS Conguration Commands Talk
Groupname subsystem.eventnumber
Conrm the creation of a new group
This environment you congure message buffering
Default
Display
Filter
Syntax Filter Net
Lter-status
Groups
Subsystem
Subsystem subsystem
Lists all events in a specied subsystem
Subsystems all
Nodisplay
Noremote
Trace-status
Nodisplayevent Group Range Subsystem
Noremoteevent Group Range Subsystem
Group group.name
Subsystem subsystem.name syslogfacility sysloglevel
Suppresses the remote logging of all ªtkrº messages
Notrace
Notrap
Notraceevent Group Range Subsystem
Syntax Notrap
Remote
Remoteevent Range Group Subsystem
Notrap range gw 19
Remote range gw 19 22 loguser loginfo
Remote subsystem TKR all loguser loginfo
Group group.name syslogfacility sysloglevel
Pin maxtraps
Remote-logging
Syntax Set remote-logging
Facility
No-msgs
Remoteipaddr
Sourceipaddr
Localid
Default-bytes-per-pkt bytes
Timestamp timeofday or uptime or off
Timeofday
Syntax Set trace
Trace
Stop-event event id
Wrap-mode off or on
Syntax Trace
ELS Net Filter Conguration Commands
Trap
Syntax Trap
Trap range gw 19
Create
Syntax Create queue
Disable
Enable
Delete
ELS Message Buffering Conguration Commands
List
Log
All
Nolog
Syntax Nolog
Set
Default value off
Entering and Exiting the ELS Operating Environment
Stop string text or none
Wrap on or off
ELS Monitoring Commands
ELS Monitoring Commands Talk
Advanced
Environment you change message buffering operation
Files
Event subsystem. event#
Subsystem subsystem.name
Displays messages for the specied event subsystem.event#
Syntax Les trace tftp
HostIPaddr
Lename
Syntax Lter Net
Groups group.name
List event ip.007
List pin
List subsystem eth
Subsystem all
Occurred on the router
Run-time information
Suppresses the displaying of messages for the specied event
Level, such as there is with Remote
Syntax Notrace
Suppresses the display of the specied tracing event
Gw.21, and gw.22
Subsystem subsystemname logging-level
Notrap subsystem tkr error
Packet Trace
Syntax Packet-trace
Remoteevent Group Range Subsystem
Remote event gw.019 loguser loginfo
Syslogfacility
Sysloglevel
Restore
Syntax Restore
Remove
Retrieve
Save
Syntax Retrieve
Syntax Save
Facility
Timestamp
Syntax Set timestamp Timeofday or uptime or off
Decode off or on
Wrap-mode off/on
Syntax statistics
Example statistics
Not
Subsys
Name of subsystem
Vector
View
Syntax View
Off
Current
Syntax Off
Reset
Subsystems
Syntax Subsystems
ELS Net Filter Monitoring Commands
Trace-Status
View
Syntax Trace-status Example
ELS Net Filter Monitoring Commands
Syntax Create queue
All Enable all currently congured lters
All Lists all currently congured lters
Lists the lter specied bylter#
ELS Message Buffering Monitoring Commands
ELS Message Buffering Monitoring Commands
Flush
Release the buffer memory for other use by the system
Nolog
Buffer-size Mbytes
Buffer-size Mbytes
Command to a remote host
New messages at the beginning of the buffer on
Buffer formatted destipaddress destlename
System prompts you for it
Scroll
Noscroll
Number
Accessing the Performance Conguration Environment
Conguring and Monitoring Performance
Performance Overview
Performance Reporting Accuracy
Performance Conguration Commands
Perf Conguration Command Summary
Talk 6 Config
T2 output
Accessing the Performance Monitoring Environment
Performance Monitoring Commands
Performance Conguration Commands Talk
Settime
Performance Monitoring Commands Talk
Report
Syntax report Example
Time
Performance Monitoring Commands Talk
Part 3. Understanding, Conguring and Operating Interfaces
221
MRS V3.2 Software Users Guide
Network Interfaces and the Gwcon Interface Command
Getting Started with Network Interfaces
Before You Continue
223
Dening Spare Interfaces
Getting Started with Network Interfaces
Accessing the Token-Ring Interface Conguration Process
Token-Ring Conguration Commands
Token-Ring Conguration Command Summary
Conguring Ieee 802.5 Token-Ring Network Interfaces
Packet-Size
Conguring Token-Ring Network Interfaces
Syntax Set Physical-address Rif-timer
Set rif-timer
Source-routing
Token-Ring 4/16 Valid Packet Sizes
Accessing the Interface Monitoring Process
Speed
Token-Ring Interface Monitoring Commands
Token-Ring Monitoring Command Summary
Dump
Syntax dump Example
Token-Ring Interfaces and the Gwcon Interface Command
Statistics Displayed for 802.5 Token-Ring Interfaces
Self-Test Pass
Self-Test Fail
Using the Gwcon Interface Command
# of times signal lost
Hard errors
Auto-removal errors
Ring recovery actions
Lobe wire faults
Burst errors
Token errors
Removes received
Using the Gwcon Interface Command
Accessing the Interface Conguration Process
LLC Conguration Commands
LLC Conguration Command Summary
Conguring and Monitoring LLC Interfaces
Conguring LLC
T1-reply-timer
N2-max-retry
N3-framesrcvd-before-ack
Rw-receive-window
T2-receive-ack-timer
Ti-inactivity-timer
Tw-transmit-window
LLC Monitoring Commands
Clear-Counters
Monitoring LLC
Syntax Clear-counters
SAP value in hex 0FE
MAX I-eld Size N1
Rcvd I-frame before ACK N3
Transmit Window Size Tw
Disconnecting
Frames refused by LLC user
Cumulative number of sessions
Number of active sessions
Resetting
RemoteBusy
FRMRReceived
Session
Access Priority
Session Id
Remote MAC addr
Source MAC addr
Current send seq Vs
Current Rcv seq Vr
Last ACKd sent frame Va
No. of frames in ACK pend q
N2-maxretry
N3-frames-rcvd-before-ack
Monitoring LLC
Using the Ethernet Network Interface
247
Number of self-tests that succeeded
Number of self-tests that failed
Using Ethernet Network Interfaces
Failed, carrier check or failed, carrier sense error
CD heartbeat error or SQE test error
Internal mac tx errors or internal MAC trans errors
Multiple collisions
Using Ethernet Network Interfaces
Accessing the Ethernet Interface Conguration Process
Ethernet Conguration Commands
Ethernet conguration prompt ETH Config, is displayed
Conguring and Monitoring the Ethernet Network Interface
Connector-Type
Ethernet Conguration Commands Talk
IP-Encapsulation
Physical-Address
Accessing the Ethernet Interface Operating Process
Ethernet Interface Monitoring Commands
Ethernet monitoring command Summary
Collisions
Ethernet Interface Monitoring Commands Talk
Syntax collisions Example
Overview of LAN Emulation
LAN Emulation Benets
255
Simple LAN Emulation Network
LAN Emulation Components
Overview of LAN Emulation
Physical Network Logical Network
Addressing in ATM
Broadcast and Unknown Server BUS
ATM uses 20-byte hierarchical addressing
ESI
ATM Addresses of LAN Emulation Components
Manual Conguration of the Signaling Version
Locating the Lecs Using Ilmi
Overview of Related Ilmi Functions
Overview of the Lecs Function
Overview of LAN Emulation
Sample Situations for Use of the Lecs Assignment Policies
ATM Address Policy
LAN Destination Policy
Elan Name Policy
More Information About TLVs
Elan Type Policy
Max Frame Size Policy
Duplicate Policy Values
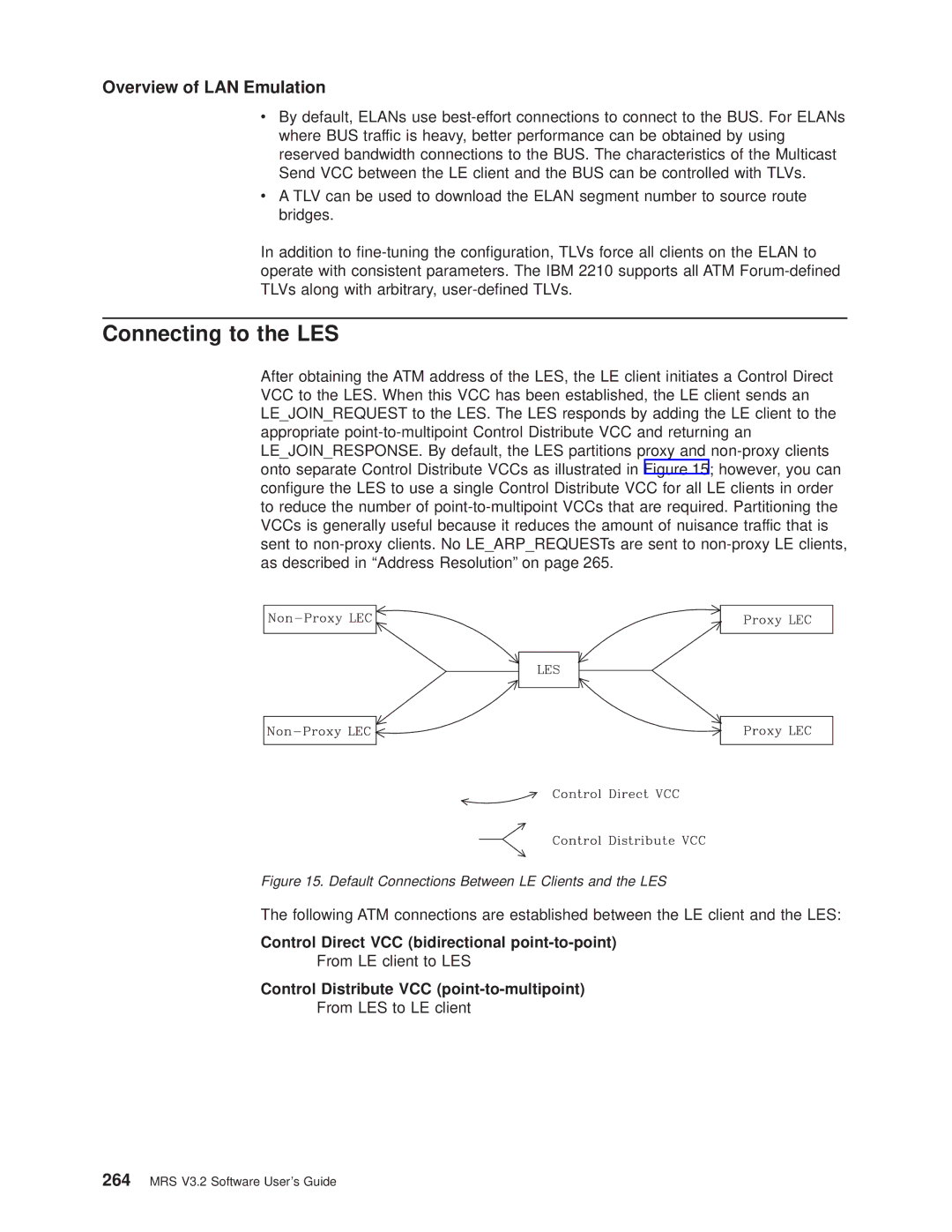
Connecting to the LES
Control Direct VCC bidirectional point-to-point
From LE client to LES
Control Distribute VCC point-to-multipoint
Address Resolution
Connecting to the BUS
Address Registration
BUS Functions
Multicast Send VCC bidirectional point-to-point
From LE client to BUS
Multicast Forward VCC point-to-multipoint
Establishing Data Direct VCCs
Overview of Extensions for LAN Emulation
Broadcast Manager
BCM Support for IP
BCM Support for IPX
BCM Support for NetBIOS
BCM Support for Source Route Bridging
LAN Emulation Reliability
LAN Emulation Redundancy
LAN Emulation Security
Key Conguration Parameters for LAN Emulation
LEC
Using ATM
How to Enter Addresses
ATM and LAN Emulation
273
Advantages of Using ATM Virtual Interfaces
ATM-LLC Multiplexing
ATM Virtual Interface Concepts
Conguring ATM and LAN Emulation
Disadvantages of using ATM Virtual Interfaces
ATM Virtual Interface Conguration Concepts
ATM Virtual Interface Conguration Concepts
Accessing the ATM Interface Conguration Process
Conguring and Monitoring ATM
277
ATM Conguration Commands
ATM Interface Conguration Commands
ATM Conguration Commands Talk
ATM Conguration Command Summary
Esi esi-address
Syntax List Conguration Esi
Example list con
Example list esi
ATM Interface Conguration Commands Talk
QoS Conguration
Syntax Qos-conguration
Max-data-rate speed
Default Value Example
Valid Values
Max-calls
Max-callers
Max-frame
Max-mp-parties
On or OFF
You are prompted for the VPI/VCI range you want to trace
65535
Uni-version
Valid Values Default Value
UNI
Network-id
Address of End System Identiers
Accessing the Virtual ATM Interface Conguration Process
ATM Virtual Interface Conguration Commands
ATM Virtual Interface Conguration Command Summary
Syntax add Example
Accessing the ATM Monitoring Process
ATM Monitoring Commands
ATM Virtual Interface Conguration Commands Talk
Syntax Remove Example remove
ATM Interface Monitoring Commands ATM INTERFACE+ Prompt
ATM Monitoring Commands Talk
Syntax Atm-llc
ATM Interface Monitoring Commands Talk
Reserved-bandwidth
Lists the reserved bandwidth on the ATM Interface
List
Wrap
Off Stops packet tracing on all VCCs
Syntax Wrap
Start
ATM-LLC Monitoring Commands
ATM Virtual Interface Monitoring Commands
ATM LLC Conguration Command Summary
Syntax List Endpoints Channels
Using LAN Emulation Clients
LAN Emulation Client Overview
291
MRS V3.2 Software Users Guide
Conguring and Monitoring LAN Emulation Clients
Conguring LAN Emulation Clients
293
Syntax Add Ethernet Token Ring Token-ring
Example config
Cong
LE Client Cong
Syntax Cong Interface#
Conguring an ATM Forum-Compliant LE Client
ARP Conguration
Conguring Forum LE Clients
Syntax Arp-conguration Example
ATM LAN Emulation Client ARP Cong Commands Summary
Add
Cong
Addmac route-descriptor
RIF-Timer for Token-Ring Forum-compliant LEC only
Syntax Rif-timer
Source-Routing for Token-Ring Forum-Compliant LEC only
Remove
IP-Encapsulation for Ethernet ATM Forum-Compliant LEC only
QoS
Syntax IP-encapsulationEthernet
Arp-aging-time
Arp-cache-size
Arp-queue-depth
Arp-response-time
Auto-cong
Valid Values Default Value Connection-completion-time
Best-effort-peakrate
155000
Bus-connect-retries
Control-timeout
Elan-name
Esi-address
¯ush-timeout
Forward-delay
Forward-disconnect-timeout
Default Value Frame-size
Initial-control-timeout
Valid Values Default Value Example
Lecs-atm-address
Les-atm-address
Any valid MAC address
Multicast-send-avg
Multicast-send-peak
Multicast-send-type
Multiplier-control-timeout
Path-switch-delay
Recong-delay-min
Recong-delay-max
Enable or Disable
Retry-count
Selector
Accessing the LEC Monitoring Environment
Default Value Unknown-time
Vcc-timeout
An integer number of frames in the range of 1 to
LEC Monitoring Commands
LE Cong monitoring command Summary
Commands in Using and Conguring Features
Arp-table
Arp
Max Table Size
Free Table Entries
Current MAC Entries Current RD Entries
IBM LEC+ list config
IBM LEC+list config
Lists the LEC conguration For Ethernet
For Token Ring
Statistics
Lists LEC statistics
VCC table
Lists VCC table
LecControlTimeout
Syntax Mib
LecCongMode
LecCongLanType
LecVccTimeoutPeriod
LecForwardDelayTime LecExpectedArpResponseTime
LecFlushTimeout
LecPathSwitchingDelay LecLocalSegmentId
LecCongDirectVpi
LecCongDirectVci
LecControlDirectInterface
LecControlDirectVpi
QoS Information
LecControlFramesOut
LecControlFramesIn
LecSvcFailures
Conguring Serial Line Interfaces
Clocking and Cable Type
317
Conguring Serial Line Interfaces
Using the X.25 Network Interface
Basic Conguration Procedures
319
Type set data-link
Setting the National Personality
Understanding the X.25 Defaults
Using the X.25 Network Interface
Set Command
National Enable Parameters
Parameter DDN Default GTE Default
Paramter DDN Default GTE Default
National Set Parameters
Support Over Isdn BRI D-Channel
Null Encapsulation
Limitations
Conguration Changes
Closed User Group Null Encapsulation
Understanding Closed User Groups
Bilateral Closed User Groups
Types of Extended Closed User Groups
Conguring X.25 Closed User Groups
Overriding Closed User Group Processing for CUG
Establishing Incoming X.25 Circuits for Closed User Groups
Using the X.25 Network Interface
Conguration Commands
25 Conguration Commands Summary
Conguring and Monitoring the X.25 Network Interface
327
Conguring the X.25 Network Interface
Calls-out value
Valid Values 1 to Default Value
Default external Default-window-size value
Default
Default NRZ Equipment-type DCE or DTE
Speed speed-setting
National-personality GTE-Telenetor DDN
Pvc low/high value
Pvc low Pvc high
Valid values 0 to Default values Two-way
Valid values 0 to Default values Svc low Svc high Outbound
Valid values Default
Default 2400 bps
Syntax Enable DdnÐaddress-translations
Incoming-calls-barred Lower-dtr Outgoing-calls-barred
Incoming-calls-barred
Lower-dtr
National Enable
Syntax National enable
DDN Default
GTE Default
Bi-cug-outgoing-access
Cug-incoming-access
Cug-outgoing-access
DDN Default GTE Default Frame-ext-seq-mode
National Disable
Clear-req retries or timer
National Set
Syntax National set
Call-req
Timer
Disconnect-procedure passive or active
Dp-timer
DDN Default GTE Default N2-timeouts
Reset retries or timer
Species the number of reset request retransmissions
DDN Default GTE Default
Maximum
Restart retries or timer
Collision-timer
Min-recall
Min-connect
National Restore
T1-timer
T2-timer
DDN Default GTE Default Truncate-called-addr-size
Bi-cugs
Cugs
Htf-address
IP example
IPX example
Enc Priority
CUD Field Usage
Valid values 0 to Default value None
Valid values 0 to Default value None Pref bi-cug
Valid values 0 to Default value None Example
Pref cug
Valid values 0 to Default value None Bi-cugs
Species the closed user group number for this DTE
Add bi-cugs
Htf-address
Adds a Defense Data Network DDN X.25 address translation
Convert HTF address
Qllc example
Default Packet Size
Maximum Packet Size
Circuit Idle Time
Maximum VCs
Request Reverse Charges
Station Type
Pri
Sec
Syntax Changeaddress
Htf-address Protocol Pvc
Htf address
Changes a Defense Data Network DDN X.25 address translation
Changes PVC, window size, and packet size denitions
Range of circuits dened by the Packet Channel Range Start
Parameter
Deletes an X.121 address translation
Cugs
Protocol prot-type
List address
Example list all
Li cugs
Detailed
Protocols
Lists all the dened PVCs
Summary
Monitoring Commands
25 Monitoring Command Summary
Example list summary
Parameters
Packet
Displays the parameters for the packet level
List svc
Physical
Displays the parameters for the physical level
Syntax Statistics all
Displays the statistics for the packet level
Statistics Displayed for X.25 Interfaces
Displays the statistics for the physical level
+interface
Statistics packet
Interface state
Packet Counters
Data Packets
Data Bytes
Switched Circuits Open
Last port reset
Input frame errors CRC error
Invalid Packets Received
Output frame counters DMA/FIFO underrun errors
Missed frame
Bits not set
Output aborts sent
Conguring the X.25 Network Interface
Using XTP
X.25 Transport Protocol
361
Using XTP
Conguration Information
DTE Address Wildcards
Local DTEs
Peer Routers
Remote DTEs
XTP Backup Peer Function
XTP configadd local-dte
Searching for a Remote DTE
Connection Request Timer
Local XTP
XTP and Closed User Groups
Conguration Procedures
Conguring XTP
Setting the Data Link
Conguring the IP Interface
Interface
Set the Internal IP address Congure XTP
Enter set speed followed by the access rate line speed
Exit the X.25 Config prompt
Enter add pvc to dene individual PVCs
Setting the Internal IP Address
Configprotocol ip IP configadd address
IP configset internal-ip-address
Dening the IP Address
XTP configadd peer-router
XTP configadd remote-dte
Add cug
Add bi-cug
At ªConguration Proceduresº on
Sample Conguration of Remote Routers
Remote 1 router
Remote DTE
Configprotocol xtp
Configprotocol xtp XTP configadd local-dte
Remote 2 router
Routers IP address?128.185.100.1
Using XTP
XTP Conguring Commands
Conguring and Monitoring XTP
375
XTP Conguring Commands Talk
Local-dte
With XTP are 0 to
Address for that call
Add local command
Remote-dte
Refer to Software Users Guide
Refer to the Software Users Guide
Syntax Change
Cug
Syntax enable-xtp
Syntax disable-xtp
Keep-alive-timer
Local-dtes
Peer-routers
Remote-dtes
XTP Monitoring Commands
XTP Monitoring Commands Talk
Displays output of all list command options
Deletelocal-dtes peer-router remote-dtes
Deletes a local interface from the XTP conguration
Deletes a peer router from the XTP conguration
Displays all the interfaces congured for XTP
List of Peer Routers
Displays all the remote interfaces congured for XTP
Pvc-detailed
Pvcs-all-detailed
Displays detailed information for all PVC denitions
Svc-detailed
Displays information for specic SVC denitions
Svcs-all-detailed
Displays information for all the SVC denitions
Using Frame Relay Interfaces
Encryption in Using and Conguring Featuresfor details
Frame Relay Overview
387
Using Frame Relay
Frame Relay Network
Management
Be allotted to the PVC whether or not the PVC uses it
Frame Relay Switched Virtual Circuits
Frame Relay Interface Initialization
Orphan-circuit commands
Orphan Circuits
For FR DTE to DTE connectivity is lost
An orphan
Enable switched-virtual-circuit command
Orphan Circuit
Frame Relay Frame
Hdlc Flags
Data Link Connection Identier Dlci
Command/Response C/R
Extended Address
Forward Explicit Congestion Notication Fecn
Backward Explicit Congestion Notication Becn
Frame Forwarding over the Frame Relay Network
Protocol Addresses
Multicast Emulation and Protocol Broadcast
Protocol Address Mapping
Option on add switched-virtual-circuit
Frame Relay Network Management
Management Status Reporting
Full Status Report
Link Integrity Verication Report
Consolidated Link Layer Management Cllm
Frame Relay Data Rates
Committed Information Rate CIR
Set CIR-defaults command
Orphan Permanent Virtual Circuit CIR
Committed Burst Bc Size
Excess Burst Be Size
Line Speed
Minimum Information Rate
Maximum Information Rate
Variable Information Rate
Circuit Congestion
CIR Monitoring
Enable cir-monitor and disable cir-monitor console commands
Congestion-monitor console commands
Congestion Monitoring
Congestion Notication and Avoidance
Congestion Notication and Throttle Down
Frame Relay Basic Conguration Procedure
Bandwidth Reservation in Using and Conguring Features
Bandwidth Reservation over Frame Relay
Displaying the Frame Relay Conguration Prompt
Example enable lmi
Command Options Description
Enabling Frame Relay PVC Management
Frame Relay Management Options
Enabling Frame Relay SVC Management
Frame Relay Conguration Commands
Conguring and Monitoring Frame Relay
Interfaces
405
Conguring Frame Relay Interfaces
Permanent-virtual-circuit
Circuit Number
Valid Values 16 to Committed Information Rate
What is the group name
Excess Burst Size
Assign Circuit Name
Is the circuit required for operation
AppleTalk Phase 2 protocol
IP protocol
IPX protocol
DN protocol
Switched-virtual-circuit
Node Number
Node address
Circuit Number or name
Default Value E.164
Remote party numbering plan
Remote party number type
Remote party subaddress
Default Value Value of the requested outgoing CIR
Default Value Same as minimum acceptable outgoing CIR
Default Value Value equal to requested outgoing Bc
Default Value Same as requested outgoing excess burst size
Default Value yes
Establish circuit to learn remote protocol addresses
Valid Values yes or no
Is multicast required for this circuit
Permanent virtual circuit
Cir-monitor
Congured with theadd permanent-virtual-circuit or add
Compression
Congestion-monitor
Switched-virtual-circuits
Multicast-emulation
No-pvc
Notify-fecn-source
Change permanent-virtual-circuit command
Encryption enabled, will encrypt all transmitted data
Enables management activity
Defaults to Ansi T1.617 Annex D management
Previously disabled Frame Relay management
Occurs between the router and the FR switch
397 for information about the default CIR values
Feature is enabled
FR 1 Config enable switched
Network emulation mode
Local party number
Local party numbering plan
Local party number type
Transmit delay
Encoding
Idle
Clocking
LMI enabled
Cllm Enabled
Timer Ty seconds
SVC network emulation mode
Timer T1 seconds
Protocol Broadcast
Emulate multicast
Congestion Monitoring
LMI N2 error threshold
LMI N3 error threshold window
Default CIR
Default Burst Size
Circuit Type
Pvc-groups
Protocol-addresses
Protocol Type
Total SVCs congured
Options
Remote subaddress
Permanent-virtual-circuit pvc#
Set Command Considerations
Example remove pvc-group PVC group name IP?
Set n3-parameter 4 set n2-parameter
Cir-defaults
Default Value 64
Physical Interface Link Type Data Connection Type
Is the default
Valid Values See ªCommitted Burst Bc Sizeº on
Clocking external or internal
Frame-size #
Ir-adjustmentincrement-% decrement-% minimum-IR
Idle ¯ag or mark
Line-speed rate
Transmit-delay #
Lmi-type rev1 or ansi or ccitt
N1-parameter count
N2-parameter max#
Accessing the Frame Relay Monitoring Prompt
Frame Relay Monitoring Commands
Default Value 11 seconds
Ty-parameter time
Monitoring Frame Relay Interfaces
List lmi and list permanent-virtual-circuit commands
Circuit name or number
Circuit state
Circuit is orphan
Frames/Bytes transmitted
Frames/Bytes received
Total Fecns
Total Becns
Mode discards
Compression errors
Encryption errors
Decryption errors
Management Status LMI enabled
Serial device handler transmit queue for this interface
Xmit frames dropped due to queue over¯ow
VC due to output queue over¯ow
Last Cllm cause code
PVCs P1 allowed
Interface down if no PVCs
Default Excess CIR
DECnet length eld
Current receive sequence
Current transmit sequence
Data compression enabled
Data encryption enabled
Active compression circuits
Active encryption circuits
Circuit#
Orphan Circuit
Type/State
Frames Transmitted
Virtual-circuits
Circuit#
Circuitname
FR 1list virtual-circuits
Circuit circuit# or name cirvol bcval beval
Required. The default setting is to trace all circuits
Information, see ªExcess Burst Be Sizeº on
Frame Relay Interfaces and the Gwcon Interface Command
Statistics Displayed For Frame Relay Interfaces
Input frame errors
Circuit, Nicknames, and State
Output aborts sent
Monitoring Frame Relay Interfaces
Using Point-to-Point Protocol Interfaces
PPP Overview
449
Using PPP
PPP Data Link Layer Frame Structure
PPP Link Control Protocol LCP
Using PPP
LCP Packets
Identier
Length
Data Option
Link Establishment Packets
Link Maintenance Packets
PPP Authentication Protocols
Link Termination Packets
Password Authentication Protocol PAP
Challenge-Handshake Authentication Protocol Chap
Microsoft PPP Chap Authentication MS-CHAP
Shiva Password Authentication Protocol Spap
Conguring PPP Authentication
Conguring a PPP Interface to Authenticate a Remote Device
Conguring PPP Callback
459
Using AAA with PPP
Example 3 Roaming callback enabled
Configadd PPP roamingcallback
PPP Network Control Protocols
AppleTalk Control Protocol
Banyan Vines Control Protocol
Bridging Protocols
Callback Control Protocol
IP Control Protocol
IPv6 Control Protocol
Using and Conguring Virtual Connections
IPX Control Protocol
OSI Control Protocol
Appn HPR Control Protocol
Commandsº in Using and Conguring Features
Conguring a VC
ªPoint-to-Point Conguration Commandsº on
ªPoint-to-Point Monitoring Commandsº on
Conguring and Monitoring Point-to-Point
Protocol Interfaces
Accessing the PPP Interface Conguration Prompt
Point-to-Point Conguration Commands
Conguring PPP Interfaces Talk
Ccp
Chap
Dials
Ecp
Enables the use of data compression on the interface
Enable chap
Ecp
Mppe mandatory/optional stateless/stateful
Mandatory
Optional
Stateless
Bcp
Tinygram Compression
Data Encryption Enabled/Disabled
Transmit Delay Counter
Algorithm List
Idle State
Ipcp compression
Send Our IP Address
Ipv6cp
Example PPP 7 Conglist lcp
Retry Timer
Authenticate remote using
Cong Request Tries
Cong Nak Tries
Ccp options
Ccp algorithms
Name
List ncp
Stac check mode 0=none, 1=LCB, 2=CRC, 3=Seq
Ncp Bcp Sets the Bridging Control Protocol BCP parameters
Ccp options
Stac # histories
Microsoft Point-to-Point Compression Mppc is used
Algorithm in the list
Compression. The valid compression algorithms are
Hdlc cable cable type
Hdlc clocking external or internal
Hdlc encoding NRZ or Nrzi
Hdlc idle ¯agor mark
Range is 0 to 15. The default is
When determining the type of compression that is enabled.
Range is 1 to 16. The default is
Receive clock lines. The range is 2400 to 2 048 000 bps
Lcp options or parameters
Maximum receive unit
Async Control Character Map
Addr/Cntl Field Compression Acfc
Protocol Field Compression PFC
Cong tries
NAK tries
Range is 1 to
Transmitted. This is done to guard against packet loss
Remote Authenticationº in Using and Conguring Features
Lowercase
Ncp parameters
Point-to-Point Monitoring Commands
Point-to-Point Monitoring Command Summary
+ network 2 PPP
Monitoring PPP Interfaces Talk
Example list cbcp
Packets
Octets
Callback attempts
Example of the List Control ECP Command
Example for Mppc compression
Denitions of Terms in the List Control CCP Example
CCP state
Example of the List Control LCP Command
Link phase
Time Since Change
Local transmit encrypter
Authenticate
Terminate
Link is being shut down
LCP State
Authentication
Example of the List Control BCP Command
Remote Username
Last Identication Rxd
Example of the List Control Nbcp Command
Remote NetBIOS Name
Example of the List Control Nbfcp Command
Denitions of Terms in the List Control BCP Example
Example of the List Control Ipcp Command
Denitions of Terms in the List Control Nbfcp Example
Remote Peer
Denitions of Terms in the List Control Ipcp Example
Example of the List Control Ipxcp Command
Dhcp State
Lease Server
Leased IP address
Example of the List Control Isrcp Command
Hprcp Command Example
Common Network Number
Local Node ID
Cong timeouts
Terminate timeouts
Bad address
Bad control
Monitoring PPP Interfaces Talk
List pap
Requests
Challenges
Responses
Successes/Failures
Failure Account Disabled
Failure Password Expired
Failure Authentication
Failure Change Password
Reset Reqs
Reset Acks
Prot Rejects
Encrypted Octets
PleaseAuthenticates
Dialbacks
Change Passwords
Mccp Call Reqs
Mccp Callbacks
Mccp ACKs
Compressed octets
Incompressible packets
Protocol rejects
Compression ratios
Brg
Stp
Nbcp
Command. See ªipº
List ip command. See ªipº
Current IP connection
List ipv6
List ipxcp
List ipx
List atcp
List dn
List osicp
List osi
List bvcp
List isr
List hprcp
List hpr
Interface No
Adapter cable
Circuit
Nicknames
Length of time since the port was reset
Alignment byte length
Too long 2048 bytes
Using the Multilink PPP Protocol
509
Using MP
MP Considerations
Multi-Chassis MP
Conguring a Multilink PPP Interface
Conguring MP on PPP Dial Circuits
Conguring MP on PPP Serial Links
Conguring MP on Layer-2-Tunneling Nets
Run on the MP interface and not the PPP dial circuits
Single bundle
Conguring Multi-Chassis MP
Hunt group
Support LCP renegotiation
Accessing the MP Conguration Prompt
MP Conguration Commands for Multilink PPP Interfaces
Conguring and Monitoring Multilink PPP Protocol MP
515
Encapsulator
Conguring MP
Syntax Encapsulator Example
Outbound calls
BAP enabled
Dialout MP link net
Max fragment size
Min fragment size
Default value inbound
Valid Values 0 to Default Value Mp parameters
Valid Values 100 to 3 Default Value
Add bandwidth %
Accessing the MP Monitoring Commands
Multilink PPP Protocol Monitoring Commands
Using add device multilink-ppp command
Monitoring MP Interface Status
Monitoring MP
Indicates that the request is not supported
Control bacp
PPP 6 list bacp
Control bod
Closed
Call Req Sent
Callback Req Sent
Timeout
Control mp
Depth
Seq order
PPP 6 list mp MP Statistic Out Bytes Compressed 61230 60259
Monitoring MP
Basic Conguration Procedure
Accessing the Sdlc Relay Conguration Environment
Configprotocol sdlc
Conguring Sdlc Relay
Sdlc Relay Conguration Commands
Conguring and Monitoring Sdlc Relay
Example add group
Group number
Interface number
Primary or Secondary
Remote±port
IP address of remote router
List for network Srly
Port
List for protocol Sdlc
Maximum frame size in bytes
Example list all
Port Status
Use the set command to congure the Srly parameters
Net Number
Indicates the IP address of the remote port
Displays the conguration of a specied group
Clocking internal or external
Idle ¯ag
Idle mark
Accessing the Sdlc Relay Monitoring Environment
Sdlc Relay Monitoring Commands
Transmit-delay value
Sdlc Relay Monitoring Commands Summary
Syntax Enable Group Port
Clear-Port-Statistics
Syntax Clear-port-statistics
Port interface# primary-or-secondary
Enable port
Syntax List All Group
All Displays the congurations of all local ports
Packets fwrd and disc
Sdlc Relay Interfaces and the Gwcon Interface Command
List group
MRS V3.2 Software Users Guide
Using Sdlc Interfaces
Conguring Switched Sdlc Call-In Interfaces
537
Congure the dial circuit
Using Sdlc Interfaces
Sdlc Conguration Requirements
Congure DLSw
Accessing the Sdlc Conguration Environment
Configset data-link sdlc
Conguring and Monitoring Sdlc Interfaces
539
Sdlc Conguration Commands
Conguring Sdlc Interfaces
Syntax Add Station Example
Enter station address
Syntax Disable Link Station
Syntax Enable Link Station
Enter station name
Include station in group poll list
Link conguration
Duplex
Modulo
Timers
Inter-poll delay
RTS hold delay
Interframe delay
Poll retry
Station all or address or link station name
Max BTU
Rx Window
Link cable type
Link clocking internal or external
Link duplex full or half
Link encoding nrz or nrzi
Link inter-frame delay seconds
Link group-poll
Link idle ¯ag
Link idle mark
Valid values 0 to Default value Example
Link poll delay
Link poll timeout
Link modulo 8 or
Link snrm timeout or retry
Link xid/test timeout or retry
Link rts-hold
Link speed
Accessing the Sdlc Monitoring Environment
Sdlc Monitoring Commands
Sdlc Monitoring Commands Summary
Syntax Add Station
+ network
Syntax disable link
Syntax clear Link Station
Link name or address
Station name or address or all
Frames
Bytes
Re-Xmit
UI-Frames
Enabled
Connecting
Recovering
Connected
List link counters
List station all
List station c1
List station c1 counters
Link poll delay or timeout or retry
Link snrme
Link modulo
Link role primary, secondary, or negotiable
Link type multipoint or point-to-point
Maximum size of packet that this station can receive
Sdlc Interfaces and the Gwcon Interface Command
Statistics Displayed for Sdlc Interfaces
Teststation name or address #frames-to-send Frame-size
Number of test frames to send
Input frame errors
RS-232
Line speed congured
Output frame counters
Conguring Sdlc Interfaces
Conguring Sdlc Interfaces
Using Binary Synchronous Relay Brly
Brly Overview
561
Sample Brly Conguration
Multipoint connections
. These examples use the following assumptions
IP address for the Primary BSC Devices local port is
Group
When conguring BRLY, keep the following in mind
Brly Considerations
Remote
Reduce the total network throughput
Devices that disconnect frequently
MRS V3.2 Software Users Guide
BSC Relay Conguration Commands
Conguring and Monitoring BSC Relay
567
Default value multipoint
Conguring and Monitoring BSC Relay
Group type
Local-port
Default value S
Station Address Character
Valid values X01 to XFF
Remote group number
Default value local
Local±port group#
Local or Remote
List for network BSC
List for protocol Brly
Link EOT
Number of pairs of SYNs
Remote Group
Use the set command to congure the BSC interface parameters
Displays the conguration of a specied group
Cable
Code ebcdic or ascii
Accessing the BSC Relay Monitoring Environment
Default value yes Frame-size
Default value mark Speed bps
Eotlink yes or no
BSC Relay Monitoring Commands
Syntax Clear Example
Router, the effects of this command are erased
Command are erased
Remote port
Local Group
Station Address
Packets Forwarded
Packets Discarded
BSC Relay Interfaces and the Gwcon Interface Command
Gwcon Talk 5 and Commands
Using the V.25bis Network Interface
Adding V.25bis Addresses
579
Using V.25bis
Timeout-no-answer commands
Set command-delay-timeoutcommand species the amount of time
Conguring the V.25bis Interface
Configadd device dial-circuit
Adding Dial Circuits
Conguring Dial Circuits
Circuit Configset selftest-delay
25bis Conguration Commands
Conguring and Monitoring the V.25bis Network Interface
583
V.25bis conguration prompt now displays on the console
25bis Conguration Commands
Local Network Address Name
Local Network Address
Non-responding addresses Retries
Call timeouts
Command Delay
Command-delay-timeout # of milliseconds
Connect-timeout # of seconds
Disconnect-timeout # of seconds
Valid values NRZ or Nrzi Default value NRZ Hdlc speed
Hdlc encoding
25bis Monitoring Commands
Add v25-bis-address command
Timeout-no-answer # of seconds
Local-address address name
25bis Operating Commands
Calls
Syntax calls Example
Site Name
Circuits
Call timeouts Command Delay
Network address name of the local port
Network dial address of the local port
Syntax Statistics Example
Type of adapter cable being used
Circuit numbers as identied by V.24 specications
Common names for the circuits
Transmit clock speed approximate
25bis and the Gwcon Commands
Statistics for V.25bis Interfaces and Dial Circuits
Vec Self-Test Passed
Type of adapter cable that is being used
Interface
CRC error
Using the V.34 Network Interface
Adding V.34 Addresses
595
Using
These commands, see ªV.34 Conguration Commandsº on
Conguring the V.34 Interface
Optional V.34 Parameters
Using V.34
Circuit Configset selftest-delay
Conguring and Monitoring the V.34 Network Interface
599
V.34 conguration prompt now displays on the console
Devices
34 Conguration Commands Summary
Conguring
Command strings sent to the attached modem
Modem strings
Initialization string
Modem-init-string
Add v34-address command Modem-init-string value
Speed # bits per second
34 Monitoring Command Summary
Monitoring Function Command
Network address name of the dial circuit
Circuits
Syntax Parameters
Example parameters
CRC
Statistics for V.34 Interfaces and Dial Circuits
Example interface
Nicknames
Conguring
Using the Isdn Interface
Isdn Overview
Isdn Adapters and Interfaces
611
Using Isdn
Dial Circuits
Oversubscribing and Circuit Contention
Addressing
Cost Control Over Demand Circuits
Caller ID and Lids
Isdn Cause Codes
Isdn Q.931 Cause Codes
Code Cause
Sample Isdn Congurations
Frame Relay over Isdn Conguration
Following topics show several typical Isdn congurations
Isdn Configset switch chan
WAN Restoral Conguration
Channelized T1/E1
Example of conguring a Channelized T1 interface
Switches/Services Supported
Switch names Valid command
Requirements and Restrictions for Isdn Interfaces Router
7set timeslot 2
You cannot boot or dump the router over an Isdn interface
Setting up and taking down B-channel connections
Isdn Interface Restrictions
Dial Circuit Conguration Requirements
Configadd isdn-address
Isdn Configset switch net5
Isdn Config set local-address-name
Conguring Isdn Parameters
TEI number of your Isdn switch
Optional Isdn Parameters
Value from 0 to 63, assigned by your provider
D-channel. For example
Default is ANSI-T1.403 For example
Conguring the Isdn Interface
T1/J1 PRI Interface
E1 PRI Interface
This section describes how to congure a dial circuit
Isdn-address command. For example
Use the set calls command. For example
Specify the timeout period for the circuit
Using ªADD ISDN-ADDRESSº at thecong prompt
Use the encapsulator command. For example
Which is the destination name by specifying a lidoutaddr
Prevent initial packets from being dropped. For example
Isdn I.430 and I.431 Switch Variants
Native I.430 Support
Native I.431 Support
Default value is none
Support
Isdn Conguration Commands
Conguring and Monitoring the Isdn Interface
Block-Calls
627
Isdn Conguration Commands
Syntax Disable Ps1
Syntax Enable Ps1
Framesize 1024 or 2048 or 4096 or
Default Value a
Default Values B8ZS
Default Value Disabled
Frame-type
Default Value ANSI-T1.403 For E1 PRI
Default Value HDB3
Default ValueDisabled Local-address-name address name
Default Value None Example
Service-prole-id B-channel# spid#
Timeout-call-address # of seconds
Timeout-call-address. It is xed at
Default Value 180 seconds
Default Value Dmspri
Dn0 directory number
Dn1 directory number
Tei auto or none or value
Cause Code
Syntax Cause code
Example add FF
Isdn Monitoring Commands
Isdn Monitoring Command Summary
Monitoring Command Function
Syntax cause code remove value
Isdn Monitoring Commands
Channels
Syntax Channels
MAC/Data-Link
NnnData
Rmt Disc
Opr Req
Dial-dump
L2Counters
L3Counters
Example for BRI using
Syntax statistics Example for BRI
Example for PRI with E1
Statistics
Example for PRI with T1 using
Example for Channelized T1
Isdn and the Gwcon Commands
Isdn and the Gwcon Commands
Circuits Be dropped and re-dialed
Conguration Information on Router Hardware and Software
Dial Circuit Conguration Commands
Conguring and Monitoring Dial Circuits
643
Conguring Dial Circuits
Nbound destination
Inbound destination
For Frame Relay, enter set data-link frame-relay
Variantsº on
Be shown for all interface types
Any inbound
SelfTest Delay Timer
Bandwidth
Base net
Callback
Anyinbound
Bandwidth kbps
V34-address command
Default value 7E
Callback Yes or No
Destination addressname
Lidused enabled or disabled
Selftest-delay# of milliseconds
Lidoutaddr addressname
Timeslot list of slots
Dial Circuit Monitoring Commands
Callback
Syntax Callback
Appendix A. Quick Conguration Reference
Conguring LAN Emulation
IPX DNA
Conguring Interfaces
Ethernet
Token-Ring
Conguring Multilink PPP MP Interfaces
Lidin
Conguring Dial-Circuits
Add another Dial Circuit Yes, No Yes No
Next, the following prompt will be shown
Default is 30 minutes
Be used for the duration of the connection
Dialoutserver
Conguring Bridging
Conguring Protocols
Panel similar to the following is displayed
Conguring IP
Conguring IPX
Token-Ringor Ethernet
Conguring IPX for Token-Ring
Following prompt is displayed
End stations
Ipxwan is enabled on any network interfaces
Following prompts are displayed
Which to build a host number
Conguring DECnet DNA
Highest Node Number
Router Level
Highest Area
DNA Configuration Saved
Tftp Boot
Bootp Boot
IBD Boot
Enabling Console Modem-Control
Restarting the Router
Appendix A. Quick Conguration Reference
MRS V3.2 Software Users Guide
Appendix B. X.25 National Personalities
GTE-Telenet
675
MRS V3.2 Software Users Guide
Appendix C. Making a Router Load File from Multiple Disks
Assembling a Load File Under DOS
Assembling a Load File Under Unix
677
Disassembling a Load File Under DOS
Resulting le gw.ldc is the assembled router load
Disassembling a Load File Under Unix
# ls -la total
# cutup gw.ldc gw # ls -la
MRS V3.2 Software Users Guide
List of Abbreviations
681
Cgwcon
DoD
Dtype
Eth
Fa-ga
Ifc#
InARP
Kbps
NetBIOS
LSreq
LSrxl
Mbps
Network Service Access Point
Random access memory
Ring error monitor
Ring indicator routing information
ROpcon
Rtype
Rxmits
Rxmt
251
252
253
List of Abbreviations
MRS V3.2 Software Users Guide
Glossary
691
Advanced Peer-to-Peer Networking APPN. An
Advanced Peer-to-Peer Networking Appn end
Advanced Peer-to-Peer Networking Appn
Advanced Peer-to-Peer Networking Appn network
Glossary
Carrier sense multiple access with collision
Control point management services CPMS. a
Control point management services unit CP-MSU
Signal detector Rlsd
Congestion. See network congestion
Data circuit-terminating equipment DCE. In a data
Digital Network Architecture DNA. The model for
Explorer frame. See explorer packet
Fragment. See fragmentation
Level
General data stream GDS. The data stream used for
Integrated services digital network ISDN. a digital
Integrated Digital Network Exchange IDNX. a
International Organization for Standardization
International Telecommunication Union ITU.
Inverse Address Resolution Protocol InARP.
Line switching. Synonym for circuit switching
Local management interface LMI. See local
Management interface LMI protocol
Local management interface LMI protocol. In NCP
Glossary
MRS V3.2 Software Users Guide
Non-Return-to-Zero Changes-on-Ones Recording
Open Systems Interconnection OSI reference
Packet mode operation. Synonym for packet
Switching
Rapid Transport Protocol RTP connection.
Ring. See ring network
Routing Table Maintenance Protocol RTMP.
Simple Network Management Protocol SNMP.
Subnetwork Access Protocol SNAP. In LANs, a
Subnet mask. Synonym for address mask
Subnetwork mask. Synonym for address mask
Synchronous Data Link Control Sdlc a
Glossary
Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol
Wildcard character. Synonym for pattern-matching
Character
MRS V3.2 Software Users Guide
Index Numerics
715
Binary synchronous communications relay Brly
Chap
Opcon
DOS
PAP
Lter
SVC FRF
MRS V3.2 Software Users Guide
Gwcon
BUS
List list
MS-CHAP
Ospf
Config Gwcon
Messages containing IP addresses 162
387 Technical support access
Unix
XTP
Readers Comments Ð Wed Like to Hear from You
How satised are you that the information in this book is
Please tell us how we can improve this book
Readers Comments Ð Wed Like to Hear from You
SC30-3681-08
Page
Ibmr
IBM