CACHE SUBSYSTEMS
32·BIT
|
| PROCESSOR |
|
|
|
| INDEX |
|
| |
|
| ADDRESS |
|
|
|
|
|
| ||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||
|
|
|
|
| ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| DATA | INDEX | TAG |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 24862468 | 7FFC |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 11223344 | 7FFB |
|
TAG | DATA | INDEX | TAG | DATA |
|
|
|
| 0010 | IF |
|
|
|
| OOOC | ||||||
|
|
|
|
| ||||||
FF | 24662466 | 7FFC | 001 | 12345678 |
|
|
|
| OOOS |
|
|
|
|
| 0004 |
| |||||
O | 7FF8 | 1FF | 11223344 | ~ |
| - |
|
| ||
| 0000 |
| ||||||||
0010 |
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||
OOOC |
|
| P.- | - | 7FFB |
| ||||
0008 | 000 | 87654321 |
|
| ||||||
|
| 12345678 | 7FFC |
| ||||||
0004 | 001 | 11235813 | I- |
|
| |||||
001 | 77777777 | 0000 | 000 | 13578246 |
|
| 0010 | 00 | ||
~9BITS~ | 1+32 |
| 1+9BITS~ | 1+32 |
| - |
|
| ||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| OOOC | l00 | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| OOOS | |
32KSRAM |
| 32KSRAM |
|
|
|
| ,,"OOOC | |||
|
|
|
| 11235813 | 0004 |
| ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 77777777 | 0000 |
|
| 64KCACHE |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 7FF8 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 0010 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 87654321 | 0008 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 0004 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 13579246 | 0000 |
|
1+32
16 MEGABYTE DRAM
231732;7·4
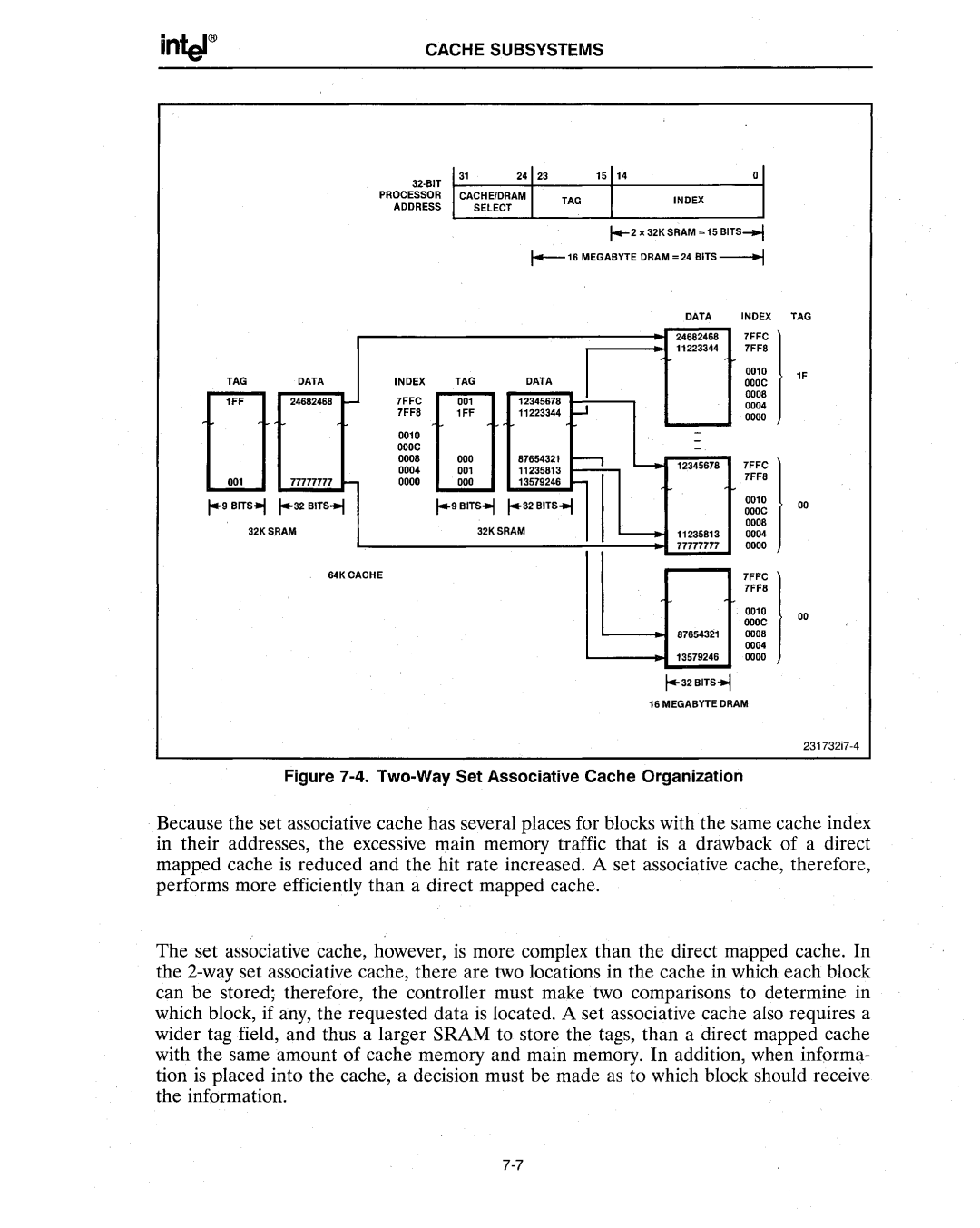
Figure 7-4. Two-Way Set Associative Cache Organization
Because the set associative cache has several places for blocks with the same cache index in their addresses, the excessive main memory traffic that is a drawback of a direct mapped cache is reduced and the hit rate increased. A set associative cache, therefore, performs more efficiently than a direct mapped cache.
The set associative cache, however, is more complex than the direct mapped cache. In the