CACHE SUBSYSTEMS
7.7.382385 Cache Organiza~ion
The cache directory and management logic are integrated into the 82385. The cache data memory consists of external SRAMs which are used to store the actual code and data. The 82385 supplies all of the necessary control signals to access the cache data memory. Via a configuration input, the 82385 can be designed as either a direct mapped cache or a two-way set associative cache.
7.7.3.1DIRECT MAPPED ORGANIZATION
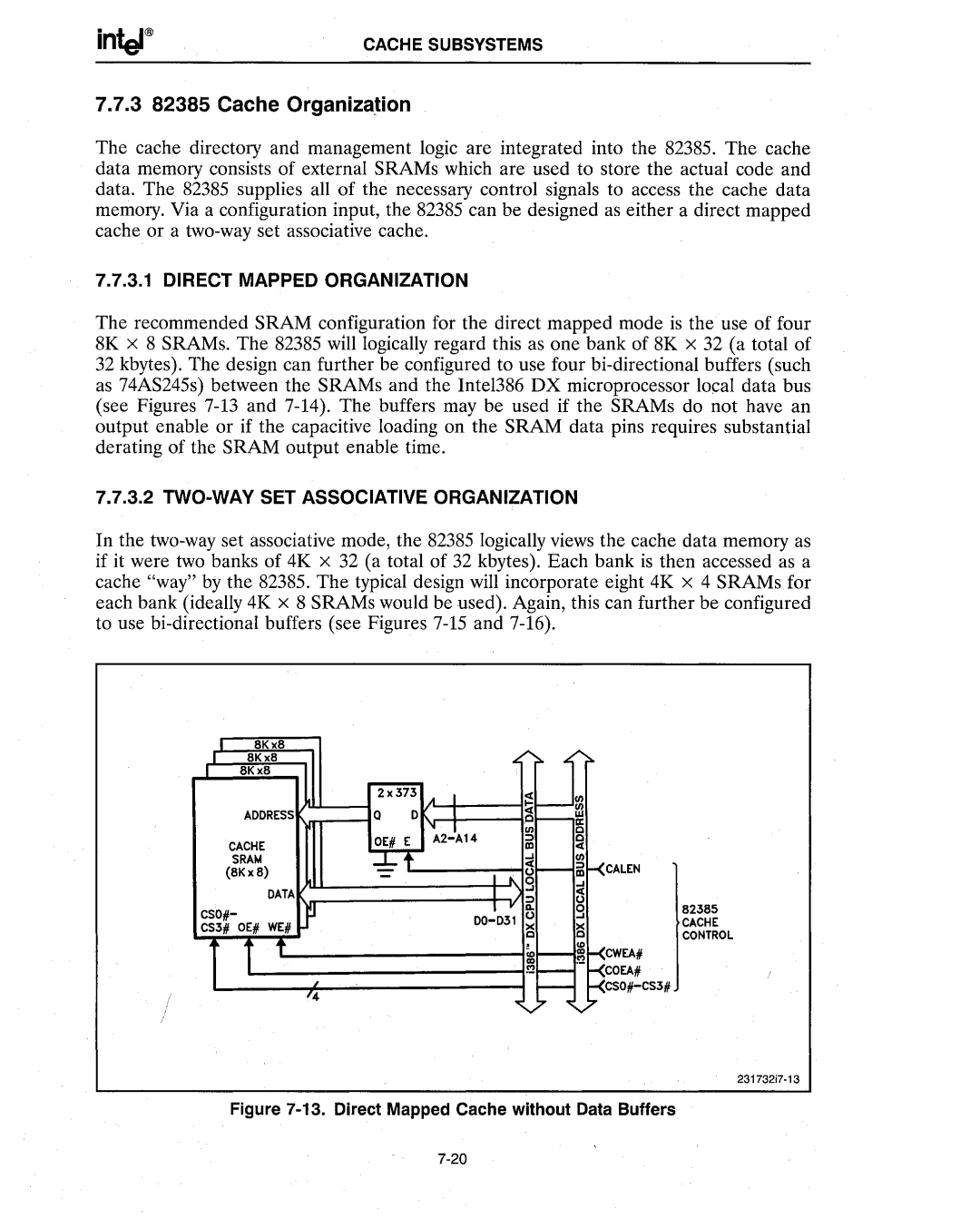
The recommended SRAM configuration for the direct mapped mode is the use of four 8K x 8 SRAMs. The 82385 will logically regard this as one bank of 8K x 32 (a total of 32 kbytes). The design can further be configured to use four bi-directional buffers (such as 74AS245s) between the SRAMs and the Intel386 DX microprocessor local data bus (see Figures 7-13 and 7-14). The buffers may be used if the SRAMs do not have an output enable or if the capacitive loading on the SRAM data pins requires substantial derating of the SRAM output enable time.
7.7.3.2TWO-WAY SET ASSOCIATIVE ORGANIZATION
In the two-way set associative mode, the 82385 logically views the cache data memory as if it were two banks of 4K x 32 (a total of 32 kbytes). Each bank is then accessed as a cache "way" by the 82385. The typical design will incorporate eight 4K x 4 SRAMs for each bank (ideally 4K x 8 SRAMs would be used). Again, this can further be configured to use bi-directional buffers (see Figures 7-15 and 7-16).
8Kx8
8Kx8
8Kx8
2x373
II"'.L---Qi | D II - + ---- i |
CACHE | |
SRAM | |
(8K x 8) | CALEN |
82385 CACHE CONTROL
ONEAl
COEAI
CSOII-CS31
/ 4
231732i7-13
Figure 7-13.Direct Mapped Cache without Data Buffers
7-20