CACHE SUBSYSTEMS
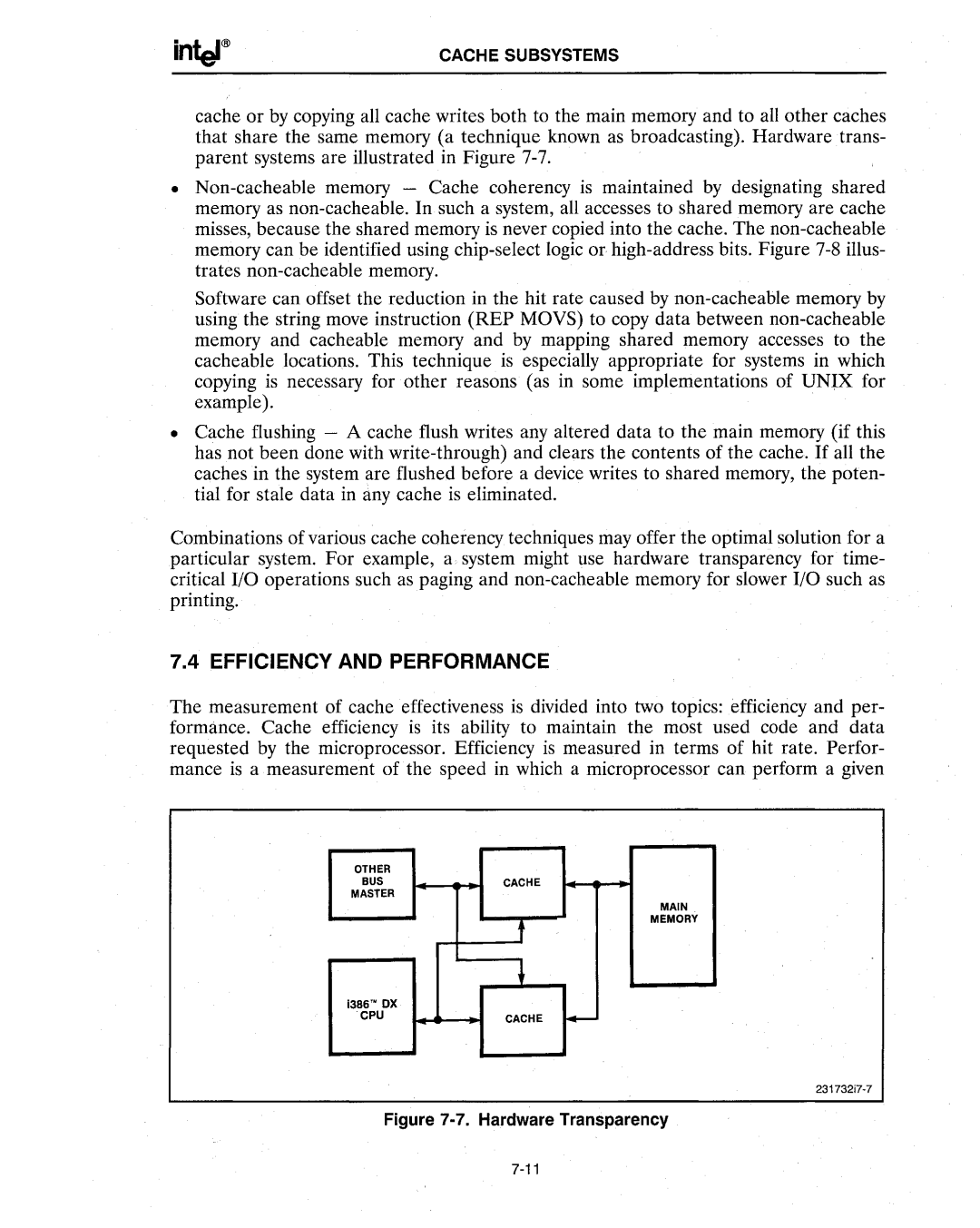
cache or by copying all cache writes both to the main memory and to all other caches that share the same memory (a technique known as broadcasting). Hardware trans- parent systems are illustrated in Figure
•
Software can offset the reduction in the hit rate caused by
•Cache flushing - A cache flush writes any altered data to the main memory (if this has not been done with
Combinations of various cache coherency techniques may offer the optimal solution for a particular system. For example, a system might use hardware transparency for time- critical 110 operations such as paging and
7.4 EFFICIENCY AND PERFORMANCE
The measurement of cache effectiveness is divided into two topics: efficiency and per- formance. Cache efficiency is its ability to maintain the most used code and data requested by the microprocessor. Efficiency is measured in terms of hit rate. Perfor- mance is a measurement of the speed in which a microprocessor can perform a given
OTHER |
|
|
BUS | CACHE |
|
MASTER | J, | MAIN |
| ||
| MEMORY | |
|
| |
i3B6~ OX | CACHE - |
|
CPU |
| |
|
|