PHYSICAL DESIGN AND DEBUGGING
A _
3 _
f | ey |
A4
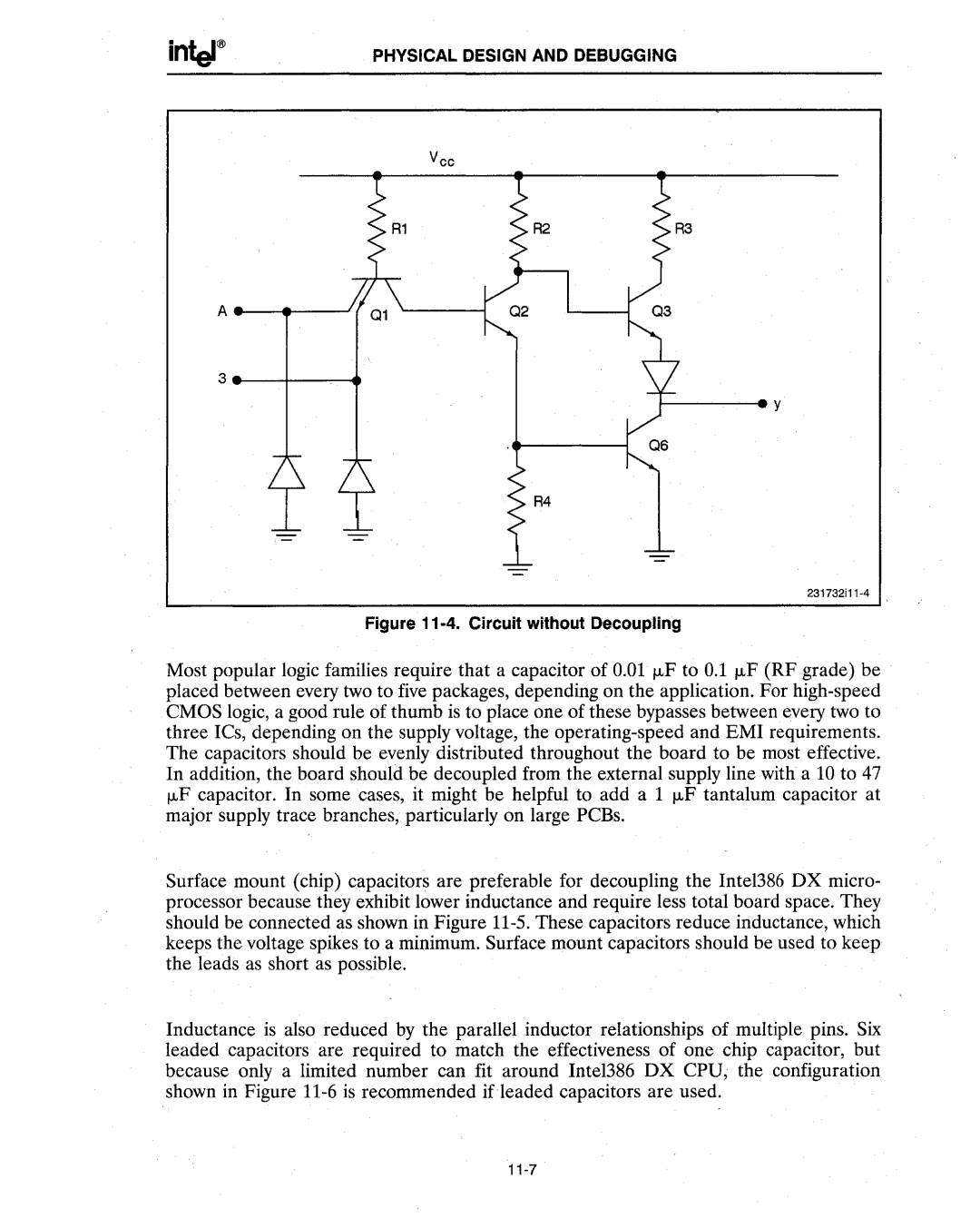
Figure 11-4. Circuit without Decoupling
Most popular logic families require that a capacitor of 0.01 f.LF to 0.1 f.LF (RF grade) be placed between every two to five packages, depending on the application. For
Surface mount (chip) capacitors are preferable for decoupling the Inte1386 DX micro- processor because they exhibit lower inductance and require less total board space. They should be connected as shown in Figure
Inductance is also reduced by the parallel inductor relationships of multiple pins. Six leaded capacitors are required to match the effectiveness of one chip capacitor, but because only a limited number can fit around Intel386 DX CPU; the configuration shown in Figure