PHYSICAL DESIGN AND DEBUGGING
[1 | 0 |
0 | m 0 =0.1 ~F |
;386 ,. OX CPU | |
~ | 0 rt] =1.0 ~F |
0 | ~ |
231732;11·5
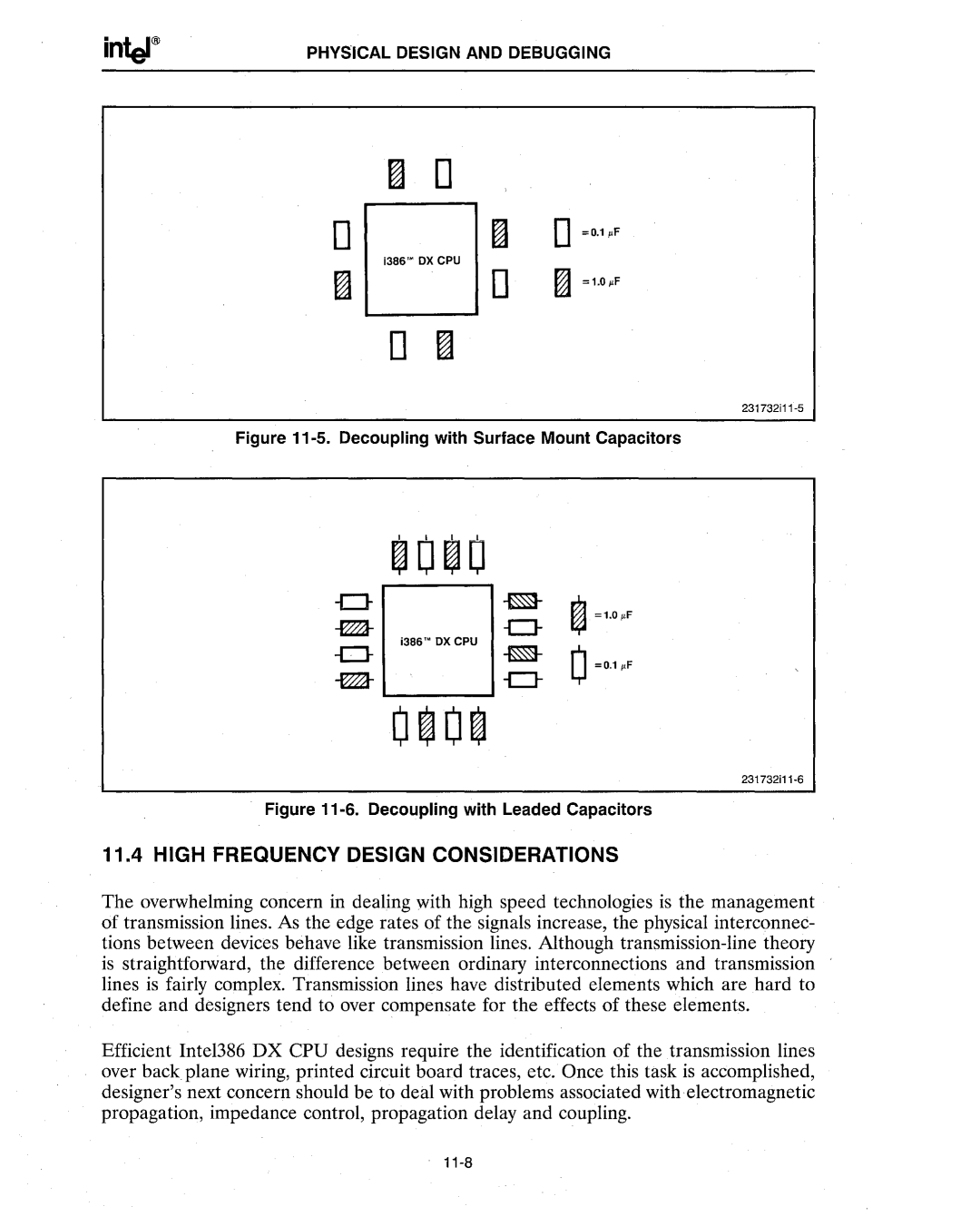
Figure 11-5. Decoupling with Surface Mount Capacitors
~o~o
~ =1.0~F | ||
CJ- |
| |
| ;386 ,. OX CPU |
|
~ o=0.1 ~F | ||
~ |
| |
O~O~
231732;11·6
Figure 11-6. Decoupling with Leaded Capacitors
11.4 HIGH FREQUENCY DESIGN CONSIDERATIONS
The overwhelming concern in dealing with high speed technologies is the management of transmission lines. As the edge rates of the signals increase, the physical interconnec- tions between devices behave like transmission lines. Although
Efficient Intel386 DX CPU designs require the identification of the transmission lines over back plane wiring, printed circuit board traces, etc. Once this task is accomplished, designer's next concern should be to deal with problems associated with electromagnetic propagation, impedance control, propagation delay and coupling.