| MEMORY INTERFACING |
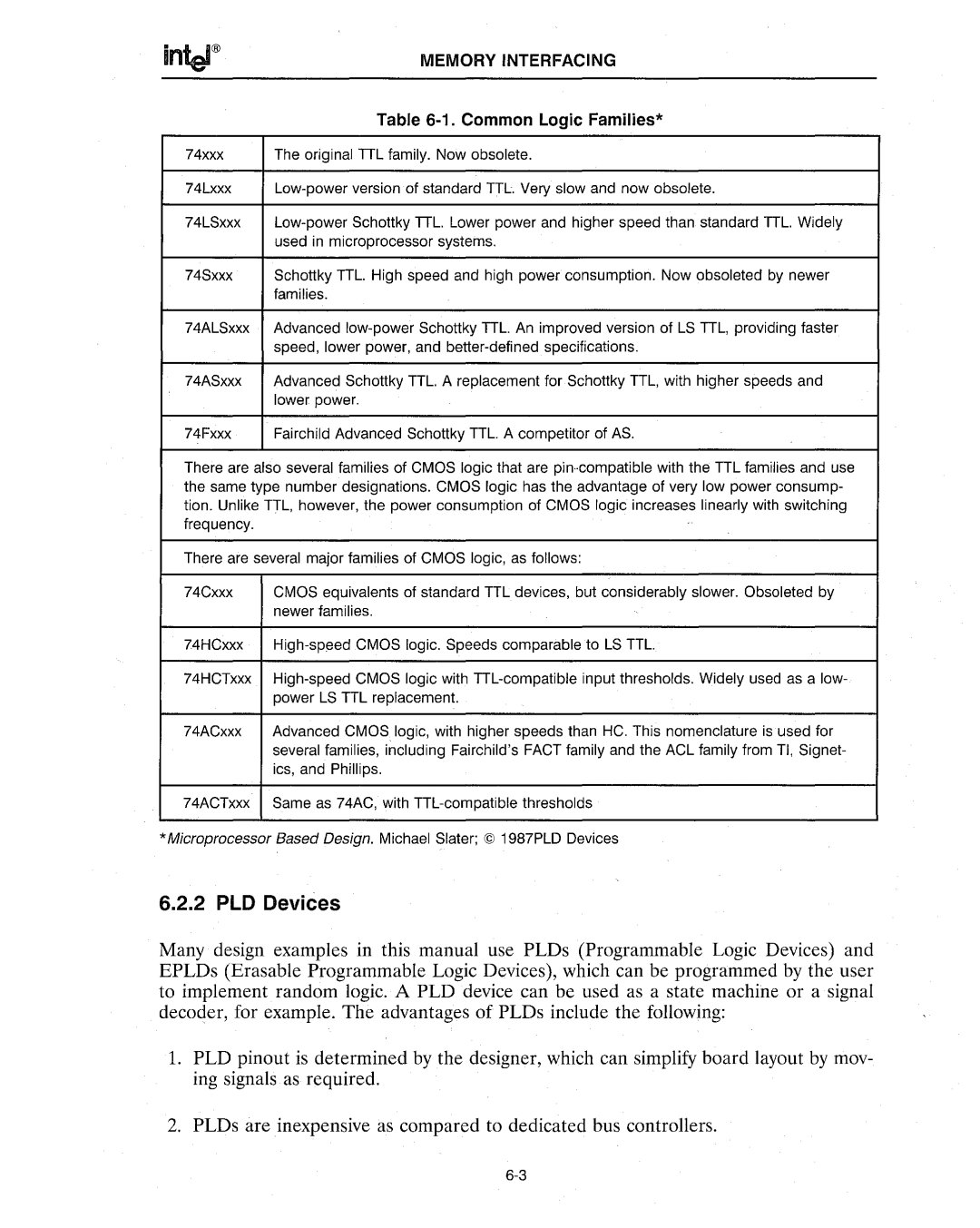
| Table |
74xxx | The original TIL family. Now obsolete. |
74Lxxx | |
74LSxxx | |
| used in microprocessor systems. |
74Sxxx | Schottky TIL. High speed and high power consumption. Now obsoleted by newer |
| families. |
74ALSxxx Advanced
| speed, lower power, and |
74ASxxx | Advanced Schottky TIL. A replacement for Schottky TIL, with higher speeds and |
| lower power. |
74Fxxx | Fairchild Advanced Schottky TIL. A competitor of AS. |
There are also several families of CMOS logic that are
There are several major families of CMOS logic, as follows:
74Cxxx | CMOS equivalents of standard TIL devices, but considerably slower. Obsoleted by |
| newer families. |
74HCxxx |
74HCTxxx
74ACxxx Advanced CMOS, logic, with higher speeds than HC. This nomenclature is used for several families, including Fairchild'sFACT family and the ACL family from TI, Signet- ics, and Phillips.
74ACTxxx Same as 74AC, with
*Microprocessor Based Design. Michael Slater; © 1987PLD Devices
6.2.2 PLD Devices
Many design examples in this manual use PLDs (Programmable Logic Devices) and EPLDs (Erasable Programmable Logic Devices), which can be programmed by the user to implement. random logic. A PLD device can be used as a state machine or a signal decoder, for example. The advantages of PLDs include the followjng:
1.PLD pinout is determined by the designer, which can simplify board layout by mov- ing signals as required.
2.PLDs are inexpensive as compared to dedicated bus controllers.