MCF5282 ColdFire Microcontroller User’s Manual
HOW to Reach US USA/EUROPE/LOCATIONS not Listed
IND
IND
Contents
Chapter Enhanced Multiply-Accumulate Unit Emac
Timing Assumptions Move Instruction Execution Times
Chapter Static RAM Sram
Chapter Cache
ColdFire Flash Module CFM
Chapter Power Management
Chapter System Control Module SCM
Clock Module
Interrupt Controller Modules
Chapter Chip Select Module
Signal Descriptions
Chapter Edge Port Module Eport
Chapter External Interface Module EIM
Chapter Synchronous Dram Controller Module
Chapter DMA Controller Module
Chapter Fast Ethernet Controller FEC
Chapter Programmable Interrupt Timer Modules PIT0-PIT3
Chapter Watchdog Timer Module
Chapter General Purpose Timer Modules Gpta and Gptb
20.3
Chapter DMA Timers DTIM0-DTIM3
Chapter Queued Serial Peripheral Interface Qspi Module
Chapter Uart Modules
Chapter I2C Interface
Chapter FlexCAN
Chapter General Purpose I/O Module
Chapter Queued Analog-to-Digital Converter Qadc
27.4.7
Reset Controller Module
Chapter Debug Support
Chapter Chip Configuration Module CCM
Chapter Ieee 1149.1 Test Access Port Jtag
Appendix a Register Memory Map
Electrical Characteristics
Chapter Mechanical Data
Paragraph Title Number 31.6.2 Nonscan Chain Operation 31-12
Illustrations
Title Number
10-7
13-4
17-13
20-20
23-10
25-31
Qadc Status Register 0 QASR0 27-22 27-12
27-53
29-39WDMREG BDM Command Format 29-36 29-40
Tables
Charge Pump Current and MFD in Normal Mode Operation
10-13
15-18
17-30
20-23
25-21
27-13
29-43
33-21 Timer Module AC Timing Specifications 33-24 33-22
Audience
Organization
Organization
Xlv
General Information
Suggested Reading
ColdFire Documentation
Conventions
Table i. Acronyms and Abbreviated Terms
Acronyms and Abbreviations
Meaning
Operand Syntax
Terminology Conventions
Table ii. Notational Conventions
Opcode Wildcard
Port Name
ACC
CCR
PST
LSW
MSW
Table iii. Revision History
Revision History
Table iii provides a revision history for this document
SST
Number Release
Revision Date Substantive Changes
Frsr
Liv
10.3.6/10-11
RAMBAR.’
Revision Number
Substantive Changes Section/Page
MCF5282 Key Features
Chapter Overview
MCF5282 Key Features
MCF5282 Key Features
MCF5282 Key Features
MCF5282 Key Features
MCF5282 Key Features
MCF5282 Block Diagram
Version 2 ColdFire Core
Cache Configuration
Configuration Tag Address Data Array Address
Cache
Flash
Sram
Debug Module
System Control Module
External Interface Module EIM
General Input/Output Ports
Power Management
Chip Select
Interrupt Controllers INTC0/INTC1
Test Access Port
Uart Modules
General-Purpose Timers GPTA/GPTB
DMA Timers DTIM0-DTIM3
Periodic Interrupt Timers PIT0-PIT3
Reset
Software Watchdog Timer
Phase Locked Loop PLL
DMA Controller
MCF5282-Specific Features
MCF5282-Specific Features
Fifo
Processor Pipelines
IAG
Dsoc
Processor Register Description
User Programming Model
Stack Pointer A7
Data Registers D0-D7
Address Registers A0-A6
Program Counter PC
Condition Code Register CCR
Bits Name Description
Emac Programming Model
Supervisor Programming Model
System Byte Condition Code Register CCR
Status Register SR
Bits
Supervisor/User Stack Pointers A7 and OTHERA7
Vector Base Register VBR
Access Control Registers ACR0, ACR1
Programming Model
Cache Control Register Cacr
Name CPU Space Rc Written with Register Name
Additions to the Instruction Set Architecture
Local Memory Registers
ISA Revision A+ New Instructions
Exception Processing Overview
Instruction Description
Exception Vector Assignments
Vector Stacked Program Assignment NumberS Offset Hex Counter
Format Field Encodings
Exception Stack Frame Definition
0x100-0x3FC Next
Processor Exceptions
Access Error Exception
Fault Status Encodings
FS30 Definition
Divide-By-Zero
Address Error Exception
Illegal Instruction Exception
Privilege Violation
Unimplemented Line-F Opcode
Unimplemented Line-A Opcode
Debug Interrupt
Reset Exception
RTE and Format Error Exception
Fault-on-Fault Halt
Trap Instruction Exception
VER REV
MAC DIV Emac FPU MMU ISA Debug
VER
D0 Hardware Configuration Info Field Description
MAC
Busw DCA Dcsiz RAM1SIZ ROM1SIZ
ICA Icsiz RAM0SIZ ROM0SIZ
ICA
16KB RAM
4KB RAM
8KB RAM
32KB RAM
Instruction Execution Timing
Timing Assumptions
10. Misaligned Operand References
Move Instruction Execution Times
Address10 Size Kbus Additional Operations CR/W
12. Move Long Execution Times
11. Move Byte and Word Execution Times
Source Destination Ax+ D16,Ax D8,Ax,Xi Xxx.wl
13. One Operand Instruction Execution Times
Standard One Operand Instruction Execution Times
Standard Two Operand Instruction Execution Times
14. Two Operand Instruction Execution Times
Standard Two Operand Instruction Execution Times
Effective Address Opcode An+ D16,An D8,An,Xn*SF Xxx.wl
Miscellaneous Instruction Execution Times
15. Miscellaneous Instruction Execution Times
D16,PC D8,PC,Xn*SF
16. Emac Instruction Execution Times
Emac Instruction Execution Times
Effective Address Opcode An+ D16,An D8,An,X Xxx.wl #xxx
17. General Branch Instruction Execution Times
Branch Instruction Execution Times
ColdFire Instruction Set Architecture Enhancements
18. BRA, Bcc Instruction Execution Times
Attributes
Operation
Assembler Syntax
Instruction Format
Assembler Syntax BYTEREV.L Dx Attributes
Byte Reverse Register Byterev
Condition Codes
Find First One in Register
Old Dx310 New Dx310
Supported Starting with ISA A+
Store/Load Status Register Strldsr
Assembler SyntaxSTRLDSR #data
Chapter Enhanced Multiply-Accumulate Unit Emac
Multiply-Accumulate Unit
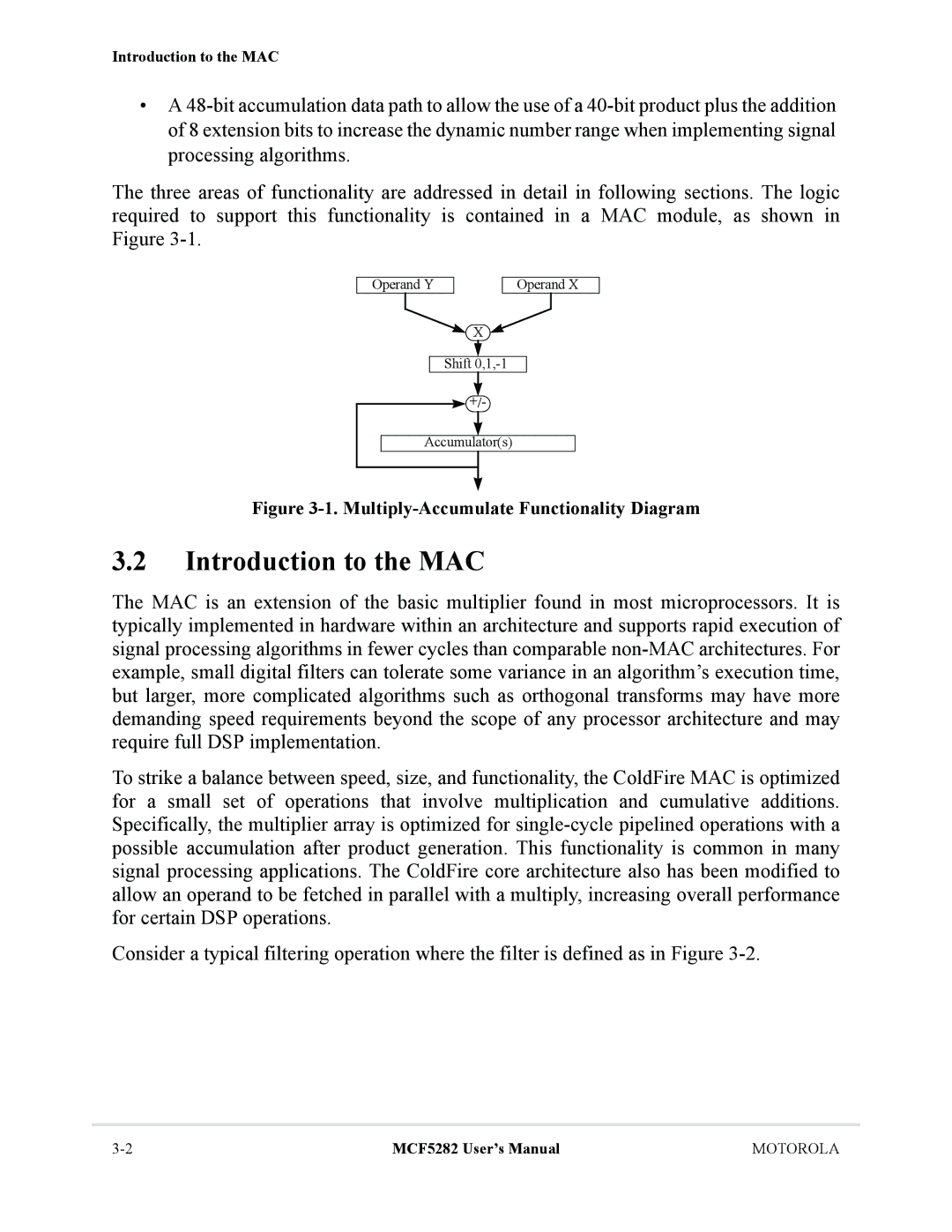
Multiply-Accumulate Functionality Diagram
Introduction to the MAC
General Operation
Infinite Impulse Response IIR Filter
Fractional Alignment
Motorola
MAC Status Register Macsr
Memory Map/Register Set
1describes Macsr fields
Macsr Field Descriptions
Summary of S/U, F/I, and R/T Control Bits
Fractional Operation Mode
Rounding
Operational Modes
Saving and Restoring the Emac Programming Model
Mask Register Mask
Following code performs the Emac state restore
MULS/MULU
MAC.sz Ry,RxSF,eay&,Rw
Emac Instruction Execution Times
Command Mnemonic Description
Emac Instruction Set Summary
3summarizes Emac unit instructions
Mac Mov
Data Representation
Accumulator Mac Old Mov New
MAC Opcodes
Two’s Complement, Signed Fractional Equation
MACSR.V =
Emac Instruction Set Summary
MACSR.Z =
Emac Instruction Set Summary
Motorola
Emac Instruction Set Summary MCF5282 User’s Manual
Cache Physical Organization
Cache Features
This chapter describes the MCF5282 cache operation
Cache Physical Organization
Cache Operation
Interaction with Other Modules
Memory Reference Attributes
Cache Coherency and Invalidation
Initial Fetch Offset vs. Clnf Bits
Cache Miss Fetch Algorithm/Line Fills
CLNF10 Longword Address Bits
Instruction Cache Operation as Defined by CACR31
CACR31 CACR10 Type of Instruction Fetch Description
Cache Registers
Cache Programming Model
Cache Registers Memory Map
Cache Control Register Cacr
Ceib DCM Dbwe DWP Eusp Clnf
Cenb CPD
Cinv Didi Disd Invi Invd
Cenb
Ceib
CACR23 CACR22 CACR21 CACR20 Configuration Operation
Cache Configuration as Defined by CACR31, 23
CACR31 CACR23 CACR22 Configuration Description
Cache Invalidate All as Defined by CACR23, 22, 21
External Fetch Size Based on Miss Address and Clnf
Access Control Registers ACR0, ACR1
Bufw
BWE
Between the processors local bus and the external bus
Sram Operation
Sram Features
Sram Programming Model
PRI1, PRI2
Sram Base Address Register Rambar
PRI1 PRI2 SPV
PRI12 Upper Bank Lower Bank Priority
Sram Initialization
Sram Base Address Register
Sram Initialization Code
Power Management
Typical Rambar Setting Examples
Following loop initializes the entire Sram to zero
Sram Programming Model
Sram Programming Model MCF5282 User’s Manual
Features
Chapter ColdFire Flash Module CFM
Block Diagram
CFM Block Diagram
Memory Map
CFM Array Memory Map
Flash Base Address Register Flashbar
CFM Configuration Field
CFM Configuration Field
Address Offset from array base Size Description
Memory Map
BA30 BA29
Register Descriptions
CFM Configuration Register Cfmcr
CFM Registers
Flash registers are described in this subsection
Bits Name Description
CFM Clock Divider Register Cfmclkd
Cfmcr Field Descriptions
Divld PRDIV8
CFM Security Register Cfmsec
Cfmclkd Field Descriptions
Cfmsec Field Descriptions
SEC150 Description
Cfmprot Field Descriptions
CFM Protection Register Cfmprot
Prot
PROTECT2
CFM Supervisor Access Register Cfmsacc
PROTECT31
Sector
Cfmsacc Field Descriptions
CFM Data Access Register Cfmdacc
Data
10. Cfmustat Field Descriptions
CFM User Status Register Cfmustat
Only one Cfmustat bit should be cleared at a time
Cbeif Ccif Pviol Accerr Blank
12. Cfmcmd User Mode Commands
CFM Command Register Cfmcmd
Command Name Description
Write Operations
CFM Operation
Read Operations
Program and Erase Operations
Thus the Flash state machine clock will be
Setting the Cfmclkd Register
Consider the following example for fSYS = 66 MHz
Program, Erase, and Verify Sequences
13. Flash User Commands
Flash Valid Commands
13summarizes the valid Flash user commands
Meaning Description
13. Example Program Algorithm
Stop Mode
Flash User Mode Illegal Operations
Master Mode
Flash Security Operation
Back Door Access
Reset
Erase Verify Check
14. CFM Interrupt Sources
Interrupt Source Interrupt Flag Local Enable
Interrupts
Cbeif Cbeie
Interrupts MCF5282 User’s Manual
Memory Map and Registers
Programming Model
Memory Map
Low-Power Interrupt Control Register Lpicr
Chip Configuration Module Memory Map
Following subsection describes the PMM registers
Lpicr Field Description
Enbstop
Xlpmipl Interrupts Level Needed to Exit Low-Power Mode
Low-Power Control Register Lpcr
Xlpmipl Settings
Lpmd Stpmd Lvdse
PLL/CLKOUT Stop Mode Operation
Low-Power Modes
Low-Power Modes
Functional Description
Doze Mode
Run Mode
Wait Mode
Stop Mode
Peripheral Shut Down
Peripheral Behavior in Low-Power Modes
Static Random-Access Memory Sram
ColdFire Core
DMA Controller DMAC0-DMA3
Sdram Controller Sdramc
Chip Select Module
Uart Modules UART0, UART1, and UART2
2.9 I2C Module
DMA Timers DMAT0-DMAT3
Queued Serial Peripheral Interface Qspi
Fast Ethernet Controller FEC
Reset Controller
Interrupt Controllers INTC0, INTC1
2.14 I/O Ports
Chip Configuration Module
Clock Module
Edge Port
Watchdog Timer
Programmable Interrupt Timers PIT0, PIT1, PIT2 and PIT3
Queued Analog-to-Digital Converter Qadc
General Purpose Timers Gpta and Gptb
FlexCAN
Functional Description
ColdFire Flash Module
2.25 BDM
Summary of Peripheral State During Low-Power Modes
CPU and Peripherals in Low-Power Modes
Jtag
BDM
Qadc
Jtag
Functional Description MCF5282 User’s Manual
Features
Overview
SCM Register Map
Memory Map and Register Definition
3124 2316 158
Internal Peripheral System Base Address Register Ipsbar
Register Descriptions
Cache
Memory Base Address Register Rambar
Ipsbar Field Description
Memory Base Address Register Rambar Rambar Field Description
BDE
Core Watchdog Control Register Cwcr
Core Reset Status Register Crsr
Crsr Field Descriptions
Register Descriptions
Core Watchdog Timer Delay
CWT CWT Time-Out Period
Core Watchdog Service Register Cwsr
Internal Bus Arbitration
Marb
SRAM1 Mpark Rambar CPU DMA EIM
FEC Sdramc
Overview
Round-Robin Mode
Arbitration Algorithms
Bus Master Park Register Mpark
Fixed Mode
Fixed Timeout Prklast Lckouttime
M2PEN BCR24BIT M3PRTY M2PRTY M0PRTY M1PRTY
Mpark Field Description
System Access Control Unit Sacu
Features
3128 2724 2320 1916 1512 118
Memory Map/Register Definition
Sacu Register Memory Map
PACR1 PACR2 PACR3
Master Privilege Register MPR
Peripheral Access Control Registers Pacr 0-PACR8
PACR6
Bits Supervisor Mode User Mode
12. Peripheral Access Control Registers PACRs
Ipsbar Offset Name Modules Controlled
DTIM0 DTIM1
UART2
Qspi
DTIM2 DTIM3
14. Gpacr Accessctrl Bit Encodings
13. Grouped PeripheralAccess Control Register
Gpacr Field Descriptions
GPACR0
15. Gpacr Address Space
Register Space Protected Modules Protected Ipsbar Offset
EPORT, WDOG, PIT0-PIT3, QADC, GPTA, Gptb
Normal PLL Mode
Modes of Operation
External Clock Mode
Low-power Mode Operation
2 11 PLL Mode
Clock Module Operation in Low-power Modes
Block Diagram
Clock Module Block Diagram
Extal
Signal Descriptions
Signal Properties
Name Function
Memory Map and Registers
Lolre MFD2 MFD1 MFD0 Locre
Register Descriptions
Synthesizer Control Register Syncr
Locen Disclk Fwkup STPMD1 STPMD0
MFD20
MFD
RFD
OSC
Synthesizer Status Register Synsr
Stpmd
Pllmode
Synsr Field Descriptions
Locks
System Clock Modes
Clock Mode
Functional Description
System Clock Modes
System Clock Generation
Clock Operation During Reset
System Clock Mode PLL Options
Clock Out and Clock In Relationships
Phase and Frequency Detector PFD
PLL Operation
Voltage Control Output VCO
Charge Pump Current and MFD in Normal Mode Operation
Charge Pump/Loop Filter
Multiplication Factor Divider MFD
PLL Lock Detection
PLL Loss of Lock Reset
PLL Loss of Lock Conditions
Alternate Clock Selection
Loss of Clock Reset
Loss of Clock Detection
Loss of Clock Summary
Loss of Clock in Stop Mode
10. Stop Mode Operation Sheet 1
Expected PLL Action
10. Stop Mode Operation Sheet 2
Stop
NRM ‘LC ‘LK
10. Stop Mode Operation Sheet 3
‘LC NRM ‘LK
10. Stop Mode Operation Sheet 4
PLL
Clock
10. Stop Mode Operation Sheet 5
Lose reference
Modes
Functional Description MCF5282 User’s Manual
Chapter Interrupt Controller Modules
10.1 68K/ColdFire Interrupt Architecture Overview
68K/ColdFire Interrupt Architecture Overview
Interrupt Prioritization
Interrupt Controller Theory of Operation
Interrupt Recognition
Interrupt Priority Within a Level
Interrupt Vector Determination
Interrupt Controller Memory Map
Memory Map
Interrupt Controller Base Addresses
Interrupt Controller Number Base Address
Interrupt Pending Registers IPRHn, IPRLn
INT
Intmask
Interrupt Mask Register IMRHn, IMRLn
Maskall
IMRLn Field Descriptions
Interrupt Force Registers INTFRCHn, INTFRCLn
Intfrc
Interrupt Request Level Register IRLRn
IRQ
11. IACKLPRn Field Descriptions
Interrupt Acknowledge Level and Priority Register IACKLPRn
Interrupt Control Register ICRnx, x = 1, 2
Level PRI
12. ICRnx Field Descriptions
Interrupt Sources
13. Interrupt Source Assignment for INTC0
DTIM1 CAP/REF
IIF
DTIM0 CAP/REF
DTIM2 CAP/REF
PIT1 PIF
Gptb TOF
PIT0 PIF
PIT2 PIF
Software and Level n Iack Registers SWIACKR, L1IACK-L7IACK
14. Interrupt Source Assignment for INTC1
Prioritization Between Interrupt Controllers
Vector
Low-Power Wakeup Operation
10-18
Introduction
Low-Power Mode Operation
Ipbus
Low-power Mode Eport Operation Mode Exit
Edge Port Module Operation in Low-power Modes
Interrupt/General-Purpose I/O Pin Descriptions
Registers
Bits Access
Edge Port Module Memory Map
EPPA7
Eport Pin Assignment Register Eppar
Eport Data Direction Register Epddr
EPPA5 EPPA4 EPPA3 EPPA2 EPPA1
Edge Port Data Register Epdr
Edge Port Interrupt Enable Register Epier
Epdd Field Descriptions
Edge Port Flag Register Epfr
Edge Port Pin Data Register Eppdr
Epdr Field Descriptions
Epfr Field Descriptions
EPF7-EPF1
11-8
Chip Select Module Signals
Chip Select Module Signals
1lists signals used by the chip select module
Signal Description
Transfer Size Port Size
Byte Enables/Byte Write Enable Signal Settings
D3124 D2316 D158 D70
Chip Select Operation
General Chip Select Operation
12.3.1.1 8-, 16-, and 32-Bit Port Sizing
External Boot Chip Select Operation
Accesses by Matches in CSARs and DACRs
BS2 BS1 BS0
Chip Select Registers
D1918 External Boot Chip Select Configuration
D1918 Boot Device/Data Port Size
Chip Select Registers
CSARs, -2,specify the chip select base addresses
Chip Select Module Registers
Chip Select Address Registers CSAR0-CSAR6
6describes Csarba
CSARn Field Description
Chip Select Mask Registers CSMR0-CSMR6
7describes Csmr fields
Csmr n Field Descriptions
SD,UC
Chip Select Control Registers CSCR0-CSCR6
8describes CSCRn fields
PS1 PS0 BEM Bstr Bstw
CSCRn Field Descriptions
No internal TA is asserted. Cycle is terminated externally
12-10
ColdFire Bus Signal Summary
Bus and Control Signals
Signal Name Description Clkout Edge
Data Transfer Operation
Bus Characteristics
TIP
Chip-Select Module Output Timing Diagram
Bus Cycle Execution
Accesses by Matches in CSCRs and DACRs
Bus Cycle States
Data Transfer Cycle States
State Cycle
Read Cycle
MCF5282
System
Write Cycle
Write cycle timing diagram is shown in Figure
3describes the six states of a basic write cycle
Fast Termination Cycles
Read Cycle with Fast Termination
Back-to-Back Bus Cycles
Burst Cycles
Line Transfers
Allowable Line Access Patterns
A32 Longword Accesses
Line Read Bus Cycles
13shows timing when internal termination is used
Line Write Bus Cycles
16. Line Write Burst 2-1-1-1, Internal/External Termination
Misaligned Operands
17shows a line burst write with one wait-state insertion
19. Example of a Misaligned Longword Transfer 32-Bit Port
13-16
Chapter Signal Descriptions
MCF5282 Block Diagram with Signal Interfaces
Signal Name Abbreviation Function External Memory Interface
MCF5282 Signal Description
Sdram Controller Signals
Chip Configuration Module
Signal Name Abbreviation Function
Clock and Reset Signals
External Interrupt Signals
2C Signals
Queued Serial Peripheral Interface Qspi Signals
FlexCAN Signals
Uart Signals
Analog-to-Digital Converter Qadc Signals
General Purpose Timer Signals
DMA Timer Signals
Debug Support Signals
Test Signals
2lists signals in alphabetical order by abbreviated name
Power and Reference Signals
MCF5282 Alphabetical Signal Index
Abbreviation Function
Vddpll
TCK
Secondary
MCF5282 Signals and Pin Numbers Sorted by Function
Chip Configuration/Mode Selection
External Memory Interface and Ports
External Interrupts Port
Chip Selects
Sdram Controller
Ethernet
FlexCAN
General Purpose Timers
UARTs
Queued Analog-to-Digital Converter Qadc
DMA Timers
Debug and Jtag Test Port Control
Power Supplies
Single-Chip Mode
Test
Pin Reset States at Reset Single-Chip Mode
External Boot Mode
Listing of signals that do not default to a Gpio function
Signal Reset Clock and Reset Signals
Address Bus A230
14.2 MCF5282 External Signals
External Interface Module EIM Signals
Data Bus D310
Transfer Acknowledge TA
Output Enable OE
Transfer Error Acknowledge TEA
Read/Write R/W
Chip Selects CS60
Transfer Start TS
Transfer In Progress TIP
Transfer Size Encoding
Sdram Controller Signals
Clock and Reset Signals
Chip Configuration Signals
External Interrupt Signals
Ethernet Module Signals
Receive Clock Erxclk
Transmit Error Etxer
Collision Ecol
Receive Data Valid Erxdv
Queued Serial Peripheral Interface Qspi Signals
14.2.9 I2C Signals
FlexCAN Signals
Uart Module Signals
General Purpose Timer Signals
DMA Timer Signals
Analog-to-Digital Converter Signals
Debug Support Signals
Development Serial Output/Test Data DSO/TDO
Breakpoint/Test Mode Select BKPT/TMS
Development Serial Input/Test Data DSI/TDI
Test Clock Tclk
Processor Status Outputs PST30
Test Signals
Debug Data DDATA30
Test Test
Power and Reference Signals
14-34
Overview
Definitions
DACR1
Block Diagram and Major Components
DACR0
Scas Sras Scke SDRAMCS10 Dramw
Command Definition
Sdram Commands
Sdram Controller Operation
Memory Map for Sdramc Registers
Dram Controller Signals
2describes the behavior of Dram signals in synchronous mode
Dram controller registers memory map is shown in Table
4describes DCR fields
Dram Control Register DCR
DCR, shown in -2,controls refresh logic
DCR Field Descriptions
DACRn Field Descriptions
Dram Address and Control Registers DACR0/DACR1
5describes DACRn fields
Bit
15-7
6describes DMRn fields
Bit Associated Access Type Access Definition
Dram Controller Mask Registers DMR0/DMR1
DMRn Field Descriptions
Generic Address Multiplexing Scheme
General Synchronous Operation Guidelines
Address Multiplexing
Address Pin Row Address Column Address
Pins
Pins Row Column
MCF5282
Row Column
15-12
Sdram Byte Strobe Connections
Burst Page Mode
Pins MCF5282
Interfacing Example
Burst Read Sdram Access
Burst Write Sdram Access
Auto-Refresh Operation
Self-Refresh Operation
Auto-Refresh Operation
Initialization Sequence
Self-Refresh Operation
Mode Register Settings
Sdram Example
25. Sdram Example Specifications
Parameter Specification
Clkout
Dacr Initialization
Sdram Interface Configuration
DCR Initialization
26. Sdram Hardware Connections
28. Dacr Initialization Values
Bits Name Setting Description
DACRs should be programmed as shown in Figure
Casl CBM Imrs
DMR Initialization
29. DMR0 Initialization Values
31. Mode Register Mapping to MCF5282 A310
Mode Register Initialization
30. Mode Register Initialization
MCF5282 Pins Sdram Pins Mode Register Initialization
Precharge Sequence
Mode Register Initialization Sequence
Initialization Code
Refresh Sequence
15-25
15-26
Chapter DMA Controller Module
DMA Module Features
Channel 0 Channel 1 Channel 2 Channel
DMA Request Control Dmareqc
DMA Transfer Overview
DMA
DMA Controller Module Programming Model
Memory Map for DMA Controller Module Registers
SAR
Source Address Registers SAR0-SAR3
Destination Address Registers DAR0-DAR3
DAR
Byte Count Registers BCR0-BCR3
BCR
DCRn Field Descriptions
DMA Control Registers DCR0-DCR3
3describes DCRn fields
BWC Sinc Ssize Dinc Dsize Start
BWC
Encoding BCR24BIT =
4describes DSRn fields
DMA Status Registers DSR0-DSR3
DSR n Field Descriptions
BSY
DMA Controller Module Functional Description
Transfer Requests Cycle-Steal and Continuous Modes
Done
Data Transfer Modes
Dual-Address Transfers
Channel Prioritization
Channel Initialization and Startup
Programming the DMA Controller Module
Data Transfer
Auto-Alignment
Termination
Bandwidth Control
16-16
Chapter Fast Ethernet Controller FEC
17.2.2.1 10 Mbps and 100 Mbps MII Interface
Full and Half Duplex Operation
Interface Options
Primary operational modes are described in this section
Address Recognition Options
17.2.2.2 10 Mpbs 7-Wire Interface Operation
Internal Loopback
FEC Top-Level Functional Diagram
PAD
17-5
Hardware Controlled Initialization
Initialization Sequence
User Initialization Prior to Asserting Ecretheren
Ecretheren De-Assertion Effect on FEC
FEC User Initialization Before Ecretheren
Microcontroller Initialization
User Initialization After Asserting Ecretheren
Microcontroller Initialization
Signal Description Emac pin
MII Mode
Wire Mode Configuration
Network Interface Options
FEC Frame Transmission
FEC Frame Reception
Ethernet Address Recognition
Ethernet Address Recognition-Receive Block Decisions
Hash Algorithm
Ethernet Address Recognitionq-Microcode Decisions
Destination Address to 6-Bit Hash
Bit DA Bit Hash Hash Decimal Hex Value
17-15
Pause Frame Field Specification
Full Duplex Flow Control
Collision Handling
Inter-Packet Gap IPG Time
Internal and External Loopback
Ethernet Error-Handling Procedure
Transmission Errors
Reception Errors
Heartbeat
Module Memory Map
Top Level Module Memory Map
Detailed Memory Map Control/Status Registers
10. FEC Register Memory Map
MIB Block Counters Memory Map
11. MIB Counters Memory Map
Mnemonic Description Offset
Ethernet Interrupt Event Register EIR
Registers
Following sections describe each register in detail
Hberr Ieeetsqe
Babr Babt GRA TXF TXB RXF RXB MII Eberr
17-25
Receive Descriptor Active Register Rdar
Interrupt Mask Register Eimr
Babr Babt GRA TXF TXB RXF RXB MII
Transmit Descriptor Active Register Tdar
Rdesactive
Ethernet Control Register ECR
Etheren Reset
Xdesactive
16. ECR Field Descriptions
MII Management Frame Register Mmfr
Data
17. Mmfr Field Descriptions
Bit Name Description
Dispreamble Miispeed
MII Speed Control Register Mscr
Dispreamble
MIB Control Register Mibc
Mibdisable Mibidle
Mibdisable
19. Programming Examples for Mscr
FCE Bcrej Prom Miimode DRT Loop
Receive Control Register RCR
Maxfl
FCE
Tfcpause Fden
Transmit Control Register TCR
GTS
22. TCR Field Descriptions
Physical Address Low Register Palr
Tfcpause
PADDR2
Physical Address High Register Paur
PADDR1
Type
24. Paur Field Descriptions
Opcode/Pause Duration Register OPD
Descriptor Individual Upper Address Register Iaur
Opcode
Bits Name Descriptions
Descriptor Individual Lower Address Ialr
IADDR1
IADDR2
27. Ialr Field Descriptions
Descriptor Group Upper Address Gaur
Descriptor Group Lower Address Galr
GADDR1
GADDR2
Fifo Transmit Fifo Watermark Register Tfwr
Xwmrk
30. Tfwr Field Descriptions
Fifo Receive Bound Register Frbr
Rbound
Receive Descriptor Ring Start Erdsr
Fifo Receive Start Register Frsr
Rfstart
Rdesstart
Transmit Buffer Descriptor Ring Start Etsdr
Xdesstart
34. Etdsr Field Descriptions
Receive Buffer Size Register Emrbr
Rbufsize
Driver/DMA Operation with Buffer Descriptors
Buffer Descriptors
Driver/DMA Operation with Transmit BDs
Driver/DMA Operation with Receive BDs
Ethernet Receive Buffer Descriptor RxBD
RO1 RO2
RO1
36. Receive Buffer Descriptor Field Definitions
Word Location Field Name Description
Erdsr
Ethernet Transmit Buffer Descriptor TxBD
TO1 TO2 ABC
TO1
17-51
17-52
Watchdog Module Operation in Low-power Modes
Low-power Mode Watchdog Operation Mode Exit
Watchdog timer module has no off-chip signals
Signals
Refer to -2for an overview of the watchdog memory map
Watchdog Timer Module Memory Map
16-bit WCR configures watchdog timer operation
Watchdog Control Register WCR
Watchdog Modulus Register WMR
WCR Field Descriptions
WMR Field Descriptions
Watchdog Service Register WSR
Watchdog Count Register Wcntr
WC9 WC8
WS9 WS8
WS7 WS6 WS5 WS4 WS3 WS2 WS1 WS0
Chapter Programmable Interrupt Timer Modules PIT0-PIT3
PIT Module Operation in Low-power Modes
PIT module has no off-chip signals
Low-power Mode PIT Operation Mode Exit
Programmable Interrupt Timer Modules Memory Map
Ipsbar Offset Access For PITx Bits Address
Doze Halted OVW PIE PIF RLD
PIT Control and Status Register Pcsr
PRE3 PRE2 PRE1 PRE0
PRE
PIT Modulus Register PMR
PIF
PIT Count Register Pcntr
Set-and-Forget Timer Operation
This subsection describes the PIT functional operation
System clock
Free-Running Timer Operation
Timeout Specifications
PIT Clock Counter
4shows the interrupt request generated by the PIT
Interrupt Request Flag Enable Bit Timeout
Interrupt Operation
PIT Interrupt Requests
Chapter General Purpose Timer Modules Gpta and Gptb
GPT Block Diagram
GPTn20
Signal Description
Function Reset State Pull-up Name Register Bit
Pin
SYNCn
Ipsbar Offset Bits Access
GPTn3
GPT Modules Memory Map
GPT Input Capture/Output Compare Select Register Gptios
IOS
Gptios Field Descriptions
GPT Compare Force Register Gpcforc
GPT Output Compare 3 Mask Register GPTOC3M
FOC
GPTOC3M Field Descriptions
GPT Output Compare 3 Data Register GPTOC3D
GPT Counter Register Gptcnt
OC3D
Gpten Tffca
GPT System Control Register 1 GPTSCR1
Gptcnt Field Descriptions
Gpten
TOV
GPT Toggle-On-Overflow Register Gpttov
GPT Control Register 1 GPTCTL1
OM3 OL3 OM2
11. GPTCL1 Field Descriptions
GPT Interrupt Enable Register Gptie
GPT Control Register 2 GPTCTL2
EDG3B EDG3A EDG2B EDG2A
GPT System Control Register 2 GPTSCR2
13. Gptie Field Descriptions
GPT Flag Register 1 GPTFLG1
GPT Flag Register 2 GPTFLG2
Ccnt
GPT Channel Registers GPTCn
Pulse Accumulator Control Register Gptpactl
PAE Pamod Pedge CLK Paovi PAI
Paclk
Pulse Accumulator Flag Register Gptpaflg
Paovf Paif
19. Gptpaflg Field Descriptions
Pulse Accumulator Counter Register Gptpacnt
Pacnt
22. Gptddr Field Descriptions
GPT Port Data Register Gptport
GPT Port Data Direction Register Gptddr
Portt
Input Capture
Prescaler
Output Compare
Event Counter Mode
Pulse Accumulator
Pulse Accumulator
Gated Time Accumulation Mode
General-Purpose I/O Ports
OM3 OL3
EDGx OMx OC3Mx Pin Data Driven Comments
23. GPT Settings and Pin Functions
Dir Function
Interrupt Request Flag Enable Bit
Reset
24lists the interrupt requests generated by the timer
Interrupts
Pulse Accumulator Overflow Paovf
Timer Overflow TOF
GPT Channel Interrupts CnF
Pulse Accumulator Input Paif
20-23
20-24
Chapter DMA Timers DTIM0-DTIM3
Key Features
DMA Timer Programming Model
Prescaler
DMA Timer Module Memory Map
Capture Mode
Output Mode
Reference Compare
DMA Timer Mode Registers DTMRn
Orri FRR CLK RST
DTMRn Field Descriptions
DMA Timer Extended Mode Registers DTXMRn
2describes the DTMRn fields
DTXMR3
3describes the DTXMRn fields
DMA Timer Event Registers DTERn
DTXMRn Field Descriptions
4describes the DTERn fields
DMA Timer Reference Registers DTRRn
DMA Timer Capture Registers DTCRn
DTERn Field Descriptions
Using the DMA Timer Modules
DMA Timer Counters DTCNn
Code Example
Calculating Time-Out Values
T0LOOP
Chapter Queued Serial Peripheral Interface Qspi Module
Module Description
Qspi RAM
Interface and Signals
Qspiclk
Operation
Qspi Input and Output Signals and Functions
Signal Name Hi-Z or Actively Driven Function
Internal Bus Interface
Qspi RAM
0x01
Receive RAM
Relative Address Register 0x00
0x0F
Baud Rate Selection
Command RAM
Transmit RAM
System Clock
Transfer Delays
Qspiclk Frequency as Function of System Clock and Baud Rate
66.67 MHz
Transfer Length
Programming Model
Qspi Registers
QMR Field Descriptions
Qspi Mode Register QMR
4gives QMR field descriptions
Value Bits per transfer
Qmrcpha = = Qdlyrqcd Qcrcont = = Qdlyrdtl
Qspi Delay Register Qdlyr
Qspics Qmrcpol =
QCD
6gives QWR field descriptions
Qspi Wrap Register QWR
5gives Qdlyr field descriptions
Qdlyr Field Descriptions
7describes QIR fields
Qspi Interrupt Register QIR
QIR Field Descriptions
Qspi Data Register QDR
Qspi Address Register QAR
Addr
8gives QCR field descriptions
Command RAM Registers QCR0-QCR15
QCR0-QCR15 Field Descriptions
Qspiclk QS2 Qspidout QS3 Qspidin
Programming Example
QSPICS30
QS4 QS5
22-17
22-18
Uart
Ucts Urts Urxd Utxd
Serial Module Overview
Uart Module Memory Map
Register Descriptions
Ipsbar Offset 3124 2316 158
Uart Mode Registers 1 UMR1n
ERR
UMR1n Field Descriptions
Parity Mode Parity Type PT=
2describes UMR1n fields
CTS
3describes UMR2n fields
Uart Mode Register 2 UMR2n
UMR2 n Field Descriptions
UMR2n Field Descriptions
Uart Status Registers USRn
4describes USRn fields
USRn Field Descriptions
5describes UCSRn fields
Uart Clock Select Registers UCSRn
RCS TCS
RCS
Uart Command Registers UCRn
UCSRn Field Descriptions
Dtin
Bits Value Command Description
UCR n Field Descriptions
Uart Transmit Buffers UTBn
Uart Receive Buffers URBn
UCRn Field Descriptions
Uipcr n Field Descriptions
Uart Input Port Change Registers UIPCRn
7describes UIPCRn fields
COS CTS
Uart Interrupt Status/Mask Registers UISRn/UIMRn
UACRs, shown in -7,control the input enable
Uart Auxiliary Control Register UACRn
8describes UACRn fields
9describes UISRn and UIMRn fields
Uart Baud Rate Generator Registers UBG1n/UBG2n
Uisr n/UIMR n Field Descriptions
10describes UIPn fields
Uart Output Port Command Registers UOP1n/UOP0n
Uart Input Port Register UIPn
11describes UOP1 and UOP0 fields
11. UOP1/UOP0 Field Descriptions
IRQ
Uart Module Signal Definitions
Ucts
Transmitter/Receiver Clock Source
12. Uart Module Signals
Programmable Divider
System Clock Baud Rates
Following sections describe how to calculate baud rates
Calculating Baud Rates
Sysclk
Therefore UBG1n = 0x00 and UBG2n = 0xD6
Transmitter and Receiver Operating Modes
Transmitter
External Clock
23-21
20. Transmitter Timing Diagram
Receiver
Fifo Stack
21shows receiver functional timing
23-24
Local Loop-Back Mode
Automatic Echo Mode
Looping Modes
Multidrop Mode
Remote Loop-Back Mode
25. Multidrop Mode Timing Diagram
Read Cycles
Bus Operation
Programming
Write Cycles
Interrupt and DMA Request Initialization
Setting up the Uart to Generate Core Interrupts
Setting up the Uart to Request DMA Service
13. Uart Interrupts
15shows the Uart module initialization sequence
Register Setting
Uart Module Initialization Sequence
14. Uart DMA Requests
26. Uart Mode Programming Flowchart Sheet 1
26. Uart Mode Programming Flowchart Sheet 2
26. Uart Mode Programming Flowchart Sheet 3
26. Uart Mode Programming Flowchart Sheet 4
26. Uart Mode Programming Flowchart Sheet 5
23-36
Interface Features
Chapter I2C Interface
Iadr
Acknowledge bit generation/detection Bus-busy detection
Ifdr
SCL SDA
24.3 I2C System Configuration
24.4 I2C Protocol
Arbitration Procedure
Repeated Start
Clock Stretching
Clock Synchronization
Handshaking
SCL1 SCL2
I2C Interface Memory Map
24.5.1 I2C Address Register I2ADR
2describes I2ADR fields
I2ADR Field Descriptions
I2FDR Field Descriptions
24.5.2 I2C Frequency Divider Register I2FDR
3describes I2FDRIC
Divider
I2CR Field Descriptions
24.5.3 I2C Control Register I2CR
4describes I2CR fields
IEN Iien
I2SR Field Descriptions
24.5.4 I2C Status Register I2SR
5describes I2SR fields
ICF Iaas IBB IAL SRW IIF
24.6 I2C Programming Examples
24.5.5 I2C Data I/O Register I2DR
Generation of Start
Post-Transfer Software Response
24.6.4 Generation of Stop
I2SR
Slave Mode
Generation of Repeated Start
Arbitration Lost
SRW=1
RXAK=
IAAS=1
Write
24-16
Chapter FlexCAN
RAM MB3 MB2 MB1 MB0
Cantx Canrx
FlexCAN Memory Map
25.1.2 External Signals
FlexCAN Memory Map
Message Buffer Structure
Can System
Message Buffers
Typical can system is shown below in Figure
Common Fields for Extended and Standard Format Frames
Message Buffer Codes for Receive Buffers
Common Extended/Standard Format Frames
Message Buffer Codes for Transmit Buffers
Fields for Standard Format Frames
Message Buffer Memory Map
Fields for Extended Format Frames
Extended Format Frames
Message Buffers
Functional Overview
Idhigh Idlow
Transmit Process
Receive Process
Message Buffer Handling
Self-Received Frames
Transmit Message Buffer Deactivation
Serial Message Buffers SMBs
Receive Message Buffer Deactivation
Remote Frames
Locking and Releasing Message Buffers
Overload Frames
Listen-Only Mode
Time Stamp
Examples of System Clock/CAN Bit-Rate/S-Clock
Configuring the FlexCAN Bit Timing
Bit Timing
Freq Mhz Time-quanta/bit Value +
FlexCAN Error Counters
FlexCAN Initialization Sequence
Low-Power Stop Mode for Power Saving
Debug Mode
Special Operating Modes
Canmcr
Auto-Power Save Mode
Interrupts
8describes the Canmcr fields
Can Module Configuration Register Canmcr
Programmer’s Model
Stop FRZ Halt Notrdy Wakemsk Softrst Frzack
Canmcr Field Descriptions
Stop
FlexCAN Control Register 0 CANCTRL0
9describes the CANCTRL0 fields
FlexCAN Control Register 1 CANCTRL1
10. Transmit Pin Configuration
Transmit Pin Configuration
11describes the CANCTRL1 fields
11. CANCTRL1 Field Descriptions
Prescaler Divide Register Presdiv
12describes the Presdiv fields
Samp
12. Presdiv Field Descriptions
FlexCAN Control Register 2 CANCTRL2
13describes the CANCTRL2 fields
13. CANCTRL2 Field Descriptions
14. Timer Field Descriptions
Free Running Timer Timer
14describes the Timer fields
Rx Mask Registers
Receive Mask Registers RXGMASK, RX14MASK, RX15MASK
12. Rx Mask Registers RXGMASK, RX14MASK, and RX15MASK
17describes the Estat fields
FlexCAN Error and Status Register Estat
16. RXGMASK, RX14MASK, and RX15MASK Field Descriptions
17. Estat Field Descriptions
Biterr
BUF15M BUF14M BUF13M
Interrupt Mask Register Imask
18describes the Imask fields
BUF10M BUF9M BUF8M
18. Imask Field Descriptions
Interrupt Flag Register Iflag
19describes the Iflag fields
19. Iflag Field Descriptions
20describes the Rxectr fields
FlexCAN Receive Error Counter Rxectr
FlexCAN Transmit Error Counter Txectr
21describes the Txectr fields
Chapter General Purpose I/O Module
MCF5282 Ports Module Block Diagram
Overview
Features
Sdram control Bit DMA timers Uart transmit/receive
Modes of Operation
External Signal Description
MCF5282 Ports External Signals
SCL
Erxer
SDA
UCTS0
Register Overview
31-24 23-16 15-8 Access
Memory Map/Register Definition
MCF5282 Ports Module Memory Map
Clra Clrb Clrc Clrd
Ddrb Ddrc
Ddreh Ddrel
Clre Clrf Clrg Clrh
Port Output Data Registers PORTn
Port Output Data Registers 8-bit
PORTn 8-bit, 7-bit, 6-bit, and 4-bit Field Descriptions
Port Data Direction Registers DDRn
PORTn bits are described in Table
Register Bits Name Description
Port Data Direction Register 7-bit
Port Pin Data/Set Data Registers PORTnP/SETn
10. Port Pin Data/Set Data Registers 8-bit
PORTnP/SETn 8-bit, 6-bit, and 4-bit Field Descriptions
Port Clear Output Data Registers CLRn
PORTnP/SETn bits are described in Table
PORTUAP/SETUA
CLRn register bits are described in Table
CLRn 8-bit,7-bit, 6-bit, and 4-bit Field Descriptions
External Boot
Reset Values for Pbcdpar Bits
Port Size Pbpa Reset Pcdpa Reset
Port B/C/D Pin Assignment Register Pbcdpar
Pepar Field Descriptions
Port E Pin Assignment Register Pepar
PEPA3
10. Reset Values for Pepar Bits and Fields
Single chip mode
Pfpar controls the pin function of port F75
Port F Pin Assignment Register Pfpar
11. Pfpar Field Descriptions
Pjpar controls the pin function of port J
Port J Pin Assignment Register Pjpar
12. Pjpar Field Descriptions
Psdpar controls the pin function of port SD
Port SD Pin Assignment Register Psdpar
Port AS Pin Assignment Register Paspar
Paspar controls the pin function of port AS
Port EH/EL Pin Assignment Register Pehlpar
14. Paspar Field Descriptions
15. Pehlpar Field Descriptions
Port QS Pin Assignment Register Pqspar
Pqspar controls the pin function of port QS
ECOL, ERXCLK, ERXDV, ERXD0, Ecrs
Ptcpar controls the pin function of port TC
Port TC Pin Assignment Register Ptcpar
PTCPA3 PTCPA2 PTCPA1 PTCPA0
Ptdpar controls the pin function of port TD
Port TD Pin Assignment Register Ptdpar
PTDPA3 PTDPA2 PTDPA1 PTDPA0
Port UA Pin Assignment Register Puapar
Puapar controls the pin function of port UA
Port Digital I/O Timing
Clkout Input PIN Register PIN Data
Initialization/Application Information
Clkout Output Data Register Output PIN
Chapter Queued Analog-to-Digital Converter Qadc
Qadc Block Diagram
Debug Mode
Modes of Operation
Port QA Signal Functions
Port QA Analog Input Signals
Port QA Digital Input/Output Signals
Port QB Signal Functions
Port QB Analog Input Signals
Multiplexed Analog Input Signals
External Trigger Input Signals
Multiplexed Address Output Signals
Port QB Digital I/O Signals
Dedicated Digital I/O Port Supply Signal
Voltage Reference Signals
Dedicated Analog Supply Signals
Multiplexed Analog Input Channels
This subsection describes the Qadc registers
Qadc Module Configuration Register Qadcmcr
Qadc Memory Map
Qadc Test Register Qadctest
Port Data Registers Portqa and Portqb
Port QA and QB Data Direction Register Ddrqa and Ddrqb
ANZ ANY ANX ANW
Qadc Control Register 0 QACR0
Control Registers
This subsection describes the Qadc control registers
Qadc Control Register 0 QACR0 QACR0 Field Descriptions
QPR6
QPR60
Prescaler fSYS Divide-by Values
Divisor
CIE1 PIE1 SSE1
Qadc Control Register 1 QACR1
CIE1
Operating Mode
Queue 1 Operating Modes
Qadc Control Register 2 QACR2
CIE2 PIE2 SSE2
Resume
CIE2
QACR2 Field Descriptions
Queue 2 Operating Modes
BQ2
This subsection describes the Qadc status registers
Status Registers
Qadc Status Register 0 QASR0
MQ2128 Operating Modes
27-20
Queued Analog-to-Digital Converter Qadc 27-21
QS9 QS8
CF1 PF1 CF2
QS7 QS6 CWP5 CWP4 CWP3 CWP2 CWP1 CWP0
11. CCW Pause Bit Response
Scan Mode Queue Operation PF Asserts?
10. QASR0 Field Descriptions
CWP
12. Queue Status
Queue 1/Queue 2 States
12. Queue Status Transition
Conversion Command Word Table CCW
Qadc Status Register 1 QASR1
BYP
IST1 IST0
15. Input Sample Times
Non-Multiplexed Input Signals Channel Number
Port Signal Name
IST10 Input Sample Times
Result Registers
17. Multiplexed Channel Assignments and Signal Designations
Multiplexed Input Signals Channel Number
Right-Justified Unsigned Result Register Rjurr
18. Rjurr Field Descriptions
Left-Justified Signed Result Register Ljsrr
Left-Justified Unsigned Result Register Ljurr
Result
Result Coherency
27.7 Functional Description
External Multiplexing
External Multiplexing Operation
18. External Multiplexing Configuration
Analog-to-Digital Converter Operation
Analog Subsystem
Module Version Options
21. Analog Input Channels
19. Qadc Analog Subsystem Block Diagram
Conversion Cycle Times
Channel Decode and Multiplexer
Sample Buffer
Bias
Digital Control Subsystem
Comparator
Successive Approximation Register SAR
Queue Priority Timing Examples
Queue Priority
22. Qadc Queue Operation with Pause
23. Status Bits
Queue Priority Schemes
22. Trigger Events
Events
23. CCW Priority Situation
24. CCW Priority Situation
26. CCW Priority Situation
28. CCW Priority Situation
30. CCW Priority Situation
32. CCW Priority Situation
34. CCW Freeze Situation
38. CCW Freeze Situation
Boundary Conditions
Scan Modes
Disabled Mode
Reserved Mode
Single-Scan Modes
Software-Initiated Single-Scan Mode
Externally Triggered Single-Scan Mode
Externally Gated Single-Scan Mode
Interval Timer Single-Scan Mode
Continuous-Scan Modes
Software-Initiated Continuous-Scan Mode
Externally Triggered Continuous-Scan Mode
Externally Gated Continuous-Scan Mode
Periodic Timer Continuous-Scan Mode
Qadc Clock Qclk Generation
Periodic/Interval Timer
42. Qadc Clock Subsystem Functions
Conversion Command Word Table
43illustrates the operation of the queue structure
43. Qadc Conversion Queue Operation
Queued Analog-to-Digital Converter Qadc 27-61
Signal Connection Considerations
Result Word Table
Analog Reference Signals
Analog Power Signals
45. Errors Resulting from Clipping
Conversion Timing Schemes
46. External Positive Edge Trigger Mode Timing with Pause
47. Gated Mode, Single Scan Timing
Analog Supply Filtering and Grounding
48. Gated Mode, Continuous Scan Timing
49. Star-Ground at the Point of Power Supply Origin
50. Input Signal Subjected to Negative Stress
Accommodating Positive/Negative Stress Conditions
Iinjn
Iinjp
Analog Input Considerations
52. External Multiplexing of Analog Signal Sources
Analog Input Pins
53. Electrical Model of an A/D Input Signal
24. External Circuit Settling Time to 1/2 LSB
Settling Time for the External Circuit
Source Resistance RF + Rsrc 100 Ω 10 kΩ 100 kΩ
25. Error Resulting from Input Leakage IOff
Error Resulting from Leakage
Interrupt Operation
Queue Queue Activity Status Interrupt Flag
Interrupt Sources
26. Qadc Status Flags and Interrupt Sources
PF1 PIE1
Chapter Reset Controller Module
Rsto
Reset Controller Signal Properties
Rsti
Name Direction Input
Reset Control Register RCR
Reset Controller Memory Map
Lvdie
Reset Status Register RSR
Lvdf
Soft WDR POR
RSR Field Descriptions
WDR
Reset Source Summary
Reset Sources
Power-On Reset
Source Type
Loss-of-Clock Reset
External Reset
Watchdog Timer Reset
Loss-of-Lock Reset
Reset Control Flow
Reset Control Flow
Internal Reset Request
Concurrent Resets
Synchronous Reset Requests
Power-On Reset/Low-Voltage Detect Reset
Reset Status Flags
28-12
Debug module is shown in Figure
Processor/Debug Module Interface
Signal Description
Debug Module Signals
Processor Status Encoding
Real-Time Trace Support
PST30 Definition Hex
Begin Execution of Taken Branch PST =
PST30 Definition Hex Binary
Clkout PST
Ddata
Abhr
Aatr
Ablr
CSR
Rev. a Shared BDM/Breakpoint Hardware
Revision a Shared Debug Resources
BDM/Breakpoint Registers
DRc4-0 Register Name Abbreviation Initial State
Aatr Field Descriptions
Address Attribute Trigger Register Aatr
5describes Aatr fields
TMM
Address Breakpoint Registers ABLR, Abhr
Address Breakpoint Registers ABLR, Abhr
7describes Abhr fields
Configuration/Status Register CSR
6describes Ablr fields
Ablr Field Description
8describes CSR fields
CSR Field Descriptions
Data Breakpoint/Mask Registers DBR, Dbmr
IPI
9describes DBR fields
Program Counter Breakpoint/Mask Registers PBR, Pbmr
10describes Dbmr fields
13describes Pbmr fields
Trigger Definition Register TDR
12describes PBR fields
12. PBR Field Descriptions
14describes TDR fields
14. TDR Field Descriptions
Edum
Background Debug Mode BDM
CPU Halt
Eduu
29-17
Clkout Dsclk DSI
BDM Serial Interface
DSO
15describes receive BDM packet fields
Receive Packet Format
Transmit Packet Format
16describes transmit BDM packet fields
17. BDM Command Summary
BDM Command Set
Section Command
Extension Words as Required
ColdFire BDM Command Format
18describes BDM fields
18. BDM Field Descriptions
Command Sequence Diagrams
16. Command Sequence Diagram
Command Sequence
Command Set Descriptions
Read A/D Register RAREG/RDREG
Write A/D Register WAREG/WDREG
Read Memory Location Read
21. Read Command/Result Formats
22. Read Command Sequence
23. Write Command Format
Write Memory Location Write
Operands are sent as 16 and 32 bits, respectively
Set is returned if a bus error occurs
Dump Memory Block Dump
25. Dump Command/Result Formats
26. Dump Command Sequence
Fill Memory Block Fill
27. Fill Command Format
28. Fill Command Sequence
Resume Execution GO
No Operation NOP
Rc encoding
Read Control Register Rcreg
19. Control Register Map
BDM Accesses of the Stack Pointer Registers A7 SSP, USP
BDM Accesses of the Emac Registers
35. Wcreg Command/Result Formats
Write Control Register Wcreg
Read Debug Module Register Rdmreg
20shows the definition of DRc encoding
20. Definition of DRc Encoding-Read
Write Debug Module Register Wdmreg
DRc40 Debug Register Definition Mnemonic Initial State
21. DDATA30/CSRBSTAT Breakpoint Response
Real-Time Debug Support
Theory of Operation
Breakpoint Status
Emulator Mode
Concurrent BDM and Processor Operation
User Instruction Set
22. PST/DDATA Specification for User-Mode Instructions
Processor Status, Ddata Definition
Instruction Operand Syntax
29-41
29-42
23. PST/DDATA Specification for MAC Instructions
24. PST/DDATA Specification for Supervisor-Mode Instructions
Supervisor Instruction Set
GND Dsclk
Reset DSI
Motorola-Recommended BDM Pinout
GND PST3 PST2 PST1 PST0 DDATA3 DDATA2 DDATA1 DDATA0
29-46
Chapter Chip Configuration Module CCM
Single-Chip Mode
Chip Configuration Module Block Diagram
1provides an overview of the CCM signals
Signal Descriptions
30.4.3 D2624, 21, 1916 Reset Configuration Override
Rcon
Write-Once Bits Read/Write Accessibility
Configuration Read/Write Access
Szen
Chip Configuration Register CCR
Following subsection describes the CCM registers
BMT
Rcsc Rpllsel Rpllref
Reset Configuration Register Rcon
Bootps
Rcsc
Chip Select Configuration
Rcsc Chip Select Configuration
Bootps Port Size Configuration
Boot Port Size
Chip Identification Register CIR
Reset Configuration
PIN PRN
Reset Configuration Pin States During Reset
10. Configuration During Reset
Clock Mode
Chip Mode Selection
D2524
Clock Mode Selection
Boot Device Selection
Output Pad Strength Configuration
11. Chip Configuration Mode Selection
13. Clock Mode Selection
Chip Select Configuration
CCM does not generate interrupt requests
Chapter Ieee 1149.1 Test Access Port Jtag
Jtag Block Diagram
Jtagen Jtag Enable
External Signal Description
31.3.1 Detailed Signal Description
Pin Function Selected
Signal State to the Disable Module
31.3.1.3 TMS/BKPT Test Mode Select / Breakpoint
TRST/DSCLK Test Reset / Development Serial Clock
Tclk Test Clock Input
Instruction Shift Register IR
Memory Map/Register Definition
Memory Map
Idcode Register
Testctrl Register
Bypass Register
Jtagcfmclkdiv Register
Boundary Scan Register
Jtag Module
TAP Controller
Jtag Instructions
Jtag Instructions
5describes public and private instructions
Instruction IR30 Instruction Summary
Idcode Instruction
External Test Instruction Extest
SAMPLE/PRELOAD Instruction
Testleakage Instruction
Enabletestctrl Instruction
Lockoutrecovery Instruction
Highz Instruction
Clamp Instruction
Initialization/Application Information
Restrictions
Bypass Instruction
Nonscan Chain Operation
Chapter Mechanical Data
Pinout
MCF5282 Pinout 256 Mapbga
Mapbga Pin Pin Functions
MCF5282 Signal Description by Pin Number
Secondary Tertiary
PG2
PG4
PG3
PF4
GPTA0
PUA1 VDD
GPTB0
PQA3 ETRIG1 VRH VDD Vssa VSS
GPTB2
PQA0 MA0 VDD Vdda
PUA3 VSS Xtal Jtagen
PQS5
Ordering Information
Motorola Part Description Speed Temperature
Orderable Part Numbers
32-8
Maximum Ratings
Rating Symbol Value Unit
Absolute Maximum Ratings1
Rating Symbol
HBM
Characteristic Symbol Value Unit
Thermal Characteristics
Thermal Characteristics
2lists thermal resistance values
Characteristic Symbol Min Max Unit
DC Electrical Specifications
DC Electrical Specifications1
Solving equations 1 and 2 for K gives
Wait Doze Stop
Phase Lock Loop Electrical Specifications
PLL Electrical Specifications
Parameter Symbol Min Max Unit
Qadc Electrical Characteristics
Qadc Electrical Specifications Operating
Qadc Absolute Maximum Ratings
Parameter Symbol Min
IOH = TBD
Sgfm Flash Program and Erase Characteristics
Flash Memory Characteristics
Qadc Conversion Specifications Operating
Num Parameter Symbol Min Max Unit
Sgfm Flash Module Life Characteristics
External Interface Timing Characteristics
10. Processor Bus Input Timing Specifications
Name Characteristic Symbol Min Max Unit Control Outputs
Processor Bus Output Timing Specifications
11. External Bus Output Timing Specifications
Timings listed in -10are shown in Figure
Data Outputs
Read/Write Internally Terminated Timing
Read Bus Cycle Terminated by TA
Read Bus Cycle Terminated by TEA
Symbol Min Max Unit
Sras Scas Dramw
13. Gpio Timing1
33.9 General Purpose I/O Timing
Sras SCAS1 Dramw
Reset and Configuration Override Timing
14. Reset and Configuration Override Timing
Num Characteristic Min Max Units
33.11 I2C Input/Output Timing Specifications
15. I2C Input Timing Specifications between SCL and SDA
Clkout Rsti Rsto
Fast Ethernet AC Timing Specifications
16. I2C Output Timing Specifications between SCL and SDA
17. MII Receive Signal Timing
MII Receive Signal Timing ERXD30, ERXDV, ERXER, and Erxclk
MII Transmit Signal Timing ETXD30, ETXEN, ETXER, Etxclk
Num Characteristic Min Max Unit
18. MII Transmit Signal Timing
MII Async Inputs Signal Timing Ecrs and Ecol
19lists MII asynchronous inputs signal timing
19. MII Async Inputs Signal Timing
MII Serial Management Channel Timing Emdio and Emdc
20. MII Serial Management Channel Timing
21lists timer module AC timings
DMA Timer Module AC Timing Specifications
Qspi Electrical Specifications
22lists Qspi timings
Jtag and Boundary Scan Timing
23. Jtag and Boundary Scan Timing
17. Test Access Port Timing
16. Boundary Scan Jtag Timing
24. Debug AC Timing Specification
Debug AC Timing Specifications
Clkout VIL
20shows real-time trace timing for the values in Table
20. Real-Time Trace AC Timing
ACR0
Table A-1. CPU Space Register Memory Map
Address Name Mnemonic Size
ACR1
I2C
Table A-2. Module Memory Map Overview
Address Module Size
Qadc
Sdramc Registers
Table A-3. Register Memory Map
Address Name Mnemonic Size SCM Registers
Chip Select Registers
DMA Registers
Uart Registers
UBG21
UISR1
UIMR1
UIP01
I2C Registers
DMA Timer Registers
Qspi Registers
Interrupt Controller
Ipsbar + 0xC56
IPRL1
SWACKR0
IPRH1
IMRH1
Global Interrupt Acknowledge Cycle Registers
FEC Registers
Gpio Registers
Portsd
Portas
Portqs
Porttc
Portbp
Portap
Seta Ipsbar +
Setb Ipsbar +
Clrg
Clra
Clrf
Clras
Clock Module Registers
Edge Port Registers
Watchdog Timer Registers
General Purpose Timer a Registers
Qadc Registers
General Purpose Timer B Registers
FlexCAN Registers
Flash Registers
MCF5282 User’s Manual
Index
Index-2
Index-3
Index-4
Index-5
Index-6
Index-7
Index-8
Index-9
Index-10
Index-11
Index-12
Index-13
Index-14
Index-15
Index-16

![]()