106CHAPTER 15: ROUTING CONFIGURATION GUIDE
Configuring a (Totally) When a large number of OSPF routers are present on a network, the LSDB of
Stub Arearouters may become so large that a great amount of storage space is occupied and CPU resources are exhausted when performing the SPF computation.
In addition, as the topology of a large network is prone to changes, enormous OSPF packets may be created, reducing bandwidth utilization. Each topology change makes all the routers perform a route recalculation.
To address this issue, OSPF divides an AS into multiple areas.
Backbone area
The area ID of the backbone area is 0. The backbone area is responsible for distributing routing information between
(Totally) Stub area
The ABR in a stub area does not distribute
To further reduce the routing table size in a stub area, you can configure the stub area as a totally stub area, where the ABR advertises neither the addresses of other areas nor the external routes.
NSSA area
Similar to a stub area, a Not So Stubby Area (NSSA) area imports no
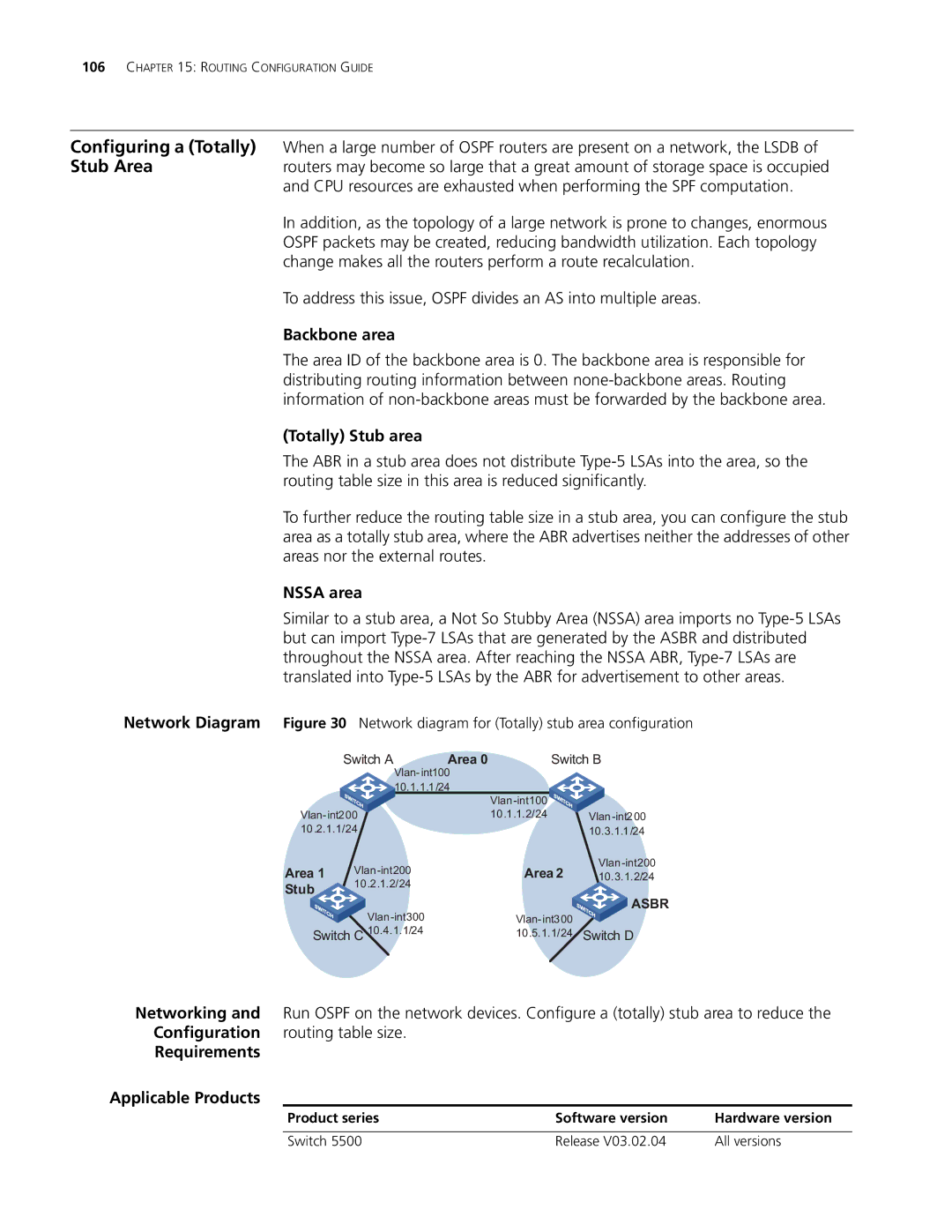
Network Diagram Figure 30 | Network diagram for (Totally) stub area configuration | ||||||
Switch A | Area 0 | Switch B | |||||
|
|
| Vlan- int100 |
|
|
| |
|
| 10.1.1.1/24 |
|
|
| ||
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
| 10.1 .1.2/24 |
| |||
10.2.1.1/24 |
|
|
|
|
| 10.3.1.1/24 | |
Area 1 |
| Area 2 | |||||
| 10.3.1.2/24 | ||||||
Stub | 10 | .2.1.2/24 |
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
| ASBR | |
|
|
| Vlan- int300 | ||||
|
|
|
| ||||
Switch C | 10.4.1.1/24 |
| 10.5.1.1/24 | Switch D | |||
Networking and | Run OSPF on the network devices. Configure a (totally) stub area to reduce the | ||
Configuration | routing table size. |
|
|
Requirements |
|
|
|
Applicable Products |
|
|
|
| Product series | Software version | Hardware version |
|
|
|
|
| Switch 5500 | Release V03.02.04 | All versions |