84CHAPTER 14: MSTP CONFIGURATION GUIDE
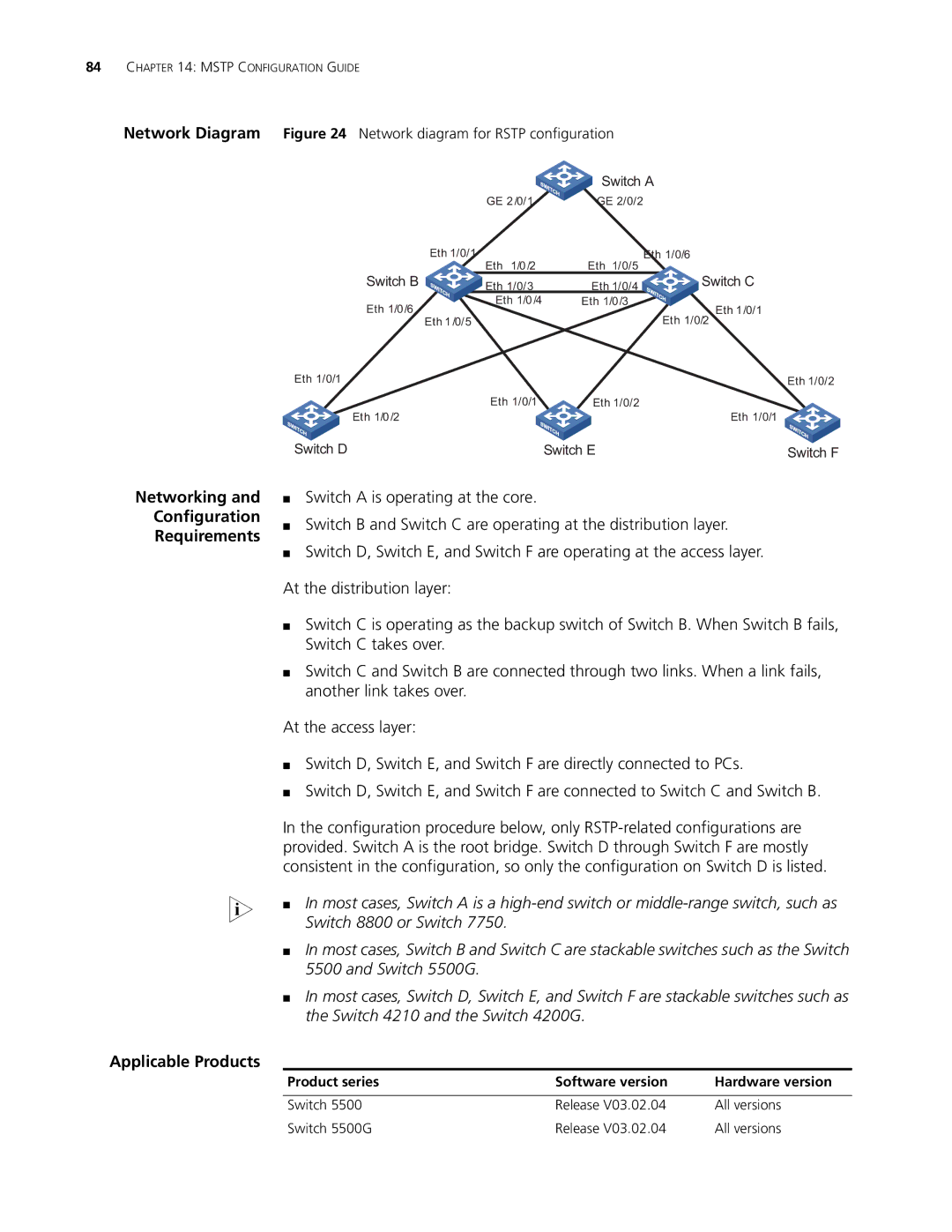
Network Diagram Figure 24 Network diagram for RSTP configuration
|
|
|
| Switch A | ||
|
|
| GE 2/0/1 | GE 2/0/2 |
|
|
| Eth 1/0/1 | Eth 1/0/5 | Eth 1/0/6 | |||
Switch B |
|
| Eth 1/0/2 |
| Switch C | |
|
| Eth 1/0/3 | Eth 1/0/4 |
| ||
Eth 1/0/6 |
|
| Eth 1/0/4 | Eth 1/0/3 |
| Eth 1/0/1 |
Eth 1/0/5 |
|
| ||||
|
| Eth 1/0/2 | ||||
Eth 1/0/1 |
|
|
|
|
| Eth 1/0/2 |
Eth 1/0/2 |
|
| Eth 1/0/1 | Eth 1/0/2 |
| Eth 1/0/1 |
|
|
|
|
| ||
Switch D |
|
|
| Switch E |
| Switch F |
Networking and
Configuration
Requirements
■Switch A is operating at the core.
■Switch B and Switch C are operating at the distribution layer.
■Switch D, Switch E, and Switch F are operating at the access layer.
At the distribution layer:
■Switch C is operating as the backup switch of Switch B. When Switch B fails, Switch C takes over.
■Switch C and Switch B are connected through two links. When a link fails, another link takes over.
At the access layer:
■Switch D, Switch E, and Switch F are directly connected to PCs.
■Switch D, Switch E, and Switch F are connected to Switch C and Switch B.
In the configuration procedure below, only
n | ■ In most cases, Switch A is a |
Switch 8800 or Switch 7750. | |
| ■ In most cases, Switch B and Switch C are stackable switches such as the Switch |
| 5500 and Switch 5500G. |
| ■ In most cases, Switch D, Switch E, and Switch F are stackable switches such as |
| the Switch 4210 and the Switch 4200G. |
Applicable Products
Product series | Software version | Hardware version |
|
|
|
Switch 5500 | Release V03.02.04 | All versions |
Switch 5500G | Release V03.02.04 | All versions |