Definity
CID
Contents
LAN Administration
Contents
Appendix a Screens Reference 243
Appendix B Private Networking 311
Appendix C Security Issues 403
Appendix G References 459
Purpose
Issue Status
Audience
Issue Status Preface
Ethernet Data Module screen is changed in Release
Screen Changes
Ethernet Data Module screen
Ppp Data Module screen
Issue StatusPreface
IP routing and the IP Route screen
Issue Status
Following chapter reorganization has been made for Release
Reorganization
Organization
Organization
Glossary
Index
Terminology
Terminology
Screen
Node
How to access this book from the web
How to order more copies
How to access this book from the web
Click Information Resources
How to Order Books
How to Comment on This Book
Tell us what you think
Tell us what you think
Where to Call for Technical Support
Where to Call for Technical Support
Telephone Number
Trademarks
Trademarks
Trademarks
Connectivity Overview
Definity Switch Connectivity
What kinds of connections are possible? Trunks
Definity Switch Connectivity Networking Overview
Networks
Call-signaling data
DCS-signaling data
Definity
Switch
Function of each circuit pack shown in is described below
IP-Interface
Tie-Trunk Circuit Packs
Pre-R7 circuit packs PI si only
Netcon si only
Isdn
Qsig
LAN
PPP
Hardware Requirements for Upgrades from Pre-R7 Switches
Release 8 Hardware Requirements
Connection Type Hardware Required
Pgate TN577
R8si model
R8csi model
Definity Connection types and capacities
Definity ECS
R8 Model Connection Type Endpoint
ISDN-PRI DCS+
ISDN-TSC
Csi
Pgate LAN
IP Softphones
IP Softphones Networking Overview
Telecommuter application
Road-warrior application
IP Softphones Networking Overview
Physical Addressing
IP Addressing
Logical Addressing
128
Class a
50% Class B
25% Class C
Network ID Range Host ID Range Total IP Addresses
1 to
128.0 to
192.0.0 to
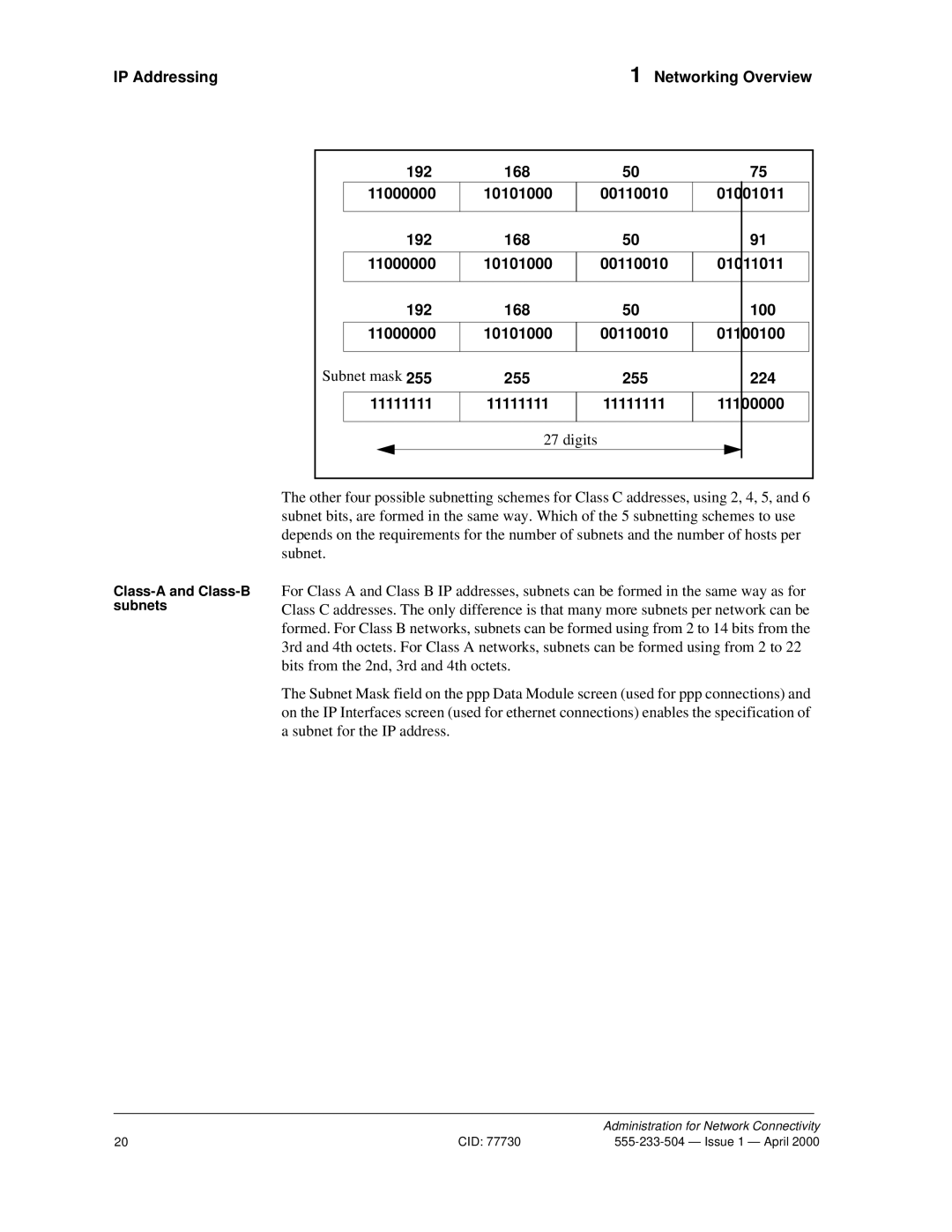
Subnetting
How subnets are created
Default Subnet Mask
Class Type Network ID Host ID
Class Type Network ID Subnet ID Host ID
11111111.00000000.00000000.00000000 255.0.0.0
No. Binary Subnet
Class-C subnets
Decimal
Bit subnets
Example
Subnet mask
255 224
11100000
Digits
Class a Class B Class C Default
Default Gateway
Security Alert
Connection When IP Routes are Needed Type
When to use IP routes
PPP
Route Type host
Switch Node Destination Gateway Route Comments Connections
DS1
LAN
IP Route Examples PPP Connections
DS1
PPP with Ethernet Connections
Default gateways for nodes 2 and 7, respectively
SW B
SW C
SW a
Ethernet-only Connections
IP route needed because
Issue 1 April
Circuit Pack Requirements Software IP Solutions
IP Solutions
Overview
IP-Connected Trunks
IP Softphones
Overview 323 Trunks
Trunk
Enabling Administration
Trunk Administration
Trunk Administration 323 Trunks
Maintenance-Related System Parameters
IP Parameters
Codec Bandwidth Requirement
UDP Port Range Min Max
Trunk Administration Task Summary
Described in the next section
Node names
IP Interfaces
Signaling Group
2 Administered NCA TSC Assignment
~ PBX ID
Trunk Group
Task 1 Assign Node Names
Trunk Administration Task Detail
Network Regions
Field Conditions/Comments
Go to page 2 of the screen
Task 1 Steps
Enter c-lan or medpro
Task 2 Define IP Interfaces
Task 2 Steps
Trunk Administration 323 Trunks Field Conditions/Comments
Task 3 Assign Link via ethernet Data Module to the LAN
Task 3 Steps
Task 4 Create a signaling group
Task 4 Steps
Configuration 4, for instructions Submit the screen
Trunk Administration2 H.323 Trunks
Are described in the Administrator’s Guide
Task 5 Create a trunk group
Open new Trunk Group form enter a tr n
If using DCS, go to screen
PBX ID
Enter group members
Task 6 Modify signaling group
Open the Signaling Group form enter ch sig
Enter values
Task 6 Steps
Task 7 Specify codecs
Task 7 Steps
Troubleshooting IP Solutions
Trunk Problem Solving
Troubleshooting IP Solutions 323 Trunks
Signaling group assignments
TGA1
TGB1
SGB1
SGA1
IP Softphone Problem Solving
LAN Administration
Supported Switches and Adjuncts
Checklist for Prerequisite Administration
Overview LAN Administration
Checklist Item
Otherwise
Overview LAN Administration Checklist Item
Configurations
Organization of this chapter
Task Summary
Supported Switches and Adjuncts
Intuity Audix LAN Setup Summary
CMS LAN Setup Summary
Configuration 1 R8r -ppp- R8si LAN Administration
Configuration 1 R8r -ppp- R8si
Task Summary
Prerequisite Administration
Configuration
Software-defined connections
Hardware connections
Switch 1 Task Assign Node Names
Steps
Switch 1 Task Assign Link via ppp Data Module to Switch
Open Data Module form enter ad da n
COS
COR
BCC
CHAP?
Switch 1 Task Assign Processor Channels
Switch 1 and specifies the destination node and machine ID
Configuration 1 R8r -ppp- R8si
Open the Processor Channel Assignment form enter ch com p
Local Session number on this switch must equal
Switch 2 Task Assign Node Names
Switch 2 Task Assign Link via ppp Data Module to Switch
This data module is assigned the next available extension
This is a display-only field
Switch 2 Task Assign Processor Channels
Open the Processor Channel Assignment form enter ch com p
End
Enable links and processor channels
Ethernet
Definity ECS R8r
Definity ECS R8csi
Task Summary
Configuration
See CentreVu CMS Software Installation and Setup
Switch 1 Task Assign IP Interfaces
End
Open Data Module form enter a da n
To CMS
Name entered on the Node Names screen
End
Switch 2 Task Enable Bus Bridge Connectivity
Open the Maintenance-Related System Parameters form enter
Node-4 Interface on the router to the subnet of Switch
Switch 2 Task Define IP Interfaces
Switch 1 Task Assign IP Interfaces page 77 for an
Add data next
Switch 2 Task Assign IP Route to Switch
Ip n
Configuration 2 R7r +CMS -ethernet- R7csi LAN Administration
Switch 2 Task- Assign Processor Channels
For this connection. The Destination Port number on
Intuity System Administration
Definity ECS administration
Intuity system administration
Network Addressing
Administer Extension Numbers, Channels Services
Administer Subscribers
IP address administered on the Lucent Intuity system
IP Address 192.168.1.125
Worksheet B LAN Data for the Lucent Intuity System
Enable links and processor channels
Hub
R8si BX.25
Ethernet node-3 Definity ECS R8si
Definity ECS R7si Definity ECS R7r
Name IP Address Default Node-1 192 Node-3
Configuration 3 R8si-x.25 R8r Gateway LAN Administration
Switch 1 Task Assign pdm Data Module
ITC
Configuration 3 R8si-x.25 R8r Gateway
Ethernet- R8si Field Conditions/Comments
Switch 1 Task Assign Link via x.25 Data Module to Switch
DTE/DCE
106 CID
Configuration 1 R8r -ppp- R8si
Add data module next
Ch com p
For each connection, the Local Session number on this switch
Issue 1 April CID 111
112 CID
Wideband transmission
For the call setup. Enter y when administering the data
Open Processor Channel Assignment form enter
116 CID
Switch 3 Task Assign Node Names
118 CID
Configuration 1 R8r -ppp- R8si
120 CID
Switch 3 Task Assign Processor Channels
Open Processor Channel Assignment form enter ch com p
122 CID
Enable links and processor channels
Ppp Definity ECS R8csi
ECS R8si
R8csi
Definity ECS R7csi Definity ECS R7si
126 CID
Extension in the dial plan Enter values
Node Name Name entered on the Node Names screen
Switch 1 Task Assign Processor Channels
130 CID
Must equal the Remote Session number on the remote switch
Ch sig n
TSC
NCA-TSC
134 CID
Switch 1 Task Assign ISDN-TSC Gateway
LAN Administration Ppp- R8csi
Configuration 4 R8csi -ISDN- R8si Gateway
Open the Isdn TSC Gateway Channel Assignment form enter
NCA TSC
As-needed means the administered NCA-TSC will be
138 CID
Switch 3 Task Enable Bus Bridge Connectivity
140 CID
Extension in the dial plan Enter values
Switch 3 Task Assign Link via ppp Data Module to Switch
Is complete that is, until after all data modules
Name Be a name entered on the Node Names screen
For this connection. This number must match the Destination
144 CID
Enable links and processor channels
Review checklist Switch 1 administration Assign node names
Ethernet Hub
Configuration 5A
Node-3 Ext
148 CID
Digits Node Name node-2 CHAP? n
150 CID
Switch 1 Task Assign IP Interfaces
152 CID
Open Data Module form enter a da n
Open the Processor Channel Assignment form enter
Issue 1 April CID 155
156 CID
Issue 1 April CID 157
Name IP Address Default Node-1-ppp 192 Node-2 Node-3 192
BCC
Bearer Capability Class. This is a display-only field
160 CID
Switch
162 CID
Switch 2 Task Assign IP Route to node-3
See IP Routing page 251 in Appendix a for more
Name IP Address Default Node-1-eth 192 Node-2 Node-3
Switch 3 Task Assign IP Interfaces
166 CID
Open Data Module form enter a da n
168 CID
End
170 CID
Definity ppp ECS R8r
PppDS1
172 CID
Configuration 5B
Submit the screen1
Issue 1 April CID 175
176 CID
Switch 1 Task Assign IP Interfaces
178 CID
Open Data Module form enter a da n
Switch 1 Task Assign Link via ppp Data Module to C-LANa
COS
Switch 1 Task Assign Link via ppp Data Module to C-LANb
Authentication Protocol security mechanism on this link
184 CID
Issue 1 April CID 185
Must equal the Remote Session number on the remote switch
Session Local
Switch 1 Task Assign IP Route C-LANa to node-3
Switch 1 Task Assign IP Route C-LANb to node-2
Issue 1 April CID 189
Name IP Address Default Node-1a-ppp 192 Node-2 Node-3
Digits Node Name node-1a-ppp CHAP? n
192 CID
Entered on the ppp Data Module screen
194 CID
System assigns the route number 4. Enter values
Name IP Address Default Node-1b-eth 192 Node-2 Node-3
Switch 3 Task Assign IP Interfaces
198 CID
Network uses 1’s
200 CID
End
202 CID
Networking Example
Network Diagram
Overview Networking Example
Ethernet 10BaseT Hub
Router
CMS
Isdn TSC
Link/Channel/TSC Map
Link/Channel/TSC Map Networking Example
ECS R6si ECS R8si
ECS R8csi
Network Map
Network Map Networking Example
R6si
R8r Gateway R8si
Switch-Node 1 Administration
Switch-Node 1 Administration Networking Example
Connection to Switch Node
DS1 Circuit Packs
Dial Plan
Dial Plan Record
Signaling Group
Synchronization Plan
Trunk Groups
Group 12 tie to Switch Node 2
Group 12 member Assignments
Group 22 data to Switch Node 2- page1
Group 22 Group Member assignments
Group 13 ISDN-PRI to Switch Node
Group 13 member Assignments
Group 14 tie to Switch Node 4
Group 14
Group 24 data to Switch Node Page1
Group 24 member Assignments
Uniform Dialing Plan
AAR Digit Analysis
Routing Patterns
Isdn TSC Gateway Channel Assignment
Pattern
Node Names
Data Modules
Data module
Pdm data module
Ppp data module
Processor Channel Assignments
Ethernet data module
Switch-Node 2 Administration
Switch-Node 2 Administration Networking Example
Trunk Goups
Group 12
Uniform Dialing Paln
Procr-intf data module
Release 6 Processor Channel Assignment Screen
Release 6 Interface Links screen
Hunt Group
Hunt Group
Switch-Node 3 Administration
Switch-Node 3 Administration Networking Example
Change synch
Group 13 ISDN-PRI
Group 13
String Min Max Pattern Type Num Reqd 221 101 Aar 222 224
Mrk Lmt List Digits Digits 113 User
Switch-Node 4 Administration4 Networking Example
Switch-Node 4 Administration
Bus Bridge
Switch-Node 4 Administration Networking Example
Group 14 member Assignments
236 CID
Change udp
Name IP Address Ppp41 192 Ppp14 CMS 192 Router 192 Ethernet1
IP Routing
240 CID
Intuity Translations for DCS Audix
CMS Administration
Intuity Translations for DCS Audix Networking Example
CMS Administration Networking Example
Screens Reference
Networking Screens
Other Network-Related Definity Screens
Screens Reference
Networking Screens Screens Reference
Networking Screens
Valid entries Usage
IP Address
Pages 2
Name
Valid Values Usage
IP Interfaces
Inter-region IP connectivity allowed?
Enable Eth Pt
Slot
Code
Sfx
Valid Value Usage
Gateway Address
Net Rgn
Connection When to Define IP Routes Type Host IP Routes
Network IP Routes
Destination Node
Route Number
LAN Board
LAN1
LAN2
Route Type
Audio Codec
IP Media Parameters
Preferences
Data Module Screens
Common Data Module Fields
Valid Entries Data Module Usage Types
Valid Entries Data Usage Module Types
Nncsspp
Valid Data Module Usage Entries Types
Port
Link
Valid Data Usage Entries Module Types
Valid Data Module Usage Values Types
Switched
TAC +
Dte, isn
Establish Connection?
Connected Data Module
Connected To
Unrestricted
Test?
Valid Usage Entries
Data Module Type
Common Fields Network uses 1’s for broadcast addresses?
Are not listed below
Common Fields
Class a Class B Class C Default
Networking Screens Screens Reference Valid Value Usage
Chap?
Destination Digits
Chap Secret
COS
Hot-line , default , or
Maintenance Extension
Physical Channel
List
External
Internal, external
Assigned Member Ext and Name Clocking
This form applies only to the r model
Specifies the data transmission rate for this connection
Set to adjunct for DCS, CMS, or Intuity Audix
Baud Rate
Sent without confirmation. Default is
Default is
Leave at 64 for normal operations
Page
Enter y if this PDM is the secondary data module used for
Communication-Interface Processor Channel
Enable
Proc Chan
Audix , dcs , fp-mwi , gateway
Gtwy-tcp , mis , msaamwl
Msaclk , msahlwc , msallwc
Msamcs , qsig-mwi , and blank
Interface Link
Interface Chan
Destination Port
Session Local
Session Remote
Mach ID
Reconfiguration
Hardware configuration
Circuit Packs
Single-carrier-stack
Carrier
Cabinet Layout
Carrier Type
Lgate
TN802
Screen for ISDN-PRI Non-Facility Associated Signaling
Screen for ISDN-PRI Facility Associated Signaling
Channels on its associated DS1 interface, and for no others
Type ISDN-PRI
Group Number
Associated Signaling
Primary D-channel
Secondary D-channel
Max Number of NCA TSC
Max number of CA TSC
Trunk Group For NCA TSC
Supplementary Service Protocol
Trunk Group for Channel Selection
Trunk Brd
Interface ID
On pages 3-6 of the ATM Signaling Group screen
Service/Feature
Enabled
As-needed Inactivity Time-out min
TSC Index
Local Ext
Networking ScreensA Screens Reference
Through Can include up to 15 digits Blank
Dest. Digits
Adjunct Name
Valid entries Usage 1719, 1720 or
H.323 signaling group type is used for H.323 trunks
5000-9999
65535
Valid entries Usage Mulaw or alaw
Valid entries Usage PROGress default ALERTing
Valid entries Usage Or etsi
Valid entries Usage T1 or E1
Valid entries Usage Host , network , or pbx
Isdn TSC Gateway Channel Assignments
Sig Group
Application
Communication Interface Links
Other Networking-Related Definity Screens
Other Networking-Related Definity Screens Screens Reference
Est Conn
Ext
Destination Number
Conn Mod
Data Module type netcon
Maximum Bit Rate
Special Dialing Option
Assigned Member Ext
Data Module type analog-dm
Abbreviated Dialing
Extended Trunk Access Call Screening
Valid entries Usage Digits 0 through
# character may only be used as
First character
Extension Number Portability Numbering Plan
EPN Code
Hop Channel Assignments Screen
Pages 1 through X of the Screen
Implementation notes
Enter an interface link number in each field
Chan for G3si
Network channel. Displays for G3si only
Node Number Routing
Partitioned Group Number
Node Number
Route Pattern
Message Waiting Indication Subscriber Number Prefixes
Routing Digits e.g AAR/ARS Access Code
Inserted Digits to form Complete Number
Stratum
1 of the screen
Port Network
Secondary
Primary
Location/Name
Slip
Uniform Dial Plan
Ext Codes
AARCode ENPNode Local TempOOS UDPCode
Ext Code, Type and associated data
AARCode ENPNode Local TempOOS
Location Code
310 CID
Contents of this Appendix
Private Networking
Description of DCS
Distributed Communications System
Distributed Communications System Private Networking
DCS Features
Attendant Control of Trunk Group Access
Alphanumeric Display for Terminals
Attendant Direct Trunk Group Selection
Automatic Circuit Assurance
Automatic Callback
Busy Verification of Terminals and Trunks
Call Coverage
DCS Call Coverage
316 CID
Call Forwarding
Call Waiting
Distinctive Ringing
Leave Word Calling
Trunk Group Busy/Warning Indication
Multiappearance Conference/ Transfer
DCS with Rerouting
Italian DCS Protocol
How to administer Enhanced DCS
Form Field
ISDN/X.25 gateway
DCS Over ISDN-PRI D-channel
How to administer DCS Over ISDN-PRI Channel
NCA-TSC
DCS feature considerations
LWC considerations
DCS Over ISDN-PRI
Busy/Warning
DCS Interactions
CAS
Operator ISDN-PRI
UDP
Busy Verification
Asai
CDR
SDN
GRS
Distinctive Ringing
Example DCS configurations
Edcs
Multiappearance
Conference/Transfer
Audix
TSC
PBX ID DCS?
FRL
TSC CA-TSC
PBX-ID
PBX ID
Switch
Ext Code Type Location
Group # Grp Type Used for DCS? DCS Sig. Method
Matching Min Max Del Replacement Net Conv Pattern String
TSC Index Processor Application Channel
DCS PBX ID NCA-TSC
Group # Grp Type Used
For Sig Sig. Group
Dialed String Min Max Rte Call Type Node Num Pat
Local Enable Establish Dest Far-end Appl Index Ext
Group # Grp Type Used for DCS Sig. Method
Centralized Attendant Service
How to administer CAS
ATM PNC?
ATM-PNC
CAS Queues
CAS Backup Service
CAS Remote Hold
Branch-generated call-identification tones
CAS Outgoing Call Routing
CAS Incoming Call Routing
Considerations Branch Attendants
Interactions
342 CID
How to administer Emergency 911 Calls
InteractionsNone
Case #1
Extended Trunk Access
Case #2
Case #4
Case #3
Abbreviated Dialing
How to administer ENP
Extension Number Portability
Inter-PBX Attendant Service
How to administer Inter-PBX Attendant Service
How to administer Private Network Access
Private Network Access
Aplt ISDN-BRI ISDN-PRI
Attendant Call Waiting
How to administer UDP
Distributed Communications System Private Networking
Switch RNX UDP Code
Extension
Considerations
354 CID
Isdn Feature Plus
How to administer Isdn Feature Plus
Isdn Feature Plus Private Networking
~ G3 Version field to ~ Isdn Feature Plus field to y
Description
Differences in Inserted Digits field
Interrogation
Interactions
Forwarding and Coverage
Qsig
Qsig Category Supported Features
Qsig Basic Call Setup
Qsig Basic Supplementary Services
Transit switch information
Transit Counter ANF-TC
Tandem switch information
Isdn numbering formats
Diversion
Call Transfer
Call Offer
Call Completion
Qsig Centralized
SS-CC Options
What you get with Qsig Centralized Audix
Other Qsig Centralized Messaging
What you do not get
Qsig Centralized Attendant Services
Attendant Service
Path Retention
Potential Drawbacks
Qsig Supplementary Services with Rerouting
Qsig Path Replacement
Qsig CAS functions in RLT-CAS
Qsig CAS functions not in RLT CAS
Qsig Transfer into Lucent Qsig Voice Mail
Qsig Value-Added Lucent Valu
Rerouting
Transfer into Qsig Voice Mail
Qsig Protocols
Temporary Signaling Connection TSCs
CA-TSC DCS only
Protocol standards
Setting Up Qsig
Qsig capabilities
~ Async. Transfer Mode ATM Trunking field is y
~ Basic Call Setup field is y
~ Basic Supplementary Services field is y
~ ISDN-BRI Trunks field is y
Numbering Format public, private, unknown, unk-pvt
Setting Up Qsig Supplementary Services
Setting Up Centralized Steps Attendant Services
Transfer into Voice Mail
Setting Up Qsig Valu Steps Call Coverage
Coverage with Qsig Diversion with Rerouting
Related Administration Terminating Extension Groups
Related Hunt Group Administration
Related Phone
Calling Party Number to AUDIX? y
Qsig Interactions
Call Forwarding Diversion
Path Replacement
Transfer Into Qsig
Voice Mail
Qsig Name
Transit Counter
382 CID
Message Waiting
Indications
Isdn Qsig BRI
Isdn Qsig
Adjunct Switch Applications Interface Asai
Called/Busy Name
386 CID
Service CAS
388 CID
Attendant Release Loop Operation
390 CID
Qsig
392 CID
Extending a Call
394 CID
Centralized Voice Mail Via Mode Code
Configuration requirements
Centralized Voice Mail Via Mode Code Private Networking
Definity ECS R8
Feature Support
Centralized Voice Mail Via Mode Code Example Configuration
Setting Up Centralized Voice Mail Via Mode Code
~ Group Type field is Isdn ~ Service Type field is TIE
~ Uniform Dialing Plan field is 4 for each node
~ Uniform Dialing Plan field is 4 or
~ Call Type field is lev0
~ Set Network Level field is
~ Type field is vmi
End
Overview
Japan TTC Q931-a Private Networking Protocols
Japan TTC Q931-a Private Networking Protocols
TTC Q931-a Protocols
~ Interface peer-master or peer-slave
Setting Up TTC Q931-a
~ Numbering format public, private, unknown, unk-pvt
Security solutions
Network Security Issues
Security concerns
Network Security Issues
Access control network topology
Private network
Private segment
Damage control application restrictions Summary
406 CID
For Definity Capacity Limits
Capacities and Resource Requirements
508
Capacities and Performance
For C-LAN Number of Sockets Required
Overview
Performance
Definitions
POE =
G3r G3si
57% 65% 52% 60%
Number CL m MedPro For GOS = P001
Boards =31
Number of MedPros needed
For Full Availability
Solution
Problem
ExampleInternet Call Center
LAN Installation
Install the C-LAN Circuit Pack
LAN Installation
Enter change system-parameters maintenance
Insert C-LAN Circuit Packs
Install C-LAN Cables Hub connection
Required. See the figure below
Other Hardware Upgrades
Wall field connection
IP Trunk Installation
Title Document Issue Number
IP Trunk Administration
Administration overview
IP Trunk Administration IP Trunk Installation
Prerequisites
Off-Premise Dialing at Remote Site
Plan call routing
NT Tasks
420 CID
Definity administration procedures
DS1 Circuit Pack
544 048
Ami-zcs Ami-basic or hdb3
Robbed-bit Cas
Mulaw
Trunk Group
424 CID
Double-click the IP Trunk Backup Restore icon
Backing up configuration manager
Restoring IP trunk
NT administration procedures
Confirming the number of available ports
Click Show All Ports
Click the Dial/Routing Plan tab
None
Routing based on Dialed String
Routing based on Line Numbers
Incoming calls
Select Terminating
Stopping IP Trunk Service
Starting IP Trunk service Change companding to A-Law
Click on Control Panel Services
Alaw
Procedures for Extension Dialing Between Sites
Non-DCS Configuration
Line Search Replace IP Address String
Line Search String Replace String
Signaling
DCS over IP Trunk IP Trunk Installation Administration
DCS over IP Trunk
IP Trunk Network Configuration
TCP/IP signaling
On Switch B
On Switch a
On Switch C
Line Search Replace String
Line
Search
Click Properties
Rerouting calls when IP transmission quality is poor
Click Monitor and Pstn Fallback
Placing a test telephone call
Setting up alerts on IP trunks
More information
Administration, consider making this a joint activity
Viewing error messages
Click Start, Programs, Administrative Tools
Testing Alerts
Alert types
Check physical
Troubleshooting IP trunk
Check LAN functions
Maintaining the performance of the IP trunk server
Use traceroute to
Configuring Microsoft NetMeeting on a PC
Configuration Wizard
Providing general
Information for
Changing Audio Settings
IP Trunk Installation Administration
DCS over IP Trunk
Making Calls to the IP trunk application from NetMeeting
Viewing error messages
Troubleshooting IP Trunk
IP Trunk Worksheets
Field Field Name Field Value Code
IP Trunk Worksheets
Worksheet
Worksheets
Fill in with Same Create Different
IP Trunk
Worksheets
1A2BX 1CX
Replace string 1F1A 2F2A
1AX
458 CID
References
Basic Definity ECS documents
BCS Products Security Handbook, 555-025-600, Issue
Definity ECS Release 8.2 Reports, 555-233-505, Issue
References
References
Call center documents
Definity ECS
Application-specific documents
CentreVu Call Management System CMS
Console operations
Definity ECS Release 7 Console Operations Quick Reference
AAR
ADU
Ansi
Aplt
ATM
Awoh
B8ZS
BB8ZS
BCC
BER
BOS
BRI
Ccis
Ccitt
Ccms
CDR
Cmdr
CMS
COR
COS
CSN
CSU
DCE
Dciu
DCP
DCS
Did
DNS
DSU
Dtdm
DTE
EIA
FAS
HDB3
Iana
Inads
Interserver routing table Glossary
Base address
IP Internet Protocol address
IP user
LAP-D
Mapd
MAC
MA-UUI
MDR
MIB
Mmch
MSA
Nema
Netcon
Nfas
NIC
OSI
Paccon
Pgate
PDM
PRI
Psdn
Pstn
PSN
Qppcn
RPN
RTP
Simple Network Management Protocol Snmp Glossary
Smdr
Snmp
SPE
TCP/IP
TCP
TDM
UNP
UDP
VCI
VPI
WAN
ZCS
Zero Code Suppression ZCS
Index
492 CID
DS1 208, 228, 233 per system
Index
314
299
383
369
498 CID
Qsig NCA-TSC
149, 159, 175, 180, 182
326
502 CID
We’d like your opinion