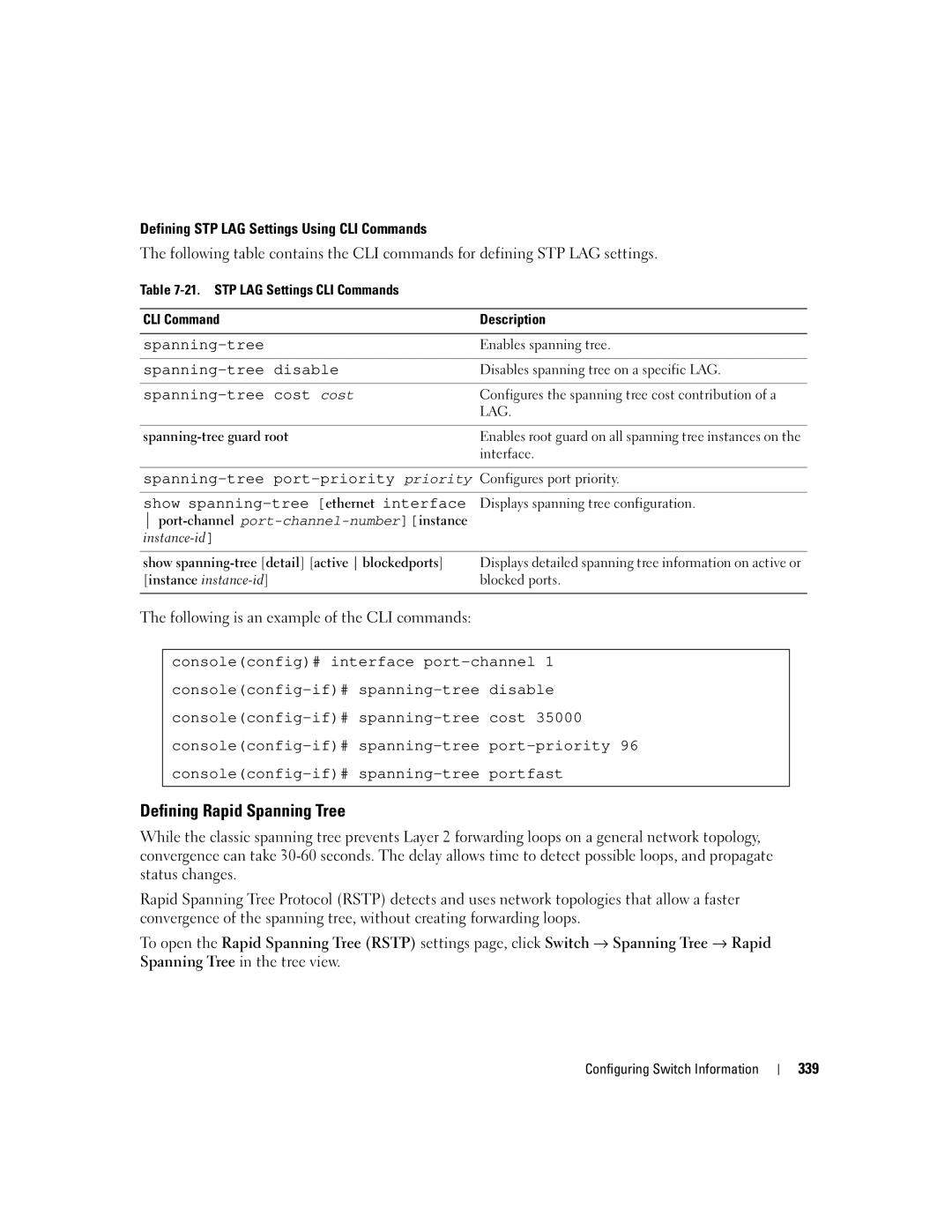
Defining STP LAG Settings Using CLI Commands
The following table contains the CLI commands for defining STP LAG settings. Table
CLI Command | Description |
|
|
Enables spanning tree. | |
|
|
Disables spanning tree on a specific LAG. | |
|
|
| Configures the spanning tree cost contribution of a |
| LAG. |
|
|
Enables root guard on all spanning tree instances on the | |
| interface. |
|
|
Configures port priority. | |
|
|
show | Displays spanning tree configuration. |
| |
| |
|
|
show | Displays detailed spanning tree information on active or |
[instance | blocked ports. |
|
|
The following is an example of the CLI commands:
console(config)# interface
Defining Rapid Spanning Tree
While the classic spanning tree prevents Layer 2 forwarding loops on a general network topology, convergence can take
Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP) detects and uses network topologies that allow a faster convergence of the spanning tree, without creating forwarding loops.
To open the Rapid Spanning Tree (RSTP) settings page, click Switch → Spanning Tree → Rapid Spanning Tree in the tree view.
Configuring Switch Information
339