3Com Switch 7750 Series
Command Reference Guide – ACL Chapter 1 ACL Commands
1-12
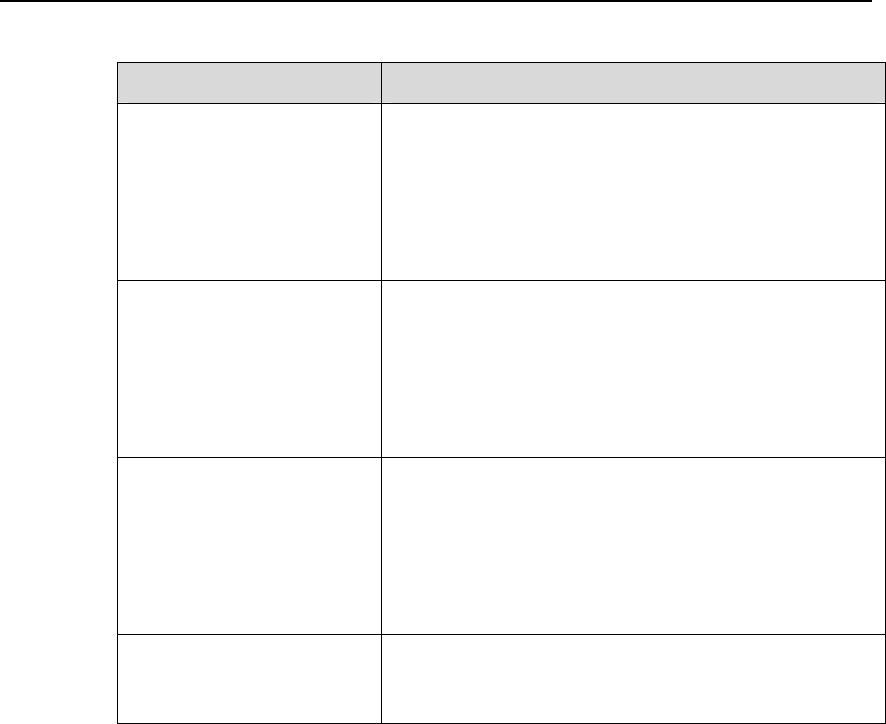
Table 1-6 Parameters description of ACL combinations
Parameter Description
ip-group { acl-number |
acl-name }
Basic and advanced ACL.
acl-number: ACL number of basic and advanced ACL,
ranging from 2,000 to 3,999.
acl-name: ACL name, case insensitive string, up to 32
characters long, beginning with an English letter (a to z
or A to Z), without space or quotation mark.
link-group { acl-number |
acl-name }
Layer 2 ACL
acl-number: ACL number of the Layer 2 ACL, ranging
from 4,000 to 4,999.
acl-name: ACL name, case insensitive string, up to 32
characters long, beginning with an English letter (a to z
or A to Z), without space or quotation mark.
user-group { acl-number |
acl-name }
User-defined ACL
acl-number: ACL number of the user-defined ACL,
ranging from 5,000 to 5,999.
acl-name: ACL name, case insensitive string, up to 32
characters long, beginning with an English letter (a to z
or A to Z), without space or quotation mark.
rule-id Number of the ACL rule, ranging from 0 to 127. If this
argument is not specified, all rules in the specified ACL
will be applied.
system-index: Specifies an interior index value which is used when an ACL rule is
applied to the port. The index value ranges from 0 to 4294,967,295. This keyword is
only available when the ACL rule number is specified in the command. After the
specified ACL takes effect, there are three scenarios when you input the index value:
z If you do not input an index value or the index value you input is 0, the system will
automatically assign an index whose value is greater than 0;
z If the input index value is not 0 and does not conflict with the interior index used
by the system, the system will adopt the index value input by you;
z If the input index value is not 0 but conflicts with the interior index used by the
system, the system will reassign an index value.
When the specified ACL rule is not effective, the system will adopt the index value
input by you.
not-care-for-interface: As for non-48-port interface card, the packet-filtering function
will take place on the interface card where the current port resides after the parameter
is chosen. As for the 48-port interface, if the number of the current port belong to the
range of 1 to 24, the packet filtering will take effect on port 1 to port 24 after the
parameter is chosen; if the number of the current port belong to the range of 25 to 48,
the packet filtering will take effect on port 25 to port 48 after the parameter is chosen.