Issue 4 September
Contents
Fundamentals of Call Vectoring
Call Prompting
Advanced Vector Routing
ANI and II-Digits Routing
Expert Agent Selection
Call Vectoring Applications
Call Vectoring Commands
Contents
Contents
Contents
Contents
Call Vectoring Management
BCMS/CMS
Operation Details for the Route-to Command
Setting Up a Call Center
Call Vectoring System Parameters
Feature Availability
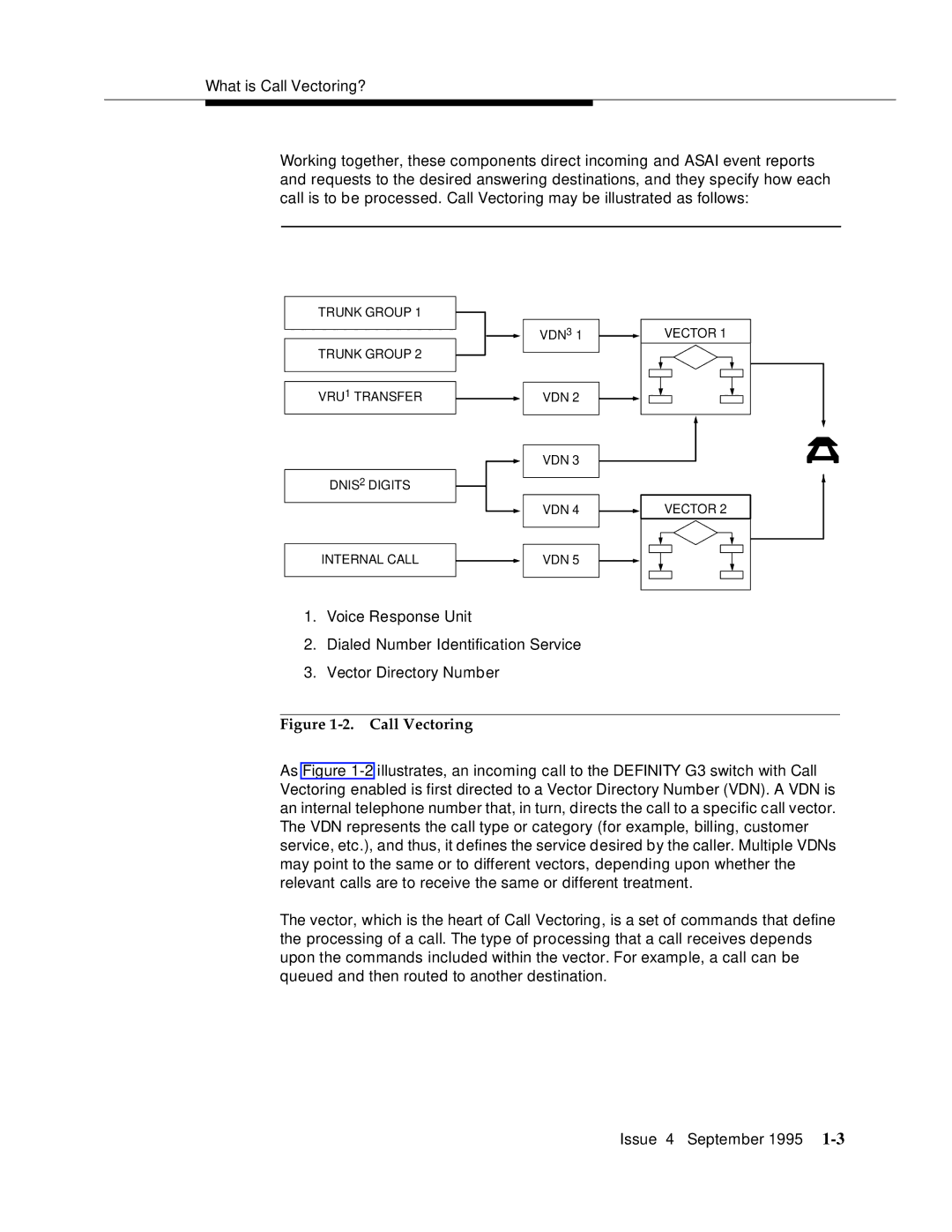
What is Call Vectoring?
About This Document1
Traditional ACD Call Processing
Call Vectoring
Vector Example
What is Expert Agent Selection EAS?
Call Vectoring Features
Intended Audience and Use Guide
Contents and Organization Guide
References
Tutorial
Introduction
Entering the Vector On-Line
Call Vector Form
Procedures for Basic Screen Administration
Call Vector Form Page 2
LAI
Enhanced Vector Editing G3V4 and later releases
Constructing a Vector One Approach
Queuing Call to Main Split
Phase 1 Queuing a Call to the Main Split
Providing Feedback and Delay Announcement
Phase 2 Providing Feedback and Delay Announcement
Page
Repeating Delay Announcement and Feedback
Phase 3 Repeating Delay Announcement Feedback
Queuing Call to Backup Split
Phase 4 Queuing a Call to a Backup Split
Phase 5 Checking the Queue Capacity
Checking Queue Capacity
Checking for Non-Business Hours Screen 1
Phase 6 Checking for Non-Business Hours
10. Checking for Non-Business Hours Screen 2
Benefits of Call Vectoring
Benefits of Call Vectoring Category Call Vectoring Benefits
Benefits of Call Vectoring Category Call Vectoring Benefits
Call Management
Fundamentals of Call Vectoring
Call Flow
Call Queuing to Splits
Caller Control
Split Queue Priority Levels
Agent Work Mode
Calling Party Feedback
Dialed Number Identification Service Dnis
Vector Directory Number
Vector Processing
Fundamentals of Call Vectoring
VDN Override
VDN Override Assigned to Originally Called VDN
VDN in a Coverage Path
Vector Control Flow
Service Observing VDNs
Programming Capabilities
Termination vs. Stopping
Command Summary
Condition Testing within the Commands
Page
Basic Call Vectoring
Functions and Examples
Command Set
Announcements
Providing Call Treatments
Forced Announcements
Delay Announcements
Information Announcements
Delays with Audible Feedback
Multiple Audio or Music Sources
Delay with Multiple Audio/Music Source Feedback
Disconnect
Busy Tone
Voice Response Scripts
Disconnecting a Call
Accessing Voice Response Scripts
Routing Calls
Multiple Split Queuing
Queuing Calls to ACD Splits
12Issue 4 September
11. Leaving Recorded Message
Leaving Recorded Messages
Option with the VDN as the Coverage Point
Interflow
Sending Calls to a Vector-Programmed Number
13. Call Interflow
Service Observing
14. Vector for Service Observing FAC
Service Observing FAC Vector
Branching/Programming
Unconditional Branching
Conditional Branching
16. Conditional Branching
Stopping Vector Processing
17. Stopping Vector Processing
Vector Chaining
Call Prompting
Touch-Tone Collection Requirements
Call Prompting Command Set Category Action Taken
Call Prompting Digit Entry
Entering Variable-Length Digit Strings
Removing Incorrect Digit Strings
Entering Dial-Ahead Digits
Treating Digits as a Destination
Treating Digits as a Destination
Vector Routing Tables
Using Digits to Collect Branching Information
Vector Routing Table
Testing for Digits In Vector Routing Table
Displaying Digits on the Agent’s Set
Using Digits to Select Options
Page
Passing Digits to an Adjunct
Passing Digits to an Adjunct
Remote Access Service Observing Vector
Creating Service Observing Vectors
Dial-Ahead Digits
User-Entered FAC and Extension
Preprogrammed FAC and Extension
11. Dial-Ahead Digits
12. Dial-Ahead Digits
Page
ASAI-Requested Digit Collection
ASAI-Provided Dial-Ahead Digits
Advanced Vector Routing
Advanced Vector Routing Command Set Category Action Taken
EWT for a Split
Expected Wait Time EWT
Passing EWT to a VRU
EWT for a Call
EWT Algorithm
When to Use Wait Time Predictions
Examples Example 1 EWT Routing and Passing Wait to a VRU
EWT Routing and Passing VRU Wait
Example 2 Notifying Callers of Wait Time Without a VRU
Notifying Callers of Wait-Time Without a VRU
EWT Routing-Routing to the Best Split
Example 3 Using EWT to Route to Best Split
Expected Wait Time EWT
Rolling ASA Split Calculation
Rolling Average Speed of Answer ASA
Rolling ASA VDN Calculation
Rolling ASA Considerations
Example
Rolling ASA Routing
VDN Calls
VDN Calls Routing
Counted Calls
ANI/II-Digits Routing Command Set Category Action Taken
ANI and II-Digits Routing7
ANI Routing
ANI Routing Example
ANI Routing Example
Vector Routing Tables with ANI
Vector Routing Table for ANI Routing
II-Digits Routing
Page
II-digits Summary Code Use
II-Digits Routing Example
II-Digits Routing Example
Look-Ahead Interflow8
Functions and Examples
Sending Switch Operation
Two Switch Configuration
Sending Switch Outflow Vector
Receiving Switch Operation
ANI
Call Acceptance Vector Command Qualification
Call Acceptance Vector Commands
Call Denial Vector Command Qualification
Call Denial Vector Commands
Neutral Vector Command Qualification
Neutral Vector Commands
Receiving Switch Inflow Vector
Tandem Switch Configuration
LAI Using a Tandem Switch
Tandem Switch Operation
Far End Switch Operation
Dnis and VDN Override in an LAI Environment
Answering Agent’s Display
Dnis Information Displayed for LAI Scenarios
Originator’s Display
ADR Example
Page
Adjunct Routing
Adjunct Routing Vector
Sending the Call Route Request
Effects of Asai Link Failure on Vector Processing
Vector Announcement 4000 ‘‘We’re sorry. We
Awaiting the Response to the Call Route Request
Treatment Step Used as a Delay for Adjunct Routing
Receiving and Implementing the Call Route
Sample Adjunct Routing Vector with Redundancy
Multiple Outstanding Route Requests
User Scenarios
Expert Agent Selection10
Identifying Caller Needs
Tourist Information/Knowledge of the Region
To Speak Spanish/Bilingual
Emergency Assistance/Handle Stressful Callers
DNIS/ISDN Called Party
Call Prompting/VRU Digits
Example of a Prompt for Entering Call Prompting Digits
Administering Skills
Host Database Lookup
Direct Agent Calling
Emergency Road Service-English-11 Route Planning-English-33
Hunt Group Form with Expert Agent Selection Optioned
VDN Skills
1st 2nd 3rd Vector
Example of VDN Skill Preferences Assignments Call type
VDN 3333 Skill Preferences
Skill Preferences Assignments for VDN
Vector Directory Number VDN Form
Vector Directory Number VDN Form
Agent Skills
Call Vector Form
Example of Agent Skill Assignments Skills Assigned
Process for Delivery of a Call to a Skill Queue
Delivering the Call to the Skill Queue
Call Prompting Vector for the Auto Club
Procedure Using Call Prompting
Super Agent Pool
Page
Modified Vector to Accommodate a Super Agent Pool
Delivery from a Skill Hunt Group
Routing the Call to an Agent
Only Direct Agent call queued
12. Example of UCD/EAD Call Scenario Time Event Skills
Result Reason
13. Example of Call Distribution via UCD/EAD UCD or Time
Agent Login ID Form
ACD Login ID Dialing
Call Routing
Login ID Name on the Voice Terminal Display
Coverage Path
Agent Restrictions
Administration Without Hardware
Feature Interactions
Agents in Multiple Splits Feature
Interactions Involving EAS
Assist
Agent Work Modes
Audible Message Waiting
Auto-Available Skills
Basic CMS
Automatic Answering with Zip Tone
Bridging
Call Coverage
Call Pickup
Class of Service
Class of Restriction
Dial Plan
OCM/EAS
Look-Ahead Interflow
Commands for OCM Predictive Calls
14. Commands for OCM Predictive Calls
Queue Status Indications
Work Mode Buttons
Remote Service Observing
Adjunct Interactions
Call Control
Feature Requests
Value Queries
Multiple Monitors
Event Notification
Adjunct-Controlled Skills
Speech-Processing Adjuncts
CMS R3V2 and later releases
EAS Agent LoginID Table
Communication Link Form
Feature-Related Parameters
Console Parameters
Coverage Groups
Vector Administration
Listed Directory Number
Malicious Call Trace
Upgrading to a G3 EAS Environment
Call Vectoring Applications11
Customer Service Center
Example 1 Customer Service Center
Example 2 Automated Attendant
Automated Attendant
Diva and Data/Message Collection
Example 3 Diva and Data/Message Collection
Page
Distributed Call Centers
Example 4 Distributed Call Centers
Example 5 Help Desk
Help Desk
Insurance Agency/Service Agency
Example 6 Field Agent Vector
Example 6 Claims Vector
Example 6 Customer Service Vector
Warranty Service with EAS
11-16Issue 4 September
Warranty Service with EAS Agent Skills are set up as follows
Network
11. Example 6 Warranty Service Call Center Part
Placing the Reservation
Resort Reservation Service with EAS
Specific Number Dialing
Texas VDN 3222 Skill Preferences
12. Example 7A Process Involving Specific Number Dialing
General Number Dialing
13. Example 7B Process Involving General Number Dialing
Call-Back Provisions
14. Example 7C Call-Back Provisions
Vector Exercises
Suggested Solution
Exercise 1 Emergency and Routine Service
Suggested Solution
Exercise 2 Late Caller Treatment
17. Late Caller Treatment
Exercise 3 Messaging Option
18. Messaging Option
Call Vectoring CommandsA
Table A-1. Command Description/Reference Table
Command Description/Reference
Table A-2. Command/Option Summary Table
Command/Option Summary
Command Basic Prompting Other Options Required
Command Job Aid
Table A-3. Vectoring Commands Generic 3 Version
EAS only
Table A-4. Vectoring Commands Generic 3 Version
Table A-5. Vectoring Commands Generic 3 Version
Check-backup skill Pri if rolling-asa
Data
Table A-6. Vectoring Commands Generic 3 Version
Table A-7. Vectoring Commands Generic 3 Version
Table A-8. Vectoring Commands Generic 3 Version
Table A-9. Vectoring Commands Generic 3 Version
Table A-10. Vectoring Commands Generic 3 Version
Command Directory
Purpose
Adjunct Routing Command
Syntax
Valid Entries
Page
Page
Answer Supervision Considerations
Routed to Station or to Attendant
CMS Interactions
Routed to Trunk
Routed to VDN
Routed to Split or to Hunt Group
Bcms Interactions
Announcement Command
Announcement extension
Announcement
BCMS/CMS Interactions
Busy
Busy Command
R3 CMS
Busy Command
Check-Backup Command
Examples
No answer supervision is returned
Backupcalls
Bcms Interactions
Collect Digits Command
Page
Page
Command is not tracked on CMS 34Issue 4 September
Converse-on Command
Operation
Page
Page
Answer Supervision Considerations
Page
Page
Page
Page
Page
CMS Interactions
Disconnect Command
Disconnect Command
Conditions = available-agent, staffed-agents
Goto Step Command
Conditions = calls-queued, oldest call-wait
Condition = rolling-asa
Condition = expected-wait
Condition = counted-calls
Comparator Condition Threshold
Counted-calls
Command Comparator Value
Option in, not-in Vectoring G3V4 Enhanced only
Operation
DCS
Goto vector vector # if unconditionally
Goto Vector Command
Goto vector
Calls-queued
Day mon, tue, wed, thu, fri, sat, sun, all
Operation
Goto Vector Command
Page
Messaging Command
Answer Supervision Considerations
CMS Interactions
Bcms Interactions
Queue-to Main Command
Answer Supervision Considerations
CMS Interactions
Bcms Interactions
Route-to number number with cov option if unconditionally
Route-to Command
Operation
Page
Coverage
Page
Dequecalls
Routed to Split or Hunt Group
Routed to VDN
Bcms Interactions
Stop
Stop Command
CMS Interactions
Multiple Audio/Music Sources Syntax G3V4 and later releases
Wait-time Command
Wait-time120 secs hearing 54795 then continue
Feature Interactions
Criteria for Success/Failure of Call Vectoring Commands
Command Success/Failure Criteria Disposition
Table A-11. Call Vectoring Command Success/Failure Criteria
Issue 4 September 1995 A-83
84Issue 4 September
Issue 4 September 1995 A-85
Call Vectoring Commands
Call Vectoring ManagementB
Implementation Requirements for Call Vectoring Features
Call Vectoring Management
Page
Page
ANI/II
Table B-5 ANI/II-Digits Requirements Feature Forms Hardware
Page
Enabling the Vector Disconnect Timer
Changing and Testing the Vector
Upgrading to a Call Vectoring Environment
Page
Basic Call Vectoring Considerations
Considerations for the Call Vectoring Features
Call Prompting Considerations
Look-Ahead Interflow Considerations
Adjunct Routing Considerations
VDN Return Destination Considerations
User Scenario Remote Access with Host Provided Security
Figure C-2. Sample Return Destination Vector with Disconnect
Considerations for the Call Vectoring Features
Unexpected Feature Operations
Troubleshooting VectorsD
Wait-time or announcement
Unexpected Command Operations
Command Step Customer Observations Causes
Table D-2. Unexpected Command Operations
Issue 4 September 1995 D-5
6Issue 4 September
Unexpected Command Operations
Command Step Customer Observations Causes
Converse Command Debugging
Placing a Call
Table D-3. Converse Command Debugging
Data Return
Display Events Form
Tracking Unexpected Vector Events
Figure D-2. Display Events Report
Display Events Report
Summary of Vector Events
During an announcement step, a collect
Queue-to main split, messaging split, or
Tracking Unexpected Vector Events
Adjunct routing step was cancelled
Check-backup split step. The call was
Troubleshooting Vectors
Queue-to main split, check-backup split
Troubleshooting Vectors
Tracking Unexpected Vector Events
Functional Differences for G2 and G3 Call Vectoring and Ease
Differences in Command Function
Queue-to Main Split and Check-Backup Split
Generic
Table E-1. G2/G3 Differences for Queuing Commands
Goto Step and Goto Vector
Table E-2. G2/G3 Differences for Goto Commands
Route-to Number
Table E-3. G2/G3 Differences for Route-to Number Command
Table E-4. G2/G3 Differences for Announcement Command
Table E-6. G2/G3 Differences for Busy Command
Table E-5. G2/G3 Differences for Wait Command
Wait-time
Busy
Table E-7. General Call Vectoring Functional Differences
General Call Vectoring Functional Differences
Messaging split command is
Differences in Defining/Interpreting Split Flows
Check backup split retries. If
R2 CMS Standards
R3 CMS Standards
G2.2 G3r
Differences Between G2 and G3r EAS
Page
Interactions Between Call Vectoring/EAS and BCMS/CMSF
BCMS/CMS Tracking in a Call Vectoring Environment
Defining and Interpreting Call Flows
Answered and Abandons
VDN Inflows and Outflows
Busies and Disconnects
Vector Inflows and Outflows
R3 CMS and Bcms Standards
Split Inflows, Outflows, and Dequeues
Messaging split command, or by
Examples of Split Flow Tracking
Comments
Table F-5 Tracking for Abandoned Calls Split Tracking
Outflow Dequeue Answer
Vector executes a route-to digits or messaging split step
Evaluating Split Performance
Page
CMS Reports
Using BCMS/CMS Reports to Evaluate Call Vectoring Activity
Bcms Reports
Tracking Entities
Using CMS in an EAS Environment
Agents and their Skills
Direct Agent Calls
VDN Skill Preferences
Non-ACD Calls
BCMS/CMS
Operation Details for the Route-to Command
Cov = n Cov = y
Table G-1. Definity G3 Route-To Command Operation
COR
Interaction
Page
Detailed Call Flow for Converse VRI Calls
Converse Call Placement
Definity
Data Passing
Page
Page
VRU Data Collection
Data Return
Script Execution
Page
Script Completion
Definity Switch Data Collection
Page
Remote Access
Security Issues
Replacing Remote Access
Front-Ending Remote Access
EAS
Vector Initiated Service Observing Security
Setting Up a Call Center
Call Vectoring/Non-EAS Option
Agent Name Extension LoginID
Actions Produced by Vector #1
Split Hunt Group Agent Extensions
Actions Produced by Vector #2
Non-EAS Worksheet #1 Call Center Objectives Worksheet
Non-EAS Worksheet #2 Current Split Operation Worksheet
Non-EAS Worksheet #3 Customer Needs Worksheet
Figure J-4. Non-EAS Worksheet #4 Vector Design Worksheet
Call Vectoring/G3 EAS Option
UCD/ EAD COR
Customer/Call Center Needs Skill Name Skill Number
VDN
Main VDNs 1st Skill 2nd Skill 3rd Skill Vector
Randy Tyler 2000 Yes 6543/AUDIX
Agent Name Skill Skill Assigned
Page
EAS Worksheet #1 Call Center Objectives Worksheet
EAS Worksheet #2 Current Split Operation Worksheet
Figure J-7. EAS Worksheet #3 Customer needs Worksheet
EAS Worksheet #3 Customer Needs Worksheet Generic
EAS Worksheet #4 Individual Agent Skill Worksheet Generic
EAS Worksheet #5 Agent Skills Worksheet Generic
EAS Worksheet #6 VDN Skill Preferences Worksheet
EAS Worksheet #7 Vector Design Worksheet
Converting a Call Center to Eask
Pre-EAS Cutover Administration for the G3V2 or later Switch
Page
Page
Issue 4 September 1995 K-5
Pre-EAS Cutover Administration for Audix
Pre-EAS Cutover Administration for CMS
Pre-EAS Cutover Administration for Messaging Server
Pre-EAS Cutover Administration for Asai
EAS Cutover
Page
Page
V4 Feature Availability
Page
Improving PerformanceM
Page
Audible Feedback
Looping Examples
Lookahead Interflow
When a agent is available Split Queueing time of 5 minutes
Figure M-5. Example Vector with Improved Performance
Figure M-7. Example Vector
Check Backup
Figure M-9. Another Example Vector with Improved Performance
After Business Hours
Other Examples
Figure M-12. Example Vector
Lookahead Interflows
All agents are busy. Please hold
Relative Processing Cost of Vector Commands
Improving Performance
G3iV1.1 and G3V2 System Parameters
Call Vectoring System Parameters
G3V3 System Parameters
G3V4 System Parameters
ACD
Glossary
GL-2Issue 4 September
Issue 4 September 1995 GL-3
GL-4Issue 4 September
Issue 4 September 1995 GL-5
GL-6Issue 4 September
Issue 4 September 1995 GL-7
GL-8Issue 4 September
Issue 4 September 1995 GL-9
GL-10Issue 4 September
Issue 4 September 1995 GL-11
GL-12Issue 4 September
Issue 4 September 1995 GL-13
GL-14Issue 4 September
Index
Symbols
IN-2Issue 4 September
Issue 4 September 1995 IN-3
IN-4Issue 4 September
Issue 4 September 1995 IN-5
IN-6Issue 4 September
Issue 4 September 1995 IN-7
IN-8Issue 4 September
Issue 4 September 1995 IN-9
IN-10Issue 4 September
Issue 4 September 1995 IN-11
IN-12Issue 4 September
Issue 4 September 1995 IN-13