Revision 3, March
DSP56301 User’s Manual
USA/EUROPE
How to reach us
Japan
ASIA/PACIFIC
Page
Page
Contents
Chapter Core Configuration
Chapter Memory Configuration
Chapter Host Interface HI32
Chapter Programming the Peripherals
Chapter Enhanced Synchronous Serial Interface Essi
Chapter Serial Communication Interface SCI
Index
Chapter Triple Timer Module
Chapter a Bootstrap Program Chapter B Programming Reference
DSP56301 User’s Manual
Figures
Xii
Pulse Width Modulation Toggle Mode, TRM =
DSP Control Register Dctr DSP PCI Control Register Dpcr
Tables
Tables
Essi Clock Sources
Overview
Manual Organization
Signal/Symbol Logic State Signal State Voltage
High True/Low True Signal Conventions
Manual Conventions
Ground2
PIN is a generic term for any pin on the chip
Ground
DSP56300 Core Features
Size Cache
Program RAM Instruction Data RAM Switch Size Cache Size
CE = MS =
Data ALU
DSP56300 Core Functional Blocks
Multiplier-Accumulator MAC
Address Generation Unit AGU
Data ALU Registers
Program Control Unit PCU
Jtag TAP and OnCE Module
PLL and Clock Oscillator
On-Chip Memory
DSP56301 Switch Memory Configuration
Internal Buses
Expansion Area
DMA
Memory Expansion Area
Peripherals
General-Purpose Input/Output Gpio signals
Host Interface HI32
Enhance Synchronous Serial Interface Essi
Serial Communications Interface SCI
Triple Timer Module
DSP56301 Documentation
Related Documents and Web Sites
Name Description Order Number
DSP56300FM/AD
Timers JTAG/OnCE Port
DSP56301 Functional Signal Groupings
Enhanced Synchronous Serial Interfaces ESSI0
ESSI1
Port a
See -2for a listing of the Host Interface/Port B Signals
DSP56301
Host Interface/Port B Detail Signal Diagram
Power Inputs
Power
Ground Signals
Ground
Phase-Lock Loop Signals
Clock Signals
Clock
PLL
External Address Bus
External Memory Expansion Port Port a
External Data Bus
External Bus Control
Arbitration is reset to the bus slave state
Signals are tri-stated
Output Tri-stated Is an active-low output that is
Output Tri-stated Is asserted for half a clock
Bclk
CAS
Interrupt and Mode Control
Interrupt and Mode Control
Signal State Type During Signal Description Name
Nonmaskable Interrupt-After
10.Host Interface
Host Interface HI32
Command 0-3/Byte Enable 0-3 -When the HI32 is programmed
Hpar
HBS
Hdak
Hperr
Hirq
Hserr
Hstop
HWR
Signal PCI Mode Enhanced Universal Bus Mode Gpio Mode Name
11.Summary of HI32 Signals and Modes
HAD10 HD2 HIO10
HP8 HAD8 HD0 HIO8 HP9 HAD9 HD1 HIO9
HAD11 HD3 HIO11
HAD12 HD4 HIO12
Gpio
12.Host Port Pins HI32
PCI
Host Target Ready Host Data Bus Enable
Bus Command/Byte Enable Host Address Bus
Reserved
Host Initiator Ready Host Data Bus Direction
Bus Grant Host Address Enable
Parity Error DMA Request
Host Device Select Host Select Acknowledge
Host Lock Bus Strobe
Bus Request Host Transfer Acknowledge
Host System Error Host Interrupt Request
Hreq is deasserted in the same PCI
Hstr
Host Stop Host Write/Read-Write
Hstop HWR/HRW
HRD/HDS
Initialization Device Select Host Read/Data Strobe
Address/Data Multiplexed Bus Data Bus
Host Bus Clock
Enhanced Synchronous Serial Interface
Hardware Reset
Host Interrupt a
Active low, open drain output pin
PC0
13.Enhanced Synchronous Serial Interface
PC1
PC2
PC3
SCK0
SRD0
PC4
PD0
14.Enhanced Serial Synchronous Interface
PD1
PD2
PD3
SCK1
SRD1
PD4
15.Serial Communication Interface
Timers
Serial Communications Interface SCI
Timer 0 Schmitt-Trigger Input/Output- When Timer
16.Triple Timer Signals
Timer 1 Schmitt-Trigger Input/Output- When Timer
Timer 2 Schmitt-Trigger Input/Output- When timer
17.JTAG/OnCE Interface
Signal Name Type State During Signal Description Reset
Jtag and OnCE Interface
Jtag and OnCE Interface DSP56301 User’s Manual
Program Memory Space
Memory Configuration
Instruction Cache
Memory Switch Modes-Program Memory
Internal Program Memory
Memory Switch Modes-X Data Memory
Program Bootstrap ROM
Memory Configuration
Data Memory Space
Internal Y Data Memory
Memory Switch Modes-Y Data Memory
Internal I/O Space-X Data Memory
External I/O Space-Y Data Memory
Dynamic Memory Configuration Switching
Internal Memory Configuration Summary
Sixteen-Bit Compatibility Mode Configuration
DSP56301 RAM Configurations
DSP56301 RAM Address Ranges by Configuration
RAM
Default
Memory Maps
None 64K $000-$FFF $000-$7FF
16-Bit Space With Default RAM 0, 0
$000-$800 $000-$BFF
16M
None 64K $000-$7FF $000-$BFF
16-Bit Space With Switched Program RAM 0, 1
$000-$BFF $000-$7FF Not addressable
Instruction Cache Enabled 1, 0
16-Bit Space With Instruction Cache Enabled 1, 0
$000-$3FF $000-$BFF Not addressable
Addressable
$0400 $0000
Core Configuration
Core Configuration
Operating Modes
Reset Description Vector
DSP56301 Operating Modes
Mode
Mode Description
Operating Mode Definitions
DSP Clkout rate must be 5/3 of the PCI clock
Address attributes selected default
Low. The DSP56301 is written with 24-bit-wide words
Bootstrap Program
Status Register SR
Central Processor Unit CPU Registers
DMA OMR
Sixteen-Bit Arithmetic Mode
Cache Enable
Do Forever Flag
Do Loop Flag
Sixteen-Bit Compatibility Mode
Scaling Rounding Bit SEquation Mode
Scaling Mode
Interrupt Mask
Priority Exceptions Exceptions Masked Permitted
Scaling Mode Integer Portion
Bit Number Bit Name Reset Value Description Limit
Extension
Unnormalized
Operating Mode Register OMR Bit Definitions
Operating Mode Register OMR
Stack Extension Enable
Stack Extension Wrap Flag
Address Attribute Priority Disable
Address Trace Enable
Asynchronous Bus Arbitration Enable
Stack Extension Overflow Flag
Memory Switch Mode
Cache Burst Mode Enable
Bus Release Timing
Synchronize Select
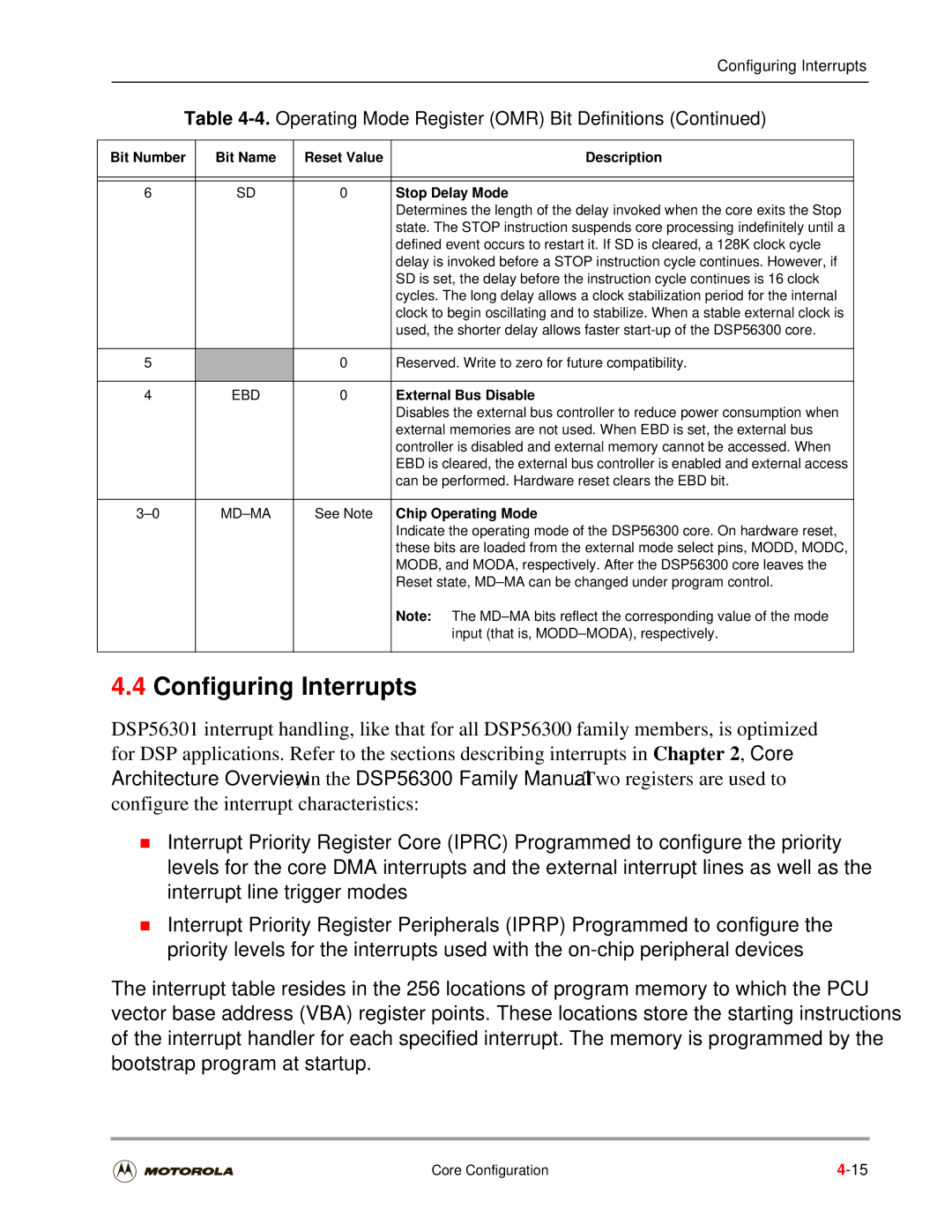
Bit Number Bit Name Reset Value Description Stop Delay Mode
Configuring Interrupts
External Bus Disable
Chip Operating Mode
Interrupt Priority Registers Iprc and Iprp
Interrupt Sources
Interrupt Table Memory Map
Interrupt Priority Level Bits
VBA$1C
VBA$1A
VBA$1E
VBA$2A
Priority Interrupt Source
Processing Interrupt Source Priorities Within an IPL
Interrupt Source Priorities Within an IPL
TIMER0 overflow interrupt
Host command interrupt
TIMER0 compare interrupt
TIMER1 overflow interrupt
PLL Control Register Pctl Bit Definitions
PLL Control Register Pctl
Bus Control Register
Bus Interface Unit BIU Registers
Bus Area 3 Wait State Control
Bus Default Area Wait State Control
Bus Area 2 Wait State Control
Bus Area 1 Wait State Control
BRP BRF7 BRF6
Dram Control Register DCR
BRF3 BRF2 BRF1
Bstr Bren BME Bple BPS1
10.DRAM Control Register DCR Bit Definitions
Bus Dram Page Size
Bus Page Logic Enable
Bus Row Out-of-page Wait States
Bus Column In-Page Wait State
Bus Number of Address Bits to Compare
Address Attribute Registers AAR0-3
Bus Address to Compare
Bus Y Data Memory Enable
Bus Packing Enable
Bus X Data Memory Enable
Bus Program Memory Enable
DIE DTM2 DTM1 DTM0
DMA Control Registers 5-0 DCR5-0
Dcon
DAM5 DAM4 DAM3 DAM2 DAM1 DAM0
DMA Transfer Mode
DMA Interrupt Enable
DTM2-0 Trigger Cleared Transfer Mode After
12.DMA Control Register DCR Bit Definitions
DMA Channel Priority
Number Value
DMA address generation logic, buses, and so forth
DPR1-0 Channel Priority
Dcon
DMA Continuous Mode Enable
OMR CDP1-0 CP1-0 Core Priority
DRS4-0 Requesting Device
Three-Dimensional Mode
DMA Request Source
DSS1 DSS0
Device Identification Register IDR
DDS1 DDS0
Jtag Boundary Scan Register BSR
Jtag Identification ID Register
Version Information Design Center
Number Identity See Note
Jtag Boundary Scan Register BSR DSP56301 User’s Manual
Programming the Peripherals
Peripheral Initialization Steps
Data Transfer Methods
Mapping the Control Registers
Polling
Data Memory
Interrupts
Advantages and Disadvantages
General-Purpose Input/Output Gpio
3 DMA
Port B Signals and Registers
Port E Signals and Registers
Port C Signals and Registers
Port D Signals and Registers
Timer Gpio
Triple Timer Signals and Registers
General-Purpose Input/Output Gpio DSP56301 User’s Manual
Host Interface HI32
Features
HI32 Features, Core-Side and Host-Side
HI32 Features in PCI Mode and Universal Bus Mode
Overview
DSP-Side Registers
PCI Configuration Space
DSP DMA Data Bus DSP Global Data Bus
Data transfer format converter
Host-to-DSP Data Path
Data Transfer Paths
DSP-To-Host Data Path
Dpmc
HI32 PCI Master Data Transfer Formats
FC1 FC0
Two least significant bytes of two Hrxm
HTF1 HTF0
Transmit Data Transfer Format
Hctr
DSP to Host Data Transfer Format
Receive Transfer Data Formats
HRF
Three least significant Hrxs bytes
Receive Transfer Data Formats
Type Entered when Description
Reset States
DSP-Side Operating Modes
HRST/HRST
PCI Mode Dctrhm = $1
Terminate and Reset Dctrhm = $0
HI32 Mode
PCI
Example 6-1. PCI /DMA Throughput 32-Bit
Multfactor
Self-Configuration Mode Dctrhm = $5
Gpio Mode Dctrhm = $4
Example 6-3. Self-Configuration Procedure for PCI Mode
Host Port Pin Functionality
Host Port Pins
PCI Bus Universal Bus Mode
DSP56301
ISA
Slave
Master
HI32 Programming Model, DSP Side
Memory Register Address Mode
HI32 DSP-Side Programming Model
Bit Number Bit Name
Mode Description Value
DSP Control Register Dctr
10.DSP Control Register Dctr Bit Definitions
Htap
Host Data Strobe Mode
Host Transfer Acknowledge Polarity
Host Read/Write Polarity
Slave Transmit Interrupt Enable
Slave Receive Interrupt Enable
Host Command Interrupt Enable
DSP PCI Control Register Dpcr
Receive Buffer Lock Enable
Insert Address Enable
11.DSP PCI Control Register Dpcr Bit Definitions
IAE
Master Access Counter Enable
Master Wait State Disable
Force
Hserr
Transaction Termination Interrupt Enable
Transfer Complete Interrupt Enable
Transaction Abort Interrupt Enable
Parity Error Interrupt Enable
BL1 BL0
DSP PCI Master Control Register Dpmc
BL4
Data Transfer Format Control
12.DSP PCI Master Control Register Dmpc Bit Definitions
A PCI DSP-to-Host transaction
A PCI Host-to-DSP transaction
DSP PCI Transaction Address High
PCI Data Burst Length
13.DSP PCI Address Register Dpar Bit Definitions
DSP PCI Address Register Dpar
BE2 BE1
AR9 AR8 AR7 AR6 AR5 AR4 AR3 AR2 AR1 AR0
C3-0 Command Type
PCI Bus Command
DSP PCI Transaction Address Low
AR1 AR0
DSP Status Register DSR
Bit Bit Name Reset Mode Description Number Value
14.DSP Status Register DSR Bit Definitions
2322212019181716
Slave Receive Data Request
Srrq UBM
Host Command Pending
Mode Description Number Value
14. DSP Status Register DSR Bit Definitions
Slave Transmit Data Request
15.DSP PCI Status Register Dpsr Bit Definitions
DSP PCI Status Register Dpsr
Rdcq MDT Hdtc Trty Tdis TAB MAB
Aper Marq Mrrq Mtrq MWS
PCI Host Data Transfer Complete
Master Data Transferred
PCI Time Out Termination
PCI Target Retry
PCI Address Parity Error
PCI Data Parity Error
PCI Target Disconnect
PCI Target Abort
15. DSP PCI Status Register Dpsr Bit Definitions
DSP Receive Data Fifo Drxr
PCI Master Wait States
PCI Master Receive Data Request
DSP Slave Transmit Data Register Dtxs
DSP Master Transmit Data Register Dtxm
16.DATH and Dirh Functionality
DSP Host Port Gpio Direction Register Dirh
DSP Host Port Gpio Data Register Dath
Memory Register
Host-Side Programming Model
17.HI32 Programming Model, Host-Side Registers
Host-Side Programming Model
Executed as Command Type
18.PCI Bus Commands
HC3/HBE3-HC0/HBE0
Ignored
19. Host-Side Registers PCI Memory Address Space
20. Host-Side Registers PCI Configuration Address Space
21. Host-Side Registers Universal Bus Mode Address Space
13.Host Interface Control Register Hctr
1 HI32 Control Register Hctr
Target Wait State Disable
Bit Bit Name Reset Mode Description Number
22.Host Interface Control Register Hctr Bit Definitions
Twsd PCI
Host Receive Data Transfer Format
Host Transmit Data Transfer Format
Slave Fetch Type
Inserted Address
SFT UBM
Cleared when the DSP56300 core writes to
Universal Bus mode Fetch SFT =
Reset, and Strq and Hstrhrrq are cleared
Data path is lost when the reset state is
Hirq
Dmae UBM
Dmae Haen
Rreq UBM
Receive Req uest Enable
Dmae Treq Rreq
Hirq Pin Hdrq pin
Hreq Hint HF5 HF4 HF3
Host Interface Status Register Hstr
Trdy
UBM UBM UBM UBM UBM UBM PCI PCI PCI PCI PCI PCI
Host Request
23.Host Interface Status Register Hstr Bit Definitions
Host interrupt a
Treq Rreq Hreq
Transmitter Ready
Host Receive Data Request
Host Transmit Data Request
15.Host Command Vector Register Hcvr
Host Command Vector Register Hcvr
Host Command Vector
24.Host Command Vector Register Hcvr Bit Definitions
Bit Bit Name Reset Value Mode Description Number
Hnmi UBM
When the DSP56300 core acknowledges the host command
Host Command
Host Master Receive Data Register Hrxm
Host Slave Receive Data Register Hrxs
Host Transmit Data Register Htxr
Universal Bus mode Dctrhm = $2 or $3
PCI Mode Dctrhm = $1
Status/Command Configuration Register CSTR/CCMR
Device ID/Vendor ID Configuration Register CDID/CVID
DPE SSE RMA RTA STA
DPR Fbbc
Signaled System Error
Detected Parity Error
Signalled Target Abort
Received Master Abort
Wait Cycle Control hardwired to zero
System Error Enable
Parity Error Response
Bus Master Enable
Class Code/Revision ID Configuration Register CCCR/CRID
HT7 HT6 HT5 HT4 HT3 HT2 HT1 HT0
Header Type hardwired to $00
HT7-0
Read-only bits that identify the layout of bytes $10-$3F
Ccls
Latency Timer High
Cache Line Size
Universal Bus Mode Base Address
Memory Space Base Address Configuration Register Cbma
PM8 PM7 PM6 PM5 PM4 MS1 MS0 MSI
Memory Base Address High/Low
Memory Base Address Low Hardwired to zeros
29. Memory Space Base Address Configuration Register Cbma
Pre-Fetch Hardwired to zero
Memory Space Hardwired to zeros
Example 6-5. Code for Setting the Csid
IL5 IL4
Interrupt Line-Interrupt Pin Configuration RegisterCILP
IL1 IL0
Maxlat
HS PH PS
HI32 Programming Model/Quick Reference
Dctr Hcie
UBM Hrsp
Rble
Dpcr Mtie
Clrt
Dpar
Dpmc
DSR HCP
Hact
Dper
Dpsr Aper
Hdtc
Rdcq
Dmae
Treq
ISA/EISA
SFT
Hnmi
Hcvr
Hrxm
Hrxs
Cccr
Ccmr RMA
Chty
Cbma MSI
Rsma Rsmb Tsma Tclk STD
GDB DDB Rclk
Tsmb TX0 CRA
SC0
Essi Enhancements
Serial Transmit Data Signal STD
Essi Data and Control Signals
Serial Receive Data Signal SRD
Serial Clock SCK
Serial Control Signal SC1
Serial Control Signal SC0
SYN TE0 TE1 TE2 SC0 SC1 SC2 SCK STD SRD
Mode and Signal Definitions
Control Bits Essi Signals
Essi After Reset
Serial Control Signal SC2
Operation
Initialization
Exceptions
Operation
Write data to all enabled transmit registers
Operating Modes Normal, Network, and On-Demand
Normal/Network/On-Demand Mode Selection
Frame Sync Selection
Frame Sync Signal Format
Synchronous/Asynchronous Operating Modes
Frame Sync Polarity
Frame Sync Length for Multiple Devices
Word Length Frame Sync and Data Word Timing
Flags
Byte Format LSB/MSB for the Transmitter
Essi Control Register a CRA
Essi Programming Model
WL2 WL1 WL0 ALC
PM7 PM6 PM5 PM4 PM3 PM2 PM1 PM0
Select SC1
Essi Control Register a CRA Bit Definitions
Word Length Control
Essi Word Length Selection
Frame Rate Divider Control
Alignment Control
Prescaler Range
Prescale Modulus Select
Crbsyn =
CRBTE1 CRBOF0 SSISRIF0
Rclock
Tclock
Shfd
Essi Control Register B CRB
OF1 OF0
ESSI0 X$FFFFB6, ESSI1 X$FFFFA6
Essi Control Register B CRB Bit Definitions
Receive Enable
Transmit Interrupt Enable
Transmit 0 Enable
TIE
Transmit 2 Enable
Transmit 1 Enable
Mode Select
Synchronous/Asynchronous
FSL1 FSL0
OF1
Serial Control Direction
Serial Output Flag
OF0
TX Frame Sync TX Serial Data
Serial Clock RX, TX Frame Sync RX, TX Serial Data
Serial Clock RX Frame Sync RX Serial Data
Essi Bit
CRB SYN Bit Operation
Receiver Interrupt or DMA Request and Flags Set
Bit Operation
SSI Control Register B CRB READ/WRITE
Frame Sync FSL0 = 0, FSL1 = Data Flags
Frame Sync FSL0 = 0, FSL1 = Data Out Flags
Transmitter Underrun Error Flag
Receiver Overrun Error Flag
Essi Status Register Ssisr
Receive Data Register Full
Receive Frame Sync Flag
Essi Receive Shift Register
Transmit Frame Sync Flag
Serial Input Flag
Essi Transmit Shift Registers
Essi Receive Data Register RX
Transmit Registers
Receive Registers
WL0
Transmit Middle Byte Transmit Low Byte Register 24 Bit
Least Significant
MSB
Essi Time Slot Register TSR
Essi Transmit Data Registers TX2-0
Transmit Slot Mask Registers TSMA, Tsmb
TS9 TS8 TS7 TS6 TS5 TS4 TS3 TS2 TS1 TS0
15.ESSI Transmit Slot Mask Register B Tsmb
RS7 RS6
Receive Slot Mask Registers RSMA, Rsmb
RS1 RS0
RS15 RS14 RS13 RS12 RS11 RS10
Port Control Registers Pcrc and Pcrd
Gpio Signals and Registers
ESSI0/ESSI1
Essi Port Signal Configurations
Port Direction Registers Prrc and Prrd
20.Port Data Registers Pdrc X$FFFFBD Pdrd X $FFFFAD
Port Data Registers Pdrc and Pdrd
Serial Communication Interface SCI
Serial Communication Interface SCI
Multidrop Mode
Synchronous Mode
Asynchronous Mode
Wired-OR Mode
I/O Signals
Address Mode Wakeup
Transmitting Data and Address Characters
SCI Serial Clock Sclk
Receive Data RXD
Transmit Data TXD
SCI Registers After Reset
SCI After Reset
Reie Sckp Stir Tmie TIE RIE Ilie
Woms RWU Wake SBK Ssftd
SCI Initialization
Preamble, Break, and Data Transmission Priority
Exceptions
Bootstrap Loading Through the SCI Boot Mode 2 or a
SCI Programming Model
WDS2 WDS1 WDS0
Bit Synchronous Data Shift Register Mode
Bit Asynchronous 1 Start, 8 Data, 1 Stop
Bit Asynchronous 1 Start, 8 Data, 1 Even Parity, 1 Stop
SCI Data Word Formats Ssftd = 0
Stir Tmie TIE RIE Ilie Woms RWU Wake SBK Ssftd WDS2
SCI Control Register SCR
Reie
SCI Transmit Interrupt Enable
Timer Interrupt Enable
SCI Receive Interrupt Enable
Idle Line Interrupt Enable
Woms
Receiver Enable
Wired-OR Mode Select
Wakeup Mode Select
Receiver Wakeup Enable
Send Break
SCI Shift Direction
WDS1 WDS0
Mode Word Formats
Word Select
Idle Rdrf Tdre Trne
SCI Status Register SSR
SCI Status Register SCI Status Register SSR Bit Definitions
Transmitter Empty
Idle Line Flag
Tdre
TCM RCM SCP COD
SCI Clock Control Register Sccr
TCM RCM
Sclk
Divide by
Bit Counter
CD11-0
Sckp = 0 + Sckp =
X1 Clock X16 Clock Sckp =
RX, TX Data Ssftd =
SCI Receive Data Shift Register
SCI Data Registers
SCI Receive Register SRX
SCI Transmit Register STX
Sclk TXD RXD
Port E Control Register Pcre
PE2 PE1 PE0
Port E Data Register Pdre
Port E Direction Register Prre
PRRE1 PRRE0
PDRE1 PDRE0
Gpio Signals and Registers DSP56301 User’s Manual
Triple Timer Module
Triple Timer Module
Individual Timer Block Diagram
Triple Timer Module Block Diagram
GDB
Tpcr
Timer Module Block Diagram
Timer After Reset
Timer Exceptions
Timer Initialization
TCSR0 Tcie
Timer Gpio Mode
Triple Timer Modes
TC3 TC2 TC1 TC0
TIO
TCR Tcpr
Mode 0 internal clock, no timer output TRM =
TLR
Output
Timer Pulse Mode
Mode 1 internal clock TRM =
Pulse width = timer clock Period
Mode 2 internal clock TRM = 1 first event
Timer Toggle Mode
Toggle Timer
= write preload = write compare Clock CLK/2 or prescale CLK
= write compare Clock CLK/2 or prescale CLK
Mode 2 internal clock TRM =
= write preload
Mode 3 internal clock TRM =
Timer Event Counter Mode
Input External
TIO Cpuclk +
= write compare Clock
10.Event Counter Mode, TRM =
Measurement Input Width Mode
Signal Measurement Modes
Input
Input width Measurement
Mode 4 internal clock TRM = 1 first event
Mode 4 internal clock TRM =
Mode 5 internal clock TRM =
Measurement Input Period Mode
First event = write preload = write compare
Input period Measurement Internal
Reads TCR period
Counting, does
May occur TOF=1
Mode 6 internal clock TRM =
Measurement Capture Mode
Interrupt Service reads TCR delay = M N clock periods
Internal
Pulse width modulation
Pulse Width Modulation PWM, Mode
PWM
16.Pulse Width Modulation Toggle Mode, TRM =
Mode 7 internal clock TRM =
17.Pulse Width Modulation Toggle Mode, TRM =
Watchdog Modes
Watchdog Pulse Mode
Pulse Watchdog
Output Internal
= write preload First event
Mode 9 internal clock TRM =
Software does not reset watchdog timer watchdog times out
Mode 10 internal clock TRM =
Watchdog Toggle Mode
Watchdog Output
Toggle
Special Cases
Triple Timer Module Programming Model
DMA Trigger
Prescaler Counter
Register Tplr
Timer Prescaler Load
23 22 21 20 19 18 17
Tplr = $FFFF83
Prescaler Source
Timer Prescaler Load Register Tplr
PS1 PS0
Prescaler Preload Value
Timer Control/Status Register Tcsr
Timer Prescaler Count Register Tpcr
TCF TOF PCE
TRM INV
Timer Overflow Flag
Timer Compare Flag
Prescaler Clock Enable
Data Output
Inverter
Timer Reload Mode
Direction
Number Function
Timer Control
Timer Overflow Interrupt Enable
Timer Compare Interrupt Enable
Timer Enable
TIO Programmed as Input TIO Programmed as Output Mode INV =
Positive polarity
Timer Load Register TLR
Pulse generated by Timer has Timer has negative
Timer Count Register TCR
Timer Compare Register Tcpr
Appendix a
DSP56301 User’s Manual
HBS
Can be stopped
Hdben
Aarv
Mscte EQU
LOOP0
Lbld
Lble
LOOP8
LOOP11
Rep Mac x0,x1,a x,lr0+
ORG PL,PL Patterns
Write to Destination
DSP56301 User’s Manual
Programming Reference
Chapter B
Table B-1.Guide to Programming Sheets
Bit Address Register Name
Internal I/O Memory Map
Table B-2. Internal I/O Memory Map X Data Memory
Peripheral Bit Address Register Name
Table B-2.Internal I/O Memory Map X Data Memory
$FFCC $FFFFCC
$FFCD $FFFFCD
$FFCB $FFFFCB
$FFCA $FFFFCA
$FFBB $FFFFBB
Essi $FFBC $FFFFBC
$FFBA $FFFFBA
$FFB9 $FFFFB9
$FFAB $FFFFAB
Essi $FFAC $FFFFAC
$FFAA $FFFFAA
$FFA9 $FFFFA9
$FFFF91
$FFFF92
$FFFF90
$FF8F $FFFF8F
Table B-3. Interrupt Sources
Interrupt Sources and Priorities
VBA$6A
Table B-3.Interrupt Sources
VBA$6C
VBA$6E
Table B-4.Interrupt Source Priorities Within an IPL
Nonmaskable Host Command Interrupt
ESSI0 receive last slot interrupt
Figure B-1.Status Register SR
Programming Sheets
Stop Delay
External Bus Disable
Memory Switch Mode
Burst Mode Enable
Irqc Mode
Irqd Mode
Irqb Mode
Irqa Mode
Interrupt Priority Register Iprp $FFFFFE Read/Write
Triple Timer IPL
Host IPL
Crystal Range Bit Xtlr
PLL Control Register Pctl $FFFFFD Read/Write
Bus Control Register BCR $FFFFFB Read/Write
Default Area Wait Control, Bits
Bus Request Hold, Bit
Bus Lock Hold, Bit
Dram Control Register DCR $FFFFFA Read/Write
Bus Y Data Memory Enable, Bit
Bus Packing Enable, Bit
Bus X Data Memory Enable, Bit
Bus Program Memory Enable, Bit
DMA Control Registers DCR5-DCR0
Reset = $000000 $FFFFE4, X$FFFFE8, X$FFFFEC Read/Write
Application
DSP Control Register Dctr Read/Write Address X FFFFC5
DSP PCI Control Register Dpcr Address XFFFFC6 Read/Write
= Enables master receive interrupts
Figure B-12.DSP PCI Master Control Register Dpmc
Figure B-13.DSP PCI Address Register Dpar
PCI Bus Command, Bits
HI32 Control Register Hctr Read/Write
Host Non-Maskable Interrupt, Bit
HI32 Command Vector Register Hcvr Read/Write
Signaled System Error, Bit
Detected Parity Error, Bit
Signalled Target Abort, Bit
System Error Enable, Bit
Read/Write
Latency Timer High, Bits
Header Type, Bits
Cache Line Size, Bits
Reset = $00000000
HI32 Memory Space Base Address Configuration Register Cbma
PCI Mode Base Address High, Bits Pre-fetch, Bit
Memory Space Indicator, Bit
Subsystem ID Register, Bits 31-16 Specifies the subsystem ID
ESSI1-X$FFFFA5 Read/Write
Essi Control Register a CRAx ESSI0-X$FFFFB5 Read/Write
ESSI1-X$FFFFA6 Read/Write
Essi Control Register B CRBx
ESSI0-X$FFFFB6 Read/Write
ESSI1-X$FFFFA4 Read/Write
Essi Transmit Slot Mask a TSMA0-1 ESSI0-X$FFFFB4 Read/Write
Essi Transmit Slot Mask B TSMB0-1 ESSI0-X$FFFFB3 Read/Write
ESSI1-X$FFFFA3 Read/Write
SCI Control Register SCR $FFFF9C Read/Write
Clock Out Divider
SCI Clock Control Register Sccr Address X$FFFF9B Read/Write
Receiver Clock Mode/Source
Timer Prescaler Load Register Tplr $FFFF83 Read/Write
Figure B-25.Timer Prescaler Load Register Tplr
TCSR1$FFFF8B Read/Write TCSR2$FFFF87 Read/Write
Timer Control/Status Register TCSR0$FFFF8F Read/Write
TLR1-X$FFFF8A Write Only TLR2-X$FFFF86 Write Only
Timer Load Register TLR0-2 TLR0-X$FFFF8E Write Only
Host Data Register HDR $FFFFC9 Write
Port B HI08
Host Data Direction Register Hddr X$FFFFC8 Write
Port C Control Register Pcrc $FFFFBF Read/Write
Port C ESSI0
Port C Direction Register Prrc $FFFFBE Read/Write
Port C Gpio Data Register Pdrc $FFFFBD Read/Write
Port D Control Register Pcrd $FFFFAF Read/Write
Port D ESSI1
Port D Direction Register Prrd $FFFFAE Read/Write
Port D Gpio Data Register Pdrd $FFFFAD Read/Write
Port E Control Register Pcre $FFFF9F Read/Write
Port E SCI
Port E Direction Register Prre $FFFF9E Read/Write
Port E Gpio Data Register Pdre $FFFF9D Read/Write
Programming Sheets DSP56301 User’s Manual
Index
Index-2 DSP56301 User’s Manual
Index-3
Index-4 DSP56301 User’s Manual
Index-5
Index-6 DSP56301 User’s Manual
Index-7
Index-8 DSP56301 User’s Manual
Index-9
Index-10 DSP56301 User’s Manual
Index-11
Index-12 DSP56301 User’s Manual
Index-13
Index-14 DSP56301 User’s Manual
Index-15
Index-16 DSP56301 User’s Manual