Brocade Network Advisor
Title Publication number Summary of changes Date
Brocade Communications Systems, Incorporated
Title Publication number Summary of changes Date
53-1003056-01
Contents
Chapter Discovery
Installing a patch Uninstalling a patch
Vii
111
Configurable preferences
Management groups overview
Displaying Network Object view
182
Viewing configured users
Users overview
181
Dashboard toolbar
Accessing a dashboard
Setting the dashboard display
Dashboard overview
53-1003056-01
Host Product List toolbar
IP tab overview
IP main toolbar
Product List toolbar
344
Viewing Call Home configurations
Call Home overview
System requirements
Launching an Telnet session from the IP tab
About third-party tools
Starting third-party tools from the application
Launching a Telnet session
Launching the SMC on Windows
Wireless management overview
Wireless devices
Server Management Console overview
Ethernet Fabrics view management
VCS mode types
Logical chassis cluster mode discovery
VCS
Converged Network Adapters
Host management
Brocade adapters
Host Bus Adapters
481
This chapter
Viewing existing PBR policies
Adding policies from saved configurations
Telemetry overview
Policy-based routing
Creating a Layer 2 ACL from a saved configuration
Layer 2 access control list management
IronWare Layer 2 ACL configuration
Fabric OS Layer 2 ACL configuration
Offline zoning
Scheduling a security configuration deployment
Zoning overview
Online zoning
671
Chapter Port Fencing
723
Chapter IP Element Manager
765
743
807
CLI configuration overview
777
778
Adding or modifying dual mode ports
Default Vlan
Remote Switched Port Analyzer
Configuration requirements for Vlan Manager
843
Mpls pre-configuration
VIP Server functions
VIP Servers overview
917
Chapter SSL Certificates for ServerIron Products
Xxx 53-1003056-01
Chapter Power Center
Chapter Policy Monitor
Fault Management
Chapter Technical Support
This chapter 1213 Configuring packet captures
Reports
1277
Dashboard main menus 1261 IP main menus IP shortcut menus
Link incident events
Product status events
Database tables and fields
This appendix
1371
Xxxviii 53-1003056-01
Xxxix
Wirelessinterface Wiredinterface Ceeportinfo
This chapter
About This Document
How this document is organized
Xliv 53-1003056-01
Fabric OS hardware and software support
Supported hardware and software
IronWare hardware and software support
Xlvii
Xlviii 53-1003056-01
Xlix
Network OS hardware and software support
What’s new in this document
Bold text
Document conventions
Text formatting
Key terms
These references are made for informational purposes only
Additional information
Brocade resources
Other industry resources
Document feedback
Getting technical help
User interface components
Getting Started
Management server and client
Management server and client
Logging into a server
Clearing previous versions of the remote client
Launching a remote client
Launching the Configuration Wizard
53-1003056-01
53-1003056-01
Select Server Active Sessions
Viewing active sessions
Active Sessions dialog box displays Figure
Select Server Server Properties
Disconnecting users
Viewing server properties
To disconnect a user, complete the following steps
Field/Component Description
Viewing port status
Management server and client Server Properties
Click Close to close the Server Properties dialog box
Server and client ports
Tftp UDP
TCP
4431,2 Https server
Json
Menu Item or Function Keyboard Shortcut
Accessibility features for the Management application
Accessibility features for the Management application
Keyboard shortcuts
Options dialog box displays
Setting the look and feel
Look and feel customization
Select Server Options
PostgreSQL database
Connecting to the database using pgAdmin
Changing the font size
Selecting File Add Server
PostgreSQL database
Suse
Odbc Data Source Administrator dialog box displays
Click the System DSN tab Click Add
Linux version RedHat Package Manager file
Save and close the odbcinst.ini file
Installing the Odbc driver on Linux systems
On the Setup psqlODBC screen click Next
Adding the Datasourse on Linux systems
Select the Connect to an existing database option
Testing the connection on Linux systems
Executing SQL queries from the CLI
On the Select database screen, complete the following steps
Supported open source software products
Changing the database user password
Open Source Software License Type
HP Software Development KIT License Agreement
Lgpl
BSD
Ireasoning
Open Source Software License Type
Supported open source software products
Patches
Installing a patch
Execute the patch file for your operating system
Uninstalling a patch
53-1003056-01
Uninstalling a patch
Discovery
IP discovery overview
IP discovery overview
53-1003056-01
Ietf standard MIB name Required MIB object Data collected
Configuration requirements
Discovery of IPv6 addresses
MIB support
IF-MIB
MIB-II
BRIDGE-MIB
Ietf standard MIB name Required MIB object Data collected
ENTITY-MIB
VDX/VCS discovery
IP-MIB
1000000533516242
Network OS discovery IP address format
VCS in-band management interface discovery
Mapping VCS in-band management
Select File Save
Standalone discovery
VCS fabric discovery
VCS fabric rediscovery
VCS fabric split and merge
Seed switch failover
Network OS 2.0 device limitations
Logical chassis cluster mode discovery
Discover Setup IP dialog box before removal of node
How the Management application handles a cluster mode change
HyperEdge stack discovery
Configuring IP profile discovery
Discover Setup IP dialog box displays
HyperEdge stack discovery
Click the Global Settings tab
Configuring IP profile discovery
Adding SNMPv1 and SNMPv2c credentials
Configuring IP simple discovery
Configuring IP simple discovery
IP Snmp credentials
Click the Snmp tab
IP Snmp credentials
HMACMD5 Hmacsha
Adding SNMPv3 credentials
CBC-DES
Editing SNMPv1 and SNMPv2c credentials
Editing SNMPv3 credentials
Deleting Snmp credentials from the list
Reordering Snmp credentials in the list
Adding user credentials
Default IP user credentials
Default IP user credentials
53-1003056-01
Editing enable prompt user credentials
Editing login prompt user credentials
To edit an enable super user, complete the following steps
Editing enable super user credentials
Deleting user credentials from the list
Reordering user credentials in the list
Click the OID Filter tab
IP Object identifier filters
Including product types
IP Object identifier filters
Product sysObjectID Vendor
Excluding product types
Click the Preferences tab
Defining global setting preferences
Defining global setting preferences
Deleting product types from the list
53-1003056-01
Reduce the managed count by completing the following steps
Configuring event-based collection
53-1003056-01
IP discovery profiles
Configuring a discovery profile
IP discovery profiles
Duplicating a discovery profile
Configuring address ranges
Select Cidr Subnet from the Entry Type list
Adding Cidr subnet addresses
Adding IP addresses
Adding subnet addresses
Excluding subnet addresses
Excluding Cidr subnet addresses
Excluding IP addresses
Editing address ranges
Editing subnet addresses
Editing Cidr subnet addresses
Editing IP addresses
Scheduling discovery
Configuring an hourly discovery schedule
Configuring a one-time discovery schedule
Configuring a weekly discovery schedule
Configuring a daily discovery schedule
Configuring a yearly discovery schedule
Configuring a monthly discovery schedule
Editing a discovery schedule
Suspending a discovery schedule
To edit a discovery schedule, complete the following steps
Editing a weekly discovery schedule
Editing a one-time discovery schedule
Editing an hourly discovery schedule
Editing a daily discovery schedule
Editing a monthly discovery schedule
Configuring advanced discovery profile preferences
Editing a yearly discovery schedule
IP discovery profiles
Creating a discovery address file
Deleting a discovery profile
Starting discovery manually
To view discovery status, complete the following steps
Starting discovery automatically
Stopping discovery
Viewing discovery status
Mailing discovery reports
Viewing discovery reports
Viewing the discovery log
Exporting discovery reports
Click Discovery Log
Adding an IP device to discovery
Individual IP device discovery
Individual IP device discovery
HMACMD5
Click the SNMPv1/v2c Read/Write tab
Click the SNMPv3 Read Only tab
Click the SNMPv1/v2c Read Only tab
Editing IP device discovery
Click the Read/Write Credentials tab
Click the SNMPv3 Read/Write tab
Click the SNMPv1/v2c Read/Write. tab
Click the SNMPv1/v2c Read Only tab
Click the Port Config Credentials tab
53-1003056-01
Select Discover Host Adapters
Host discovery
Deleting IP devices from discovery
Discovering Hosts by Network address or host name
Host discovery
Click Close on the Discover Host Adapters dialog box
Importing Hosts from a CSV file
Host discovery
Importing Hosts from a Fabric
Importing Hosts from a VM manager
Host discovery
To edit Host credentials, complete the following steps
Editing Host adapter credentials
Click Discover
Removing a host from active discovery
Rediscovering a previously discovered fabric
Deleting a host adapter from discovery
Viewing the host discovery state
Troubleshooting host discovery
IconDescription
Select Discover VM Managers
VM Manager discovery
VM Manager discovery requirements
Discovering a VM manager
VM Manager discovery
Clear to disable vSphere client plug-in registration
Click Close on the Discover VM Managers dialog box
Editing a VM manager
To edit VM manager discovery, complete the following steps
Rediscovering a previously discovered VM manager
Excluding a host from VM manager discovery
Including a host in VM manager discovery
Removing a VM manager from active discovery
Viewing the VM manager discovery state
Deleting a VM manager from discovery
IP Rediscovery
Troubleshooting VM manager discovery
Rediscovering IP devices
Click Rediscover
Rediscovering IP devices from the Product List
Rediscovering a group
Enabling password validation on rediscovery
Management groups overview
Management Groups
Displaying Network Object view
Product group overview
Creating a static product group
Static product groups
Product group overview
Editing a static product group
Duplicating a static product group
Creating a dynamic product group
Dynamic product groups
Userdefinedproperty1 up to
Select Value or Regular Expression from the Type list
Duplicating a dynamic product group
Editing a dynamic product group
Viewing test results
Viewing product group properties
Product Group Properties dialog box displays
Performance list
Click OK to close the dialog box
Properties tab
Products tab
Port Groups
Port Groups
Deleting a product group
Creating a port group
Editing a port group
Duplicating a port group
Ports tab
Viewing port group properties
Deleting a port group
Configurable preferences
Application Configuration
Server Data backup
Select Server Backup in the Category list
What is backed up?
Management server backup
Configuring backup
130 53-1003056-01
Enabling backup
Clear the Enable Backup check box Click Apply or OK
Disabling backup
Viewing the backup status
Changing the backup interval
Reviewing backup events
Starting immediate backup
Select Server Backup in the Category list Click Backup Now
Restoring data
Server Data restore
Restoring data to a new server
SAN data collection
136 53-1003056-01
Icmp
Product communication protocols
Snmp
FTP
Netconf
To configure event storage, complete the following steps
Event storage settings
Configuring event storage
Event storage settings Product communication protocols
Select Event Storage in the Category list
Flyover settings
Configuring flyovers
Storing historical events purged from repository
Options dialog box Flyovers pane, Connection tab
Properties table
Turning flyovers on or off
Name settings
Viewing flyovers
Fixing duplicate names
Select Configure Names
Click Fix Duplicates
Configure Names dialog box displays Figure
Name settings Select one of the following options
Viewing names
Adding a name to an existing device
Applying a name to a detached WWN
Adding a name to a new device
Click Apply Names
Click Export
Removing a name from a device
Editing names
Exporting names
Click Import
Importing Names
Searching for a device by name
To import names, complete the following steps
Searching for a device by WWN
Miscellaneous security settings
Configuring login security
Configuring the server name
Select Security Misc in the Category list
Registering a server as a Syslog recipient automatically
Syslog Registration settings
Configuring the login banner display
Disabling the login banner
Configuring the Syslog listing port number
Snmp Trap Registration settings
Registering a server as a Snmp trap recipient automatically
Snmp Trap forwarding credential settings
Snmp Trap forwarding credential settings
Configuring the Snmp trap listing port number
Configuring Snmp v1 and v2c credentials
Configuring Snmp v3 credentials
Configuring the server IP address
Software Configuration
Client/Server IP
156 53-1003056-01
Configuring an explicit server IP address
Click OK on the Login Banner
Configuring the application to use dual network cards
You can configure the following preferences for IP products
Software Configuration
IP preferences
Configuring change manager preferences
Configuring deployment preferences
Configuring custom report preferences
Configuring deployment report preferences
Configuring Mpls polling service preferences
Configuring IP device manager preferences
Configuring image repository preferences
Configuring Mpls management preferences
Configuring sFlow data collector preferences
Configuring name service preferences
Configuring polling service preferences
Configuring sFlow accounting preferences
Configuring SSL certificates preferences
Configuring sFlow monitoring preferences
Configuring syslog file reader preferences
Configuring Snmp preferences
Configuring Tftp preferences
Configuring memory allocation settings
Memory allocation settings
Server Heap Size
Configuring asset polling
Configuring SAN communication
Product communication settings
Viewing the network size status
Select the Connect using Http option
Configuring the preferred IP format
Select the Connect using Https Http over SSL only option
Configuring IP communication
Http
FTP/SCP/SFTP server settings
Configuring an internal FTP server
Accessing the FTP server folder
Configuring an internal SCP or Sftp server
Select the Use External FTP Server and/or SCP Server option
Configuring an external FTP, SCP, or Sftp server
Select FTP/SCP/SFTP in the Category list
Testing the FTP, SCP, and Sftp server
Select SCP from the Preferred Protocol Secured list
Select Sftp from the Preferred Protocol Secured list
Configuring the server port
Server port settings
To configure server settings, complete the following steps
Options dialog box displays Figure
Support mode settings
Configuring support mode settings
Select Support Mode in the Category list
Configuring the server log file purge limit
Fips Support
Users overview
User Account Management
Users dialog box displays Click the Users tab, if necessary
Viewing configured users
To view configured users, complete the following steps
Select Server Users
183
184 53-1003056-01
To create a new user account, complete the following steps
User accounts
Creating a new user account
User accounts
186 53-1003056-01
Copying a user account
Editing a user account
Copying and pasting user preferences
Disabling a user account
To re-activate a user account, complete the following steps
Enabling a user account
Deleting a user account
Unlocking a user account
To create a new role, complete the following steps
Roles
Creating a new role
Roles
Copying a role
Editing a role
Adding privileges to a role
Deleting a role
To delete a role, complete the following steps
Removing privileges from a role
Areas of responsibility
Areas of responsibility
Creating an AOR
Copying an AOR
Editing an AOR
Assigning products to an AOR
Deleting an AOR
Users dialog box displays Click the Policy tab
Password policies
Configuring a password policy
Removing products from an AOR
199
Viewing password policy violators
Click View Policy Violators
Authentication Server Groups on the Management server
Click the Authentication Server Groups tab
Assigning roles and AORs to an AD group
Loading an AD group
Removing roles and AORs from an AD group
To load an AD group, complete the following steps
Close the Active Directory Users and Computers dialog box
Deleting an AD group
Creating an AD user account
Open the Active Directory Users and Computers console
Assigning an AD user to an AD group
Configuring roles and AORs on the external Ldap server
Defining user accounts on the external Ldap server
Click OK Close the Management console
User profiles
Select Start Run Type adsiedit.msc and press Enter
Click OK on the User Profile dialog box
User profiles Configure CLI credentials
Viewing your user profile
Select Server User Profile
To edit your user profile, complete the following steps
Changing your password
Editing your user profile
User profiles
To view your password policy, complete the following steps
Viewing your password policy
Click Optional Messages Reset
Resetting optional messages
Configuring e-mail notification
Configuring CLI credentials
Configuring the CLI credential policy
Dashboard overview
Dashboard Management
212 53-1003056-01
Toolbar
Dashboard toolbar
Dashboards expand navigation bar
Dashboard messages
General dashboard functions
Accessing a dashboard
Creating a user-defined dashboard
Filtering the dashboards list
Deleting a user-defined dashboard
Setting the dashboard display
Customizing the dashboard widgets and monitors
218 53-1003056-01
Printing the dashboard display
Exporting the dashboard display
Attaching and detaching the Dashboard tab
Setting the network scope
Creating a customized network scope
Editing a user-defined network scope
Setting the data display time frame
Deleting a user-defined network scope
Product Status and Traffic dashboard
Default dashboards
IP Port Health
Status widgets
Access Point Status widget
Status widgets
Color Type
Customizing the Access Point Status widget
ColorSeverity
Events widget
Customizing the Events widget
Accessing additional data from the Events widget
Customizing the Host Adapter Inventory widget
Host Adapter Inventory widget
IP Inventory widget
Customizing the IP Inventory widget
Accessing additional data from the IP Inventory widget
IP Status widget
IP Status widget displays the device status as a pie chart
Viewing additional IP product data
Accessing additional data from the IP Status widget
Status widget
Fabric Watch widgets
Fabric Watch widgets
Out of Range Violations widget
Customizing the Out of Range Violations widget
Port Health Violations widget
Customizing the Port Health Violations widget
Performance monitors
Accessing additional data from the widget
Monitor title Description Data collectors
Displaying monitors on the Performance Dashboard
Performance monitors Preconfigure performance monitors
Click the Customize Dashboard icon
Accessing additional data from top or bottom port monitors
Top Port Alignment Errors monitor
Performance monitors Click OK
Performance monitors
Top Port C3 Discards monitor
Top Port C3 Discards RX to monitor
Top Port CRC Errors monitor
243
Top Port Discards monitor
Accessing additional data from the Top Port Discards monitor
Top Port Encode Error Out monitor
Top Port Errors monitor
Top Port Errors monitor
Accessing additional data from the Top Port Errors monitor
Top Port Overflow Errors monitor
Top Port Receive EOF monitor
Top Port Runtime Errors monitor
Top Port Sync Losses monitor
Top Port Too Long Errors monitor
Top Port Traffic monitor
Accessing additional data from the Top Port Traffic monitor
Top Port Underflow Errors monitor
Top Port Utilization Percentage monitor
255
Bottom Port Utilization Percentage monitor
Top Product CPU Utilization monitor
Top Product Memory Utilization monitor
Top Product Response Time monitor
Top Product Temperature monitor
261
Top Products with Unused Ports monitor
Editing a preconfigured performance monitor
Monitor types
User-defined performance monitors
Measures
Top or bottom product performance monitors
Top or bottom port performance monitors
Distribution performance monitors
Port measures types
User-defined performance monitors
Time series performance monitors
Accessing additional data from the Distribution monitors
Add Performance Dashboard Monitor dialog box displays
Configuring a user-defined product performance monitor
Accessing additional data from the sFlow monitors
Top sFlows performance monitors
271
Click OK on the Add Performance Dashboard Monitor dialog box
Adding targets to a user-defined performance monitor
Performance Dashboard Monitor Targets dialog box displays
Configuring a user-defined port performance monitor
274 53-1003056-01
MAC Vlan
Configuring a user-defined sFlow performance monitor
Viewing product distribution data details
Viewing port distribution data details
Configuring a monitor from a performance graph
Utilization Legend
View Management
IP tab overview
Main toolbar
IP main toolbar
Product List toolbar
Topology Map toolbar
Host Product List toolbar
IP Product List
Host topology map toolbar
Product List functions
Topology Map
286 53-1003056-01
IP tab overview Topology keyboard shortcuts
Master Log
Keyboard Shortcut Description
Anchoring or floating the Minimap
Minimap
Resizing the Minimap
Status bar
IP product icons
Icon legend
CNA
Host product icons
Icon legend
Vlan
Event icons
IP group icons
IP port icons
IP product status icons
Customizing the main window
Customizing the main window
Zooming in and out of the Connectivity Map
Zooming
Displaying columns
Exporting the topology
Customizing application tables
Zooming out
Changing the order of columns
Exporting table information
Resizing the columns
Sorting table information
Copying table information
Expanding and collapsing tables
Product List customization
Adding a property label
Searching for information in a table
Deleting a property label
Editing a property label
Searching for a device
Search
Restricting a search by node
Address Finder
Address Finder
Searching for an exact match
Clearing search results
Select Tools Address Finder
Finding IP addresses
Address Finder dialog box displays
303
Finding MAC addresses
305
IP topology view manager
Network Object view functions
Network Objects view
Clearing the Network Objects Product List filter
Filtering devices in the Network Objects Product List
Network Objects view
L2 Topology view
IP Topology view
IP Topology view
Ethernet Fabrics view
Ethernet Fabrics view
Vlan Topology view
STP/RSTP topology
ElementDescription
Viewing STP/RSTP topology
Element Description
Generating an STP/RSTP Report
Exporting an STP/RSTP Report
Vlan Topology view STP/RSTP Topology map elements
Mailing an STP/RSTP Report
Host Topology view
Host Topology view Click Save
314 53-1003056-01
Topology map elements
IP topology map components
IP topology map components
Logical
Icon Description Products
Connections
Topology map layout
Viewing flyovers on the topology map
Orthogonal
Organic
Hierarchical
Orthogonal Merge Lines
Circular
Selecting a topology map layout
Free Form
Creating a customized layout
Creating customized topology links
Customizing the Topology Map
Adding a background image to a map
Click OK on the Topology Background Map dialog box
Deleting a background image from the library
Select Portrait or Landscape from the Orientation area
Printing a map
Enabling port actions
Port actions
Displaying port properties for an attached device
Disabling port actions
Port actions
Accessing performance monitoring
330 53-1003056-01
MRP Topology overview
MRP Topology
Viewing a MRP Topology map
Master
Viewing a MRP ring
Viewing a MRP ring MRP Topology map elements
Error
Selecting a topology map layout
Configuring the application to show a dashed line
336 53-1003056-01
337
Creating a customized layout
Click the Starting Point row
Customizing the MRP Topology map
Enter the ring ID, for example, Ring
Viewing MRP properties
Refreshing MRP Topology data
Click Close on the MRP Topology Options dialog box
341
Viewing MRP properties
Call Home
Call Home
System requirements
Viewing Call Home configurations
346
347
To show a Call Home center, complete the following steps
Showing a Call Home center
Hiding a Call Home center
Showing a Call Home center
Editing the IBM Call Home center
Editing a Call Home center
Click Edit Centers beneath the Call Home Centers list
Click Edit Centers beneath the Call Home Centers table
Backup Connection field
Editing an e-mail Call Home center
Primary Connection field
Enter a password in the Smtp Server Settings Password field
Enter a user name in the Smtp Server Settings Username field
Call Home alert e-mail messages
Fcip
Editing the EMC Call Home center
Editing the HP LAN Call Home center
Enabling a Call Home center
To enable a Call Home center, complete the following steps
Enabling supportSave
Select Monitor Event Notification Call Home
Testing the Call Home center connection
Testing the Call Home center connection
Disabling a Call Home center
Viewing Call Home status
Viewing Call Home status
Assigning a device to the Call Home center
Assigning a device to the Call Home center
Removing a device from a Call Home center
Removing all devices and filters from a Call Home center
To define an event filter, complete the following steps
Defining an event filter
Click OK on the Call Home Event Filter dialog box
Assigning an event filter to a device
Assigning an event filter to a Call Home center
Assigning an event filter to a Call Home center
Removing all event filter from a Call Home center
Overwriting an assigned event filter
Overwriting an assigned event filter
Searching for an assigned event filter
Removing an event filter from a device
Removing an event filter from a device
Searching for an assigned event filter
About third-party tools
Third-party tools
Starting third-party tools from the application
Select Tools Product Menu ToolName
Launching a Telnet session
Launching an Element Manager
Launching an Telnet session from the IP tab
Adding a tool
Select Configure Element Manager HCM. HCM Agent displays
Select Tools Setup
Launching HCM Agent
Entering the server IP address of a tool
Adding an option to the Tools menu
Removing an option from the Tools menu
Changing an option on the Tools menu
Adding an option to a device’s shortcut menu
Changing an option on a device’s shortcut menu
Removing an option from a device’s shortcut menu
374 53-1003056-01
Server Management Console overview
Server Management Console
Launching the SMC on Windows
Launching the SMC on Linux
Services tab
Monitoring and managing Management application services
Services tab
Click Stop Cimom
Stopping all services
Stopping the Cimom services
Refreshing the server status
Click Change Database Password
Starting all services
Restarting all services
Changing the database password
Viewing server port numbers
Ports tab
Select Radius Server from the Primary Authentication list
AAA Settings tab
Configuring Radius server authentication
AAA Settings tab
Local Database
Configuring a Radius server
Configuring Ldap server authentication
Select Ldap Server from the Primary Authentication list
Configuring an Ldap server
For Primary Authentication, select TACACS+ Server
Configuring TACACS+ server authentication
Configuring a TACACS+ server
Configuring Common Access Card authentication
Select CAC from the Primary Authentication list
For Primary Authentication, select Switch
Configuring switch authentication
For Primary Authentication, select Windows Domain
Configuring Windows authentication
Authentication Audit Trail log displays
Configuring local database authentication
Displaying the client authentication audit trail
For Primary Authentication, select Local Database
Capturing technical support information
Restore tab
Technical Support Information tab
Restoring the database
To upgrade HCM, complete the following steps
HCM Upgrade tab
Upgrading HCM on the Management server
SMI Agent Configuration Tool Select the HCM Upgrade tab
SMI Agent Configuration Tool
SMI Agent Configuration Tool
Launching the Smia configuration tool on Windows
Management Console dialog box
Smia Configuration Tool dialog box
Launching the Smia configuration tool on Unix
Service Location Protocol SLP support
Launching a remote Smia configuration tool
Smia Configuration Tool dialog box displays
Slptool commands
SLP file locations on Unix systems
SLP on Unix systems
SLP file locations on Windows systems
SLP on Windows systems
Home tab
Authentication tab
Authentication tab
Click the Authentication tab
Configuring Cimom server authentication
Cimom tab
Configuring the SMI Agent port number
Configuring the Cimom Bind Network Address
Configuring the Cimom log
To import a certificate, complete the following steps
Certificate Management tab
Click the Certificate Management tab
Exporting a certificate
Viewing a certificate
Deleting a certificate
Summary tab
SMI Agent Configuration Tool Click the Summary tab
Managed Ports
Log Level
Licensed Ports
412 53-1003056-01
Wireless management overview
Wireless Management
Wireless device discovery
Wireless devices
Device Name Firmware required
Wireless devices on the dashboard
Wireless devices on the dashboard
View management
Wireless device properties
View management
Element Manager
Launching the Element Manager
Browser and system requirements
Launching a Telnet session
Configuration repository and backup management
Save and close the file
CLI configuration management
Vlan management
Cluster mode
Performance management
Fault management
Policy Monitors
AP Products report
Contact
Status
Firmware version
Location
424 53-1003056-01
VCS
VCS Management
Fabric cluster mode
VCS mode types
This section contains these topics
Logical chassis cluster mode discovery
Logical chassis cluster operations
Ethernet Fabrics view management
428 53-1003056-01
429
Serial firmware update and activation for Network OS devices
Network OS
Support for Network OS VDX 2740 embedded switch
Dynamic product group
VCS product groups
Port profiles
Static product group
Life of a port profile
Ampp characteristics
Port profile Vlan profile QoS profile
Ampp event Applicable behavior and failures
Ampp events and behavior
Assigning MAC addresses to a port profile
Port profile configuration using the management application
Click Add Offline MACs
Managing offline MAC addresses
Related topics
Click Add Assign MACs dialog box displays
Comparing port profiles
Profile Comparison Summary dialog box
Profile Comparison Summary list
Vlan Settings
Profile Properties
Deploying port profiles
QoS Settings
ACL Settings
FCoE Settings
FRU monitoring
System Monitor support on Network OS VDX platforms
Alert notifications
System thresholds
Resource monitoring
SFP parameter Description Suggested SFP impact
SFP parameter monitoring
Security monitoring
Port statistics monitoring
Interface error types
To diagnose traceroute, you can do either of the following
Select Monitor Diagnostics Traceroute
Ethernet fabric traceroute
Tracing Ethernet fabric routes
Source address format Condition
TCP UDP
Request Source port number Destination port number
Ethernet fabric traceroute Trace Route example
Browse to the directory where you want to save the data
Exporting diagnostic data
450 53-1003056-01
Host management
Host Management
Model number Description
Brocade adapters
Host Bus Adapters
Following sections describe the three Brocade adapter types
Fabric Adapters
Converged Network Adapters
AnyIOTM technology
HCM software
HCM software
HCM features
Click Add on the Discover VM Managers dialog box
Host adapter discovery
VM Manager
Adding a VM Manager
Deleting a VM Manager
HCM and Management application support on ESXi systems
ESXi CIM listener ports
Add Host Adapters dialog box
Adding host adapter credentials for ESXi
Select CIM server ESXi only as the Contact option
Select Host Adapter Software from the Configure menu
Adapter software
Adapter software
Importing a driver into the repository
Driver repository
Deleting a driver file from the repository
Boot image repository
Boot Image Management dialog box
Importing a boot image into the repository
Click Import on the Boot Image Repository dialog box
Downloading a boot image to a selected host
Backing up boot image files
Bulk port configuration
Configuring host adapter ports
Deleting a boot image from the repository
Add Port Configuration dialog box, shown in , displays
Adding a port configuration
Bulk port configuration
Click Add on the Configure Host Adapter Ports dialog box
466 53-1003056-01
Adapter Port Configuration Status dialog box displays
Deleting a port configuration
Configuring FAWWNs on switch ports
Editing a port configuration
Duplicating a port configuration
Click Start to save the changes to the switch
Enabling the Fawwn feature on a switch or AG ports
Disabling the Fawwn feature on a switch or AG ports
Select Configure Fabric Assigned WWN. or
Manually assigning a Fawwn to a switch or AG port
Auto-assigning a Fawwn to a switch or AG port
Modifying a Fawwn on a switch or AG port
FAWWNs on attached AG ports
Deleting a Fawwn from a switch or AG port
Click the Attached AG Ports tab
Moving an AG port Fawwn across switches
Adding AG port FAWWNs
Deleting AG port FAWWNs
Host adapter management privileges
Role-based access control
Host adapter administrator privileges
Role-based access control
FC port measures HBA port measures CNA port measures
Host performance management
Host security authentication Counters
Host security authentication
Host security authentication
SupportSave on adapters
Host fault management
Adapter events
Filtering event notifications
Host fault management
Syslog forwarding
Configuring backup to a hard drive
Backup support
Select the Include FTP Root directory check box
Select the Enable Backup check box Click Apply or OK
FCoE overview
Fibre Channel over Ethernet
Enhanced Transmission Selection
Enhanced Ethernet features
Enhanced Ethernet features
Dcbx protocol
FCoE protocols
FCoE protocols supported
Ethernet jumbo frames
Ethernet link layer protocols supported
Copying switch configurations to selected switches
Saving running configurations
FCoE licensing
Saving running configurations
Device type Configuration possibilities
DCB configuration management
Lldp profiles
Switch policies
Switch policies
DCB map and Traffic Class map
Minimum DCB configuration for FCoE traffic
DCB configuration
DCB configuration
Creating a DCB map to carry the LAN and SAN traffic
Select Configure DCB
To configure LLDP, complete the following steps
Configuring Lldp
To configure the DCB interface, complete the following steps
Select Configure Element Manager Admin
Select Assign the Global Configuration
Creating the FCoE Vlan to carry FCoE traffic
Adding a LAG
Save the running-config file to the startup-config file
Apply the Vlan classifier group to the DCB interface
Click Add LAG or Edit LAG
L2 Mode Select Access or Trunk
Add LAG or Edit LAG dialog box displays, as shown in Figure
Editing a DCB switch
Editing a DCB port
497
Editing a LAG
499
Enabling a DCB port or LAG
Deleting a LAG
QoS configuration
Priority group ID
Strict priority No bandwidth % configuration Allowed
Creating a DCB map
Off
503
Deleting a DCB map
Editing a DCB map
Assigning a DCB map to a port or link aggregation group
QoS configuration
Editing a Traffic Class map
Creating a Traffic Class map
Select Traffic Class from the Map Type list
Deleting a Traffic Class map
Select Traffic Class in the Map Type list
Changing the Vlan ID on the default FCoE map
FCoE provisioning
FCoE provisioning
Enabling or disabling the FCoE map on the port
Adding a Vlan classifier rule
Vlan classifier configuration
Vlan classifier configuration
Deleting a Vlan classifier rule
Editing a Vlan classifier rule
Deleting a Vlan classifier group
Creating a Vlan classifier group
Configuring Lldp for FCoE
LLDP-DCBX configuration
LLDP-DCBX configuration
515
Deleting an Lldp profile
Editing an Lldp profile
802.1x authentication
802.1x authentication
Assigning an Lldp profile to a port or ports in a LAG
16 802.1x authentication
Enabling 802.1x authentication
Disabling 802.1x authentication
Setting 802.1x parameters for a port
519
Deploying DCB product, port, and LAG configurations
Switch, port, and LAG deployment
Switch, port, and LAG deployment
Deploy to Ports dialog box
522 53-1003056-01
523
Network OS switches in VCS mode
Network OS switches in VCS mode
Viewing switches in VCS mode
Supported VCS platforms
Viewing FCoE parameters on the Network OS switch
Viewing QoS parameters on the Network OS switch
Lldp Profiles list
Viewing LLDP-DCBX parameters on the Network OS switch
Available Rules
Vlan Classifiers
Viewing the 802.1x parameter on the Network OS switch
Viewing ports in VCS mode
Viewing port parameters on the Network OS switch port
QoS DCB parameters on the Network OS switch port
Viewing QoS parameters on the Network OS switch port
QoS-DCB
QoS non-DCB parameters on the Network OS switch port
Viewing FCoE parameters on the Network OS switch port
QoS Non-DCB
Viewing the 802.1x parameter on the Network OS switch port
Viewing LLDP-DCBX parameters on the Network OS switch port
Port Control
Viewing LAGs in VCS mode
Viewing LAG parameters on the Network OS switch LAG
Re-authentication Interval sec
Minimum Links
Viewing QoS parameters on the Network OS switch LAG
QoS DCB parameters on the Network OS switch LAG
Type
QoS non-DCB parameters on the Network OS switch LAG
Viewing FCoE parameters on the Network OS switch LAG
Enable LLDP-DCBX check box
Viewing LLDP-DCBX parameters on the Network OS switch LAG
DCB performance
DCB performance
Real-time performance graph
Generating a real-time performance graph from the SAN tab
Generating a real-time performance graph from the IP tab
Historical performance graph
Generating a historical performance graph
Historical Performance Graph dialog box displays
FCoE login groups
Historical performance report
Generating a historical performance report
539
FCoE login groups
Adding an FCoE login group
FCoE login groups Click OK
Editing an FCoE login group
FCoE Login Group Confirmation and Status dialog displays
Disabling the FCoE login management feature on a switch
Deleting one or more FCoE login groups
Select a group from the Login Groups list and click Delete
Viewing virtual FCoE ports
Virtual FCoE port configuration
Enabling the FCoE login management feature on a switch
Virtual FCoE port configuration
Select the Virtual FCoE Ports tab
Clearing a stale entry
Virtual FCoE Ports tab displays, as shown in Figure
545
546 53-1003056-01
Telemetry overview
Telemetry
Policy-based routing
Viewing existing PBR policies
549
Adding rules to a policy
Adding a new policy
551
Editing a policy
Adding policies from saved configurations
Editing a rule
Deploying a PBR policy on demand
Deleting a policy or rule
Click OK on the Deploy to Products PBR dialog box
Saving a PBR policy deployment
Select Save deployment only
Scheduling a PBR policy deployment
Configuring an hourly deployment schedule
Configuring a one-time deployment schedule
Configuring a weekly deployment schedule
Configuring a daily deployment schedule
Configuring a monthly deployment schedule
Enabling or disabling ACL accounting
Resetting ACL counters
Configure Security ACL Accounting
ACL Accounting
Click OK on the Port Selection Layer 2/3 ACL dialog box
Viewing ACL counters
Select the Clear all counters on device check box
Port Selection Layer 2/3 ACL dialog box displays
560 53-1003056-01
Security Management
Layer 2 access control list management
Security overview
Creating a Layer 2 ACL configuration IronWare
IronWare Layer 2 ACL configuration
Add Layer 2 ACL Configuration dialog box displays
MAC
Click OK on the Add Layer 2 ACL Configuration dialog box
Editing a Layer 2 ACL configuration IronWare
Copying a Layer 2 ACL configuration IronWare
566 53-1003056-01
567
Select the Clear ACL Assignment option
Clearing Layer 2 ACL assignments IronWare
Creating a standard Layer 2 ACL configuration Fabric OS
Fabric OS Layer 2 ACL configuration
DeviceName Layer 2 ACL Configuration dialog box displays
Copying a standard Layer 2 ACL configuration Fabric OS
Editing a standard Layer 2 ACL configuration Fabric OS
Click OK on the Edit Layer 2 ACL Configuration dialog box
Select Extended from the Type list
Creating an extended Layer 2 ACL configuration Fabric OS
572 53-1003056-01
Copying an extended Layer 2 ACL configuration Fabric OS
Editing an extended Layer 2 ACL configuration Fabric OS
574 53-1003056-01
Clearing Layer 2 ACL assignments Fabric OS
Deleting a Layer 2 ACL configuration from the application
Creating a Layer 2 ACL from a saved configuration
Deleting a Layer 2 ACL configuration from the switch
Viewing Layer 2 ACL configuration on a fabric Network OS
Network OS Layer 2 ACL configuration
Viewing Layer 2 ACL configuration on a device Network OS
Viewing Layer 2 ACL configuration on an interface Network OS
Click OK on the Port Selection Layer 2 ACL dialog box
Layer 3 access control list policy
Creating a standard L3 ACL configuration
Add L3 ACL Configuration dialog box displays
Layer 3 access control list policy
Click OK on the Add L3 ACL Configuration dialog box
Creating a L3 ACL from a saved configuration
Edit L3 ACL Configuration dialog box displays
Editing a standard L3 ACL configuration
Click OK on the Edit L3 ACL Configuration dialog box
Click Duplicate
Copying a standard L3 ACL configuration
Creating an extended L3 ACL configuration
Click OK on the Duplicate L3 ACL Configuration dialog box
586 53-1003056-01
L3 ACL Advanced Settings dialog box displays
Editing an extended L3 ACL configuration
Copying an extended L3 ACL configuration
589
Add L3 ACL IPv6 Configuration dialog box displays
Creating an IPv6 L3 ACL configuration
Click OK on the Add L3 ACL IPv 6 Configuration dialog box
Editing an IPv6 L3 ACL configuration
Copying an IPv6 L3 ACL configuration
Assigning a L3 ACL configuration to an interface
Deleting a L3 ACL configuration
Click OK on the DeviceName L3 ACL Configuration dialog box
595
Clearing L3 ACL assignments
Configuring hit statistics
Configuring the ACL configuration type and operations
Configuring L3 ACL advanced settings
599
600 53-1003056-01
3qosp3time-exceeded
Viewing existing networks
Network configuration
To view all existing networks, complete the following steps
Creating a network
Layer 3 access control list policy Click the Networks tab
Editing a network
Deleting a network
Copying a network
Viewing existing network groups
Network group configuration
Click the Network Groups tab
Creating a network group
Review the List of Network Groups table
To create a network group, complete the following steps
To edit a network group, complete the following steps
Editing a network group
To copy a network group, complete the following steps
Copying a network group
Click OK on the Duplicate Network Group dialog box
Deleting a network group
Service configuration
To delete a network group, complete the following steps
Viewing existing services
TCP UDP
Creating a service
Copying a service
Editing a service
Deleting a service
Review the List of Service Groups table
Service group configuration
Viewing existing service groups
Click the Service Groups tab
To create a service group, complete the following steps
Creating a service group
Click Add Add Service Group dialog box displays
To edit a service, complete the following steps
Editing a service group
To copy a service, complete the following steps
Copying a service group
Click OK on the Duplicate Service Group dialog box
Deleting a service group
Media Access Control MAC filter management
Media Access Control MAC filter management
Creating a MAC filter configuration
Add MAC Filter dialog box
Creating a MAC filter from a saved configuration
Editing a MAC filter
Click OK on the MAC Filter Saved Configurations dialog box
Copying a MAC filter
626 53-1003056-01
Assigning MAC filters
Deleting a MAC filter
Clearing MAC filter assignments
Adding a MAC filter configuration to an interface
Security configuration deployment
Security configuration deployment
Deploying a security configuration on demand
Click OK on the Deploy to Products Layer 2 ACL dialog box
Saving a security configuration deployment
Deploy to Product/Ports dialog box
Scheduling a security configuration deployment
Select an ACL in the list and click Edit
Edit Layer 2 ACL Configuration dialog box displays
634 53-1003056-01
635
636 53-1003056-01
Zoning overview
Zoning
Green Zone
Online zoning
Zoning naming conventions
Offline zoning
Zone database size
Zoning configuration
Configuring zoning
Zone database size
Viewing zone properties
Creating a zone
Click New Zone
Select Save to Switch from the Zone DB Operation list
Zoning configuration
Adding members to a zone
Removing a member from a zone
Creating a member in a zone
Click New Member
Renaming a zone
Duplicating a zone
Deleting a zone
Click Zoning Policies
Enabling or disabling the default zone for fabrics
Select Configure Zoning Fabric
Customizing the zone member display
Editing a zone alias
Creating a zone alias
Click New Alias
Removing an object from a zone alias
Click Export Alias
Exporting zone aliases
Renaming a zone alias
Deleting a zone alias
Click New Configuration
Creating a zone configuration
Duplicating a zone alias
Zone Configuration Properties dialog box displays
Viewing zone configuration properties
Adding zones to a zone configuration
Removing a zone from a zone configuration
Click Activate
Activating a zone configuration
Click the Active Zone Configuration tab
Deactivating a zone configuration
Click Deactivate
Deleting a zone configuration
Renaming a zone configuration
Creating an offline zone database
Duplicating a zone configuration
Select Delete from the Zone DB Operation list
Deleting an offline zone database
Merging fabrics
Refreshing a zone database
Select Refresh from the Zone DB Operation list
Select Compare from the Zone DB Operation list
Merging two zone databases
Creating a common active zone configuration in two fabrics
Select an offline zone database from the Zone DB list
Saving a zone database to a switch
Exporting an offline zone database
You cannot export an online zone database
Importing an offline zone database
Zoning administration
Rolling back changes to the offline zone database
To compare two zone databases, complete the following steps
Comparing zone databases
Managing zone configuration comparison alerts
Clearing the fabric zone database
Setting change limits on zoning activation
Select Undo CheckOut from the Zone DB Operation list
Removing all user names from a zone database
Finding a member in one or more zones
Select Clear All from the Zone DB Operation list
Finding a zone configuration member in the zones list
Finding zones in a zone configuration
Finding a zone member in the potential member list
Listing un-zoned members
Listing zone members
Replacing zone members
Removing an offline device
Click OK on the Offline Device Management dialog box
Replacing an offline device by name
Replacing an offline device by WWN
670 53-1003056-01
About port fencing
Port Fencing
About port fencing
Viewing port fencing configurations
673
Thresholds
C3 Discard Frames threshold
Invalid words threshold
Link Reset threshold
Protocol error threshold
Invalid CRCs threshold
Adding thresholds
Adding thresholds
State Change threshold
Adding a C3 Discard Frames threshold
Add C3 Discard Frames Threshold dialog box displays
Port Fencing dialog box
Add Invalid CRCs Threshold dialog box displays
Adding an Invalid CRCs threshold
Add Invalid Words Threshold dialog box displays
Adding an Invalid Words threshold
Adding a Link Reset threshold
Add Link Reset Threshold dialog box displays
Select Protocol Error from the Violation Type list
Adding a Protocol Error threshold
Add Protocol Error Threshold dialog box displays
Add State Change Threshold dialog box displays
Adding a State Change threshold
Assigning thresholds
Avoiding port fencing inheritance
Unblocking a port
Editing a C3 Discard Frames threshold
Editing thresholds
Click OK on the Edit C3 Discard Frames Threshold dialog box
Click OK on the Edit Invalid CRCs Threshold dialog box
Editing an Invalid CRCs threshold
Editing an Invalid Words threshold
Editing thresholds
Click OK on the Edit Invalid Words Threshold dialog box
Editing a Link Reset threshold
Editing a Protocol Error threshold
Click OK on the Edit Link Reset Threshold dialog box
Editing a State Change threshold
Click OK on the Edit Protocol Error Threshold dialog box
Viewing thresholds
Finding assigned thresholds
Viewing all thresholds on a specific Fabric OS device
Removing thresholds from individual objects
Removing thresholds
Removing thresholds from the thresholds table
Removing thresholds
Ficon Environments
Ficon configurations
Planning the configuration
Configuring a switch for Ficon operation
Configuring a switch for Ficon operation
697
Select Discover Fabrics
Configuring the switch
Click Add License
Click Download
701
Configuring an Allow/Prohibit Matrix
Configuring Ficon display
703
Manual Allow/Prohibit dialog box displays, as shown in on
Configuring an Allow/Prohibit Matrix manually
Click Analyze Zone Conflicts
Click Manual Allow/Prohibit
Click OK on the Manual Allow/Prohibit dialog box
Save As/Duplicate dialog box displays, as shown in on
Copying an Allow/Prohibit Matrix configuration
707
Confirmation message displays, as shown in on
Activating an Allow/Prohibit Matrix configuration
Deleting an Allow/Prohibit Matrix configuration
Activating an Allow/Prohibit Matrix configuration
Clearing port names
Changing the Allow/Prohibit Matrix display
Cascaded Ficon fabric
Changing window arrangement
Configuring a cascaded Ficon fabric
Cascaded Ficon fabric
Enabling DLS
Cascaded Ficon fabric merge
713
Merging two cascaded Ficon fabrics
Set up merge options screen displays
TOV
Specify the Cable length between switch ports
Range is form 10 through 500 km. The default is 50 km
Resolving merge conflicts
717
To view port groups, complete the following steps
Select Configure Port Groups
Viewing port groups
Port Groups dialog box displays, as shown in on
To edit a port group, complete the following steps
Swapping blades Click OK
Swapping blades
721
722 53-1003056-01
Element Manager overview
IP Element Manager
Element Manager CLI
Element Manager CLI
Accessing the IP Element Manager CLI
Element Manager interface overview
Accessing the Element Manager interface
Select Configure Element Manager GUI
Element Manager interface overview
Build Label
Switch properties
Serial #
Port Count
727
Properties dialog box Ports tab
Element Manager toolbar
Displaying port properties
Port Mode
Tx Power
Rx Power
Temperature Tx Bias Current
Comparing physical and virtual port properties
Comparing physical port properties
You can compare physical and virtual port properties
Comparing physical and virtual port properties
Search
Status indicator icons
Table capabilities
Real Time Graph/Table Historical Graph/Table
Performance data
Real-time performance monitoring
Historical performance monitoring
Configuring Vlan
Configure dialog box
Resetting port counters
Enable or Disable
Management Module switchover
Changing the standby Management Module to active
MR Switch Over Status dialog box
Switch Fabric Module
Port mirroring
Configuring port mirroring
Port mirroring
Adding a port to port mirroring
Select Configure Port Mirroring
Editing a port in port mirroring
SFlow
Configuring sFlow in Element Manager
Deleting a port from port mirroring
Web Management interface
Accessing the Web Management interface
Select Configure Element Manager Web
Web Management interface
Element Manager Front Panel
Web Management interface troubleshooting
Accessing the IP device front panel
Select Configure Element Manager Front Panel
Configuration repository
Configuration Repository and Backup
Configuration repository
745
Saving the configuration status
747
Comparing product configurations
Viewing the configuration
749
Restoring a configuration
Searching the configuration repository
Exporting a configuration to a text file
Viewing configuration deviation status
Configuration deviation
Change tracking
754 53-1003056-01
Configuration Snapshots tab displays, as shown in Figure
Configuration snapshots
Comparing configuration snapshots
Configuration snapshots
Generating a configuration snapshot report
Viewing the pre- and post-configuration snapshot
Click Save Snapshot
Saving a configuration snapshot
Searching the configuration snaphots
Scheduling a configuration backup
Schedule backup
763
Edit Automatic Configuration Backup dialog box displays
Disabling a backup schedule
Configuration requirements
IP Configuration Wizard
DNS
Payloads
Payloads
Payload name Description Product Payloads
Interface Payloads
Creating a payload configuration
Select Configure Configuration Wizard
Payload name Description
Creating a payload configuration
769
770 53-1003056-01
Save to Flash
Don’t Save to Flash or Reload
Save to Flash and Reload
Configuration dialog box Deployment Schedule pane
773
Select a configuration from the Product Configurations list
Duplicating a payload configuration
Modifying a payload configuration
Duplicating a payload configuration
Modifying a payload configuration
Deleting a payload configuration
Deploying a payload configuration
Deploying a payload configuration
CLI configuration overview
CLI Configuration Management This chapter
Viewing existing templates
Select Configure CLI Configuration
Viewing existing templates
To create a new configuration, complete the following steps
Product configuration templates
Creating a new product configuration
Product configuration templates
780 53-1003056-01
781
CLI Template dialog box Parameters tab
783
CLI Credentials dialog box
Changing product credentials
Importing parameter values into a configuration
Select a row in the Parameters table Click Preview
Previewing CLI commands
Previewing CLI commands Different values for each target
Same value for each target
Copying a product configuration
CLI command guidelines
CLI command guidelines
Editing a product configuration
To test a configuration, complete the following steps
Testing a configuration
Editing the CLI responses properties file
Valid and invalid responses from devices
Failureresponseend
Editing the Network OS CLI responses properties file
Successresponsestart
Successresponseend
Valid and invalid responses from devices
Configuration command response validation
To delete a configuration, complete the following steps
Deleting a configuration
Using a dash character in CLI Configuration manager
Configuration error checking
Deploying a configuration on demand
CLI configuration deployment
Creating a monitoring configuration
Monitoring configurations
796 53-1003056-01
797
Show interface ethernet $portSLOTPORTSlot#/Port#
799
Copying a monitoring configuration
Editing a monitoring configuration
Viewing CLI deployment reports
CLI deployment reports
Select Reports Product CLI
Product CLI Report displays
CLI configuration scheduling
Configuring a one-time deployment schedule
Configuring an hourly deployment schedule
CLI configuration scheduling
Configuring a daily deployment schedule
Configuring a weekly deployment schedule
Configuring a monthly deployment schedule
Configuring a yearly deployment schedule
806 53-1003056-01
Obtaining software files
Image Repository for IP Products
Products supporting the image import
Boot image management
Viewing the list of boot images
Products supporting the image import
Select Configure Firmware Management
Manually importing boot images
Deleting boot images from the Management application
Deploying boot images to products
Software image management
Software image management
Viewing the list of software images
Manually importing software images
Click OK on the Import Software Image dialog box
Automatically retrieving software images from products
Deleting software images from the Management application
Right-clickConfiguration Schedule Backup
Schedule Backup dialog box displays, as shown in Figure
Deploying software images to products
Viewing the list of unified images
Unified image management
Unified image management
Import Firmware Image from File dialog box displays
Importing unified images into the Management application
Click OK on the Manual Import Unified Image dialog box
Complete the following steps
Updating unified images
Deploying unified images to products
Deleting unified images from the Management application
Serial firmware update and activation for NOS devices
Vlan Management
Default Vlan
Vlan Manager
Super-aggregated Vlan
Remote Switched Port Analyzer
Private Vlan
Transparent LAN Support
Configuration requirements for Vlan Manager
Vlan Manager tabs
Feature VCS FC mode Logical chassis mode Standalone mode
Displaying a list of VLANs
Vlan management in a VCS environment
Displaying VLANs in the Vlan view
824 53-1003056-01
Displaying VLANs by products
826 53-1003056-01
Adding or modifying port VLANs
Port VLANs
828 53-1003056-01
Select Configuration Manager Vlan Manager
Adding or modifying dual mode ports
Assigning DCB ports to a Vlan
L2 mode Tagged mode
Adding Vlan properties
832 53-1003056-01
Deleting a port Vlan in Product view
Modifying port Vlan properties
Deleting port VLANs from products
Deleting a port Vlan in Vlan view
Select a Save Configuration option
Spanning Tree Protocol configuration
Deploying Vlan configurations
Spanning Tree Protocol configuration
Configuring STP or Rstp on a port Vlan
FOS Vlan Mstp
Target context STP type
IOS Vlan STP, Rstp
STP, RSTP, Mstp
Deploying an STP configuration on a port Vlan
Configuring Mstp on a product
Adding an Mstp instance
Assigning an Mstp instance to a Vlan
Managing IP addresses on an SVI
Vlan routing
Vlan routing
Deploy IP Configuration dialog box
Vlan routing Click the Deploy now option
Select a Save Configurations option
Mpls Management
Mpls pre-configuration
Mpls licensing
Mpls Licensed and Configured Products group
Mpls overview
Configuring LDP
LSP
Select Configure Mpls LSP
Viewing LSP Admin Group information
Select the Admin Groups tab Figure
Select the Paths tab Figure
Viewing LSP path information
Select the Rsvp LSPs tab Figure
Viewing Rsvp LSP information
Related topics Mpls overview
Viewing saved LSP configurations
LSP
Adding an LSP admin group
Duplicating an LSP admin group
Editing an LSP admin group
Adding an LSP path
Deleting an LSP admin group
You can edit an LSP path by taking the following steps
Editing an LSP path
Duplicating an LSP path
LSP Delete Path Configuration wizard displays Figure
Deleting an LSP path
Configuring advanced Rsvp LSP settings
Admin Groups Selector dialog box
858 53-1003056-01
859
860 53-1003056-01
Rsvp LSP Advanced Settings Fast Reroute tab
Bypass LSP
Deleting an Rsvp LSP
Delete Rsvp LSP Configuration wizard displays Figure
Editing an Rsvp LSP
Duplicating an Rsvp LSP
Select the saved configuration Click the Duplicate button
Editing a saved LSP configuration
Duplicating a saved LSP configuration
Select the saved configuration Click the Edit button
Select Monitor Mpls LSP Topology
Deleting a saved LSP configuration
Select the saved configuration Click the Delete button
Displaying LSP Topologies
LSP right-click options on the Topology View
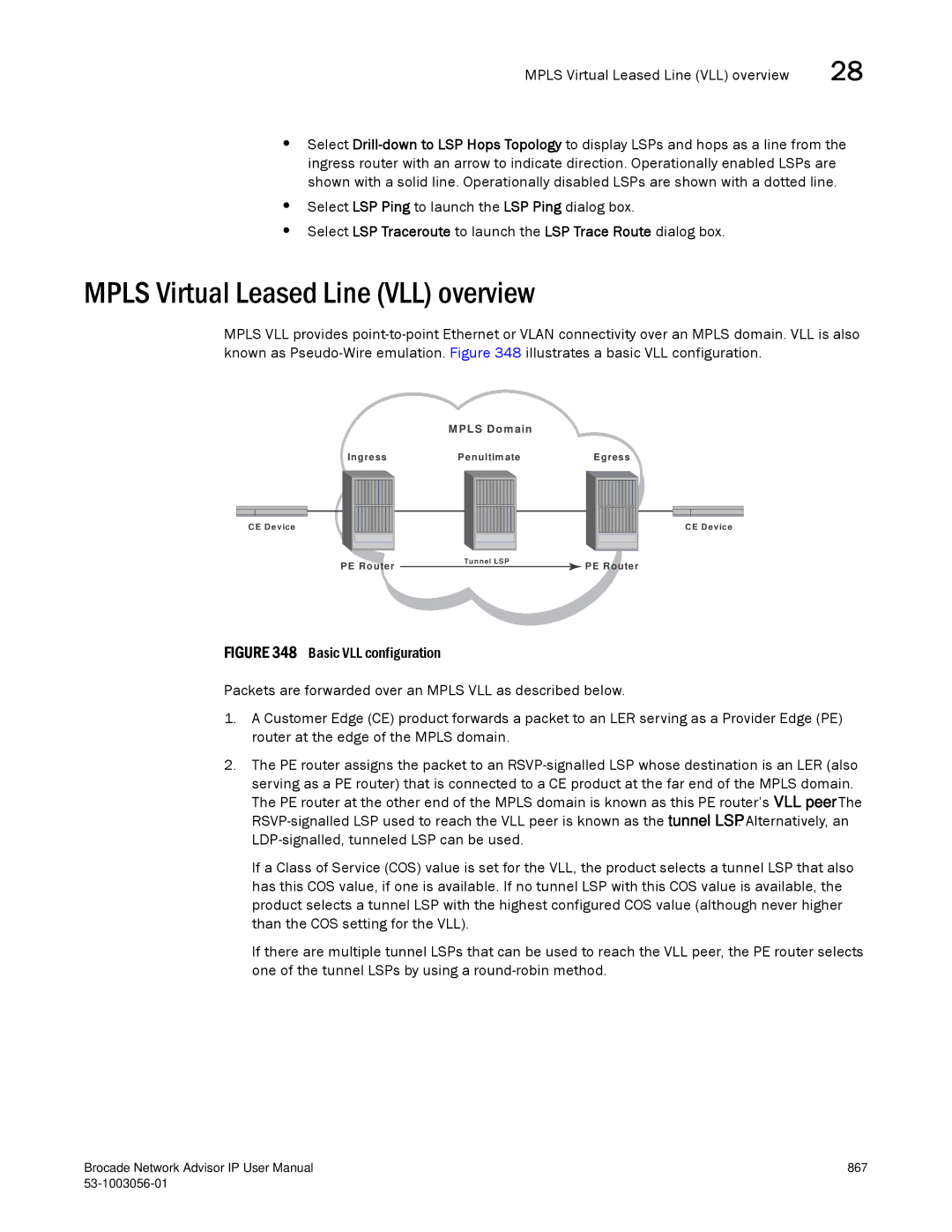
Mpls Virtual Leased Line VLL overview
868 53-1003056-01
VLL manager
Select Configure Mpls VLL
Viewing VLL instances
Status
VLL Mode
Tag Mode
To view current saved VLL configurations, do the following
Viewing Saved VLL configurations
To add a new VLL instance do the following
Adding or editing a VLL instance
Configuring devices using the VLL Manager
VLL Configuration wizard Port Configuration dialog box
VLL Configuration wizard Deploy Target Actions dialog box
Deploying target actions using the VLL Manager
VLL configuration wizard Deployment Properties
Deploying VLL properties using the VLL Manager
VLL configuration wizard Deployment Schedule dialog box
Scheduling deployment using the VLL Manager
Reviewing the VLL Manager summary
Reviewing the VLL Manager configuration
To edit a VLL instance, do the following
Creating a new VLL instance using duplicate
Editing a VLL instance
Deleting VLL instances
Select Monitor Mpls VLL
Filtering VLL traffic monitoring
VLL Monitor Dialog box displays Figure
VLL
Virtual Private LAN Services Vpls overview
883
Vpls Manager
Select Configure Mpls Vpls
Vpls Manager
Viewing Vpls instances and peer topologies
Endpoint settings PE Devices
Vpls settings
Vpls Manager Peer Topology tab
To view current Vpls configurations, do the following
Viewing Saved Vpls configurations
Adding or editing a Vpls instance
Vpls Configuration wizard Device Configuration dialog box
Configuring devices using the Vpls Manager
Row is added to the Configured Endpoint Settings list
Configuring endpoint settings
Deployment Properties page displays Figure
Deploying target actions using Vpls Manager
Vpls Configuration wizard Deployment Properties dialog box
Deploying Vpls properties using Vpls Manager
Vpls Configuration wizard Deployment Schedule dialog box
Scheduling deployment using Vpls Manager
Creating a new Vpls instance from a duplicate
Reviewing the Vpls Manager summary
Deleting a Vpls instance
Editing a Vpls instance
To edit a Vpls instance, do the following
Select Monitor Mpls Vpls
Filtering for Vpls traffic monitoring
Vpls Monitor dialog box displays Figure
Vcid pools
Select Configure Mpls Vcid Pool
Vcid pools
Viewing, creating, and deleting Vcid pools
Configuring a maintenance association
802.1ag Connectivity Fault Management
802.1ag CFM
Add Maintenance Association dialog box displays
900 53-1003056-01
Edit Maintenance Association dialog box displays
Editing a maintenance association
802.1ag Connectivity Fault Management
Click Close on the Configure 802.1ag CFM dialog box
902 53-1003056-01
903
28 802.1ag Connectivity Fault Management
Adding a MEP to a maintenance association
905
Editing a MEP
907
Viewing the MEPs in a maintenance association
Deleting a maintenance association
Checking the connectivity status of remote MEPs
Sending a loopback message
Click Loopback
Sending a linktrace message
Click Linktrace
Configuring frame delay
915
916 53-1003056-01
Viewing the VIP Servers
Select Configure Application Delivery VIP Servers
VIP Servers
VIP Servers overview
Viewing the VIP Servers
Viewing VIP Server information
Viewing VIP Server information
VIP Servers list
Disabling servers or server ports
Enabling or disabling servers or server ports
Server port statistics
Enabling servers or server ports
Deleting a row from the Server Port Statistics list
Gslb Manager
Global Server Load Balancing
Viewing the Gslb Manager
Select Configure Application Delivery Gslb
To view the Gslb Manager, perform the following steps
To create a Gslb policy, perform the following steps
Gslb policy management
Creating a Gslb policy
Gslb policy management
926 53-1003056-01
Applying metrics on the Metrics tab
Adding a prefix on the Prefix tab
Connection Load Weights
Importing IP addresses from a file
Deleting a prefix from the Prefix list
930 53-1003056-01
Gslb site management
Adding a site configuration
Gslb site management
Adding ServerIron ADX products to the site
Managing zones
Gslb zone configuration
Adding a zone configuration
Gslb zone configuration
Add Hosts dialog box
Adding a host to a zone
Deleting a zone configuration
Editing the list of IP addresses and weights
List of IP Addresses and Weights dialog box displays
Controller configuration
Controller configuration
Controller Configuration tab displays
Creating a new Gslb controller configuration
939
Deploying a controller configuration
Scheduling a deployment
One Time Hourly Daily Weekly Monthly Yearly
SSL certificates
SSL Certificates for ServerIron Products
Certificate View tab Figure Product View tab Figure
SSL certificate configuration
Accessing SSL certificates on the Certificate View tab
SSL Certificates dialog box has two tabs
945
SSL Certificates dialog box Product View tab
Accessing SSL certificates on the Product View tab
Generating a certificate signing request
948 53-1003056-01
949
Related topic
Adding an SSL certificate and key file
Editing an SSL certificate and key file
Viewing SSL certificate details
Duplicating an SSL certificate and key file
Importing certificates and keys from file locations
Importing certificates and keys from products
Exporting certificates and keys
Deploying certificates and keys
Creating key passwords
958 53-1003056-01
Chaining SSL certificates
Appending SSL certificates
960 53-1003056-01
Deleting SSL certificates
962 53-1003056-01
Introduction to the Deployment Manager
Editing a deployment configuration
Select Configure Task Scheduler
Deployment Manager
Duplicating a deployment configuration
Generating a deployment report
Deleting a deployment configuration
Deploying a configuration
Viewing deployment logs
Searching the configuration snapshots
Generating a deployment configuration snapshot report
967
968 53-1003056-01
SAN performance overview
Performance Data
SAN performance overview
SAN performance measures
SAN performance management requirements
Example of default access control list
Example of Snmp
Example of setting Snmp
974 53-1003056-01
Snmp SET
Snmp GET
FCIP-MIB YES
Select Monitor Performance Real-Time Graph
SAN real-time performance data
Generating a real-time performance graph
SAN real-time performance data
Real Time Performance Graphs dialog box displays
Filtering real-time performance data
Open the Real Time Performance Graphs dialog box
Graph display
Fcip Snmp
Exporting real-time performance data
Performance statistics counters
Protocol
HBA, CNA
Http
HBA, CNA HCM API
FC, GE
Type Protocol Source OID value
IP performance monitoring and traffic analysis
IP configuration requirements
Monitoring real-time performance
IP real-time performance monitoring
IP real-time performance monitoring
984 53-1003056-01
Removing products and ports from real-time performance
Adding products and ports to real-time performance
Click Sources from the Real Time Graphs/Tables dialog box
Click Mibs tab in the Available Measures area
Adding measures to products
Removing measures from products
Select measures Real Time Graphs/Tables dialog box displays
Adding measures to ports
Adding collectibles to monitoring
Removing measures from ports
Configuring the performance graph display
Configuring the performance graph
Removing collectibles from monitoring
Show data points graph
Minutes Hours Day
Configuring graph options
Graph Options dialog box Historical Graphs/Tables dialog box
993
Spreadsheet .csv Image .png
Exporting a graph
Printing a graph
Choose Export File Format dialog box displays
IP historical performance monitoring
Name Collector Basics
Editing system collectors
Displaying historical data collectors
IP historical performance monitoring
997
Adding or editing a historical data collector
Enabling a historical data collector
999
1000 53-1003056-01
1001
1002 53-1003056-01
1003
1004 53-1003056-01
Adding third-party device MIB objects manually
Configuring a MIB walk instance
Duplicating a historical data collector
Select Monitor Performance Historical Data Collectors
Deleting a historical data collector
Adding, editing, or duplicating a user-defined expression
Duplicating system data collectors
1007
Complete the following steps to delete an expression
Deleting an expression
Select the Data Monitoring tab
Viewing Historical Graphs/Tables
NetIron Historical Graph display
Select the Collection Status Summary tab
Mouse functions for graphs
To map a MIB name, use the following format
MIB data collectors
Mapping a MIB object to a unit name
MIB data collectors
Complete the following steps to create a report
IP Custom performance reports
Creating a custom report
IP Custom performance reports
1015
Time Settings Sampling Granularity
1017
Click the Identification tab
Exporting an Snmp Monitor report
Interpreting the Snmp Monitor report
Configuring sFlow
IP sFlow configuration
IP sFlow configuration
Interface Payload sFlow Settings dialog box displays
IP sFlow configuration Click Next
Interface Speed Sampling rate
Product Payload SFlow Destination dialog box displays
Click Next
Select the Report Definitions tab
Creating custom sFlow reports
IP sFlow configuration Select the Product & Port tab
1026 53-1003056-01
1027
IP sFlow configuration Select the Layer 3 & 4 tab
Add Report Definitions dialog box, User Identification tab
Select the User Identification tab
Add Report Definitions dialog box, Time Settings tab
Select the Result Settings tab
Add Report Definitions dialog box, Result Settings tab
1033
Select Monitor Traffic Analysis Custom Reports
Scheduling custom sFlow reports
1035
1036 53-1003056-01
IP Traffic analyzer monitoring and sFlow reports
Device-level configuration requirements
Suspending a custom sFlow report schedule
Select Monitor Traffic Analysis Monitor sFlow
802.1X configuration requirements
Displaying sFlow monitoring reports
IP Traffic analyzer monitoring and sFlow reports
Report list
Selecting a report
Measure list
Interpreting an sFlow traffic report
Save and close the ipconfig.properties file
This field shows the date and time the report was requested
Viewing top MAC talkers
Category list, select L3/L4 Reports
Viewing top Vlan talkers
Viewing all IPv4 Layer 3 or Layer 4 Top Talkers
Viewing all Layer 3 and Layer 4 traffic
Reports list, select IPV4 Next list, select TCP
Viewing IPv4 top TCP talkers
TCP
Viewing IPv4 top UDP talkers
Category list, select L3 or L4 Reports
Viewing IPv4 top Icmp talkers
Icmp
Viewing IPv6 Top Talkers
Viewing IPv4 Others
Viewing other Layer 3 or Layer 4 Top Talkers
Complete the following steps to change these combinations
Enabling and viewing TCP reports
Defining invalid TCP packet combinations
RST-SYN RST-FIN RST-PSH RST-URG FIN-SYN
Valid TCP flags report
Displaying the invalid TCP Flags report
Type list, select Invalid TCP Flags
Viewing VCS fabric Top Talker reports
Viewing BGP paths report
Select Monitor Traffic Analysis Traffic Accounting
Troubleshooting sFlow reports
IP traffic accounting
IP traffic accounting
1055
1056 53-1003056-01
Frame Monitor
Frame Monitor
Scsi
Frame types
Scsi RW
Frame Monitoring requirements
Creating a custom frame monitor
Frame Monitor Configuration Status dialog box
Assigning a frame monitor to a port
Editing a frame monitor
Removing a frame monitor from a port
Finding frame monitor assignments
Removing a frame monitor from a switch
1064 53-1003056-01
Power center overview
Power Center
Data monitoring
Select Monitor Power Center
Viewing PoE data for products
To view PoE data for a port, complete the following steps
Viewing PoE data for ports
To filter port details, complete the following steps
Filtering port details
Viewing attached device properties
1070 53-1003056-01
To view a PoE chart, complete the following steps
Viewing PoE charts
1072 53-1003056-01
1073
Refreshing PoE data
PoE power on demand
PoE power on demand
Configuring automatic data refresh
Powering up PoE-capable ports on demand
Powering down PoE-capable ports on demand
Scheduling an power up deployment
Schedule PoE power deployment
Schedule PoE power deployment
1079
1080 53-1003056-01
Configuring a yearly deployment schedule
Scheduling a power down deployment
Updating a power deployment schedule
Scheduled Ports ScheduleName dialog box displays
Click Show Ports
Deleting a power deployment schedule
Adding a PoE product threshold
PoE thresholds
PoE thresholds
PoE Consumption Consumption %
PoE Allocation
Adding a PoE port threshold
Port allocation Port consumption Port consumption %
Thresholds dialog box Choose one of the following measures
To view PoE thresholds, complete the following steps
Viewing PoE thresholds
Updating a PoE threshold
To update a PoE threshold, complete the following steps
Disabling PoE thresholds
To enable PoE thresholds, complete the following steps
To disable PoE thresholds, complete the following steps
Enabling PoE thresholds
Viewing PoE performance
Monitoring real time power performance on products
Viewing PoE performance
Deleting PoE thresholds
1094 53-1003056-01
1095
Monitoring real time power performance on ports
1097
1098 53-1003056-01
Policy monitor overview
Policy Monitor
Policy monitor overview
Fabric policy monitors
Switch and router policy monitors
1102 53-1003056-01
Host policy monitors
1104 53-1003056-01
Frequency Weekly
Preconfigured policy monitors
Next Run Next time the policy will run using the format
Management policy monitor
Viewing policy monitor status
Viewing existing policy monitors
Select Monitor Policy Monitor
Adding a policy monitor
1109
Add Policy Monitor dialog box, Switch/Router Checks tab
1111
Add Policy Monitor dialog box, Hosts Checks tab
Policy monitor scheduling
Configuring a one-time policy monitor schedule
Configuring a monthly policy monitor schedule
Configuring an hourly policy monitor schedule
Configuring a daily policy monitor schedule
Configuring a weekly policy monitor schedule
Deleting a policy monitor
Editing a policy monitor
Viewing a predefined configuration rule
Configuration rules
Predefined configuration rules
Configuration rules Port Profile Interface Rule expressions
Viewing configuration rule details
Add Configuration Rule dialog box displays Figure
1118 53-1003056-01
1119
Click Cancel on the Add Configuration Rule dialog box
Adding a configuration rule
Click OK on the Add Configuration Rule dialog box
Duplicating a configuration rule
Click the Switch/Router Checks tab
Editing a configuration rule
Click Add Configuration Rule
Click OK on the Edit Configuration Rule dialog box
Exporting a configuration rule
Importing a configuration rule
Deleting a configuration rule
Adding a configuration condition
Viewing predefined configuration conditions
Add Configuration Rule dialog box displays
Add Condition dialog box displays Figure
Select Add Condition
Selecting a product
Duplicating a configuration condition
You cannot edit a predefined configuration condition
Editing a user-defined configuration condition
Predefined conditions
Configuration rules Predefined conditions
Policy Monitor dialog box displays Click Add
Viewing a predefined configuration block
Add Block dialog box displays Figure
Adding a configuration block
Configuration rules Add Monitor dialog box displays
Select Add Block
Select the Switch/Router Checks tab
Duplicating a configuration block
You cannot edit a predefined configuration block
Editing a user-defined configuration block
Predefined blocks
Deleting conditions and blocks
Click Delete Click Yes on the confirmation message
Running a policy monitor
Viewing a policy monitor report
Viewing a policy monitor report
1137
Click Export File Download dialog box displays Click Save
Exporting a policy monitor report
Click History
Viewing historical reports for all policy monitors
Viewing historical reports for a policy monitor
Policy Monitor dialog box displays
Viewing historical reports for a policy monitor
Fault management overview
Fault Management
Event Purging
Event notification
Restrictions
Supported IP address types
1143
Defining filters
Setting up basic event filtering
Defining filters
Click Advanced
Setting up advanced event filtering
1146 53-1003056-01
Snmp traps
Snmp Trap Recipients dialog box, shown in , displays
Adding a trap recipient to one or more switches
Select Monitor Snmp Setup Product Trap Recipients
Snmp traps
Snmp Trap Forwarding dialog box, shown in , displays
Removing a trap recipient from one or more switches
Select Monitor Snmp Setup Trap Forwarding
Snmp trap forwarding
Adding a trap destination
Select the Enable trap forwarding check box
Adding a new trap filter
1152 53-1003056-01
Event reception
Accept Snmp v1/v2c traps with only these community strings
Event Reception dialog box, shown in , displays
Do not accept Snmp v1/v2c traps
Accept Snmp v1/v2c traps with any community string
Privacy protocol Authentication Result Credential type
Snmp traps Snmp security and authentication
Adding an Snmp v3 credential
Importing a new MIB into the Management application
Adding an Snmp v1 or v2c community string
Trap customization
Registering traps
Customizing a registered trap definition
Unregistering a registered trap
Click the Registered button
Select a product group from the Fabric / Products list
Reverting the customization of a registered trap to default
Snmp informs
Enabling or disabling Snmp informs
Adding a syslog recipient
Syslogs
Syslogs
Removing a syslog recipient
To remove a syslog recipient, complete the following steps
Syslog Forwarding dialog box, shown in , displays
Select Monitor Syslog Configuration Syslog Forwarding
Select the Enable syslog forwarding check box
Adding a syslog forwarding destination
Adding a syslog filter
1165
Select Monitor Event Processing Event Actions
Event action definitions
Snort message forwarding
Creating an event action definition
Event action definitions
Selecting an event for an event action
1168 53-1003056-01
Configuring varbind filters
Sources pane of the Add Event Action dialog box
Selecting source address products and ports
Click Next to advance to the Sources pane
Configuring event action policies
Editing event actions
1174 53-1003056-01
1175
Acknowledging special events
Special events handling
1177
Configuring event action e-mail settings
Modifying an event action definition
Click Cancel to cancel the operation
Deleting an event action definition
Configuring event actions for Snort messages
Click the Import Snort Rule button
Pseudo events
Import Snort Rule File dialog box displays, shown in Figure
Pseudo Events dialog box, shown in , displays
Displaying pseudo event definitions
Creating pseudo event definitions
Select Monitor Event Processing Pseudo Events
Setting pseudo event policies
Filtering pseudo event traps
1185
Deleting a pseudo event definition
Editing a pseudo event definition
Adding a pseudo event on the escalation policy
1188 53-1003056-01
Adding a pseudo event on the resolving policy
1190 53-1003056-01
Adding a pseudo event on the flapping policy
1192 53-1003056-01
Event custom reports
Event custom reports
Defining report settings
Select Reports Event Custom Reports
Defining the report identity
1196 53-1003056-01
To filter a report definition, complete the following steps
Filtering a report definition
Add/Edit Report Definition dialog box Filter tab
Add/Edit Report Definition dialog box Product tab displays
Filtering report events by date and time
1200 53-1003056-01
Editing a report definition
Deleting a report definition
Event custom report schedules
Event custom report schedules
Adding or editing an event report schedule
One Time
Event logs
Event logs
Viewing event logs
Copying part of a log entry
Exporting the entire log
Copying an entire log entry
Mailing selected event details from the Master Log
Mailing all event details from the Master Log
Displaying event properties from the Master Log
Click Close to close the Event Properties dialog box
Event logs Event Properties
Event Field Description
Select Table Copy Table
Copying part of the Master Log
Copying the entire Master Log
Exporting the Master Log
Filtering events in the Master Log
‘unnamed’ filter
Deleting a Filter
‘none’ filter
Editing a Filter
Duplicating a Filter
Packet Capture Pcap
Configuring packet captures
Select Configure Packet Capture Pcap
Configure Pcap dialog box, shown in , displays
1214 53-1003056-01
Server and client support save
Technical Support
Capturing Server and Client support save data
Capturing Server support save data
Capturing Client support save data
Server and client support save
Client support save using a command line interface
Click the Schedule tab
Device technical support
Scheduling technical support information collection
Device technical support
Select the Enable scheduled Technical Support Data check box
1221
Click OK on the Technical SupportSave dialog box
Starting immediate technical support information collection
Click the Generate Now tab, if necessary
Progress
Click Close on the Technical SupportSave Status dialog box
Field Description
Firmware Type
Viewing the technical support repository
Type Default location Default naming convention
Mail button
Saving technical support information to another location
Click OK on the Technical Support Repository dialog box
Available SupportSave
Mailing technical support information
Select the file you want to delete in the table Click Delete
Deleting technical support files from the repository
1229
1230 53-1003056-01
Browser requirements
Reports
Reports overview
Viewing IP reports
Select E-mail as Html Select E-mail as CSV
Exporting and saving IP reports to a file
Exporting IP reports to e-mail recipients
Select Export as Html Select Export as CSV
IP Wired Products report
IP report contents
IP Wired Products report
Export button
Detailed Product Report
Stacking Units
IP Addresses
Stacking Port
Realtime
Modules
Controller Cluster
Cluster Peer MCT
Physical Ports
GRE Tunnels
AP List Count
Detailed Cluster Report
System Name values
System Information
Nodes
FC Ports
IP Module report
Physical Media
IP Layer 3 Vlan report
IP Port VLANs report
Field/ComponentDescription
IP Subnet report Layer 3 Vlan report fields and components
IP Subnet report
Port Name
IP Address report
MAC Address report
IP Address report
IP Stacking Ports Realtime report
IP Physical Ports Realtime report
IP Physical Ports Realtime report
IP Physical Media Realtime report
IP Physical Media Realtime report
Select Reports Deployment
IP Deployment reports
Viewing a deployment report
IP Deployment reports
Reports Template Manager overview
Preconfigured reports
Reports Template Manager overview
User-defined reports
Select Reports Report Manager
Accessing the Report Template Manager
Report Template Manager dialog box displays Figure
Viewing a report
Exporting a report template
Importing a report template
Deleting reports
Report content and functions
Product Count
Products List report
IP address of the product
Displayed for products that support stacking
Physical port information for each port on the product
Product Report
Cluster
Ports Tx/Rx Ratio report
Total Received MB
Summary table Location
Device Name
Detailed Product Report
Max Tx Utilization %
Low Traffic Ports report
Max Rx Utilization %
Exporting data from the report
Dashboard main menus
Menu Command Command Options
Application menus
This appendix
Edit Menu
Command Command Options
IP main menus
IP main menus
Discover Menu
Element Manager. Select to configure a selected device
Configure Menu
Lsan Zoning Device Sharing. Trial and Licensed version
Monitor Menu
Reports Menu
IP shortcut menus
IP shortcut menus
Tools Menu
Launches the Real-Time Graphs / Tables dialog box
Component Menu/Submenu Commands Comments
IP shortcut menus IP Subnet
IronWare device
L2 ACL
DCB
VCS/VDX
Third-party device
1273
1274 53-1003056-01
Event reason code FRU code/Event type Description Severity
Call Home Event Tables
IP Call Home Event
Network OS Call Home Event
Call Home Event Tables Network OS Call Home Event
Product status events
Event Categories
Product audit events
Security events
Security events
Security events for FC devices
Security events for IP devices
Management server events
User action events
Trap name
Product events
IP Performance monitoring events
Product events
IP Performance monitoring events
About user privileges
User Privileges
Privilege Description No Privilege Read-Only Read/Write
About user privileges Application privileges and behavior
Event Notification Setup button in the Users dialog box
Setup Mail server used to Send e-mail Disables Event
Syslog Registration
Options command
Registration
Forwarding dialog box Monitor menu Event Storage option
Performance Graphs dialog box and enables all controls
Management command
Enables the Security L2
Update and OK
Policy monitors Command on the Monitor Menu
Disables Policy Monitor Enables Policy Monitor
Logs menu
Configure Switch Replicate menu
Server Options menu
Monitor Technical
SupportSave, Upload Repository command Upload Failure Data
View Repository Technical Support menu Repository commands
Capture, and View
1291
Compare and Export
Cancel and Help buttons
Zoning
Compare/Merge dialog
Compare/Merge dialog Zone Config tab
Switch, Activate
Lsan Zoning Device
Edit Limits command
Zoning Scope list does
IP CLI
About user privileges IP privileges and behavior
Filter
IP L3 ACL
Profile tab
IP Mpls VLL
IP Mpls Vpls
IP MPLS- LSP
About Roles and Access Levels IP privileges and behavior
About Roles and Access Levels
Application Features and Role Access Levels
1299
IP Mpls LSP
Viewing SAN device properties
Device Properties
Viewing Fabric properties
Viewing SAN device properties Fabric properties
Viewing SAN device properties
Click OK on the FabricName Properties dialog box to close
Viewing SAN device properties Device properties
Remote Switch WWN
Preshared key configured
Remote Switch Name
Remote Switch IP
ICL
Viewing Storage properties
Select Edit Properties
Viewing SAN device properties
Viewing iSCSI Properties dialog box
ISNS Service
Command Descriptor Block Count
Digest Error Count
ISCSI Service
Viewing port properties
Active FC4 Types
Class of Service
Additional Port Info
Address
Viewing SAN device properties Port properties
Locked Port Type
Long Distance Setting
ISCSI button
ISCSI Capable
Port State
Symbolic Name
Troubleshooting list
Port Speed Gb/s
User Port #
IP device properties
Viewing IP device and port properties
IP device properties Port properties
Alias
VCS Mode
Config Mode
Detailed Report button
IP device properties
Show list
Profile Mode
Access Points tab
Port Profiles tab
Device MAC
Connected switch \ Port
Transceiver Temperature
Chassis-Power Supply section of Detailed Report
Viewing VCS fabric properties
Fabric Status
Licensed Features
Access Gateway Mode
Nodes tab
Associated MACs list
MAC Count
VLANs
Domain Count
Native VLAN/VLAN
IP device properties
1324 53-1003056-01
FC Ports properties Identifier The identifier of the port
Host properties
Host properties
SFP/Port Optics
Field Description
Viewing adapter port properties
Host properties Adapter port properties
Click OK to close
Properties customization
Adding a property field
Properties customization Adapter port properties
Deleting a property field
Editing a property field
Editing a property field directly
Properties customization
Characters
Regular Expressions
Construct Matches
Posix character classes US-ASCII only
Regular Expressions Characters
Character classes
Predefined character classes
Boundary matches
Regular Expressions Posix character classes US-ASCII only
Java.lang.Character classes simple java character type
Classes for Unicode blocks and categories
Logical operators
Regular Expressions Greedy quantifiers
Reluctant quantifiers
Possessive quantifiers
Special constructs non-capturing
Regular Expressions Back references
Regular Expressions
CLI Templates
CLI Templates
HyperEdge Stack Port Deletion
HyperEdge Stack Enable
HyperEdge Stack Disable
HyperEdge Stack Port Creation
HyperEdge Peri Port Creation
IronWare OS Enable Web Element Manager
IronWare OS Configure L3-Access-List
CLI Templates HyperEdge Stack Trunk Deletion
MCT Cluster Undeployment
CLI Templates IronWare OS Configure L2-Access-List
MCT Cluster Creation
MCT Cluster Deployment
MCT Client Creation
Mpls Loopback Interface Configuration
Mpls Core Interface Configuration
CLI Templates MCT Cluster Deletion
Ampp
CLI Templates Mpls Endpoint Configuration
Network OS Configure CRC Align Errors Monitor
Network OS Associate MAC to Port Profile
Network OS Configure Inter Frame Gap Violation Fencing
CLI Templates Network OS Configure Extended L2 Access List
Network OS Configure Inter Frame Gap Violation Monitor
Network OS Configure Standard L2 Access List
Network OS Configure RX Symbol Errors Monitor
Network OS Create CoS Mutation Map
Network OS Create Vlan Classifier Group
CLI Templates Network OS Create Lldp Profile
Network OS Create Port Profile
Network OS Create Traffic Class Map
CLI Templates Network OS Create Vlan Classifier Rule
Network OS Update ACL on Port Profile
Network OS Update QoS on Port Profile
Network OS Update Vlan on Port Profile
Private Vlan Add native Vlan mode to Pvlan trunk
CLI Templates Private Vlan Configure Vlan as a Pvlan
Private Vlan Delete Pvlan configuration from Vlan
Private Vlan Configure Pvaln mode in L2 interface
$PRIMARYVLANIDINTEGER $SECONDARYVLANIDINTEGER
Private Vlan Delete Pvlan mapping from promiscuous port
Private Vlan Delete Pvlan associations from host port
Private Vlan Delete Pvaln associations from trunk port
VRF Delete Route Targets Export and/or Import Configuration
VRF Route Distinguisher Configuration
VRF Maximum routes configuration for IPV4 Address Family
VRF Route Targets Export and/or Import Configuration
IronWare OS Vlan Remove interfaces from Vlan as untagged
IronWare OS Vlan Configure virtual routing interface
IronWare OS Vlan Enable Spanning Tree Protocol on IOS Vlan
CLI Templates VRF Display VRF Information
Network OS Vlan Vlan Interface Deletion
Network OS Vlan Layer2 Switch Port Configuration
Network OS Vlan Native Vlan Configuration
Network OS Vlan Vlan Interface Creation
Network OS Vlan Disable Access Interface Configuration
Network OS Vlan Access Interface Configuration
Network OS Vlan Enable Spanning Tree Protocol on NOS Vlan
1356 53-1003056-01
Troubleshooting
Browser troubleshooting
Application Configuration Wizard troubleshooting
Client browser troubleshooting
Client browser troubleshooting
Configuration backup and restore troubleshooting
Element Manager troubleshooting
Firmware download troubleshooting
Firmware download troubleshooting
Sw0FID128admin sshutil delknownhost
Launch Client troubleshooting
Launch Client troubleshooting
Select Start Settings Control Panel Java
Master Log and Switch Console troubleshooting
Master Log and Switch Console troubleshooting
Unix operating systems
Select Discover IP Products
Patch troubleshooting
Patch troubleshooting
Click the Global Settings tab
Server troubleshooting
Professional edition login troubleshooting
Professional edition login troubleshooting
Server Management Console troubleshooting
Server Management Console troubleshooting
Management console errors
Supportsave troubleshooting
Supportsave troubleshooting
Select Properties
Problem Master log warning message
Technical support data collection troubleshooting
Wireless troubleshooting
Technical support data collection troubleshooting
Zoning troubleshooting Wireless troubleshooting
Zoning troubleshooting
Zoning troubleshooting
Achcallcenter
Achcallcenterconfig
Database Fields
Database tables and fields
Achinfo
Database tables and fields Achevent
Acheventfiltermap
Achfilter
Aordevicegroupmap
Adapterportconfigdetails
Adapterportconfigproperty
Adapterdriverfiledetails
Aorinmportgroupmap
Aordevicemap
Aorfabricmap
Aorhostmap
Birtreportparameter
Availableflyoverproperty
Birtreportruntemplate
Database tables and fields Birtreportruntemplate
Birtreportscheduleconfig
Bootimagedrivermap
Bootimagefiledetails
Capability
Database tables and fields Bootimagefiledetails
Bootlunsequence
Bootlunsequencedetail
Database tables and fields Card
Ceduserpreference
Cardcapability
Cedapplication
Cedapplicationmember
Ceeport
Cfgbackuparchive
Changelog
Database tables and fields Cfgbackuparchive
Clitemplate
Clientview
Database tables and fields Clitemplate
Cluster
Clientviewcolumn
Clientviewmember
Clientviewmemberhost
Cnaethport
Cnaethportconfig
Cnaproductconnectivity
Cnaport
Database tables and fields Cnaethportconfig
Collector
Collectortargetentry
Configblock
Collectormibobjectentry
Collectorsnmpexpressionentry
Coreswitch
Configcondition
Database tables and fields Coreswitch
Coreswitchdetails
Coreswitchcapability
Coreswitchchecksum
Coreswitchcollection
Database tables and fields Coreswitchdetails
Cryptohost
Cryptolun
Database tables and fields Cryptolun
Cryptoswitch
Cryptotargetcontainer
Database tables and fields Cryptoswitch
Customfavoritesobjectlist
Database tables and fields Cryptotargetcontainer
Dashboard
Dashboardprovider
Database tables and fields Dashboard
Dashboardcanvas
Dashboardcanvaspreference
Dashboardwidget
Database tables and fields Dashboardwidget
Defaultfavorites
Dashboardwidgetpreference
Defaultwidgetpreference
Database tables and fields Defaultfavorites
Deploymentconfiguration
Deploymenthandler
Database tables and fields Deploymentconfiguration
Deploymentproductstatus
Deploymentreporttemplate
Database tables and fields Deploymentproductstatus
Deploymentstatus
Device
Deploymenttargetmap
Database tables and fields Device
Tacpluspasswordreadonl
Tacpasswordportcfg
Tacpasswordreadonly
Tacpluspasswordportcfg
Mplsmanagestate
Licensedfeatures
Trapregistered
Portcount
=SSH =HTTPS =WINGHTTPS Poecapable
Isdcbswitch
Productfamily
Netconftransport
Vcslicensed
Isprincipalswitch
Wirelesstype
Vcsid
Deviceenclosure
Deviceconnection
Database tables and fields Deviceenclosure
Devicefdmidetails
Deviceenclosuremember
Devicegroup
Database tables and fields Devicefdmidetails
Devicegroupentry
Devicemacgroupmapping
Database tables and fields Devicegroup
Devicenode
Deviceport
Database tables and fields Devicenode
Deviceportmacaddressmap
Deviceportgigeportlink
Encryptionengine
Diskusage
Encryptiongroup
Database tables and fields Encryptionengine
Database tables and fields Encryptiongroup
Encryptionkmipparameters
Encryptiongroupmember
Ethernetcloud
Encryptiontapepool
Ethernetisl
Database tables and fields Ethernetisl
Event
Eventdescription
Database tables and fields Event
Eventcallhome
Eventcategory
Eventfwdfilter
Eventdetails
Eventinstance
Database tables and fields Eventfwdfilter
Eventmodule
Eventorigin
Eventnotification
Eventpolicy
Eventpolicysourceentry
Database tables and fields Eventpolicy
Database tables and fields Eventpolicysourceentry
Eventrule
Eventprocessormap
Database tables and fields Eventrule
Fabric
Eventruleaction
Database tables and fields Fabric
Fabriccollection
Fabricchecksum
Fabricmember
Database tables and fields Fabriccollection
Fabricdiscoverypolicy
Fabricdiscoverypolicyrule
Fabricvcsclustermap
Fabricthresholdsetting
Favorites
Database tables and fields Fabricmember
Fcipcircuitportmap
Database tables and fields Favorites
Fcipporttunnelmap
Fciptunnel
Database tables and fields Fciptunnel
Fciptunnelcircuit
Database tables and fields Fciptunnelcircuit
Circuitstatusstring
Mismatchedconfigurations
Securityflag
Circuitstatus
Fciptunnelperformance
Fcoedevice
Feature
Featureeditionmap
Featuresusage
Ficondeviceport
Database tables and fields Featuresusage
Firmwarefiledetail
Foundrydevice
Firmwareswitchdetail
Foundrymodule
Fporttrunkgroup
Database tables and fields Foundrymodule
Foundryphysicaldevice
Foundryphysicalport
FRU
Database tables and fields FRU
Ftpserver
Generatedreport
Database tables and fields Generatedreport
Gigeport
Gretunnelinterface
Gigeportethernetcloudlink
Gigeportstats
Globalvlan
HBA
Hacluster
Database tables and fields HBA
Hbanodemap
Hbaport
Supportedcos
Switchip
Operatingtopology
SUPPORTEDFC4TYPES
Hbaportdetail
Database tables and fields Hbaportdetail
Hbaportfcoedetails
Hbaportdeviceportmap
Database tables and fields Hbaportfcoedetails
Hbaremoteport
Hbaremoteportlun
Database tables and fields Hbaremoteport
Hostdiscoveryoption
Hbatarget
Healthstatus
Healthtargetstatus
Hostdiscoveryreqgroup
Database tables and fields Hostdiscoveryoption
Hostdiscoveryrequest
Hypervvirtualmachine
Database tables and fields Hostdiscoveryrequest
IFL
Hypervvmhbaportmap
Interface
Database tables and fields Interface
Interfacedeploymentconfig
Ipdevicelicense
Ipinterface
Database tables and fields Ipdevicelicense
Ipportgroup
ISL
Iproute
Ipsubnetvlan
Ipxnetworkvlan
Islconnection
Sourceswitchportid
Targetswitchportid
Database tables and fields ISL
Targetmasterport
Isltrunkgroup
Masterconnectionid
Sourcemasterport
Isltrunkmember
L2ACCESSCONTROLENTRY
Keyvault
L2ACLINTERFACEDEPLOYMAP
Database tables and fields L2ACCESSCONTROLENTRY
L2ACCESSCONTROLLIST
L2ACLDEVICEDEPLOYMAP
L3ACLINTDEPLOYMENTMAP
Database tables and fields L2ACLINTERFACEDEPLOYMAP
L2NEIGHBOR
L3ACLDEVICEDEPLOYMENTMAP
Database tables and fields L3ACLINTDEPLOYMENTMAP
LAG
Lagmember
Database tables and fields Lagmember
Lastconfigupdatetime
Launchincontextmodule
Database tables and fields Launchincontextmodule
License
Licensedowngradedetails
Licenserule
Licensefeaturemap
Licensedfeature
Database tables and fields Licensedowngradedetails
Lsanproxydevice
Lsantagconfig
Lock
Lsandevice
Mctclient
Lsanzonedbconfig
Lsanzone
Lsanzonemember
Macgroup
Database tables and fields Macfilter
Macfilterdevdeploymentmap
Macfilterintdeploymentmap
Managedelement
Macgroup
Mapsevent
Macgroupmember
Mapseventdetails
Database tables and fields Mapsevent
Mapseventcauseaction
Marchingants
Mapspolicy
Measure
Messagerecipient
Module
Migrationhistory
Database tables and fields Module
Moduleslotpresent
Mplsadmingroup
Mplsadmingroupinterfacerelation
Mplslsp
Mplspathhop
Mplspath
Mplsrsvplsp
Mplsrsvplspactuallyroutedhop
Mplsrsvplspadmingroup
Mplsrsvplspadmingroupcontainer
Database tables and fields Mplsrsvplsp
Mplsrsvplspparameters
Mplsrsvplspfrrparameters
Mplsrsvplsptunnelresource
Mplsservice
Database tables and fields Mplsrsvplspparameters
Mplsrsvplsppath
Mplsservicedevicerelation
Database tables and fields Mplsservice
Mplsserviceendpointrelation
Mrpringdevice
Database tables and fields Mplsserviceendpointrelation
Mplsservicepeerrelation
Mrpring
Database tables and fields Mrpringdevice
Nicprofile
N2FPORTMAP
Networkvlan
Networkscopetype
Npflowdefinition
Database tables and fields Nportwwnmap
Npsubflow
Database tables and fields Npflowdefinition
Ouiguesseddevicemap
Perfcollector
Passwordhistory
Pbrinterfaceconfig
Ouivendor
Pbrruleacllist
Pbrpolicy
Pbrrule
Pbrnexthop
Phantomport
Database tables and fields Pbrruleacllist
Physicaldevice
Physicalinterface
Database tables and fields Physicaldevice
Physicalport
Pmcollectormeasuresetting
Pmcollectortargetsetting
Database tables and fields Physicalinterface
Pmcollectortimeseriesmapping
Database tables and fields Pmcollectortargetsetting
Pmdashboardwidget
Pmdatacollector
Database tables and fields Pmdashboardwidget
Database tables and fields Pmdatacollector
Pmmeasure
Pmstatsagingpolicy
Pmwidgettargetentry
Pmwidgetmeasuretype
Pmwidgetmeasuretypeentry
Pmwidgetmonitortype
Poethreshold
Database tables and fields Pmwidgettimeseriesentry
Pmwidgettopncollectorentry
Pmwidgetuserentry
Policyrulemap
Database tables and fields Poethreshold
Poethresholdevent
Policyrule
Portbottleneckstatus
Portbottleneckconfig
Portcommissioncimomserver
Portfencingpolicy
Database tables and fields Portcommissioncimomserver
Portfencingpolicymap
Portprofile
Database tables and fields Portfencingpolicymap
Portprofiledomain
Portprofileqosmap
Portprofiledomainmap
Portprofileinterfacemap
Portprofilemacmap
Portprofilevlanmap
Portprofileqospfcmap
Portvlan
Database tables and fields Portvlan
Privilege
Productapp
Qrtzcrontriggers
Protocolvlan
Qrtzblobtriggers
Qrtzcalendars
Qrtzpausedtriggergrps
Qrtzlocks
Qrtzjobdetails
Qrtzjoblisteners
Qrtztriggers
Database tables and fields Qrtzschedulerstate
Qrtzsimpletriggers
Qrtzjtriggerlisteners
Quorumcardgroupmapping
Recoverycardgroupmapping
Raslog
Querybaseddevicegroup
Resourcefabricmap
Reporttype
Reporttemplate
Reportdrilldowntemplate
Ruleblockmap
Role
Resourcehostmap
Roleprivilegemap
Rulelogicalexpressionmap
SAN
Sanconnection
Database tables and fields Sanconnection
Scomhost
Securitypolicy
Currentreading
Sensor
Selectedflyoverproperty
Sensorid
Sflowhoursummary
Sflowcheckpoint
L3SRCADDR
Inpriority
Outpriority
Srcmac
Sflowminutebgp
Sflowiprouteinfo
Sflowminutemac
Database tables and fields Sflowminutebgp
Sflowminutebgpslnum
SFLOWMINUTEL3SLNUM
Sflowminutevlan
Database tables and fields Sflowminutemac
Sflowminutemacslnum
Sflowminutesummary
SFLOWREPORTL4SOURCE
Database tables and fields Sflowminutevlan
Sflowminutevlanslnum
SFLOWREPORTL3SOURCE
Database tables and fields Sflowstaging
Sflowstagingslnum
Smartcard
Snmpcredentials
Database tables and fields Smartcard
Smiasanname
Snapshotproductstatus
Database tables and fields Snmpcredentials
Snmpdata
Mibindex
Database tables and fields Snmpdata
SNMPDATA1DAY
SNMPDATA2HOUR
Snmpexprdata
SNMPDATA30MIN
SNMPEXPRDATA1DAY
Snmpprofile
Database tables and fields SNMPEXPRDATA1DAY
SNMPEXPRDATA30MIN
Snmpexpression
Readcommunitystring
Database tables and fields Snmpprofile
Writecommunitystring
Sslcertificate
Snmptrapcredential
SNMPV3FORWARDINGCREDENTIAL
Sourceobjecttype
Database tables and fields Sslcertificate
Sslkey
Sslcertificatevipservermap
Stpport
Sslkeypassword
Database tables and fields Sslkey
Statsaging
Stpport
Stpinstance
Switchbottleneckconfig
Database tables and fields Stpinstance
Field
Switchconfig
Switchconfigdetail
Switchlicense
Switchport
Switchmodel
Database tables and fields Switchport
Qosenabled
Npivenabled
Fcfastwriteenabled
Islrrdyenabled
Logicalportwwn
Defaultareaid
Eportdisabled
Logicalportnumber
Switchportperformance
Database tables and fields Switchportperformance
Targettype
Switchthresholdsetting
Systemcardenginemapping
Systemproperty
TIMESERIESDATA1DAY
Thresholdmeasure
Thresholdpolicy
Timeseriesdata
TIMESERIESDATA2HOUR
Database tables and fields TIMESERIESDATA1DAY
TABLE\399 TIMESERIESDATA30MIN
TIMESERIESDATA11DAY
TIMESERIESDATA1
Sumvalue
Minvalue
Database tables and fields TIMESERIESDATA11DAY
TIMESERIESDATA12HOUR
TIMESERIESDATA130MIN
TIMESERIESDATA2
Database tables and fields TIMESERIESDATA130MIN
TIMESERIESDATA22HOUR
TIMESERIESDATA21DAY
TIMESERIESDATA230MIN
Database tables and fields TIMESERIESDATA22HOUR
TIMESERIESDATA3
TIMESERIESDATA31DAY
Database tables and fields TIMESERIESDATA3
TIMESERIESDATA32HOUR
TIMESERIESDATA330MIN
Database tables and fields TIMESERIESDATA32HOUR
TIMESERIESDATA41DAY
TIMESERIESDATA4
TIMESERIESDATA430MIN
TIMESERIESDATA42HOUR
Database tables and fields TIMESERIESDATA430MIN
Toolapp
Toolpath
Trill
Trilltrunkmember
Trilltrunkgroup
Trunkgroupinterface
Trunkgroupmember
User
Userdefinednetworkscope
Database tables and fields User
Useraormap
Userdefineddevicedetail
Userrealtimemeasuremapping
Userrealtimemeasuresetting
Content
Userpreference
Vportdetail
Userresourcemap
Userrolemap
Userstatemap
Vcnpeer
Vcnmember
Vcsclustermember
Vcnpeer
Vcemprofile
Virtualcircuitinterface
Database tables and fields Vcemprofile
Vipserver
Vipserverbinding
Virtualfcoeportmacmember
Virtualfcoeport
Virtualfcoeportstat
Virtualportwwndetails
Database tables and fields Virtualfcoeportstat
Database tables and fields Virtualportwwndetails
Virtualswitch
Database tables and fields Virtualswitch
Domainidoffset
Fcoeloginenabled
Insistentdidmode
DOMAINMODE239
Monitored
Hifenabled
Mapsenabledactions
CLUSTER1 Vcsid
Vlan
Vlanintmacgrouprelation
Vlaninterfacemember
Vlaninterfacerelation
Vlanintctagrelation
Vmotionevent
Vllendpointrelation
Vmdatastoredetails
Database tables and fields Vmotionevent
Vmotionpnicdetails
Vmdatacenter
Vmdvport
Vmdvportgroup
Database tables and fields Vmdvport
Database tables and fields Vmdvportgroup
Vmdvswitch
Vmdvswitchhostmember
Database tables and fields Vmdvswitch
Vmfchba
Database tables and fields Vmfchba
Vmhost
Vmfchbadeviceportmap
Database tables and fields Vmhost
Vmhostproxyswitch
Vmhostenddevconnectivity
Vmhostproxyswitchpnicspec
Database tables and fields Vmhostproxyswitch
Vmhostvirtualnic
Database tables and fields Vmhostvirtualnic
Vmnetworksettings
Vmnicteamingpolicy
Database tables and fields Vmnicteamingpolicy
Vmpath
Vmphysicalnic
Vmsecuritypolicy
Database tables and fields Vmphysicalnic
Vmstandardvswitchport
Vmstandardvirtualswitch
Vmstdvswitchportgroup
Vmstorage
Database tables and fields Vmstdvswitchportgroup
Vmstoragehbaremoteportmap
Vmvcenter
Vmtrafficshapingpolicy
Vmvcentermember
Database tables and fields Vmvcenter
Vmvirtualethernetadapter
Database tables and fields Vmvirtualethernetadapter
Vmvirtualmachine
Vplsendpointrelation
Database tables and fields Vmvirtualmachine
Vmvirtualmachinedatastoremap
Vplsdevicerelation
Vrconndomaingroup
Vrconndomain
Vrconnfcconnection
Vrconnmoduleport
Vrconnmodule
Vrconnserverprofile
Wirelessproductdetails
Vrconnwwn
Wtarchive
Wirelessproductrelation
Zone
Zonedb
Zonealias
Zonealiasinzone
Zonealiasmember
ZONEIN-ZONESET
Zonedbconfig
Zonedbcontent
Zonedbusers
Views
Adapterportconfiginfo
Views
Agconnectioninfo
Cnaethportconfiginfo
Bootimagefiledetailsinfo
Cnaportdetailsinfo
Cnaportinfo
CNAETHPORT.MTU CNAPORT.ALARMWARNING
CNAETHPORT.HARDWAREPATH, CNAETHPORT.STATUS
CORESWITCH.ID
Coreswitchdetailsinfo
Cryptolun LUN, Cryptohost
CORESWITCHDETAILS.DESCRIPTION
Coreswitch Left Outer Join Coreswitchdetails
Cryptohostluninfo
DASHBOARD.CREATEDBY
CRYPTOTARGETCONTAINER, ENCRYPTIONENGINE, Cryptoswitch
Cryptotargetengineinfo
Dashboardpreferencesinfo
Deploymentinfo
Deploymentconfiguration
Deploymentlog
Deviceconnectioninfo
EEMONITORSTATS1DAYINFO
EEMONITORSTATS5MININFO
EEMONITORSTATS30MININFO
EEMONITORSTATS2HOURINFO
TEPORTSTATS30MININFO
TEPORTSTATS5MININFO
TEPORTSTATS1DAYINFO
TEPORTSTATS2HOURINFO
CORESWITCH.IPADDRESS
Switchinfo
CORESWITCH.MAXVIRTUALSWITCHES
VIRTUALSWITCH.CORESWITCHID = CORESWITCH.ID
CORESWITCH, VIRTUALSWITCH, FABRICMEMBER, Fabric
Deviceinfo
DEVICEPORT.NUMBER DEVICEPORT.PORTID
DEVICENODE.SIMULATED
DEVICEPORT.IPPORT DEVICEPORT.HARDWAREADDRESS
Devicenodeinfo
DEVICENODE.FABRICID = SWITCHINFO.FABRICID
N2FPORTMAP Switchport Agnport Switchport Agfport
N2FPORTMAPINFO
Devicenode
Deviceportinfo
DEVICEPORTGIGEPORTLINK.DIRECTATTACH
Devportgigeportlinkinfo
DEVICENODE.FDMIHOSTNAME
Deviceport
Islconnectioninfo
Devportmacaddrmapinfo
Islinfo
ISL.DESTPORTNUMBER
FABRIC.ID = ISL.FABRICID
DESTSWITCHPORT.VIRTUALSWITCHID = DESTVIRTUALSWITCH.ID
Ethernetislinfo
Eventdetailsinfo
Eventinfo
Fabricinfo
FABRICMEMBER.FABRICID = FABRIC.ID
Fciptunnelcircuitinfo
FCIPTUNNELCIRCUIT.DSCPDATA
Fciptunnelcircuit
Fciptunnelinfo
FCIPTUNNEL.DSCPCONTROL
Fruinfo
Fcoedeviceinfo
Gigeportecloudlinkinfo
Hbaportdetailsinfo
Gigeport Switchport Coreswitch
HBAPORT.DEVICEPORTID HBAPORT.CONFIGUREDSTATE
Gigeportinfo
HBAPORT.SUPPORTEDFC4TYPES HBAPORT.SUPPORTEDCOS
HBAPORTDETAIL.PREBOOTDISABLED
HBATARGET.TRUSTED
Hbatargetinfo
Hbaport
HBATARGET.DEVICEPORTID
HBAREMOTEPORT.IOLATENCYAVERAGE
Healthstatusinfo
HBAREMOTEPORT.VENDOR HBAREMOTEPORT.PRODUCTID
HBAREMOTEPORT.CURRENTSPEED
DEVICEENCLOSURE.TYPE
Hostdiscoveryrequestinfo
HOSTDISCOVERYREQUEST.ID
HOSTDISCOVERYOPTION.VMPORT
Hostdiscoveryrequest
Iflinfo
HOSTDISCOVERYREQUEST.DEVICEENCLOSUREID = DEVICEENCLOSURE.ID
Isltrillinfo
ISL Device Vcsdevice
Isltrunkgroupmemberinfo
ISL.DESTDOMAINID ISL.DESTPORTNUMBER
DESTDEVICE.MANAGEDELEMENTID AS Destmeid
Isltrunkinfo
L2NEIGHBOR
ISLINFO.SOURCESWITCHID = ISLTRUNKGROUP.VIRTUALSWITCHID
L2NEIGHBORINFO
Mapseventdetailsinfo
TEMPMODULE.MODULEID TEMPMODULE.NUMPORTS
Moduleinfo
FOUNDRYMODULE.MODULEID FOUNDRYMODULE.SERIALNUM
Nportwwnmapinfo
MODULE.MODULEID MODULE.NUMPORTS MODULE.ISPRESENT
PHYSICALDEVICE.DEVICEID
Productinfo
Phantomportinfo
Lastseentimestamp
TEMPDEVICE.FABRICWATCHSTATUS
TEMPDEVICE.RBRIDGEID TEMPDEVICE.IPADDRESS
TEMPDEVICE.ISROUTER, TEMPDEVICE.ISSLB
TOTIMESTAMPTEMPDEVICE.FIRSTSEENTIME,YYYYMMDDHH24MISS as
TEMPDEVICE.FIRSTSEENTIME
Portbottleneckstatinfo
Portbottleneckconfinfo
Portgroupinfo
Portprofileinfo
Roleprivilegeinfo
Portprofile
Portprofileinterfaceinfo
Portprofilemacinfo
PORTPROFILE.ACTIVATED PORTPROFILEQOSMAP.DCBMODE
Protocolvlaninfo
Portvlaninfo
Sflow
Sflowminutemacview
SFLOWMINUTEL3VIEW
Scomeemonitorinfo
Eemonitor
Sensorinfo
SOURCEPORT.ID = EEMONITOR.SOURCEPORTID
Smartcardusageinfo
SWITCHCONFIG.ID= SWITCHCONFIGDETAIL.SWITCHCONFIGID
Switchconfiginfo
Switchdetailsinfo
SWITCHCONFIG, Switchconfigdetail
VIRTUALSWITCH.FMSMODE
CORESWITCH, VIRTUALSWITCH, FABRICMEMBER, Coreswitchdetails
VIRTUALSWITCH.MANAGEDELEMENTID
DEVICE.IPADDRESS, DEVICE.DEVICEID
Switchdiscoveredmacinfo
Switchportinfo
SWITCHPORT.ID
CORESWITCH.TYPE as Switchtype
Switchsnmpinfo
Timeseriesdatainfo
TIMESERIESDATA12HOUR.MEASUREID
Timeseriesdataview
Union ALL
From timeseriesdatainfo tsd
Trillinfo
Userroleresourceinfo
Trilltrunkinfo
Virtualfcoeportinfo
Virtualportwwndetails
CORESWITCHDETAILS.CORESWITCHID = CORESWITCH.ID
VIRTUALPORTWWNDETAILS.SWITCHID
Virtualportwwndetailsinfo
VLANINTERFACERELATION.VLANDBID = PORTVLAN.VLANDBID
Vmaddressinfo
Vlanintclassifierinfo
DEVICE.DEVICEID
INTERFACE.DEVICEID = DEVICE.DEVICEID
Vmconnectivityinfo
MACGROUP.ID
DEVICEMACGROUPMAPPING.MACGROUPDBID = MACGROUP.ID
DEVICEENCLOSURE.ID AS Hostdbid
VMPATH.HBAPORT = DEVICEPORT.WWN
Vmnetworkconnectivityinfo
DEVICE.MANAGEDELEMENTID
VMSTDVSWITCHPORTGROUP.VMSTANDARDVIRTUALSWITCHID
Pnicmac
VMHOSTENDDEVCONNECTIVITY.INTERFACEID
VMHOST.DEVICEENCLOSUREID
Switchname
VMPATH.HBAPORTBPCHAR = SOURCEPORT.WWN
Vmdatastoredetailsinfo
Vmeemonitorinfo
Vmpath Vmvirtualmachine
Vmluninfo
Vmhostinfo
Vmstatisticsinfo
SWITCHTEPORTSTATS.TRANSMITOK SWITCHTEPORTSTATS.RECEIVEOK
SWITCHPORT.PORTID SWITCHPORT.PORTNUMBER
VMPATH.HBAPORTBPCHAR = DEVICEPORT.WWN
VCEMPROFILE.DISCOVERYSTATUS
Vrconnmoduleinfo
VRCONNMODULE.ID VRCONNMODULE.VRCONNDOMAINID
VRCONNDOMAIN.FIRMWAREVERSION
Union Select distinct VRCONNMODULE.ID
Vrconnnpivinfo
Vrconnmoduleportinfo
DEVICENODE.FABRICID USERDEFINEDDEVICEDETAIL.NAME
Vmmdiscoveredmacinfo
USERDEFINEDDEVICEDETAIL.WWN = VRCONNWWN.PORTADDRESS
Vmvirtualethernetadapterinfo
Events
ZONEDB.ID = ZONEDBCONFIG.ZONEDBID
Zonedbinfo
Apusage
Sflowminutevlanview
Sflowminutebgpview
Physicaldeviceinfo
Managedelementinfo
Slotinfo
Snmpdatainfo
Snmpdataview
Snmpexprdatainfo
Where sw.id = sp.virtualswitchid = de.managedelementid
Device PHYSICALINTERFACE, Physicalport
Vmvnetworkinfo
Vcsclustermemberinfo
$BODY$
Resetvcslicensed
Trilltrunkgroup
Select
Wirelessinterface
Wiredinterface
CEEPORT.AMPPPROFILEMODE
Ceeportinfo
L3.SUBNETMASK
Deviceipaddress
CEEPORT.GIGEPORTID = GIGEPORT.ID
1688 53-1003056-01
Index
Access levels defined
Ampp
CNA
EMC, 354 HP LAN, 355 IBM
Hosts, 101
CUP, Ficon
1692 53-1003056-01
FTP
Ficon
Gslb
State, 102
Mstp
Monitor
Rbac
New device, adding name
NOS
Columns, 284 product overview, 453 products
1043
SVI
1699
WWN
Edit, 880
1701