Page
Copyright 2007-2008 Nortel Networks. All rights reserved
Nortel Networks software license agreement
Legal Information
Exclusive Remedy
Software License Agreement
Page
SSH Source Code Statement
OpenSSL Project License Statements
NN47250-100 Version
How to get help Introducing the Nortel Wlan 2300 System
NN47250-102 Version
Getting help from the Nortel web site
How to get help
How to get help NN47250-100 Version
Nortel Wlan 2300 System Documentation
Introducing the Nortel Wlan 2300 System
Planning, Configuration, and Deployment
Installation
Configuration and Management
Safety and Advisory Notices
Menu Name Command
Bold text
Italic text
CLI Conventions
Using the Command-Line Interface
Command Prompts
Clear fdb dynamic port port-list vlan vlan-id
Set enablepass
Set port enable disable port-list
Clear interface vlan-idip
MAC Address Notation
MAC Address Wildcards
Port Lists
Command-Line Editing
Using CLI Help
Set ap port-list ap-numname name
WSS# show i?
WSS# show ip ?
WSS# show ip telnet
Using the Command-Line Interface NN47250-100 Version
See Also enable on
Access Commands
Disable
Enable
Quit
Set enablepass
Syntax set enablepass
WSS# set enablepass Enter old password old-password
Disable on Enable on
Access Commands NN47250-100 Version
Clear ap on
Port Commands
Port Type Set port type ap on Set ap on
Clear port type on
Clear port counters
Clear ap
Clear port media-type
Clear port-group
Clear port name
Clear port mirror
Syntax clear port type port-list
Network Port Defaults
Configuration from all the specified ports
Clear port type
Set port type ap on Set port type wired-auth on
Monitor port counters
WSS# clear port type
WSS# monitor port counters
Key Controls for Monitor Port Counters Display
Output for monitor port counters
Displayed for All Options
Octets
Number of packets received that were 64 bytes long
See Also show port counters on
Reset port
Syntax reset port port-list
WSS# reset port
See Also set port on
Set ap
2350-1 to
2382-1 to
2380-1 to
2360/61-1 to
See Also reset port on
Set port
Set port-group
Syntax set port-group name group-nameport-listmode on off
WSS# set port-group name server1 1-5 mode on
Mode on off
Set port media-type
Syntax set port mirror source-portobserver observer-port
Set port mirror
Syntax set port media-type port-listrj45
2380# set port media-type 2 rj45
Syntax set port port name name
WSS# set port 17 name adminpool
Set port name
WSS# set port 1 observer
Set port poe
Set port negotiation
Syntax set port speed port-list10 100 1000 auto
WSS# set port poe 7,9 disable
WSS# set port poe 7,9 enable
Set port speed
Set port type ap
Syntax set port trap port-listenable disable
WSS# set port trap 17-18 enable
Set port trap
Port-list
List of physical ports
Radiotype 11a 11b 11g Radio type
Version New values for model option added
AP Access Port Defaults
WSS# set ap 1 radio 1 antennatype
Set port type wired-auth
WSS# set port type ap 2 model 2330 poe enable
WSS# set port type ap 4-6 model 2330 poe enable
Web-portal
Wired Authentication Port Defaults
Last-resort
None
Port port-list
WSS# set port type wired-auth
Show port counters
Clear port type on Set port type ap on
Syntax show port-group name group-name
Show port-group
Output for show port-group
WSS show port counters octets port
Output for show port media-type
GBIC-The Gbic fiber interface is enabled
RJ45-The RJ-45 copper interface is enabled
Show port media-type
Show port poe
Show port mirror
See Also set port poe on
Output for show port poe
WSS# show port status
Show port status
Output for show port status
Syntax show port status port-list
No connector-GBIC slot is empty
Up-The port is enabled
Down-The port is disabled
Wa-Wired authentication port
System Services Commands
Clear banner motd
Clear history
See Also history on
Wildebeest# clear prompt success change accepted. WSS#
Clear prompt
Clear system
Syntax clear prompt
None
Help
WSS# clear system location
Help
See Also clear history on
Set auto-config
History
Quickstart
Syntax set auto-config enable disable
2360# set vlan 1 port 7 success change accepted
WSS# set auto-config enable success change accepted
WSS# save config
Set banner motd
Set length
Set confirm
Syntax set license activation-key
Set license
Syntax set length number-of-lines
WSS# set length
Syntax set prompt string
Set prompt
Set system contact
See Also show licenses on
23x0#set system country code CA
Set system countrycode
23x0#set system contact tamara@example.com
Syntax set system countrycode code
WSS# set system idle-timeout
Set system idle-timeout
See Also show config on
Syntax set system idle-timeout seconds
Set system location
Set system ip-address
Syntax set system name string
Set system name
See Also set license on
Show banner motd
Show licenses
Show load
Syntax show system
Show license command
Show system
See Also show system on
Show system output
Show tech-support
System Services Commands
System Services Commands NN47250-100 Version
Vlan Commands
WSS# clear fdb port 3,5
Clear fdb
WSS# clear fdb static vlan blue
WSS# clear fdb dynamic
All
Clear security l2-restrict
Clear security l2-restrict counters
Syntax clear security l2-restrict counters vlan vlan-idall
Vlan-id Port port-list
Clear vlan
WSS# clear security l2-restrict counters vlan abcair
Syntax clear vlan vlan-id port port-list tag tag-value
WSS# clear vlan red port 4 tag
Set vlan port on Show vlan config on
Set fdb
WSS# clear vlan green port
Set fdb agingtime
Set security l2-restrict
See Also show fdb agingtime on
Mode
Enable disable
Set vlan name
Syntax set vlan vlan-numname name
Syntax set vlan vlan-id port port-list tag tag-value
Set vlan port
See Also set vlan port on
WSS# set vlan 3 name marigold
Syntax set vlan vlan-idtunnel-affinity num
Set vlan tunnel-affinity
Show fdb
WSS# set vlan beige port 16 tag
WSS# show fdb
WSS# show fdb all
WSS# show fdb agingtime
Show fdb agingtime
Output for show fdb
Syntax show fdb agingtime vlan vlan-id
See Also show fdb on
Show fdb count
Show roaming station
See Also set fdb agingtime on
Show roaming vlan
Output for show roaming station
See Also show roaming vlan on
WSS# show roaming vlan
Syntax show roaming vlan
Syntax show security l2-restrict vlan vlan-idall
Show roaming station on Show vlan config on
Show security l2-restrict
Output for show roaming vlan
Output for show security l2-restrict
Enabled. Forwarding of Layer 2 traffic from clients is
Disabled. Layer 2 forwarding is not restricted
Show tunnel
Output for show tunnel
Show vlan config
See Also show vlan config on
Syntax show vlan config vlan-id
Output for show vlan config
See Also
Vlan Commands NN47250-100 Version
Clear qos
Quality of Service Commands
Syntax set qos cos-to-dscp-map level dscp dscp-value
Set qos cos-to-dscp-map
WSS# clear qos
WSS# clear qos dscp-to-qos-map
Show qos
Set qos dscp-to-cos-map
Show qos dscp-table
See Also show qos dscp-table on
See Also show qos on
IP Services Commands
Show ntp on
Set ntp update-interval on
Set ntp on
Set ntp server on
Clear interface
Syntax clear interface vlan-idip
WSS# clear interface mauve ip
Clear ip dns domain
Clear ip alias
WSS# clear ip dns server
Clear ip dns server
Clear ip route
Syntax clear ip dns server ip-addr
WSS# clear ip telnet success change accepted
Clear ip telnet
Clear ntp server
Syntax clear ip telnet
Clear snmp community
Clear ntp update-interval
Syntax clear ntp update-interval
WSS# clear ntp update-interval success change accepted
Syntax clear snmp notify target target-num
Clear snmp notify profile
Clear snmp notify target
Syntax clear snmp notify profile profile-name
Clear summertime
Clear snmp usm
Clear timezone
Clear system ip-address
Ping
Host Count num-packets
Count-5
Syntax set arp permanent static dynamic ip-addrmac-addr
Set arp
See Also traceroute on
WSS# ping
WSS# set arp agingtime
Set arp agingtime
Set interface
Syntax set arp agingtime seconds
Set interface dhcp-client
WSS# set interface default ip 10.10.10.10/24
Syntax set interface vlan-idip dhcp-client enable disable
Enables the Dhcp client on the Vlan
Clear interface on Show dhcp-client on Show interface on
WSS# set interface corpvlan ip dhcp-client enable
Default-router ip-addr
Set interface dhcp-server
Primary-dns and secondary-dns
Default-router
Set interface status
Dns-domain
Syntax set ip alias name ip-addr
Syntax set ip dns enable disable
Set ip alias
Set ip dns
WSS# set ip dns domain example.com
WSS# set ip dns enable
Set ip dns domain
Syntax set ip dns domain name
Secondary
Set ip dns server
Syntax set ip dns server ip-addrprimary secondary
Primary
Set ip https server
Syntax set ip https server enable disable
WSS# set ip https server enable
Enable Enables the Https server Disable
WSS# set ip route default 10.5.4.1
WSS# set ip route 192.168.4.0 255.255.255.0 10.5.4.2
WSS# set ip route 192.168.5.0/24 10.5.5.2
Set ip ssh
Syntax set ip snmp server enable disable
WSS# set ip snmp server enable
Set ip snmp server
Crypto generate key on Set ip ssh on Set ip ssh server on
Syntax set ip ssh server enable disable
Set ip ssh server
WSS# set ip ssh port
Syntax set ip telnet port-num
Syntax set ip telnet server enable disable
Set ip telnet
Set ip telnet server
Enable Enables the NTP client Disable
WSS# set ip telnet server enable
Syntax set ntp enable disable
WSS# set ntp enable
Set ntp server
Set ntp update-interval
Set snmp community
WSS# set snmp community name switchmgr1 notify-read-write
Read-notify Notify-only Notify-read-write
WSS# set snmp community read-write goodcommunity
Default profile-name
Set snmp notify profile
Drop send
ApOperRadioStatusTraps-Generated when
AutoTuneRadioPowerChangeTraps-Generated
ClientAuthorizationSuccessTraps-Generated
ClientAuthenticationFailureTraps-Generated
Cont
RFDetectUnAuthorizedSsidTraps-Generated
RFDetectSpoofedSsidAPTraps-Generated when
See Also
Show snmp notify profile on
Snmp-engine-id
Security unsecured authenticated encrypted
Set snmp notify target
SNMPv3 with Informs
SNMPv3 with Traps
Security unsecured authenticated encrypted
Timeout num
Retries num
SNMPv2c with Informs
Community-string Community string Profile profile-name
SNMPv2c with Traps
SNMPv1 with Traps
WSS# set snmp notify target 2 10.10.40.10 v1 trap
V2c
Syntax set snmp protocol v1 v2c usm all enable disable
WSS# set snmp protocol all enable
Set snmp protocol
Set snmp security
Set snmp usm
WSS# set snmp security encrypted
Allow get and set operations and so on
Snmp-engine-id ip ip-addr local hex hex
Specifies a unique identifier for the Snmp
String Engine
Specifies the access level of the user
Auth-pass-phrase string option
Second , third , fourth , or last
Set summertime
WSS# set snmp usm snmpmgr1 snmp-engine-id local
Start
23x0# set summertime PDT success change accepted
End
End of the time change period
Yyyy-year
Set timedate
Mmm-month
Dd-day
Set timezone
Syntax set timezone zone-name -hours minutes
23x0# set timezone PST
WSS# show arp
Show arp
Output for show arp
Syntax show arp ip-addr
Show dhcp-client
WSS# show dhcp-client
Output for show dhcp-client
WSS# show dhcp-server
Show dhcp-server
See Also set interface dhcp-client on
Syntax show dhcp-server interface vlan-id verbose
Output for show dhcp-server verbose
Output for show dhcp-server
WSS# show interface
Show interface
See Also set interface dhcp-server on
Syntax show interface vlan-id
Output for show interface
Show ip alias
Syntax show ip dns
Show ip dns
Output for show ip alias
Output for show ip dns
Show ip https
Show ip https
WSS show ip https
Destination
Show ip route
Output for show ip https
Syntax show ip route destination
Output for show ip route
Show ip telnet
Show ip telnet
WSS show ip telnet
WSS show ntp
Show ntp
Output for show ip telnet
Syntax show ntp
Synced
Output for show ntp
Show snmp community
Show snmp counters
Show snmp notify profile
Syntax show snmp status
Show snmp notify target
Show snmp status
Syntax show snmp notify target
23x0# show summertime
Show snmp usm
Show summertime
Syntax show summertime
Show timezone
Show timedate
WSS-remote show vlan
Telnet
Syntax telnet ip-addr hostname port port-num
WSS# telnet
WSS-remote Session 0 pty tty2.d terminated tt name tty2.d
Traceroute
Error Messages for traceroute
See Also ping on
WSS# traceroute server1
AAA Commands
Clear accounting
Syntax clear accounting admin dot1x system user-wildcard
System
Clear authentication admin
Syntax clear authentication admin user-wildcard
WSS# clear accounting dot1x Nin
WSS# clear authentication console Regina
Clear authentication console
WSS# clear authentication admin Jose
Syntax clear authentication console user-wildcard
Wired
Clear authentication dot1x
Clear authentication last-resort
WSS# clear authentication dot1x ssid finance *@thiscorp.com
WSS# clear authentication proxy ssid mycorp
Clear authentication mac
Clear authentication proxy
WSS# clear authentication mac ssid thatcorp aabbcc
Syntax clear location policy rule-number
Clear authentication web
Set authentication proxy on Show aaa on
Clear location policy
Syntax clear mac-user mac-addr
Clear mac-user
Clear mac-user attr
WSS# clear location policy
Syntax clear mac-user mac-addrgroup
Clear mac-user group
Syntax clear mac-usermac-addr attr attribute-name
WSS# clear mac-user 010203040506 attr filter-id
WSS# clear mac-usergroup eastcoasters
Clear mac-usergroup
Clear mac-usergroup attr
Syntax clear mac-usergroup group-name
Clear user
Clear mobility-profile
Syntax clear user username attr attribute-name
WSS# clear user Hosni attr session-timeout
Clear user attr
WSS# clear user Nin
Clear usergroup
Clear user group
WSS# clear usergroup cardiology attr time-of-day
Set accounting admin console
Clear usergroup attr
Syntax clear usergroup group-name attr attribute-name
Method1 Method2 Method3 Method4
WSS# set accounting admin Natasha start-stop local
Set accounting dot1x mac web last-resort
Start-stop Stop-only
Ssid ssid-name
Method1 method2 method3 method4
Mac
Web
Set accounting system
WSS# set accounting dot1x Nin stop-only sg2
WSS# set accounting system shorebirds
For more information, see Usage
Set authentication admin
WSS# set authentication admin Jose sg3
Set authentication console
User-wildcard Method1 Method2 Method3 Method4
WSS# set authentication console * none
Set authentication dot1x
Already been authenticated
Or a period .. For details, see User Wildcards on
Bonded
Protocol Method1 Method2 Method3 Method4
Sg1 sg2 sg3 success change accepted
Wired
Set authentication last-resort
Set authentication mac
Set service-profileauth-fallthru on Show aaa on
WSS# set authentication ssid mycorp2 mac ** local
Set authentication proxy
WSS# set authentication proxy ssid mycorp ** srvrgrp1
Set authentication web
WSS# set authentication web ssid ourcorp rnd* local
Optionally, you can add the suffix .out to the name
Set location policy
Deny
Permit
Neq-Applies the location policy rule to all usernames
Show location policy command
Clear location policy rule-numbercommand
Eq-Applies the location policy rule to all usernames
Clear location policy on Show location policy on
Set mac-user
WSS# set location policy deny if user eq *.theirfirm.com
WSS# set location policy permit vlan floor2 if port 3-7,12
Syntax set mac-user mac-addrgroup group-name
WSS# set mac-user 010203040506 group eastcoasters
Clear mac-user on Show aaa on
Syntax set mac-usermac-addr attr attribute-name value
Set mac-user attr
Authentication Attributes for Local Users
Encryption-type
End-date
Filter-id
Mobility-profile
Mobility-profile on
Ssid
Service-type
Session-timeout
By the set dot1x reauth-period command is
With start-date,end-date, or both
Time-of-day
1600,th1000-1600
Day wk0900-1700,sa2200-0200
Vlan-name
$u-Username $v-VLAN $s-SSID $p-Service profile name
WSS# set mac-user 010203040506 attr filter-id acl-03.in
Url
Clear mac-user attr on Show aaa on
For a list of authorization attributes, see on
Set mac-usergroup attr
WSS# set mac-usergroup eastcoasters attr vlan-name orange
Or wired authentication port on the WSS
Ports and wired authentication port on the WSS
Set mobility-profile
WSS# set mobility-profile name magnolia port
Set mobility-profile mode
Syntax set mobility-profile mode enable disable
WSS# set mobility-profile mode enable
Set user
Syntax set user username password encrypted string
WSS# set user Nin password goody
WSS# set user admin password chey3nne
WSS# set user Tamara attr mobility-profile tulip
WSS# set user Nin password 29Jan04
Set user attr
WSS# set user Tamara attr vlan-name orange
WSS# set user Hosni group cardiology
Set user group
Set usergroup
Syntax set user username group group-name
Clear usergroup on Clear usergroup attr on Show aaa on
Syntax set web-portal enable disable
Set web-portal
Syntax set usergroup group-name attr attribute-name value
Show aaa
User Nin
Show aaa Output
UP operating
Show accounting statistics
WSS# show accounting statistics
Syntax show accounting statistics
Show accounting statistics Output
Radius server
Local WSS database
Show mobility-profile
Show location policy
AAA Commands NN47250-100 Version
23x0# clear domain security
Mobility Domain Commands
Clear domain security
Syntax clear domain security
See Also set mobility-domain member on
Clear mobility-domain
Clear mobility-domain member
Set domain security
Syntax set mobility-domain member ip-addrkey hex-bytes
Set mobility-domain member
Syntax set domain security none required
WSS# set domain security required
WSS# set mobility-domain member
Set mobility-domain mode member seed-ip
Set mobility-domain mode member secondary-seed- ip
Clear mobility-domain on Show mobility-domain config on
Set mobility-domain mode seed domain-name
WSS# set mobility-domain mode member secondary-seed-ip
Clear mobility-domain member on Show mobility-domain on
Show mobility-domain
Show mobility-domain config
Syntax show mobility-domain config
WSS# show mobility-domain config
Show mobility-domain Output
Syntax show mobility-domain
WSS# show mobility-domain
Mobility Domain Commands NN47250-100 Version
23x0# clear network-domain
Network Domain Commands
Clear network-domain
Syntax clear network-domain
Syntax clear network-domain peer ip-addrall
Clear network-domain mode
Syntax clear network-domain mode seed member
Clear network-domain peer
See Also set network-domain peer on
Set network-domain mode member seed-ip
See Also set network-domain mode member seed-ip on
Clear network-domain seed-ip
Clear network-domain on Show network-domain on
WSS# set network-domain mode member seed-ip
Set network-domain peer
Syntax set network-domain peer ip-addr
Show network-domain
Set network-domain mode seed domain-name
WSS# set network-domain mode seed domain-name California
Set network domain peer command
Output if WSS is the Network Domain seed
Show network-domain Output
Syntax show network-domain
WSS# show network-domain
Output if WSS is a Network Domain member
Network Domain Commands NN47250-100 Version
Set ap radio radio-profile on
AP Commands
Set ap radio mode on
Set ap upgrade-firmware on
Set service-profilersn-ie on
Set service-profileweb-portal-acl on
Set service-profileauth-psk on
Set service-profilewpa-ie on
Set service-profile psk-raw on
Set service-profile cipher-wep104 on
Set service-profile cipher-wep40 on
Set service-profile psk-phrase on
Set ap radio auto-tunemax-power on
Set radio-profileauto-tunepower-config on
Set radio-profileauto-tunepower-interval on
Set radio-profileauto-tunepower-lockdown on
Syntax clear ap ap-numberimage
Clear ap image
See Also set ap image on
Clear ap local-switching vlan-profile
Syntax clear ap ap-numberlocal-switching vlan-profile
WSS# clear ap 7 local-switching vlan-profile
Radio
Clear ap radio
Radio-Specific Parameters
Syntax clear ap port-listap ap-numradio 1 2 all
Option dap removed for AP
802.11b/g-6
802.11a-Lowest valid
Channel number for Country of operation
Clear ap radio load-balancing group
Clear ap boot-configuration
Syntax clear ap boot-configuration ap-num
WSS# clear ap 1 boot-configuration
Clear radio-profile
Countermeasures parameter added
Clear service-profile
Long-retry
Short-retry
Soda logout-page
Soda failure-page
Soda remediation-acl
Soda success-page
Option radio num auto-tune min-client-rate
Reset ap
Set ap auto
Option force-image-download added
WSS# set ap auto
Configurable Profile Parameters for APs
Set ap auto persistent
Set ap auto mode
Syntax set ap auto mode enable disable
WSS# set ap auto mode enable
WSS# set ap auto persistent 10 success change accepted
Set ap auto radiotype
11a-802.11a
Syntax set ap auto persistent ap-numall
Set ap bias
WSS# set ap auto radiotype 11b
Syntax set ap port-listap ap-numauto bias high low
WSS# set ap 1 bias low
See Also show ap config on
Syntax set ap port-list ap ap-num auto blink enable disable
Set ap blink
Enables or disables the static IP address for the AP
Set ap boot-configuration ip
WSS# set ap 3-4 blink enable
Mode enable disable
Set ap boot-configuration mesh mode
Set ap boot-configuration mesh psk-phrase
WSS# set ap 7 boot-configuration mesh mode enable
Syntax set ap ap-numberboot-configuration mesh psk-raw hex
Set ap boot-configuration mesh psk-raw
WSS# set ap 7 boot-configuration mesh ssid wlan-mesh
Set ap boot-configuration mesh ssid
Switch-ip ip-addr
Set ap boot-configuration switch
Vlan tag value. You can specify a number from
Set ap boot-configuration vlan
Enables or disables use of the specified Vlan tag on the AP
Vlan-tag tag-value
Syntax set ap num fingerprint hex
Set ap security on Show ap config on Show ap status on
Set ap fingerprint
Set ap force-image-download
Auto on
WSS# set ap 69 force-image-download enable
Set ap group
Syntax set ap port-list ap ap-num auto group name
WSS# set ap 4 group none
Show ap config on Show ap group on
Set ap image
WSS# set ap 1,4,7 group loadbalance1
WSS# set ap 7 local-switching mode enable
Set ap local-switching mode
Set ap local-switching vlan-profile
Syntax set ap ap-numberlocal-switching mode enable disable
WSS# set ap 7 local-switching vlan-profile locals
Set ap name
Syntax set ap port-list ap ap-numname name
Indoors
Set ap radio antenna-location
WSS# set ap 1 name techpubs
WSS# set ap 22 radio 1 antenna-location outdoor
See Also set ap radio antennatype on
Set ap radio antennatype
Ap port-list Ap ap-num radio 1 radio
Set ap radio auto-tune max-power
Deprecated in WSS Software Version
WSS# set ap 7 radio 1 auto-tune max-power
Set ap radio auto-tune max-retransmissions
Set ap radio auto-tune min-client-rate
WSS# set ap 5 radio 1 channel
WSS# set ap 11 radio 1 channel 1 tx-power
Set ap radio tx-power on Show ap config on
Set ap radio channel
Ap ap-number
Set ap radio min-tx-datarate
Set ap radio link-calibration
Set ap radio load-balancing
Syntax set ap ap-numradio 1 2 load-balancing enable disable
WSS# set ap 7 radio 1 load-balancing disable
Set ap radio load-balancing group
Set ap radio mode
Syntax set ap port-listauto radio 1 2 mode enable disable
WSS# set ap 7 radio 1 load-balancing group room1
Radio-profile name
WSS# set ap 1-5 radio 1 mode enable
WSS# set ap 1-3 radio 2 mode enable
Set ap radio radio-profile
Set ap radio tx-power
Set ap radio channel on Show ap config on
WSS# set ap 5 radio 1 tx-power
Set ap security
Syntax set ap security require optional none
WSS# set ap security none
Set ap sticky-bit
Set ap upgrade-firmware
Syntax set ap port-listauto upgrade-firmware enable disable
WSS# set ap 9 upgrade-firmware disable
WSS# set band-preference 11a
Set load-balancing mode
Syntax set load-balancing mode enable disable
Syntax set band-preference none 11bg 11a
Max
WSS# set load-balancing mode disable
Set load-balancing strictness
Syntax set load-balancing strictness low med high max
WSS# set load-balancing strictness max
Syntax set radio-profile name active-scan enable disable
Set radio-profile 11g-only
Set radio-profile active-scan
Set radio-profile auth-psk
Set radio-profile auto-tune channel-config
WSS# set radio-profile radprof3 active-scan disable
Set radio-profile auth-dot1x
WSS# set radio-profile rp2 auto-tune channel-config disable
Set radio-profile auto-tune channel-holddown
WSS# set radio-profile rp2 auto-tune channel-holddown
WSS# set radio-profile rp2 auto-tune channel-interval
Set radio-profile auto-tune channel-interval
Syntax set radio-profile name auto-tune channel-lockdown
Set radio-profile auto-tune power-backoff-timer
Set radio-profile auto-tune power-config
Set radio-profile auto-tune channel-lockdown
Started
Set radio-profile auto-tune power-interval
WSS# set radio-profile rp2 auto-tune power-config enable
Defaults The default power tuning interval is 300 seconds
WSS# set radio-profile rp2 auto-tune power-lockdown
Set radio-profile auto-tune power-lockdown
WSS# set radio-profile rp2 auto-tune power-interval
Syntax set radio-profile name auto-tune power-lockdown
Syntax set radio-profile name beacon-interval interval
Set radio-profile auto-tune power-ramp-interval
WSS# set radio-profile rp2 auto-tune power-ramp-interval
Set radio-profile beacon-interval
Set radio-profile cipher-wep104
Set radio-profile beaconed-ssid
Set radio-profile cipher-ccmp
Set radio-profile cipher-tkip
Rogue
Configured
Set radio-profile countermeasures
WSS# set radio-profile radprof3 countermeasures rogue
Set radio-profile dtim-interval
Set radio-profile crypto-ssid
Set radio-profile frag-threshold
Syntax set radio-profile name frag-threshold threshold
WSS# set radio-profile rp1 frag-threshold
Set radio-profile long-retry
Set radio-profile max-rx-lifetime
Set radio-profile max-tx-lifetime
WSS# set radio-profile rp1 max-tx-lifetime
Set radio-profile mode
Defaults for Radio Profile Parameters
Syntax set radio-profile name mode enable disable
Countermeasures
Rfid-mode Disable
Service-profile
Wmm-powersave Disable
Wmm-powersave
11g-only
Rfid-mode
Syntax set radio-profile name preamble-length long short
Set radio-profile preamble-length
Set radio-profile psk-phrase
Set radio-profile psk-raw
WSS# set radio-profile rp1 qos-mode svp
Set radio-profile qos-mode
Set radio-profile rate-enforcement
Syntax set radio-profile name qos-mode svp wmm
Enables data rate enforcement for the radios in the radio
Disables data rate enforcement for the radios in the radio
Set radio-profile rfid-mode
Syntax set radio-profile name rts-threshold threshold
Syntax set radio-profile name rfid-mode enable disable
WSS# set radio-profile rfid-mode enable
Set radio-profile rts-threshold
Set radio-profile service-profile
Defaults for Service Profile Parameters
Syntax set radio-profile name service-profile name
Cipher-wep40 Disable
Cipher-ccmp Disable
Cipher-tkip Enable
Cipher-wep104 Disable
Shared-key-auth Disable
No-broadcast Disable
Proxy-arp Disable
Rsn-ie Disable
2.0,5.5,11.0
12.0,24.0
Auto
2.0
Web-portal-acl Portalacl
Portal-acl setting
Timeout
Wpa-ie Disable
WSS# set radio-profile rp2 service-profile wpaclients
Set radio-profile wep active-multicast-index
Set radio-profile shared-key-auth
Set radio-profile short-retry
Set radio-profile tkip-mc-time
See set service-profilewpa-ie on
Set radio-profile wmm-powersave
Syntax set radio-profile name wmm-powersave enable disable
WSS# set radio-profile rp1 wmm-powersave enable
Set service-profile attr
Syntax set service-profile name attr attribute-name value
WSS# set service-prof sp2 attr vlan-name blue
WSS# set service-profile wpaclients auth-dot1x disable
Set service-profile auth-dot1x
WSS# set service-prof sp2 attr mobility-profile tulip
Syntax set service-profile name auth-dot1x enable disable
Set service-profile auth-fallthru
Last-resort
Web-portal
WSS# set service-profile wpaclients auth-psk enable
Set service-profile auth-psk
WSS# set service-profile rndlab auth-fallthru web-portal
Syntax set service-profile name auth-psk enable disable
Mesh-service-profile Mesh service profile
Set service-profile beacon
Set service-profile bridging
Syntax set service-profile name beacon enable disable
Set service-profilecac-session on Show service-profile on
Set service-profile cac-mode
Syntax set service-profile name cac-mode none session
WSS# set service-profile sp1 cac-mode session
WSS# set service-profile sp1 cac-session
Set service-profile cac-session
Set service-profile cipher-ccmp
Syntax set service-profile name cac-session max-sessions
WSS# set service-profile sp2 cipher-tkip disable
Set service-profile cipher-tkip
WSS# set service-profile sp2 cipher-ccmp enable
Syntax set service-profile name cipher-tkip enable disable
Set service-profile cipher-wep104
WSS# set service-profile sp2 cipher-wep104 enable
Enables 104-bit WEP encryption for WPA clients
WSS# set service-profile sp2 cipher-wep40 enable
Set service-profile cipher-wep40
Set service-profile cos
Syntax set service-profile name cipher-wep40 enable disable
WSS# set service-profile sp1 dhcp-restrict enable
Set service-profile dhcp-restrict
Syntax set service-profile name cos level
WSS# set service-profile sp1 cos
Enables keepalives
Set service-profile idle-client-probing
Set service-profile keep-initial-vlan
WSS# set service-profile sp1 idle-client-probing disable
Set service-profile load-balancing-exempt
See Also show service-profile on
WSS# set service-profile sp3 keep-initial-vlan enable
WSS# set service-profile sp1 long-retry-count
Set service-profile long-retry-count
WSS# set service-profile sp3 load-balancing-exempt enable
Syntax set service-profile name long-retry-count threshold
Enables mesh services for the service profile
Set service-profile mesh
Set service-profile no-broadcast
Syntax set service-profile name mesh mode enable disable
Syntax set service-profile name proxy-arp enable disable
Set service-profile proxy-arp
Syntax set service-profile name no-broadcast enable disable
WSS# set service-profile sp1 no-broadcast enable
Set service-profile psk-phrase
WSS# set service-profile sp1 proxy-arp enable
Syntax set service-profile name psk-phrase passphrase
Set service-profile psk-raw
Set service-profile rsn-ie
Syntax set service-profile name psk-raw hex
Set service-profile shared-key-auth
Syntax set service-profile name rsn-ie enable disable
WSS# set service-profile sprsn rsn-ie enable
WSS# set service-profile sp1 short-retry-count
Set service-profile short-retry-count
WSS# set service-profile sp4 shared-key-auth enable
Syntax set service-profile name short-retry-count threshold
Set service-profile soda agent-directory
Set service-profile soda enforce-checks
Network
Set service-profile soda mode on Show service-profile on
Set service-profile soda failure-page
WSS# set service-profile sp1 enforce-checks disable
Syntax set service-profile name soda failure-page
Syntax set service-profile name soda logout-page
Set service-profile soda logout-page
WSS# set service-profile sp1 soda mode enable
Set service-profile soda mode
WSS# set service-profile sp1 soda logout-page logout.html
Syntax set service-profile name soda mode enable disable
Set service-profile soda remediation-acl
Set service-profile soda success-page
Syntax set service-profile name soda success-page
Set service-profile ssid-name
WSS# set service-profile sp1 soda success-page success.html
Syntax set service-profile name ssid-name ssid-name
Syntax set service-profile name ssid-type clear crypto
Set service-profile ssid-type
Set service-profile static-cos
WSS# set service-profile clearwlan ssid-name guest
Syntax set service-profile name tkip-mc-time wait-time
Set service-profile tkip-mc-time
Syntax set service-profile name static-cos enable disable
WSS# set service-profile sp1 static-cos enable
Set service-profile transmit-rates
WSS# set service-profile sp3 tkip-mc-time
11g-1.0, 2.0, 5.5, 6.0, 9.0, 11.0, 12.0, 18.0
Beacon-rate rate
Multicast-rate
Beacon-rate
WSS# set service-profile sp1 user-idle-timeout
Set service-profile user-idle-timeout
Set service-profile web-portal-acl
Syntax set service-profile name user-idle-timeout seconds
Syntax set service-profile name web-portal-form url
Set service-profile web-portal-form
Syntax set service-profile name web-portal-acl aclname
WSS# set service-profile sp3 web-portal-acl creditsrvr
WSS# dir corpa
WSS# mkdir corpa
WSS# set service-profile sp1 web-portal-logout mode enable
Set service-profile web-portal-logout
Set service-profile web-portal-logout logout-url
Set service-profile web-portal-session-timeout
WSS# set service-profile sp1 web-portal-session-timeout
Set service-profile wep active-multicast-index
Set service-profile wep active-unicast-index
WSS# set service-profile sp2 wep active-multicast-index
WSS# set service-profile sp2 wep active-unicast-index
WSS# set service-profile sp2 wep key-index 1 key aabbccddee
Set service-profile wep key-index
Set service-profile wpa-ie
Syntax set service-profile name wep key-index num key value
WSS# show ap arp
WSS# set service-profile sp2 wpa-ie enable
Show ap arp
Syntax show ap arp ap-number
Output for show ap arp
Show ap config
Syntax show ap config port-listradio 1
Set ap local-switching mode on Set vlan-profile
WSS# show ap config
Output for show ap config
802.11a
802.11b
802.11g
WSS# show ap counters
Show ap unconfigured on Show radio-profile on
Show ap counters
Syntax show ap counters port-listradio 1
Output for show ap counters
Use the show sessions network session-id session-idcommand
Output for show ap counters
See Also show sessions network on
Show ap dual-home
WSS# show ap fdb
Show ap fdb
Output for show ap fdb
Syntax show ap fdb ap-number
Show ap qos-stats
WSS# show ap qos-stats
Clears the counters after displaying their current values
WSS# show ap etherstats
Show ap etherstats
Output for show ap qos-stats
Syntax show ap etherstats port-listap-num
Output for show ap etherstats
WSS# show ap mesh-links
Show ap group
Show ap mesh-links
Syntax show ap mesh-links ap-number
Terse
Show ap status
Output for show ap mesh-links
Syntax show ap status terse port-listall radio 1
Tuning
Radio state information, to indicate when an
Configured antenna model number
Power settings that are configured by RF Auto
WSS# show ap status terse
Output for show ap status
Image downloaded-The AP has received a boot
But has not yet begun booting
Booting-The AP has asked the WSS for a boot
Image downloading-The AP is receiving a boot
Sweep Mode indicates that a disabled radio is
Configure succeed state indicates that the AP
Has received configuration parameters for
Protection mode remains in effect until
Radio
But no external antenna is configured on
Antenna is configured on the radio but no
Indicates that an external antenna was detected
Output for show ap status terse and show ap status terse
Show ap vlan
WSS# show ap vlan
Set vlan-profile Set ap local-switching mode on
Output for show ap vlan
Syntax show ap vlan ap-number
WSS# show auto-tune attributes ap 2 radio
Show auto-tune attributes
Output for show auto-tune attributes
Syntax show auto-tune attributes ap ap-numradio 1 2all
Set radio-profileauto-tunepower-backoff-timer on
Show auto-tune neighbors
Syntax show auto-tune neighbors ap ap-numradio 1 2all
Rssi
Output for show auto-tune neighbors
WSS# show ap boot-configuration
Show ap boot-configuration
Output for show ap boot-configuration
Syntax show ap boot-configuration ap-num
Serial-id serial-ID
Show ap connection
Syntax show ap connection ap-numserial-id serial-ID
Connection
WSS# show ap connection serial-id
Show ap config on Show ap global on Show ap unconfigured on
Output for show ap connection
WSS# show ap connection Total number of entries
WSS# show ap global
Show ap global
Output for show ap global
Syntax show ap global ap-numserial-id serial-ID
Show ap unconfigured
Syntax show ap unconfigured
WSS# show ap unconfigured
Show ap connection on Show ap global on
Output for show ap unconfigured
This WSS switch as a member
Show load-balancing group
Syntax show radio-profile name ?
Show radio-profile
Output for show load-balancing group
WSS# show load-balancing group blue
WSS# show radio-profile default
Output for show radio-profile
SpectraLink Voice Priority SVP
Wmm-AP forwarding queues provide standard
Priority handling for WMM devices
Svp-AP forwarding queues are optimized for
Syntax show service-profile name ?
Show service-profile
Profile output
Unencrypted
Output for show service-profile
Crypto-Wireless traffic for the Ssid is
Clear-Wireless traffic for the Ssid is
None-Denies authentication and prohibits
Last-resort-Automatically authenticates the user
Allows access to the Ssid requested by
User, without requiring a username and password
Session-CAC is based on the number of active
None-CAC is disabled
None-The key is not configured
Preset-The key is configured
PSK-preshared key authentication
Radios in the radio profile mapped to this service
Authentication-Lists the authentication methods
802.1X-dynamic authentication
FieldDescription
AP Commands
AP Commands NN47250-100 Version
STP Commands
Set spantree uplinkfast on
Show spantree uplinkfast on
Clear spantree portpri
Clear spantree portcost
Resets the cost for all VLANs
Clear spantree portvlancost
Clear spantree portvlanpri
WSS# clear spantree statistics 5,11,19-22
Clear spantree statistics
Syntax clear spantree portvlanpri port-listall vlan vlan-id
Syntax clear spantree statistics port-listvlan vlan-id
See Also show spantree on
Set spantree
Set spantree backbonefast
See Also show spantree statistics on
Set spantree fwddelay
Set spantree hello
See Also show spantree backbonefast on
Set spantree portcost
Set spantree maxage
WSS# set spantree portcost 3,4 cost
Snmp Port Path Cost Defaults
Syntax set spantree portfast port port-listenable disable
Set spantree portfast
Set spantree portpri
Set spantree portvlancost
See Also show spantree portfast on
Priority value All
Set spantree portvlanpri
WSS# set spantree portvlancost 3,4 cost 20 vlan mauve
Cost cost All
Set spantree uplinkfast
Set spantree priority
See Also show spantree uplinkfast on
WSS# set spantree uplinkfast enable
WSS# show spantree vlan default
Show spantree
Bridge Max Age 20 sec Hello Time 2 sec Forward Delay 15 sec
Output for show spantree
Show spantree backbonefast
See Also show spantree blockedports on
Syntax show spantree backbonefast
WSS# show spantree backbonefast
WSS# show spantree blockedports vlan default
Show spantree blockedports
See Also set spantree backbonefast on
Uplink fast convergence information for all ports
Show spantree portfast
Syntax show spantree portfast port-list
WSS# show spantree portfast
Syntax show spantree portvlancost port-list
Show spantree portvlancost
Output for show spantree portfast
See Also set spantree portfast on
Statistics for all ports
Show spantree statistics
Syntax show spantree statistics port-listvlan vlan-id
WSS# show spantree statistics
Inactive
Output for show spantree statistics
Output for show spantree statistics
Output for show spantree statistics
Syntax show spantree uplinkfast vlan vlan-id
Show spantree uplinkfast
Output for show spantree uplinkfast
See Also clear spantree statistics on
See Also set spantree uplinkfast on
STP Commands NN47250-100 Version
Statistics Show igmp statistics on Clear igmp statistics on
Igmp Snooping Commands
Clear igmp statistics
Syntax clear igmp statistics vlan vlan-id
See Also show igmp on
Set igmp
Set igmp lmqi
See Also show igmp statistics on
Set igmp mrouter
Set igmp mrsol
See Also show igmp mrouter on
See Also set igmp mrsol on
Set igmp mrsol mrsi
Set igmp oqi
See Also set igmp mrsol mrsi on
Vlan vlan-id
Syntax set igmp proxy-report enable disable vlan vlan-id
Set igmp proxy-report
WSS# set igmp oqi 200 vlan orange
Syntax set igmp qi seconds vlan vlan-id
WSS# set igmp proxy-report disable vlan orange
Set igmp qi
Set igmp qri
WSS# set igmp qri 50 vlan orange
Syntax set igmp querier enable disable vlan vlan-id
Set igmp querier
Syntax set igmp qri tenth-seconds vlan vlan-id
See Also show igmp receiver-table on
Set igmp receiver
Set igmp rv
See Also show igmp querier on
WSS# show igmp vlan orange
Show igmp
WSS# set igmp rv 4 vlan orange
Syntax show igmp vlan vlan-id
Dvmrp PIM
Output for show igmp
Quer-IGMP query
Conf Static multicast port configured by an
Administrator
Madv-Multicast advertisement
Show igmp mrouter
Syntax show igmp mrouter vlan vlan-id
WSS# show igmp mrouter vlan orange
Set igmp mrouter on Show igmp mrouter on
Show igmp querier
Output for show igmp mrouter
Syntax show igmp querier vlan vlan-id
WSS# show igmp querier vlan orange
See Also set igmp querier on
WSS# show igmp querier vlan default
Show igmp receiver-table
Output for show igmp querier
VLANs
WSS# show igmp receiver-table vlan orange
WSS# show igmp receiver-table group 237.255.255.0/24
WSS Software displays the multicast receivers on all
Syntax show igmp statistics vlan vlan-id
Show igmp statistics
Output for show igmp receiver-table
See Also set igmp receiver on
Output for show igmp statistics
See Also clear igmp statistics on
Igmp Snooping Commands NN47250-100 Version
WSS# clear sessions console
Session Management Commands
WSS# clear sessions admin
Clear sessions
WSS# clear sessions network mac-addr
Clear sessions network
See Also show sessions on
WSS# clear sessions telnet client
Show sessions
Telnet
Console
Mac-addr mac-addr
Show sessions network
Show sessions telnet client Output
See Also clear sessions on
Session-id output
Verbose output
WSS show sessions network verbose
WSS show sessions network
WSS show sessions network mac-addr 00055d7e981a
WSS show sessions network user E
WSS# show sessions network session-id
Show sessions network summary Output
Description
Additional show sessions network verbose
AAA-VLAN is from Radius or the local database
IP address and port number of the WSS managing the AP
Serial number and radio number of the AP
Amount of time the session has been on this AP
Show sessions network session-id Output
DOT1X
See Also clear sessions network on
Session Management Commands NN47250-100 Version
Clears all security ACLs
Security ACL Commands
Clear security acl
Syntax clear security acl acl-name all editbuffer-index
Set security acl ip acl135 hits #2
WSS# show security acl info all
Set security acl ip acl133 hits #1
Set security acl ip acl134 hits #3
Clear security acl map
WSS# clear security acl map acljoe port 4
Out
Type Class Mapping
Commit security acl
WSS# clear security acl map all
Syntax commit security acl acl-nameall
Syntax rollback security acl acl-nameall
Hit-sample-rate
Rollback security acl
See Also show security acl on
Set security acl
By UDP packets
Any
Immediate precedence
Minimum delay
Routine precedence
Priority precedence
WSS# commit security acl all
WSS# set security acl ip acl123 deny 192.168.2.11
Tag tag-list
Set security acl map
WSS set security acl map acl133 port 4
WSS port or ports
Set security acl ip acl153 hits #3
Configuration file
Set security acl hit-sample-rate
Syntax set security acl hit-sample-rate seconds
Index Counter ACL-name
Show security acl
Show security acl dscp
WSS# show security acl hits
WSS# show security acl editbuffer
Show security acl editbuffer
Show security acl hits
Syntax show security acl info all editbuffer
WSS# show security acl info
Show security acl info
Syntax show security acl hits
Syntax show security acl info acl-nameall editbuffer
Show security acl map
Show security acl resource-usage
Show security acl resource-usage Output
False-No security ACLs are mapped
True-A default action types is defined
False-No default action type is defined
True-Security ACLs are mapped
False-No security ACLs are mapped to incoming
True-Security ACLs are mapped to incoming traffic
Cryptography Commands
Certificate
Crypto ca-certificate
Eap
PEM-formatted
WSS# crypto certificate admin
Crypto certificate
See Also show crypto ca-certificate on
Ssh
Crypto generate key
Crypto generate request on Crypto generate self-signed on
Domain
See Also show crypto key ssh on
WSS# crypto generate key admin
Syntax crypto generate request admin eap web
Crypto generate request
Maximum string length for State Name increased
WSS# crypto generate request admin
Email Address admin@example.com
Webaaa option renamed to web
Syntax crypto generate self-signed admin eap web
Crypto generate self-signed
Crypto certificate on Crypto generate key on
WSS# crypto generate self-signed admin
Syntax crypto otp admin eap web one-time-password
Crypto otp
WSS# crypto generate otp eap hap9iN#ss
Syntax crypto pkcs12 admin eap web file-location-url
Crypto pkcs12
See Also crypto pkcs12 on
WSS# crypto pkcs12 eap 2048full.p12
See Also crypto otp on
WSS# copy tftp//192.168.253.1/2048full.p12 2048full.p12
WSS# crypto otp eap hap9iN#ss
WSS# show crypto ca-certificate
Syntax show crypto ca-certificate admin eap web
Show crypto ca-certificate
Show crypto ca-certificate Output
WSS# show crypto certificate eap
Syntax show crypto certificate admin eap web
Show crypto certificate
Crypto certificate Output
Show crypto key domain
Show crypto key ssh
See Also crypto generate key on
Cryptography Commands NN47250-100 Version
Clear server group on
Radius and Server Groups Commands
Syntax clear radius deadtime key retransmit timeout
Clear radius
Clear radius client system-ip
See Also set radius proxy port on
Clear radius proxy client
Clear radius proxy port
See Also set radius proxy client on
Clear server group
Clear radius server
See Also set server group on
Set radius
Set radius client system-ip
WSS# set radius proxy client address 10.20.20.9 key radkey1
Set radius proxy client
Set radius proxy port
Syntax set radius proxy client address ip-address
Set radius server
WSS# set radius proxy port 3-4 tag 104 ssid mycorp
Ssid ssid-name Ssid supported by the third-party AP
Encrypted-key-No key Author-password-nortel
Members server
Set server group
Group-name Server group name of up to 32 characters
23x0# set server group shorebirds load-balance enable
23x0# set server group shorebirds load-balance disable
Set server group load-balance
Radius and Server Groups Commands NN47250-100 Version
802.1X Management Commands
WSS# clear dot1x bonded-period
Clear dot1x bonded-period
Clear dot1x max-req
Syntax clear dot1x max-req
Clear dot1x port-control
Clear dot1x quiet-period
Clear dot1x reauth-max
Clear dot1x reauth-period
Clear dot1x timeout auth-server
Clear dot1x tx-period
Clear dot1x timeout supplicant
Set dot1x bonded-period
Syntax set dot1x authcontrol enable disable
WSS# set dot1x authcontrol enable
Set dot1x authcontrol
Set dot1x key-tx
Set dot1x max-req
See Also show dot1x on
Set dot1x port-control
WSS# set dot1x max-req
WSS# set dot1x port-control forceauth
Set dot1x reauth
Set dot1x quiet-period
Set dot1x reauth-period
Set dot1x reauth-max
Set dot1x timeout supplicant
Set dot1x timeout auth-server
Syntax set dot1x tx-period seconds
Syntax set dot1X wep-rekey enable disable
Set dot1x tx-period
Set dot1x wep-rekey
Show dot1x
Set dot1x wep-rekey-period
WSS# show dot1x clients
WSS# show dot1x config
WSS # show dot1x stats
Show dot1x stats Output
520 802.1X Management Commands
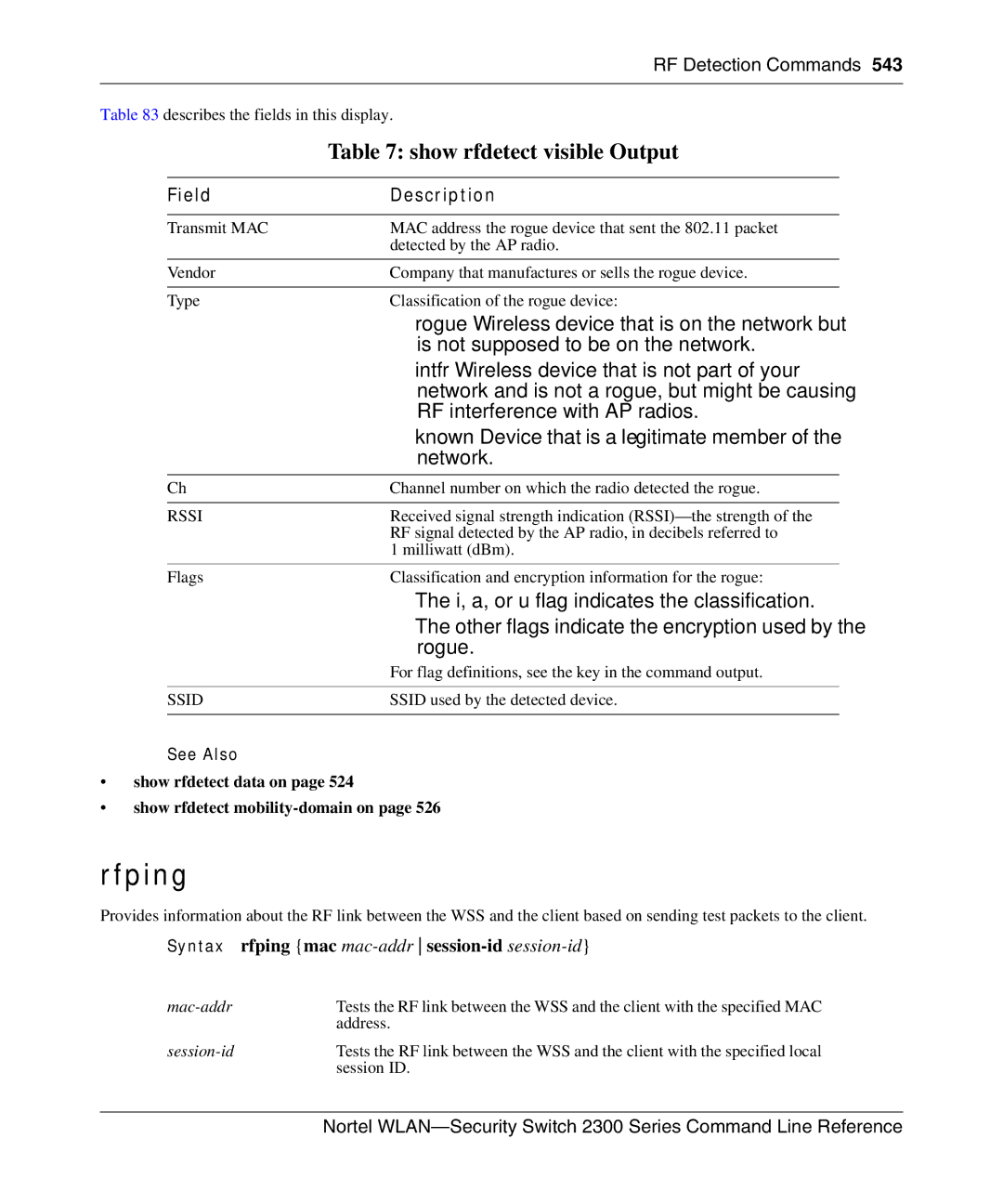
Show rfdetect visible on
RF Detection Commands
Rogue Information Show rfdetect clients on
Show rfdetect data on
Syntax clear rfdetect black-list mac-addr
Clear rfdetect attack-list
Clear rfdetect black-list
Syntax clear rfdetect attack-list mac-addr
Clear rfdetect ssid-list
Clear rfdetect ignore
WSS# clear rfdetect vendor-list client aabbcc000000
Clear rfdetect vendor-list
Set rfdetect attack-list
Syntax clear rfdetect vendor-list client ap mac-addrall
Set rfdetect ignore
Set rfdetect black-list
23x0# set rfdetect ignore aabbcc112233
Syntax set rfdetect log enable disable
23x0# set rfdetect log enable
Set rfdetect log
Set rfdetect signature
Set rfdetect ssid-list
See Also show log buffer on
WSS# set rfdetect vendor-list client aabbcc000000
Set rfdetect vendor-list
WSS# set rfdetect ssid-list mycorp
Syntax set rfdetect vendor-list client ap mac-addr
Show rfdetect black-list
Show rfdetect attack-list
WSS# show rfdetect clients mac 000c4163fd6d
Show rfdetect clients
Show rfdetect clients Output
Syntax show rfdetect clients mac mac-addr
Show rfdetect clients mac Output
Show rfdetect countermeasures
Syntax show rfdetect countermeasures
WSS# show rfdetect countermeasures
Syntax show rfdetect counters
Show rfdetect counters
Show rfdetect countermeasures Output
See Also set radio-profile countermeasures on
Syntax show rfdetect data
Show rfdetect data
Show rfdetect data Output
WSS# show rfdetect ignore Total number of entries
Show rfdetect ignore
Show rfdetect mobility-domain
Syntax show rfdetect ignore
WSS# show rfdetect mobility-domain ssid nrtl-webaaa
Bssid and ssid options added
Vendor, Type, and Flags fields added
WSS# show rfdetect mobility-domain
Show rfdetect mobility-domain Output
Show rfdetect mobility-domain ssid or bssid Output
Show rfdetect ssid-list
WSS# show rfdetect vendor-list
Show rfdetect vendor-list
Show rfdetect visible
Syntax show rfdetect vendor-list
Version Vendor, Type, and Flags fields added
Show ap status command
Mac-addr Base MAC address of the Nortel radio
Shows neighbor information for radio
Show rfdetect data on Show rfdetect mobility-domain on
Rfping
Show rfdetect visible Output
Syntax rfping mac mac-addrsession-id session-id
WSS# rfping mac 000e9bbfad13
Rfping Output
Backup
File Management Commands
Tftp/ip-addr / filename
Syntax backup system tftp/ip-addr/filenameall critical
WSS# backup system tftp/10.10.20.9/sysabak critical
Dir on Restore on
Clear boot backup-configuration
Clear boot config
Copy
Be one of the following
Syntax copy source-url destination-url
Source-url
Destination-url
WSS# copy tftp//10.1.1.1/closetwss closetwss
WSS# copy tftp//10.1.1.107/WSS020101.020 boot1WSS020101.020
Delete
WSS# copy floorwss tftp//10.1.1.1/floorwss
Dir
WSS# copy testconfig tftp//10.1.1.1/testconfig
WSS# delete testconfig
Syntax dir subdirname file core boot0 boot1
WSS# dir
WSS# dir old
WSS# dir file
WSS# dir core
Install soda agent
WSS# dir boot0
Output for dir
Uninstall soda agent on Set service-profile soda mode on
Load config
WSS# install soda agent soda.ZIP agent-directory sp1
Syntax load config url
Save config on Show boot on Show config on
WSS# load config
WSS# load config testconfig1
Syntax md5 boot0 boot1filename
WSS# mkdir corp2
Pubs# md5 boot0WSS040003.020
Mkdir
Syntax mkdir subdirname
Reset system
Syntax reset system force
WSS# reset system
Restore
Save config
See Also backup on
Rmdir
Syntax set boot backup-configuration filename
Set boot backup-configuration
Syntax save config filename
WSS# save config testconfig1
Set boot partition
Set boot configuration-file
Show boot
New fields, Configured boot version and Backup
Boot configuration, added
Output for show boot
Area area
Show config
Syntax show config area area all
Configuration area. You can specify one of the following
Show version
New options added for remote traffic monitoring snoop
Rfdevice changed to rfdetect
WSS# show version details
WSS# uninstall soda agent agent-directory sp1
Uninstall soda agent
See Also show boot on
Syntax uninstall soda agent agent-directory directory
Install soda agent on Set service-profile soda mode on
File Management Commands NN47250-100 Version
WSS# clear log trace
Trace Commands
Clear log trace
Syntax clear log trace
Save trace
Clear trace
WSS# save trace traces/trace1
Set trace authentication
Set trace authorization
WSS# set trace authentication user jose
Level 5 is the default
Set trace dot1x
User-readable information. If you do not specify a level
WSS# set trace sm mac-addr
Set trace sm
Show trace
Syntax show trace all
WSS# show trace
WSS# clear snoop snoop1
Snoop Commands
Clear snoop
Syntax clear snoop filter-name
Examples clear snoop map filter-nameap ap-numradio 1
Clear snoop map
WSS# clear snoop map snoop2 ap 3 radio
WSS# clear snoop map all
Set snoop
Set snoop map
WSS# set snoop snoop1 observer 10.10.30.2 snap-length
Examples set snoop map filter-nameap ap-numradio 1
Filter. See show snoop stats on
Set snoop mode
Enable Stop-after num-pkts
WSS# set snoop map snoop1 ap 3 radio
WSS# show snoop
WSS# set snoop snoop1 mode enable stop-after
Show snoop
Syntax show snoop
Show snoop map
Show snoop info
Show snoop stats
Clear snoop map on Set snoop map on Show snoop on
Examples show snoop stats filter-nameap-numradio 1
Show snoop stats Output
Snoop Commands NN47250-100 Version
WSS# clear log server
System Log Commands
Clear log
Syntax clear log buffer server ip-addr
Logging state enabled or disabled
Set log
Severity
Defaults
Set log mark
See Also show log config on
Set log trace mbytes
Show log buffer
Diagnostic purposes. No action is required
Reboot or shut down
Error-The WSS is missing data or is unable to
Problems have occurred. These are logged for
Show log trace
Show log config
Syntax show log config
WSS# show log config
Number of log entries starting from the oldest
Conditions are not resolved, the WSS can reboot
Error-The WSS is missing data or is unable to form
Positive number for example, +100, displays that
WSS# show log trace +5 facility Rogue
WSS# show log trace facility ?
System Log Commands NN47250-100 Version
Boot Prompt Commands
Boot autoboot
Autoboot
See Also boot on
Syntax autoboot on on OFF off
Boot
Boot boot FN=WSS010101.020 DEV=boot1
Change
Change on Show on
Boot on Create on Delete on Dhcp on Next on Show on
Boot change
Boot create
Create
Change on Delete on Next on Show on
Syntax dhcp on on OFF off
Boot delete
Boot dhcp
Dhcp
Fver on Version on
Syntax dir c d e f boot0 boot1
Boot dir
Diag
Fver
Syntax fver c d e f boot0 boot1 filename
Boot fver boot1
Syntax help command-name
See Also ls on
Boot help fver
See Also help on
Reset
Boot next
Next
Show
Boot reset
Storage or a flash card
Compact flash. Boots using nonvolatile
Boot show
Output for show
Secondary partition of the flash card
Nonvolatile storage area containing boot
Partition
Primary partition of the flash card in the flash
Version
Boot version
Enables the poweron test flag
Test
Dir on Fver on
Numerics
Command Index
NN47250-100 320658-G Version
Delete 539
Command Index
282
340
Command Index
Command Index
MAC addresses 12 in user globs Vlan globs
Command Index NN47250-100 320658-G Version
Page
Nortel WLAN-Security Switch 2300 Series Release