3CRWXR10095A, 3CRWX120695A, 3CRWX440095A
Wireless LAN Mobility System
3Com Corporation 350 Campus Drive Marlborough, MA USA
Contents
Set system location
Clear banner motd Clear history Clear prompt
104
102
126 Display ip alias 127
187
174 Set summertime 177 Set system ip-address 179
180 Set timezone 181 Display dhcp-client 182
183 Display snmp community 186
245
267
MAP Access Point Commands by Usage
272 Clear radio-profile 274 Clear service-profile 275 276
Set user group 258 Set usergroup 259 Set web-aaa 260
318
STP Commands
414
Security ACL Commands by Usage 423 clear security acl
395
Set spantree portvlanpri 396 Set spantree priority 397
448 Crypto certificate 449
Commands by Usage 447
Display security acl hits 430 Display security acl info 431
432
503
500
530
525
525 Display rfdetect visible 526
528
Clear log trace 562 Clear trace
Dir Display boot 547 Display config 548
549
561
Register Your Product 607
System LOG Commands
Page
List conventions that are used throughout this guide
Conventions
„ Wireless LAN Switch Manager 3WXM Release Notes
„ Wireless LAN Switch and Controller Release Notes
Documentation
„ Document part number and revision on the title
Comments
Pddtechpubscomments@3com.com
„ Document title
Example
Overview
Set enablepass
Clear interface vlan-idip
Clear fdb dynamic port port-list vlan vlan-id
Notation
Text Entry
Conventions
MAC Address
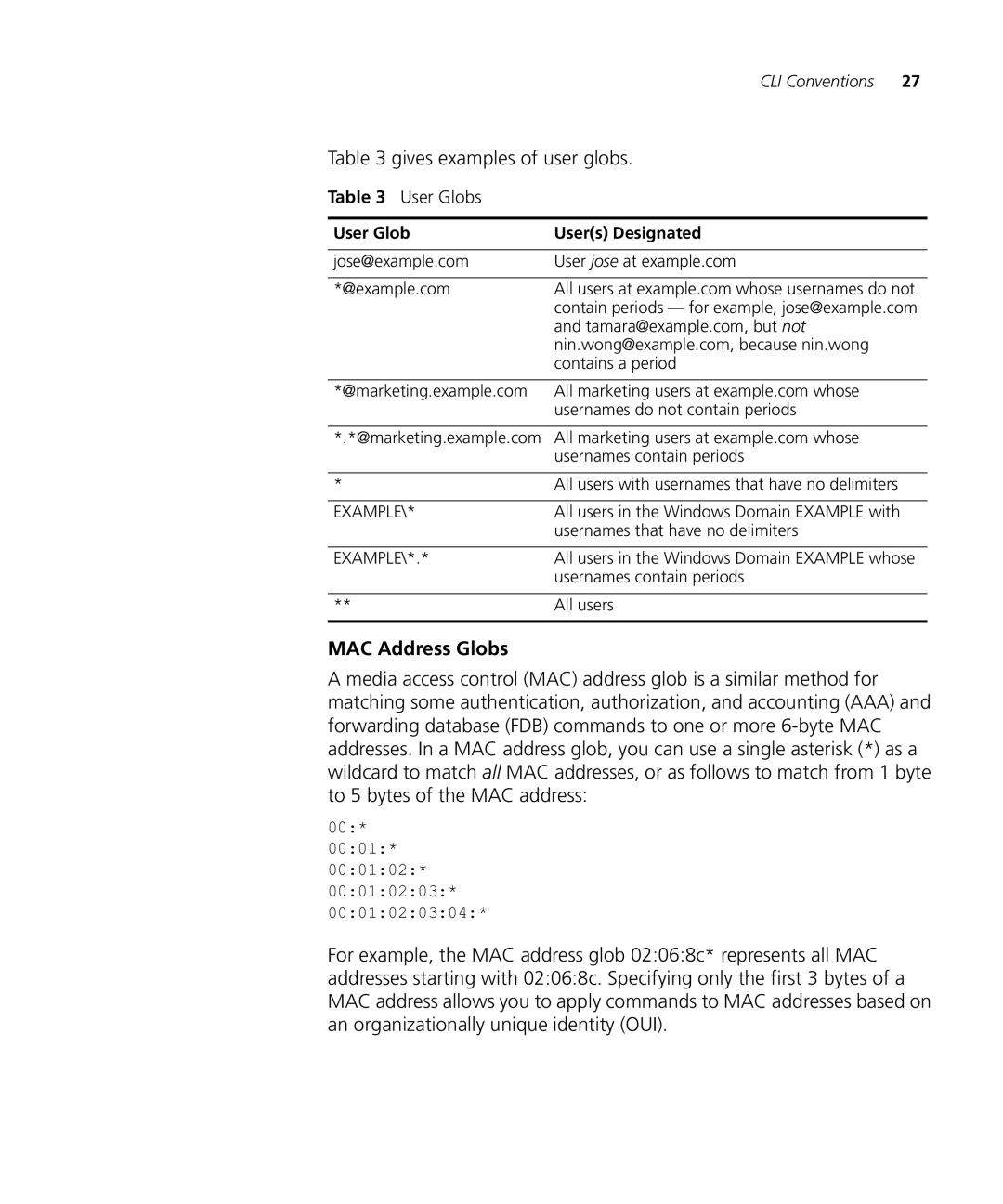
User Globs
Masks
Subnet Masks
Wildcard Masks
Gives examples of user globs
MAC Address Globs
User Globs
„ a single port number. For example
WX1200# set port enable
Vlan Globs
Matching Order for Globs
Operating systems
Command-Line
WX1200# reset port
Editing
WX1200# display i Tab
Using CLI Help
At your access level, type the help command. For example
WX1200# display i?
WX1200# display ip telnet
Understanding Command Descriptions
Set ap dap name command has the following complete syntax
WX1200# display ip ?
Usage
Commands by
Disable
Syntax disable Defaults None
Quit
Enable
Set enablepass
Access Commands
To located commands in this chapter based on their use
System Service Commands
„ display banner motd on
Banner with an empty banner by typing the following command
Clear banner motd
Clear history
Clear system
Clear prompt
Motd
Display banner
Display
Base-information
„ clear banner motd on
See Also „ set license on
Defaults None Access All
Display license
Display system
Display system output
Describes the fields of display system output
Nvram size /SDRAM size percent of total
Syntax help
WX switch
„ Using CLI Help on
Help
„ clear history on
Set auto-config
History
Syntax history
Set auto-config
Common Name remoteswitch1@example.com
Enable the Dhcp client on Vlan
Enable the auto-config option
WX-1200#crypto generate key admin 1024 key pair generated
Save the configuration changes
„ Delimiting character that begins and ends the message
Syntax set banner motd text
Syntax set confirm on off
Set confirm
See Also „ clear banner motd on „ display banner motd on
That might have a large impact on the network
WX4400# set confirm off
Set length
Examples To turn off these confirmation messages, type
WX4400# clear vlan red
Installs an upgrade license, for managing more MAPs
Set license
See Also „ display license on
Syntax set prompt string
Set prompt
Country Codes
Set system contact Stores a contact name for the WX switch
Set system
Countrycode
Country Code
Country Codes
WX1200# set system country code CA
Ip-address
Mobility Domain
„ ip-addr- IP address, in dotted decimal notation
Syntax set system name string
Syntax set system location string
Set system name
System Service Commands
Locate commands in this chapter based on their use
Port Commands
„ set dap on
That are using the MAP
Clear dap
Removes a Distributed MAP
Syntax clear port-group name name
Clear port-group
„ name name Name of the port group
See Also „ set port-groupon „ display port-groupon
See Also „ display port status on „ set port name on
Clear port
Preference
Clear port name Removes the name assigned to a port
Port
Clear port type
„ display port preference on
„ set port preference on
Counters
Display port
Display port-groupShows port group information
WX1200 display port counters octets port
Syntax display port-group all name group-name
Output for display port-group
Describes the fields in the display port-group output
See Also „ clear port-groupon „ set port-groupon
Describes the fields in this display
Display port
Output for display port preference
WX4400# display port preference Port Preference
Syntax display port status port-list
WX1200# display port status
Output for display port status
„ set port speed on
Monitor port
See Also „ clear port type on
„ set port negotiation on
Key Controls for Monitor Port Counters Display
WX4400# monitor port counters
Output for monitor port counters
Correct length but contained an invalid
See Also „ display port counters on
Set dap
Reset port
Port Commands
Set dap
Set port
Following command removes Distributed MAP
Administratively disables or reenables a port
Syntax set port enable disable port-list
With no spaces
See Also „ reset port on
Configured together as a single logical link
Single logical link
Syntax set port port name name
Name or number in other CLI commands
Set port name
See Also „ clear port-groupon „ display port-groupon
WX1200# set port negotiation 2 enable
Following command enables autonegotiation on port
Syntax set port negotiation port-listenable disable
WX1200# set port negotiation 3,5 disable
Set port poe
Access points
Following command enables PoE on ports 4
See Also „ set port type ap on „ set port type wired-authon
WX4400# set port preference 2 rj45
Set port speed
Changes the speed of a port
Syntax set port preference port-listrj45
Set port trap
Set snmp profile command
WX1200# set port trap 3-4 enable
Mp-352mp-372- MAP access point model
„ poe enable disable Power over Ethernet PoE state
„ 11a 802.11a „ 11b 802.11b „ 11g 802.11g
„ radiotype 11a 11b 11g Radio type
Defaults All WX ports are network ports by default
MAP Access Port Defaults
WX1200# set port type ap 1-3,5 model ap3750 poe enable
WX1200# set port type ap 1-3,5 model ap8250 poe enable
Set port type
Wired-auth
Before changing the port type from ap to wired-author from
Command
Vlan membership
Wired Authentication Port Details
See Also „ clear port type on „ set port type ap on
Port Commands
Vlan Commands
Clear fdb
Deletes an entry from the forwarding database FDB
Syntax clear fdb perm static dynamic
Clear vlan
„ display fdb on
Port from the VLAN, make sure you specify the port number
Displays entries in the forwarding database
Following command completely removes Vlan marigold
See Also „ set vlan port on „ display vlan config on
Display fdb
WX4400# display fdb all
WX4400# display fdb
Describes the fields in the display fdb output
See Also „ clear fdb on
Output for display fdb
See Also „ set fdb agingtime on
Agingtime
Station
Display roaming
Describes the fields in the display
See Also „ display roaming vlan on
Output for display roaming station
Output for display roaming vlan
Syntax display roaming vlan
WX4400# display roaming vlan
Syntax display tunnel
See Also „ display vlan config on
Display tunnel
Output for display tunnel
WX1200# display vlan config burgundy
Display vlan config
Output for display vlan config
Syntax display vlan config vlan-id
Set fdb
Adds a permanent or static entry to the forwarding database
Syntax set fdb perm static
Syntax set fdb agingtime vlan-idage seconds
See Also „ clear fdb on „ display fdb on
Syntax set vlan vlan-numname name
Set vlan name
See Also „ display fdb agingtime on
Creates a Vlan and assigns a number and name to it
Set vlan port
Adds ports 1 through 3 to the Vlan
Tag value to be the same but some other switches do
Set vlan
Tunnel-affinity
See Also „ display roaming vlan on „ display vlan config on
To locate commands in this chapter based on their use
IP Services Commands
DNS
IP Services Commands by Usage
Syntax clear interface vlan-idip
Access Enabled History Introduced in MSS Version
Clear interface
Removes an IP interface
Clear ip alias
See Also „ display ip alias on
Syntax clear ip alias name
WX1200# clear ip dns domain
Clear ip dns domain Removes the default DNS domain name
„ ip-addr- IP address of a DNS server
Syntax clear ip dns domain
See Also „ display ip route on „ set ip route on
Default is an alias for IP address 0.0.0.0/0
Clear ip route
„ clear ip dns domain on
Clear ip telnet
Defaults The default Telnet port number is
Telnet management traffic to its default
Removes an NTP server from a WX switch configuration
Clear ntp
Update-interval
„ display snmp community on
Clear snmp
Community
Syntax clear snmp community name comm-string
Clear snmp usm
Clear snmp profile
Clear snmp trap
Receiver
Syntax clear summertime
See Also „ set snmp usm on „ display snmp usm on
Use the address
Clear timezone
Syntax display arp ip-addr
Display arp
Usage All
Shows the ARP table
„ set arp on
„ set arp agingtime on
Output for display arp
Output for display interface
Shows the IP aliases configured on the wireless LAN switch
Display ip alias
See Also „ set interface on „ set interface status on
„ set ip alias on
Examples The following command displays the DNS information
Display ip dns
„ clear ip alias on
Syntax display ip https
Display ip https
Shows information about the Https management port
Output for display ip dns
WX4400# display ip https
Output for display ip https
WX4400# display ip route
Display ip route
Shows the IP route table
Syntax display ip route destination
FieldDescription
Output of display ip route
Output for display ip telnet
Syntax display ip telnet
WX4400 display ip telnet
Output for display ntp
Examples To display NTP information for a WX switch, type
Display ntp
Shows NTP client information
„ set ntp server on „ set summertime on „ set timezone on
Display snmp
Configuration
Shows Snmp settings on a wireless LAN switch
Examples To display Snmp settings on a WX switch, type
Output of display snmp configuration
WX1200# display summertime
Defaults There is no summertime offset by default
Summertime
Syntax display summertime
WX1200# display timedate
Syntax display timezone
WX4400# display timezone
„ set timedate on „ set timezone on
Defaults „ count
„ traceroute on
Set arp
WX1200# set arp agingtime
Following command disables ARP aging
See Also „ set arp agingtime on
Syntax set arp agingtime seconds
Set interface
Syntax set interface vlan-idip dhcp-client enable disable
Dhcp-client
„ clear interface on
Defaults The Dhcp server is enabled by default on a new
Configures the MSS Dhcp server
„ enable Enables the Dhcp server
„ disable Disables the Dhcp server
Syntax set interface vlan-idstatus up down
See Also „ display dhcp-serveron
See Also „ clear ip alias on „ display ip alias on
Aliases as shortcuts in CLI commands
Set ip alias
Set ip dns
WX1200# set ip dns domain example.com
Syntax set ip dns domain name
Syntax set ip dns server ip-addrprimary secondary
Set ip route
WX switch is disabled
Syntax set ip https server enable disable
Syntax set ip route default ip-addr mask
Set ip route
Syntax set ip snmp server enable disable
Secure Shell SSH management traffic
WX4400# set ip snmp server enable
Set ip ssh
„ clear snmp notify target on
„ set ip ssh server on
Absolute-timeout
„ set ip ssh absolute-timeouton
„ set ip ssh idle-timeouton
Idle-timeout
Also disabled
Set ip ssh server
Telnet management traffic
Maximum number of SSH sessions supported on a WX switch is
Set ip telnet
History -Introduced in MSS Version
Syntax set ip telnet server enable disable
Set ntp server
Enables or disables the NTP client on a wireless LAN switch
Configures a wireless LAN switch to use an NTP server
Set ntp
NTP server
RFC 1305, Network Time Protocol Version 3 Specification
Defaults The default NTP update interval is 64 seconds
Implementation and Analysis
User. SNMPv3 does not use community strings
Set snmp
Set snmp community
Set snmp notify
Target
SNMPv3 with Informs
Usm trap user username
SNMPv3 with Traps
SNMPv2c with Informs
SNMPv1 with Traps
SNMPv2c with Traps
Success change accepted
Snmp notification types
„ notification-type- Any of the items in Table
Point
Snmp notification types
WX-1200#set snmp notify profile snmpprofrfdetect send
RFDetectRogueDisappearTraps success change accepted
Syntax set snmp protocol v1 v2c usm all enable disable
WX-1200# set snmp security encrypted success change accepted
Community strings
Versions, use the set snmp community command to configure
Set snmp trap
Set snmp usm
„ auth-type none md5 sha auth-pass-phrase string
IP Services Commands
WX-1200# set snmp usm securesnmpmgr1 snmp-engine-id
Auth-type sha auth-pass-phrase myauthpword
Encrypt-type 3des encrypt-pass-phrase mycryptpword
WX1200# set summertime PDT success change accepted
WX4400# set interface taupe ip 10.10.20.20/24
Following
WX4400# set timedate date feb 29 2004 time 235800
Sets the time of day and date on the wireless LAN switch
Set timedate
Syntax set timedate date mmm dd yyyy time hhmmss
It is enabled
Set timezone
WX1200# set timezone PST
Output for display dhcp-client
Syntax display dhcp-client
WX-1200# display dhcp-client
WX-1200#display dhcp-server
See Also „ set interface dhcp-clienton
Display dhcp-serverDisplays MSS Dhcp server information
Syntax display dhcp-server interface vlan-id verbose
Describe the fields in these displays
Output for display dhcp-server
Display dhcp-server
Output for display dhcp-client verbose
See Also „ set interface dhcp-serveron
WX-1200#display snmp community
Displays the configured Snmp community strings
Outpot for display snmp community
Syntax display snmp community
Displays Snmp statistics counters
Syntax display snmp counters
WX-1200#display snmp counters
WX-1200#display snmp notify profile
Syntax display snmp notify profile
See Also „ clear snmp profile on „ set snmp profile on
Syntax display snmp notify target
WX-1200#display snmp notification target
User Name of the Snmp user EngineID
Output for display snmp notification target
WX-1200#display snmp status
Output for display Snmp status
Switch has booted
„ display snmp notify target on „ display snmp usm on
Output for display snmp usm
WX-1200#display snmp usm USM users
See Also „ clear snmp usm on „ display snmp usm on
Telnet
Opens a Telnet client session with a remote device
WX4400# telnet
See Also „ clear sessions on „ display sessions on
Defaults
„ dnf Disabled
Traceroute
Ctrl+C
„ no-dns- Disabled „ port
„ queries „ size „ ttl
„ wait
„ ping on
Error messages for traceroute
Locate commands in this chapter based on their use
This chapter presents AAA commands alphabetically. Use to
AAA Commands by Usage
Display accounting statistics on
WX4400# clear accounting dot1x Nin
Syntax clear accounting admin dot1x user-glob
Admin
Clear authentication
Syntax clear authentication console user-glob
WX4400# clear authentication console Regina
ConsoleConsole
Syntax clear authentication dot1x ssid ssid-namewired
Syntax clear authentication mac ssid ssid-namewired
Clear authentication Removes a MAC authentication rule. mac
Syntax clear authentication last-resort ssid ssid-namewired
WX4400# clear authentication last-resort wired
Access Enabled History -Introduced in MSS
WX4400# clear authentication mac ssid thatcorp aabbcc
Syntax clear authentication proxy ssid ssid-nameuser-glob
See Also „ set authentication proxy on
„ on Clear authentication Removes a WebAAA rule. web
WX-1200#clear authentication proxy ssid mycorp
Syntax clear location policy rule-number
Syntax clear mac-user mac-addr
User who is authenticated by a MAC address
Clear mac-user
Radius server
For your Radius server
WX switch, for a user who is authenticated by a MAC address
Group
ACL from the profile of a user at MAC address
Mac-usergroup
Clear
Mac-usergroup attr
„ set mobility-profileon
„ set mobility-profile mode on
Mobility-profile
Clear user
„ set user on
Database on the WX switch, for a user with a password
Clear user attr
Nin
„ clear usergroup on
Clear user group
Clear usergroup
Usergroup
Syntax clear usergroup group-name attr attribute-name
Time-Of-Day attribute from the group
Displays all current AAA settings
Secion added to indicate the state of the WebAAA feature
Display aaa
Display aaa Output
Describes the fields that can appear in display aaa output
Display aaa Output
Statistics output
Stored in the local database on the WX switch
Display accounting
Statistics
Display accounting statistics
„ clear location policy on
On an WX switch
Display location
Policy
Admin console
Set accounting
Are sent
Authenticated by MAC authentication
Server when the user roams
Accesses the switch using Telnet or Web Manager
Authenticated by
Set accounting dot1x mac web
Set authentication
Set authentication admin
Following methods in priority order. MSS applies multiple
Through the switch’s console
Completing logon
Globs on
For more information, see Usage
Syntax set authentication dot1x ssid ssid-namewired
Set authentication dot1x
AAA Commands
Success change accepted
Syntax set authentication last-resort
235
Syntax set authentication mac
Set authentication mac
Proxy
Syntax set authentication web ssid ssid-namewired
WX-1200#set authentication proxy ssid mycorp ** srvrgrp1
AAA Commands
Set location policy
For details, see Vlan Globs on
Set location policy
WX4400# set location policy deny if user eq *.theirfirm.com
Tempvendora into Vlan kiosk1
Set mac-user
See Also „ clear mac-useron „ display aaa on
Authentication Attributes for Local Users
Filter-id outboundacl.out
Authentication Attributes for Local Users
YY/MM/DD-HHMM
Time-of-day
WX4400# set mac-user 010203040506 attr filter-id acl-03.in
Syntax set mac-usergroup
See Also „ clear mac-user attr on „ display aaa on
Syntax set mobility-profile name name port none all
See Also „ clear mac-usergroup attr on „ display aaa on
AAA Commands
„ set user attr on „ set usergroup on
Syntax set mobility-profile mode enable disable
Set user
Orange
Set user attr
29Jan04
„ clear user on
Server
That exists in the local database on the WX switch
Set user group
„ clear user attr on
Assigns authorization attributes for the group
To add a user to a group, user the command set user group
Set usergroup
Examples To disable WebAAA, type the following command
Syntax set web-aaa enable disable
Set web-aaa
Mobility Domain Commands by Usage
To locate commands in this chapter based on their use
Member
Mobility-domain
See Also „ set mobility-domain member on
Display mobility-domain config
Displays the configuration of the Mobility Domain
Status
WX4400# display mobility-domain status
Display mobility-domain Output
Command is rejected
Set
Syntax set mobility-domain member ip-addr
192.168.1.8
Mode member
Seed, this command overwrites that configuration
Seed-ip
Syntax set mobility-domain mode seed domain-name
Set mobility-domain mode seed domain-name
Mobility Domain Commands
Commands
Type Command Set ap dap radio auto-tune max-power on
Set ap dap radio auto-tunemin-client-rateon
Clear ap dap
Radio
Syntax clear ap port-listdap dap-num radio 1 2 all
WX1200# clear ap 3 radio
Radio-Specific Parameters
Syntax clear radio-profile name parameter
Syntax clear service-profile name
„ name Service profile name
See Also „ clear radio-profileon „ set radio-profile mode on
WX4400# display dap config
WX1200# display ap config
DAP
Output for display ap config
„ set port type ap on „ set ap dap bias on
WX1200# display ap counters
Tkip Pkt Replays
Output for display ap counters
Ccmp Pkt Replays
See Also „ display sessions network on
WX-1200#display dap qos-stats
Output for display ap dap qos-stats
Output of display ap etherstats
Syntax display ap dap etherstats port-listdap-num
WX4400# display dap etherstats
Access point groups
„ name Name of an MAP group or Distributed MAP group
Syntax display ap dap group name
„ set ap dap group on
Output for display ap group
WX1200# display ap group loadbalance1
WX4400# display dap status
MAP
WX1200# display ap status
Output for display ap status
Output for display ap status
Syntax display auto-tune attributes
Decide whether to change channel or power settings
Display auto-tune
Attributes
See Also „ display auto-tune neighbors on
Output for display auto-tune attributes
WX1200# display auto-tune attributes ap 2 radio
Ap map-numradio 1 2all
Neighbors
3Com radio can hear
Syntax display auto-tune neighbors
Display auto-tune Neighbors ap 2 radio
Output for display auto-tune neighbors
Display dap global command
Display dap
Connection
Output of display dap connection
Dap connection serial-id M9DE48B6EAD00
Syntax display dap global dap-numserial-id serial-ID
WX4400# display dap global
Output for display dap global
Network port is a member of a Vlan
Unconfigured
But that are not configured on any WX switches
Longer appears in the command’s output
Syntax display radio-profile name ?
Output for display dap unconfigured
Radio-profile
Displays radio profile information
Output for display radio-profile
WX4400# display radio-profile default
Tune Channel
Ssid
„ ? Displays a list of service profiles
Service-profile
Displays service profile information
„ name Displays information about the named service profile
Display service-profile
Other WPA parameters
Reset ap dap
Configurable Template Parameters for Distributed MAPs
Dap auto mode enable command
Usage lists the configurable template parameters and their
Listed in . The commands are listed in the See Also section
WX1200# set dap auto success change accepted
Syntax set dap auto mode enable disable
See Also „ set dap auto on
Radiotype
Template
„ Radio type „ 11a-802.11a „ 11b-802.11b „ 11g-802.11g
Syntax set ap port-listdap dap-numauto bias high low
See Also „ display ap dap config on
Syntax set dap num fingerprint hex
Blink enable disable
„ ap port-list- List of MAP access ports to add to the group
WX1200# set ap 4 group none success change accepted
Set ap dap name Changes an MAP name
„ antennatype ANT5060 ANT5120 ANT5180 internal
„ antennatype ANT1060 ANT1120 ANT1180 internal
Radio 1 2 auto-tune max-power power-level
Set ap dap radio auto-tune max-power
Radio 1 2 auto-tune max-retransmissions retransmissions
Set ap dap radio auto-tune max- retransmissions
Set ap dap radio auto-tune max- retransmissions
Set ap dap radio channel
Sets an MAP radio’s channel
Syntax set ap port-listdap dap-numradio 1
„ display ap dap config on
Set ap dap radio auto-tune min-client-rate
Radio 1 2 auto-tune min-client-rate rate
Set ap 6 radio 1 min-client-rate
Examples
Radio 1 2 mode enable disable
Set ap dap radio mode
Enables or disables a radio on an MAP access point
Following command enables radio 2 on ports 1 through
Defaults None
Sets an MAP radio’s transmit power
Set ap dap radio tx-power
Syntax set dap security require none optional
WX-1200#set dap security require
Set ap dap
Upgrade-firmware
11g-only
Set radio-profile
Syntax set radio-profile name active-scan enable disable
Set radio-profile auto-tune channel-config
Syntax set radio-profile name auto-tune channel-holddown
Set radio-profile auto-tune channel-holddown
Syntax set radio-profile name auto-tune channel-interval
Set radio-profile auto-tune channel-interval
Syntax set radio-profile name auto-tune power-backoff-timer
Set radio-profile auto-tune power-backoff- timer
WX4400# set radio-profile rp2 auto-tune power-backoff-timer
Set radio-profile auto-tune power-config
Set radio-profile auto-tune power-interval
Beacon-interval
Following command disables countermeasures in radio profile
Clients from being able to use rogue access points
„ rogue Configures radios to attack rogues only
Defaults Countermeasures are disabled by default
Syntax set radio-profile name dtim-interval interval
Syntax set radio-profile name long-retry threshold
Syntax set radio-profile name frag-threshold threshold
Syntax set radio-profile name max-rx-lifetime time
Syntax set radio-profile name max-tx-lifetime time
Mode
Set radio-profile mode
WX4400# set radio-profile rp1 mode enable
Syntax set radio-profile name
Syntax set radio-profile name rts-threshold threshold
Syntax set radio-profile name service-profile name
Parameter Default Value To Default Value
Defaults for Service Profile Parameters
Set radio-profile auth-psk command
349
Wmm
Short-retry
Syntax set service-profile Name auth-dot1x enable disable
WPA IE
Set service-profile auth-fallthru
Syntax set service-profile name auth-psk enable disable
Syntax set service-profile name beaconed enable disable
Cipher-ccmp
Set service-profile
Cipher-tkip
Cipher-wep104
Use the set service-profile wep commands
Cipher-wep40
Syntax set service-profile name psk-phrase passphrase
Syntax set service-profile name psk-raw hex
Syntax set service-profile name rsn-ie enable disable
See Also „ set service-profilecipher-ccmpon
Syntax set service-profile name ssid-name ssid-name
Set service-profile auth-psk command
Syntax
See Also „ set service-profilessid-typeon
Syntax set service-profile name tkip-mc-time wait-time
See Also „ set service-profilessid-nameon
WX4400# mkdir corpa-ssid success change accepted
Ssid managed by the service profile
Syntax set service-profile name web-aaa-form url
Web-aaa-form
Set service-profile wep active-multicast- index
„ copy on „ dir on
„ mkdir on
Syntax set service-profile name wep active-unicast-index num
Set service-profile wep active-unicast- index
Wep key-index
Syntax set service-profile name wpa-ie enable disable
STP Commands by
Table to locate commands in this chapter based on their use
STP Commands by Usage
Syntax clear spantree portcost port-list
STP root bridge in all VLANs on a WX switch
Clear spantree
Portcost
„ set spantree portpri on
Portpri
Portvlancost
„ clear spantree portvlanpri on
„ clear spantree portcost on
Portvlanpri
See Also „ display spantree statistics on
„ clear spantree portpri on
Syntax display spantree
Spantree vlan default
Root
Output for display spantree
„ display spantree blockedports on
Or disabled
Display spantree
Backbonefast
Blockedports
„ set spantree backbonefast on
See Also „ display spantree on
Output for display spantree portfast
Portfast
For one or more network ports
See Also „ set spantree portfast on
Syntax display spantree statistics
Port’s VLANs
„ port-list- List of ports
Syntax display spantree portvlancost port-list
WX4400# display spantree statistics
Topology change Timer value Hold timer
Vlan Vlan ID
Output for display spantree statistics
Configpending
Switch is the root or is attempting to become the root
Syntax display spantree uplinkfast vlan vlan-id
See Also „ clear spantree statistics on
„ set spantree uplinkfast on
Set spantree
An indirect link
Examples The following command enables STP on all VLANs
Configured on a WX switch
Following command disables STP on Vlan burgundy
„ display spantree backbonefast on
Fwddelay
„ all Changes the maximum age on all VLANs
Issues a topology change message
Maxage
VLANs to 4 seconds
65,535. STP selects lower-cost paths over higher-cost paths
Type. lists the defaults for STP port path cost
STP Port Path Cost Defaults
Path to the STP root bridge
Portvlancost command
Syntax set spantree portpri port-listpriority value
See Also „ display spantree portfast on
To 20 in Vlan mauve
Bridge for a specific Vlan on a wireless LAN switch
„ all Changes the cost on all VLANs
Type. See on
„ all Changes the priority on all VLANs
Path to the STP root bridge, on one Vlan or all VLANs
Ports
Highest priority through 255 lowest priority
Uplinkfast
Priority
See Also „ display spantree uplinkfast on
Igmp Commands by Usage
Igmp Snooping Commands
Clear igmp statistics
Display igmp
See Also display igmp statistics on
TTL
Output for display igmp
TTL
Mrouter
Syntax display igmp mrouter vlan vlan-id
WX1200# display igmp Mrouter vlan orange
Defaults None Access Enabled
Only one querier
Syntax display igmp querier vlan vlan-id
WX1200# display igmp querier vlan red
WX1200# display igmp querier vlan default
Output for display igmp mrouter
WX1200# display igmp querier vlan orange
„ set igmp querier on
Receiver-table
See Also „ set igmp receiver on
Output for display igmp receiver-table
Igmp Receiver-table group 237.255.255.0/24
WX1200# display igmp statistics vlan orange
Shows Igmp statistics
„ vlan vlan-id Vlan name or number. If you do not specify a
Syntax display igmp statistics vlan vlan-id
From the multicast routers in the subnet
Output of display igmp statistics
See Also „ set igmp rv on
Wireless LAN switch
From 1 through 65,535
VLANs on a wireless LAN switch
VLAN, the timer change applies to all VLANs
Set igmp lmqi
See Also „ display igmp statistics on
Syntax set igmp mrouter port port-listenable disable
See Also „ set igmp mrsol mrsi on
Enables or disables multicast router solicitation by a WX
Syntax set igmp mrsol enable disable vlan vlan-id
Set igmp mrsol
Syntax set igmp oqi seconds vlan vlan-id
Set igmp oqi
See Also „ set igmp mrsol on
All VLANs on a WX
„ set igmp qri on
Set igmp
Proxy-report
„ set igmp lmqi on
Syntax set igmp qi seconds vlan vlan-id
Set igmp qi
Set igmp qri
VLANs on a WX
Group. You can specify a value from 1 through 65,535
Syntax set igmp querier enable disable vlan vlan-id
Syntax set igmp receiver port port-listenable disable
See Also „ display igmp querier on
Set igmp rv
Set igmp rv
Igmp Snooping Commands
Security ACL
Security ACL Commands
Syntax clear security acl acl-name all editbuffer-index
WX4400# commit security acl acl133 configuration accepted
Syntax clear security acl map acl-nameall vlan vlan-id
Syntax commit security acl acl-nameall
WX4400# commit security acl all
WX4400# display security acl
Syntax display security acl dscp
Syntax display security acl editbuffer
Examples The following command displays the table
See Also „ set security acl on
WX-1200#display security acl dscp
Syntax display security acl hits
WX4400# display security acl editbuffer
See Also „ hit-sample-rateon „ set security acl on
WX4400# display security acl hits
Syntax display security acl info acl-nameall editbuffer
Syntax display security acl map acl-name
Display security acl
Map
Security ACL is assigned
WX4400# display security acl map acl111
Resource-usage
ACL acl111 is mapped
Support for your Product on
WX4400# display security acl resource-usage
Output of display security acl resource-usage
Output of display security acl resource-usage
Hit-sample-rate
Packets filtered by the security ACL or hits
Syntax hit-sample-rate seconds
Syntax rollback security acl acl-nameall
Protocol, or IP, ICMP, TCP, or UDP packet information
Set security acl
By Icmp packets
By TCP packets
By UDP packets
„ ip „ tcp „ udp „ icmp
Security ACL Commands
Set security acl
WX4400# set security acl ip acl123 deny 192.168.2.11
Set security acl map
Security ACL Commands
Cryptography Commands by Usage
To locate commands in this chapter based on their use
Syntax crypto ca-certificate admin eap webaaa
See Also „ display crypto ca-certificateon
Syntax crypto certificate admin eap webaaa
Access Enabled History -Introduced in MSS Version
See Also display crypto key ssh on
Syntax crypto generate key admin eap ssh webaaa 512 1024
Syntax crypto generate request admin eap webaaa
Email Address admin@example.com
WX4400# crypto generate request admin
See Also „ crypto certificate on „ crypto generate key on
Syntax crypto generate self-signed admin eap webaaa
WX4400# crypto generate self-signed admin
Crypto otp
„ crypto pkcs12 on
Crypto pkcs12
WX4400# crypto otp eap hap9iN#ss
See Also „ crypto otp on
Display crypto ca-certificate Output
Display crypto
Ca-certificate
Pkcs #7 certificate
Describes the fields of the display
On the WX switch
Syntax display crypto certificate admin eap webaaa
Certificate
Syntax display crypto key ssh
See Also crypto generate key on
Cryptography Commands
Radius Commands by Usage
Locate commands in this chapter based on their uses
Clear radius
Syntax clear radius client system-ip
See Also „ display aaa on „ set radius client system-ipon
Syntax clear radius proxy port all
See Also „ set radius proxy client on
See Also „ set radius proxy port on
Syntax clear radius proxy client all
See Also „ display aaa on „ set radius server on
Syntax clear radius server server-name
Syntax clear server group group-nameload-balance
„ set server group on
Set radius
Set radius client
System-ip
„ clear radius server on
WX4400# set radius client system-ipsuccess change accepted
Set radius proxy
Port
„ clear radius proxy client on
To 32 characters long, with no spaces or tabs
Set radius server
WX1200# set server group shorebirds members heron egret
Load-balance group
„ group-name- Server group name of up to 32 characters
Sandpiper
Radius and Server Group Commands
Performance
On the switch
Commands on
802.1X Commands by Usage
See Also „ display dot1x on „ set dot1x bonded-periodon
Resets the Bonded Auth period to its default value
Clear dot1x
Bonded-period
„ set dot1x max-reqon
Port-control
Quiet-period
See Also „ display dot1x on „ set dot1x reauth-periodon
Reauth-max
Reauth-period
„ set dot1x reauth-maxon
Supplicant
„ set dot1x timeout auth-serveron
„ set dot1x timeout supplicant on
Auth-server
Tx-period
Display dot1x
„ set dot1x tx-periodon
WX4400# display dot1x clients
WX1200# display dot1x config
Type the following command to display 802.1X statistics
Explains the counters in the display dot1x stats output
WX4400# display dot1x stats
Port-control command
Set dot1x
Authcontrol
Machine to start reauthentication for the user
Authentication is enabled
Examples To enable per-port 802.1X authentication on wired
Authentication ports, type the following command
See Also „ display dot1x on „ clear dot1x bonded-periodon
Syntax set dot1x key-tx enable disable
See Also „ clear dot1x max-reqon „ display dot1x on
See Also „ display dot1x on
See Also „ display port status on „ display dot1x on
Authentication dot1X command
To a supplicant after a failed authentication
Syntax set dot1x reauth enable disable
Syntax set dot1x quiet-period seconds
Before the supplicant client becomes unauthorized
See Also „ display dot1x on „ clear dot1x reauth-maxon
Syntax set dot1x reauth-max number-of-attempts
See Also „ display dot1x on „ clear dot1x reauth-periodon
Set dot1x timeout
Attempts reauthentication
Out a request to a Radius authentication server
Out an authentication session with a supplicant client
Syntax set dot1x timeout supplicant seconds
Syntax set dot1x tx-period seconds
Broadcast and multicast encryption keys
Syntax set dot1X wep-rekey enable disable
Wep-rekey
See Also „ display dot1x on „ clear dot1x tx-periodon
To 300 seconds
Defaults The default is 1800 seconds 30 minutes
Wep-rekey-period
„ seconds Specify a value between 30 and 1,641,600 19 days
Telnet sessions
Clear sessions
VLANs, or session ID
Network
To clear session 9, type the following command
WX4400# clear sessions network mac-addr
WX1200# clear sessions network session-id
Display sessions
WX4400 display sessions admin
WX4400 display sessions console
WX4400 display sessions telnet
Display sessions telnet client Output
See Also „ clear sessions on
Syntax display sessions network
WX1200# display sessions network mac-addr 00055d7e981a
„ Summary display See on „ Verbose display See on
„ display sessions network session-id display See on
WX1200# display sessions network
WX1200# display sessions network session-id
WX1200# display sessions network verbose
Additional display sessions network verbose Output
Display sessions network summary Output
Time
Display sessions network session-id Output
802.1X protocol on a wired authentication port
See Also „ clear sessions network on
Session Management Commands
RF Detection Commands by Usage
To locate the commands in this chapter based on their use
Removes a MAC address from the attack list
Examples The following command clears MAC address
Clear rfdetect
Attack-list
Black-list
Countermeasures Mac Clear rfdetect
Ignore
„ set rfdetect ssid-liston
Ssid-list
„ display rfdetect ignore on
„ set rfdetect ignore on
„ display rfdetect vendor-liston
Vendor-list
Display rfdetect
„ set rfdetect vendor-liston
RF Detection Commands
Display rfdetect countermeasures Output
Countermeasures
Mobility Domain
Domain
Displays information about the APs detected by a WX switch
Data
Syntax display rfdetect data
WX1200# display rfdetect data
Display rfdetect data Output
Ignore list
Syntax display rfdetect ignore
WX4400# display rfdetect ignore Total number of entries
WS1200# display rfdetect mobility-domain
Bssid mac-addr Displays rogues that are using the specified
During RF detection scans
Syntax display rfdetect mobility-domain
WS1200# display rfdetect mobility-domain ssid 3Com-webaaa
Ssid 3Com-webaaa
Following command displays detailed information for a Bssid
Display rfdetect mobility-domain Output
WX1200# display rfdetect mobility-domain bssid 000b0e0004d1
Display rfdetect mobility-domain ssid or bssid Output
„ clear rfdetect ssid-liston
WX switch
„ display rfdetect data on
Displays the entries in the permitted Ssid list
Visible
Display ap dap status command
WX1200# display rfdetect visible Radio
Display rfdetect visible Output
Set rfdetect
Active-scan
Addresses of APs and clients
Configured. WX switches do not share client black lists
Configured. WX switches do not share attack lists
Examples The following command adds MAC address
Defaults The client black list is empty by default
Countermeasures Mac Set rfdetect ignore
Set rf detect
See Also „ display log buffer on
Signature
WX switches in a Mobility Domain
Device’s OUI is in the permitted vendor list
Examples The following command adds Ssid mycorp to the list
Only for the SSIDs that are on the list
Permitted SSIDs
Trailing 000000 value is required
Syntax display rfdetect attack-list
WX1200# display rfdetect attack-list
WX1200# display rfdetect black-list
Displays the wireless clients detected by an WX switch
Clients
Syntax display rfdetect black-list
WX1200# display rfdetect Clients
Display rfdetect clients Output
Display rfdetect clients mac Output
From the wired side of the network addressed to
File Management Commands
„ tftp/ip-addr/filename- Name of the archive file to create
Dir command output
Locally on the switch
Tape archive tar format
Syntax clear boot config
„ Copies a file from a Tftp server to nonvolatile storage
„ reset system on
Copy
Performs the following copy operations
WX4400# copy floorwx tftp//10.1.1.1/floorwx
WX4400# copy test-config new-config
Syntax delete url
File or the running configuration
Delete
Immediately deletes the specified file
Dir
Describes the fields in the dir output
„ copy on „ delete on
Output for dir
Describes the fields in the display boot output
Display boot
Reboot and configured for use after the next reboot
Access Access
Display config
Displays the configuration running on the WX switch
Syntax display config area area all
Display version
See Also „ load config on „ save config on
And, optionally, for any attached MAP access points
WX4400# display config area vlan
WX1200# display version details
WX1200# display version
Output for display version
Load config
Running configuration with the commands in the loaded file
Describes the fields in the display version output
WX4400# load config testconfig1
Following command loads configuration file testconfig1
Syntax load config url
WX4400# load config
Creates a new subdirectory in nonvolatile storage
Mkdir
Reset system
Restarts an WX switch and reboots the software
„ dir on „ rmdir on
Generate new key pairs and certificates on the switch
Restore
Removes a subdirectory from nonvolatile storage
„ backup on
WX1200# restore system tftp/10.10.20.9/sysabak
Rmdir
„ dir on „ mkdir on
Save config
Saves the running configuration to a configuration file
Syntax save config filename
Testconfig1
Set boot
Configuration-file
Configuration
Syntax set boot partition boot0 boot1
File Management Commands
Trace Commands
Deletes the log messages stored in the trace buffer
Deletes running trace commands and ends trace processes
Clear log trace
Clear trace
WX4400# display trace
WX switch, or all possible trace options
Display trace
Syntax display trace all
Authentication
Save trace
Set trace
See Also „ clear trace on „ display trace on
Authorization
Set trace dot1x
Syntax set trace sm mac-addr mac-address port port-num
Set trace sm
Trace Commands
Snoop Commands
Clear snoop
Clear snoop map
„ display snoop info on
„ display snoop map on
Set snoop
„ set snoop map on
„ display snoop on
Chapter Snoop Commands
WX1200# set snoop snoop1 observer 10.10.30.2 snap-length
Radio 2 of the MAP. This option does not apply to
Set snoop map
Filter
Radio 1 of the MAP
All snoop filters
Set snoop mode
To an MAP radio and enable the filter
Enable stop-afternum-pkts- Enables the snoop filter
Displays the MAP radio mapping for all snoop filters
Display snoop map command
For all snoop filters configured on a WX switch
Display snoop
WX1200# display snoop info snoop1
Display snoop info Shows the configured snoop filters
See Also „ clear snoop on
Syntax display snoop filter-name
Examples display snoop stats filter-namedap-numradio
Snoop map snoop1
Snoop1
Display snoop stats Output
Snoop stats snoop1
Chapter Snoop Commands
Syntax clear log buffer server ip-addr
Clear log
See Also „ clear log trace on
You can view event messages archived in the buffer
Log buffer facility ?
WX4400# display log buffer facility AAA
„ set log on „ clear log on
„ display log config on
Log config
„ clear log on
Syntax display log trace +-/number-of-messages
Address in dotted decimal notation
Set log
Storage
„ console Sets log parameters for console sessions
„ trace Sets log parameters for trace files
See Also
See Also „ display log config on
Set log trace
Mbytes
System LOG Commands
Boot Prompt
Boot Prompt Commands
Autoboot
„ FN=filename System image filename
Boot
„ BT=type Boot type
„ DEV=device Location of the system image file
„ change on „ display on
Syntax change
Change
Syntax create
Create
Syntax delete
Usage When you type the delete command, the next-lower
Examples To remove the currently active boot profile, type
Profiles, see display on
Syntax diag
Diag
Syntax display Defaults None
„ change on „ create on „ delete on „ next on
Output of display command
Fver
„ ls on
For an individual command
„ command-name- Boot prompt command
Displays a list of the boot prompt commands
Syntax next
Next
Command at the boot prompt
Reset
Resets a WX switch’s hardware
Syntax reset
Test
„ on Enables the poweron test flag
„ OFF Disables the poweron test flag
Defaults The poweron test flag is disabled by default
Syntax version
Dir or fver command
Type the following command at the boot prompt
Version
Purchase
Services
Register Your
Product
Downloads
Access Software
Troubleshoot
Online
Contact Us
Latsupportanc@3com.com
Country Telephone Number
Index
Delete 544, 597 diag Dir 545, 598 disable 33 display
Index
Index
Index
Traceroute Version