Sros Command Line Interface
Publication Number
Table of Contents
Reference Guide Introduction
CLI Introduction
Enable
Command Reference GuideUnderstanding Configuration Modes
Using CLI Shortcuts
Config-eth 0/1#ip address
Command Reference GuidePerforming Common CLI Functions
Understanding CLI Error Messages
Debug Undebug all
Command Descriptions
Command Descriptions
Basic Mode Command SET
Basic Mode Command Set
Enable
Enable #configure terminal Config#enable password password
Enable
Logout
Ping address
Address
Ping
Show clock
Show snmp
Show snmp
Show version
Show version
Telnet address
Telnet
Traceroute address
#traceroute
Enable Mode Command SET
Sros Command Line Interface Reference Guide
Sros Command Line Interface Reference Guide
Clear access-list listname
#clear access-list MatchAll
Enable #clear arp-cache
Clear arp-cache
Enable #clear arp-entry
Clear arp-entry address
Enable #clear bridge
Clear bridge group#
Enable #clear buffers max-used
Clear buffers max-used
Enable #clear counters ethernet 0/1
Clear counters interface
Enable #clear crypto ike sa
Clear crypto ike sa policy priority
Clear crypto ipsec sa
Enable #clear dump-core
Clear dump-core
Enable #clear event-history
Clear event-history
Clear ip bgp * as-number ip address in out soft
Out
Soft
#clear ip bgp
Clear ip igmp group group-address interface
#show ip igmp groups
#clear ip igmp group #show ip igmp groups
#clear ip igmp group ethernet 0/1
#clear ip igmp group
Clear ip policy-sessions
Usage Examples
Enable #clear ip policy-stats
Enable #clear ip policy-stats MatchALL
Clear ip policy-stats classname entry policy class #
Clear ip prefix-list listname
#clear ip prefix-list test
Clear ip route
#clear ip route
Enable #clear lldp counters
Clear lldp counters
Clear lldp counters interface interface
Enable #clear lldp neighbors
Clear lldp neighbors
Enable #clear pppoe
Clear pppoe interface id
Enable #clear process cpu max
Clear process cpu max
Clear qos map
Clear qos map map name
#clear qos map
#clear qos map priority
Enable #clear spanning-tree counters interface eth 0/1
Clear spanning-tree counters interface interface
Enable #clear spanning-tree detected-protocols
Interface
Enable #clock auto-correct-DST
Clock auto-correct-dst
Enable #clock no-auto-correct-DST
Clock no-auto-correct-dst
Enable #clock set 034200 22 Au
Clock set time day month year
Clock timezone text
Enable #clock timezone -4-Santiago
Following list shows sample cities and their timezone codes
Configure
#copy startup-config backup.bak
#copy running-config startup-config
Copy source destination
#copy myfile.biz newfile.biz
Enable #copy console config
Copy console filename
Enable #copy flash tftp
Copy flash destination
Enable #copy configfile interface adsl 0/1
Copy filename interface interface slot/port
Copy tftp destination
#copy tftp flash
Copy xmodem destination
#copy xmodem flash Destination filename newfile.biz
Debug aaa
#debug aaa
Debug access-list listname
Enable #debug access-list MatchAll
Enable #debug atm events
Debug atm events
Enable #debug atm oam
Debug atm oam vcd loopback end-to-end segment Llid
Debug atm packet interface atm vc ATM port VPI/VCI vcd vcd
Number
Debug bridge
#debug bridge
Enable #debug crypto ipsec
Ike
Ike negotiation
Ipsec
Debug backup
Enable #debug backup
Enable #debug dialup-interfaces
Debug dialup-interfaces
Enable #debug dynamic-dns verbose
Debug dynamic-dns verbose
Verbose Turns on verbose messaging
Enable #debug firewall
Debug firewall
Debug frame-relay events llc2 lmi
Events
Llc2
Lmi
Enable #debug frame-relay multilnk
Debug frame-relay multilink interface
Debug hdlc errors verbose
Enable #debug hdlc verbose
Enable #debug interface ethernet
Debug interface interface
Enable #debug interface adsl events
Debug interface adsl events
Debug ip bgp events in out keepalives updates
Updates
In/out
Keepalives
Enable #debug ip dhcp-client
Debug ip dhcp-client
Enable #debug ip dhcp-server
Debug ip dhcp-server
Enable #debug ip dns-client
Debug ip dns-client
Enable #debug ip dns-proxy
Debug ip dns-proxy
Debug ip icmp send recv
Send
#debug ip icmp
Debug ip igmp group-address
#debug ip igmp
Debug ip ospf
Debug ip rip events
#debug ip rip
Debug ip tcp events
#debug ip tcp events
Debug ip tcp md5
#debug ip tcp md5
Enable #debug ip udp
Debug ip udp
Debug isdn events
#debug isdn events
Debug lldp rx tx verbose
Shows information about received packets
Shows information about transmitted packets
Verbose Shows detailed debugging information
Enable #debug port-auth packet rx
Debug port-auth general packet both rx tx supp-sm
General
Both
Debug ppp authentication errors negotiation verbose
Authentication
Errors
Enable #debug ppp authentication
Enable #debug pppoe client
Debug pppoe client
Debug radius
#debug radius
Debug sntp
Debug spanning-tree config events general root
Config
Root
#debug spanning-tree general
Enable #debug spanning-tree bpdu all
Debug spanning-tree bpdu receive transmit all
Receive
Transmit
Enable #debug system
Debug system
Enable #dir
Dir
Disable
#disable
Erase filename startup-config
#erase startup-config
Enable #events
Events
#logout
Reload cancel in delay
Cancel
Enable #reload
#reload cancel
Show access-lists listname
#show access-lists
Enable #show arp
Show arp
Enable #show atm pvc interface atm
Show atm pvc traffic interface atm interface
Show atm pvc Show atm pvc traffic interfaces atm interface
Pvc
Enable #show bridge
Frame-relay slot/port
Show buffers
#show buffers
Enable #show buffers users
Show buffers users
Enable #show cflash
Show cflash
Show clock detail
Detail
Show clock
Show configuration
#show configuration
Copyright 2005 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P 113
Show connections
#show connections
Enable #show crypto ca certificates CA Certificate
Show crypto ca certificates crls profiles
Client configuration
Show crypto ike
Pool
Policy
Enable #show crypto ike policy Crypto IKE Policy
Show crypto ipsec
Transform-set
Show crypto map
Port number
Enable #show debugging
Show debugging
Show backup interfaces
Enable #show backup interfaces Backup interfaces
Show dialin interfaces
#show dialin interfaces Dialin interfaces
Show dynamic-dns
#show dynamic-dns eth 0/1
Enable #show event-history
Show event-history
Enable #show flash
Show flash
Enable #show frame-relay lmi
Show frame-relay
Frame-relay
#show frame-relay pvc
Active Inactive Deleted Static Local
Enable #show frame-relay fragment
Show frame-relay fragment frame-relay port.sublink
Enable #show frame-relay fragment frame-relay
Dlci = 17 Fragment Size =
Enable #show frame-relay multilink
Show frame-relay multilink interface detailed
Show hosts
#show hosts
Enable #show interfaces t1 1/1
Show interfaces interface
Total-24-hourintervals
#show interfaces modem 1/2 modem 1/2 is UP
#show interfaces dds 1/1
#show interfaces fr
Atuc
Show interfaces shdsl
Performance statistics
Performance-statistics
Total-24-hour
LOS
Enable #show interfaces shdsl 1/1
Technology Review
Show ip access-lists listname
Enable #show ip access-lists
Enable #show ip arp
Show ip arp
Show ip bgp
#show ip bgp
Show ip bgp network ip /length network-mask
#show ip bgp 10.15.240.0/28
Show ip bgp neighbors ip address
Advertised-routes
#show ip bgp neighbors
#show ip bgp neighbors 10.15.43.34 advertised-routes
Network NextHop Metric Path 0.0/8 10.15.43.17 100 0.0/9
Show ip dhcp-client lease interface
#show dhcp-client lease
Show ip dhcp-server binding client ip address
#show ip dhcp-server binding
Enable #show ip igmp groups
Show ip igmp groups group-address
Enable #show ip igmp interface eth 0/1 is UP
Show ip igmp interface interface
Enable #show ip interfaces
Show ip interfaces interface brief
Brief
Show ip mroute group-addressinterface summary
#show ip mroute
Show ip ospf
#show ip ospf
Show ip ospf database
Area id
Enable #show ip ospf database Ospf router with ID
Enable #show ip ospf interface ppp
Show ip ospf interface interface type interface number
Enable #show ip ospf neighbor
Enable #show ip ospf summary-address
Show ip ospf summary-address
Enable #show ip policy-class
Show ip policy-class policyname
Enable #show ip policy-sessions
Show ip policy-sessions policyname
Enable #show ip policy-stats
Show ip policy-stats policyname
Show ip prefix-list detail summary listname
Summary
#show ip prefix-list test ip prefix-list test 4 entries
Show ip protocols
#show ip protocols
Enable #show ip route rip
Connected
Ospf
Rip
Copyright 2005 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P 165
Enable #show ip traffic IP statistics
Show ip traffic
Show lldp
#show lldp
Show lldp device system name
#show lldp device Router
Show lldp interface interface
#show lldp interface ethernet 0/1 eth 0/1 TX/RX
Show lldp neighbors interface interface detail
Copyright 2005 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P 171
Show lldp neighbors statistics
#show lldp neighbors statistics
Enable #show memory heap
Show memory heap
Heap
65520 131056
Show output-startup
#show output-startup
Enable #show port-auth supplicant interface eth 0/2
Show port-auth supplicant interface interface id summary
Show pppoe
#show pppoe ppp
Enable #show processes cpu
Show processes cpu
Show qos map
#show qos map qos map priority map entry
#show qos map priority qos map priority
#show qos map priority 10 qos map priority
#show qos map interface frame-relay 1 fr
Enable #show queue fr
Show queue atm interface id frame-relay interface id ppp
Interface id
Enable #show queuing
Show queuing fair
Fair
Show radius statistics
#show radius statistics
Copyright 2005 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P 185
Show sntp
Show sntp
Enable #show spanning-tree
Show spanning-tree bridgegroup#
Show startup-config
#show startup-config
Copyright 2005 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P 189
Show startup-config checksum
#show startup-config checksum
#show running-config checksum
Enable #show tcp info
Show tcp info control block
Enable #show users
Show users
Enable #show version
Enable #telnet 10.200.4.15 User Access Login Password
Enable #terminal length
Terminal length text
Enable #traceroute
Enable #undebug all
Undebug all
#wall Reboot in 5 minutes if no objections
Wall message
Enable #write memory
Write erase memory network terminal
Erase
Global Configuration Mode Command SET
Router#configure terminal
Copyright 2005 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P 201
Password-prompt
Banner
Fail-message
Username-prompt
Config#aaa authentication enable default line
None
Line
Groupname
None
Config#aaa group server radius myServers config-sg-radius#
Aaa group server radius listname
Aaa on
Group groupname
Example
Copyright 2005 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P 208
Config#aaa processes
Aaa processes threads
Banner exec login motd character message character
Login
Exec
Motd
Config#no bridge 17 protocol ieee
Bridge group# protocol ieee
Boot config cflash flash filename cflash flash backup file
Config#boot config flash myconfig
Cflash
Flash
No-backup
Config#boot system flash myimage.biz
Crypto ca authenticate name
Config#crypto ca authenticate testCAprofile
Quit
Crypto ca certificate chain name
Crypto ca enroll name
Config#crypto ca enroll MyProfile
Config#crypto ca import MyProfile certificate
Crypto ca import name certificate
END Certificate
Config#crypto ca import MyProfile crl
Crypto ca import name crl
Config#crypto ca profile MyProfile
Crypto ca profile name
Config#crypto ike policy 1 config-ike#
Crypto ike
Local-id address
Enable #configure terminal
Config#crypto ike local-id address
Copyright 2005 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P 225
Config-eth 0/1#no shutdown config-eth 0/1#exit
Crypto ike remote-id
Asn1-dn name
John*@domain.com
Domain.com
Crypto ike remote id address 10.10.10.0
Copyright 2005 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P 229
Crypto ipsec transform-set setname parameters
Syntax Description
Copyright 2005 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P 231
Crypto map
Ipsec-ike
Ipsec-manual
Config#crypto map testMap 10 ipsec-ike
Enable password md5 password
Md5
Config#event-history on
Event-history on
Event-history priority error fatal info notice warning
Error
Info
Fatal
Config#event-history priority info
Ftp authentication listname
Config#ftp authentication MyList
Config#ftp authentication default
Config#hostname Atlrtr
Hostname name
Config#interface serial 1/1
Interface port-type slot/port
Interface frame-relay label point-to-point
Point-to-point
Config#bind 5 t1 1/1 9 fr
Config#interface fr
Config#interface hdlc
Config-hdlc 7#ip address 193.44.69.1
Interface hdlc label
Config#bind 5 t1 1/1 9 hdlc
Config#interface loopback
Interface loopback label
Config#interface ppp
Config-ppp 7#ip address 193.44.69.1
Interface ppp label
Config#bind 5 t1 1/1 9 ppp
Interface tunnel id
Config#interface tunnel 1 config-tunnel 1#
Ip access-list extended listname
Any
Port list
Discard Port
Pim-auto-rp
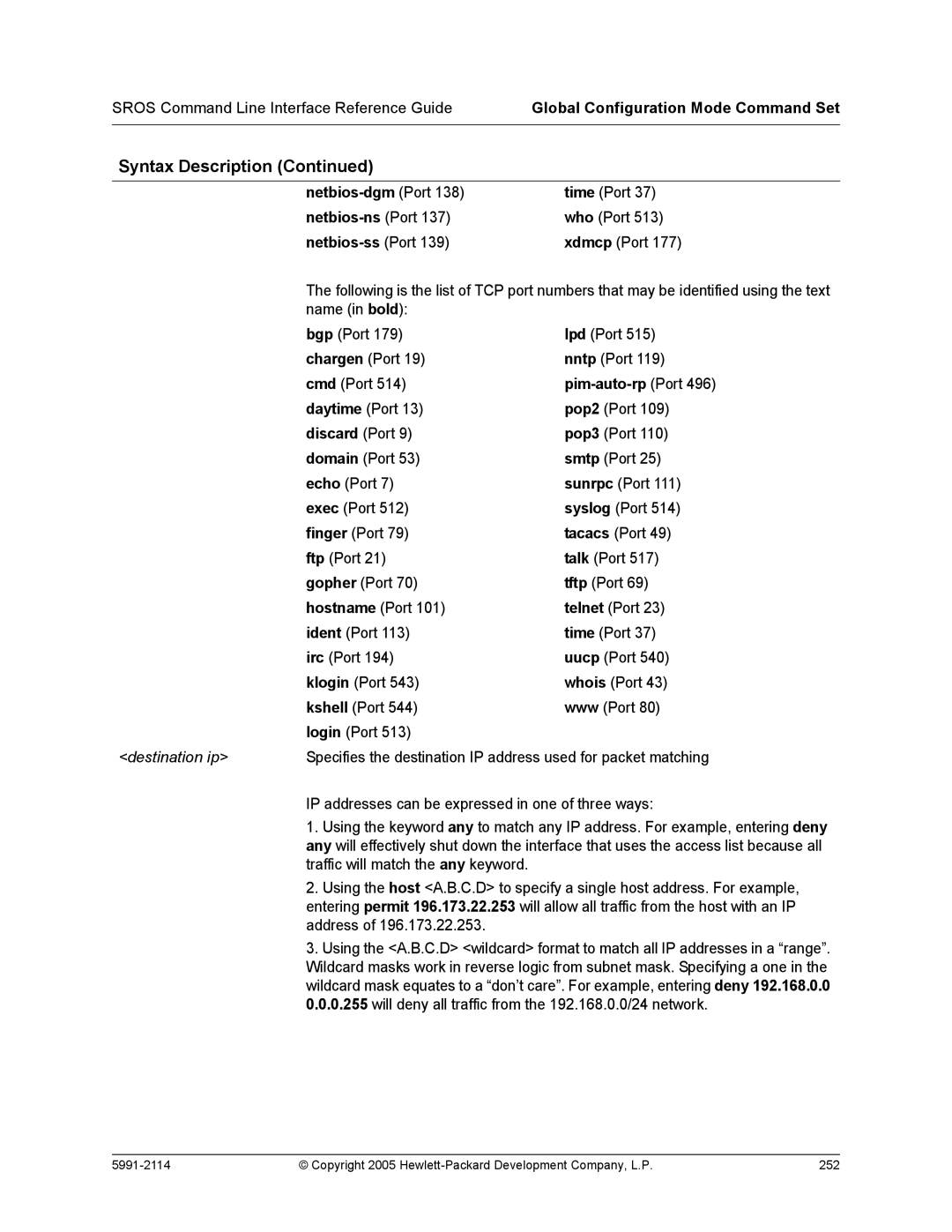
Netbios-dgm Port 138 netbios-ns Port 137 netbios-ss Port
Destination ip
Range 0 to
Copyright 2005 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P 254
Allow list access list names
Copyright 2005 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P 256
Ip access-list standard listname
Config#ip access-list standard MatchAll
Remark
Log
Permit or deny any
Copyright 2005 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P 259
Lost
Ip classless
Ip crypto
Ip default-gateway ip address
Config#no ip routing Config#ip default gateway
Ip dhcp-server excluded-address start ip end ip
Config#ip dhcp-server ping packets
Ip dhcp-server ping packets #packets
Ip dhcp-server ping timeout milliseconds
Config#ip dhcp-server ping timeout
Config#ip dhcp-server pool Sales
Ip dhcp-server pool name
Config#ip domain-lookup
Ip domain-lookup
Config#ip domain-name procurve
Ip domain-name name
Config#ip domain-proxy
Ip domain-proxy
Ip firewall
Security data processing will be attempted
Config#ip firewall
Concepts
Packet Flow
Attack Protection
Attacks that send TCP URG Yes
Application Specific Processing
Config#no ip firewall alg ftp
Ip firewall alg ftp pptp sip
Config#ip firewall check reflexive-traffic
Ip firewall check reflexive-traffic
Config#ip firewall attack-log threshold
Ip firewall attack-log threshold value
Config#ip firewall check syn-flood
Ip firewall check syn-flood
Config#ip firewall check winnuke
Ip firewall check winnuke
Config#ip firewall policy-log threshold
Ip firewall policy-log threshold value
Ip forward-protocol udp port number
Copyright 2005 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P 284
Ip ftp access-class policyname
Ip ftp agent
Config#ip ftp source-interface loopback
Ip ftp source-interface interface
Config#ip host mac 10.2.0.2 config#ip host dal
Ip host name address1
Config#ip igmp join
Ip igmp join group-address
Config#ip mcast-stub helper-address
Ip mcast-stub helper-address ip address
Ip multicast-routing
Config#ip name-server 172.341.1.111
Ip policy-class policyname max-sessions number
Max-sessions
Copyright 2005 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P 294
Copyright 2005 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P 295
Ip policy-timeoutprotocol range port seconds
Allports
Ftp-data Port
Copyright 2005 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P 298
Ip prefix-list listname description text
Description
Config#ip prefix-list test seq 10 permit 0.0.0.0/0 le
Deny
Config#ip radius source-interface ethernet 0/1
Ip radius source-interface interface
Ip route ip address subnet mask interface or ip address
Ip routing
Config#ip snmp agent
Ip snmp agent
Config#ip sntp source-interface loopback
Ip sntp source-interface interface
Config#ip subnet-zero
Ip subnet-zero
Config#ip tftp source-interface loopback
Ip tftp source-interface interface
Line console telnet line-number ending number
Console
Config#line console 0 config-con0#
Config#line telnet 0 4 config-telnet0-4#
Reinitialization-delay
Minimum-transmit-interval
Transmit-interval
Ttl-multiplier
Config#lldp minimum-transmit-interval
Config#lldp reinitialization-delay
Config#lldp transmit-interval
Config#lldp transmit-interval 15 config#lldp ttl-multiplier
Logging console
Logging email address-listemail address email address
Config#logging email on
Logging email on
Logging email priority-level error fatal info notice warning
Config#logging email priority-level warning
Config#logging email receiver-ip
Logging email receiver-ip ip address
Logging email sender
Config#logging email source-interface loopback
Logging email source-interface interface
Logging facility facility type
Logging forwarding on
Config#logging forwarding priority-level warning
Config#logging forwarding receiver-ip
Logging forwarding receiver-ip ip address
Config#logging forwarding source-interface loopback
Logging forwarding source-interface
Config#mac address-table aging-time
Mac address-table aging-time aging time
Interface
Qos map mapnamesequence number
Copyright 2005 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P 327
Enable-username name
Radius-server
Challenge-noecho
Deadtime minutes
Copyright 2005 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P 329
Radius-server host
Acct-port1813 Auth-port1812
Config#router ospf config-ospf#
Router ospf
Config#router rip config-rip#
Router rip
Copyright 2005 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P 333
Snmp-server chassis-id id string
Snmp-server community community view viewname ro rw
Listname
Config#snmp-server contact Network Administrator
Snmp-server contact string
Snmp-server enable traps trap type
Config#snmp-server enable traps snmp
Config#snmp-server host 190.3.44.69 traps My Community snmp
Snmp-server host address traps community trap type
Copyright 2005 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P 339
Config#snmp-server location 5th Floor Network Room
Snmp-server location string
Snmp-server management-url URL
Config#snmp-server management-url-label watch
Snmp-server management-url-label label
Config#snmp-server source-interface ethernet 0/1
Snmp-server source-interface interface
Config#snmp-server view block 1.3.6.1.2.1.2. included
Snmp-server view view-name oidtree excluded included
Config#sntp server time.nist.gov
Config#sntp server time.nist.gov version
Sntp server address or hostname version
Spanning-tree bpduguard default
Config#spanning-tree bpduguard default
Spanning-tree edgeport bpdufilter default
Config#spanning-tree edgeport bpdufilter default
Spanning-tree forward-time seconds
Spanning-tree hello-time seconds
Config#spanning-tree max-age
Spanning-tree max-age seconds
Spanning-tree mode rstp stp
Config#spanning-tree mode rstp
Rstp
Stp
Config#spanning-tree pathcost method long
Spanning-tree pathcost method short long
Config#spanning-tree priority
Spanning-tree priority value
Username username password password
Config#username procurve password procurve
Dhcp Pool Command SET
Dhcp Pool Command Set
Client-identifier identifier
Client-id
Fecn Becn
Client-name name
Default-routeraddress secondary
Dns-serveraddress secondary
Domain-name domain
Hardware-addresshardware-address type
Ieee802
Copyright 2005 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P 363
Host address subnet mask or prefix length
Config#ip dhcp-server pool MyPool config-dhcp#lease
Config#ip dhcp-server pool MyPool config-dhcp#lease 0
Config#ip dhcp-server pool MyPool config-dhcp#lease 0 0
Lease days hours minutes
Netbios-name-serveraddress secondary
Netbios-node-type type
Config-dhcp#netbios-node-type
Network address subnet mask or prefix length
Config#ip dhcp-server pool MyPool config-dhcp#ntp-server
Ntp-serverip address
Option option value ascii hex ip value
Hex
Config#ip dhcp-server pool MyPool config-dhcp#tftp-server
Tftp-server server
Timezone-offset offset
IKE Policy Command SET
IKE Policy Command Set
Attribute policynumber
Client authentication host
Client authentication host xauth-type generic otp radius
Config-ike#client authentication host xauth-type radius
Client authentication server list listname
Config-ike#client authentication server list clientusers
Client configuration pool poolname
Config-ike#client configuration pool ConfigPool
Initiate main aggressive
Main
Aggressive
Config-ike#local-id address fqdn user-fqdn ipaddress or fqdn
Local-id address asn1-dn fqdn user-fqdnipaddress or name
Copyright 2005 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P 381
Nat-traversal version allow disable force
Following example disables version 2 on Ike policy
Config#crypto ike policy
Config-ike#respond anymode
Peer ip address any
Copyright 2005 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P 384
Config-ike#respond anymode config-ike#initiate main
Respond main aggressive anymode
IKE Policy Attributes Command SET
IKE Policy Attributes Command Set
Authentication dss-sig pre-share rsa-sig
Config-ike-attribute#authentication pre-share
Dss-sig
Pre-share
Encryption aes-xxx-cbc des 3des
Aes-128-cbc aes-192-cbc aes-256-cbc des 3des
Group 1
Hash md5 sha
Lifetime seconds
IKE Client Command SET
IKE Client Command Set
Config-ike-client-pool#dns-server 172.1.17.1
Dns-serveraddress1 address2
Config-ike-client-pool#ip-range 172.1.1.1
Ip-rangestart ip end ip
Netbios-name-serveraddress1 address2
Config-ike-client-pool#netbios-name-server 172.1.17.1
Crypto MAP IKE Command SET
Crypto Map IKE Command Set
Antireplay
Ike-policypolicy number
Config#ip access-list extended NewList
Match address listname
Copyright 2005 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P 400
Config-crypto-map#set peer
Set peer address
Set pfs group1 group2
Group1
Group2
Set security-association lifetime kilobytes seconds value
Config#crypto ipsec transform-set Set1 esp-3des esp-sha-hmac
Set transform-setsetname1 setname6
Crypto MAP Manual Command SET
Copyright 2005 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P 406
Copyright 2005 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P 407
Copyright 2005 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P 408
Copyright 2005 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P 409
Address Enter the IP address of the peer device
Authenticator
Set session-key inbound outbound
Inbound
Outbound
Copyright 2005 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P 412
74686973206973206D7920636970686572206B6579
Gateway
Set transform-set setname
Radius Group Command SET
Radius Group Command Set
Server acct-port port number auth-port port number
CA Profile Configuration Command SET
CA Profile Configuration Command Set
Crl optional
Email address email address
Ca-profile#email address joesmith@company.com
Enrollment retry count period
100
Enrollment terminal
Ca-profile#enrollment terminal
Enrollment url url
Fqdn fqdn
Ca-profile#fqdn company.com
Ip-address address
Ca-profile#ip-address
Password password
Ca-profile#password procurve
Serial-number
Subject-name name
Ca-profile#subject-name cert
Certificate Configuration Command SET
Certificate Configuration Command Set
Certificate serial-number
Config-cert-chain#no certificate ca
Certificate ca serial-number
Crl
Ethernet Interface Configuration Command SET
Ethernet Interface Configuration Command Set
Access-policy policyname on
Full-duplexon page 448 half-duplexon
Access-policy policyname
Policyname
Associate the access policy with the Ethernet 0/1 interface
Copyright 2005 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P 438
Config#interface eth 0/1 config-eth 0/1#arp arpa
Arp arpa
Config#interface eth 0/1
Bandwidth value
Config#interface eth 0/1 config-eth0/1#bridge-group
Bridge-group group#
Crypto map mapname
NAT/ACP
Copyright 2005 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P 444
Username password
Dynamic-dns dyndns dyndns-custom dyndns-static hostname
Config-atm1.1#dynamic-dns dyndns-custom host user pass
Encapsulation 802.1q
Config#interface ethernet 0/1
Full-duplex
Half-duplex
Ip access-group listname in out
Ip address dhcp
Dlci high order Dlci lower
Config#interface eth 0/1 config-eth 0/1#ip address dhcp
Ip address address mask secondary
Secondary
Ip dhcp release
Ip dhcp renew
Ip helper-address address
Copyright 2005 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P 458
Ip igmp
Copyright 2005 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P 460
Config-eth 0/1#ip mcast-stub downstream
Ip mcast-stub downstream
Config-eth 0/1#ip mcast-stub upstream
Ip mcast-stub upstream
Ip ospf
Ip ospf authentication message-digest null
Config-eth 0/1#ip ospf authentication null
Message-digest
Null
Config-eth 0/1#ip ospf network broadcast
Ip ospf network broadcast point-to-point
Broadcast
Point-to-point
Ip proxy-arp
Ip rip receive version version
Ip rip send version version
Ip route-cache
Ip unnumbered interface
Lldp receive
Config-eth 0/1#lldp send-and-receive
Mac-address address
Config#interface eth 0/1 config-eth 0/1#mtu
Mtu size
Username username
Config#interface eth 0/1 config-eth 0/1#snmp trap
Snmp trap
Snmp trap link-status
Spanning-tree bpdufilter enable disable
Spanning-tree bpduguard enable disable
Config#interface eth 0/1 Config-eth0/1#spanning-tree cost
Spanning-tree cost cost value
Spanning-tree edgeport
Spanning-tree link-type auto point-to-point shared
Auto
Shared
Spanning-tree port-priority priority level
Config#interface ethernet 0/1 config-eth 0/1#speed
Speed 10 100 auto
Mb Ethernet
Vlan-id vlan id native
Native
DDS Interface Configuration Command SET
DDS Interface Configuration Command Set
Config#interface dds 1/1
Clock rate rate
Config#interface dds 1/1 config-dds 1/1#clock source line
Clock source option
Data-coding scrambled
Config#interface dds 1/1 config-dds 1/1#loopback line
Loopback dte line remote
Dte
Remote
Config#interface dds 1/1 config-dds1/1#remote-loopback
Remote-loopback
Config#interface dds 1/1 config-dds 1/1#snmp trap
Copyright 2005 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P 493
Serial Interface Configuration Command SET
Router#configure terminal Routerconfig#interface serial 1/1
Et-clock-source source
Config#interface serial 1/1 config-ser 1/1#ignore dcd
Ignore dcd
Invert etclock
Config#interface serial 1/1 config-ser 1/1#invert rxclock
Invert rxclock
Invert txclock
Serial-mode mode
Config#interface serial 1/1 config-ser 1/1#shutdown
Shutdown
Config#interface serial 1/1 config-ser 1/1#snmp trap
Config-ser 1/1#no snmp trap link-status
T1 Interface Configuration Command SET
T1 Interface Configuration Command Set
Config#interface t1 1/1 Config-t1 1/1#clock source line
Clock source internal line through through t1 interface id
Internal
Through
Config#interface t1 1/1 config-t1 1/1#coding ami
Coding ami b8zs
Config#interface t1 1/1
Fdl ansi att none
Framing d4 esf
D4 superframe format SF
Esf Extended SF
Config#interface t1 1/1 config-t1 1/1#lbo long
Lbo long value
Config#interface t1 1/1 config-t1 1/1#lbo short
Lbo short value
Loopback network line payload
T1 Network Interface
Loopback remote line fdl inband
Fdl
Inband
Loopback remote payload
Remote-alarm rai
Rai
Config#interface t1 1/1 config-t11/1#remote-loopback
Config-t1 1/1#show test-pattern Qrss Errored Seconds
Show test-pattern
Copyright 2005 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P 517
Tdm-group group number timeslots 1-24speed 56
Timeslots
Test-pattern ones zeros clear insert p215 p220 p511 qrss
DSX-1 Interface Configuration Command SET
Router#configure terminal Routerconfig#interface t1 1/2
Config#interface t1 1/2 config-t1 1/2#coding ami
Config#interface t1 1/2 config-t1 1/2#framing d4
Esf Extended superframe format
Config#interface t1 1/2 config-t11/2#line-length
Line-length value
Copyright 2005 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P 524
Loopback remote line inband
Config#interface t1 1/2 config-t11/2#remote-loopback
Signaling-mode message-oriented none robbed-bit
Message-oriented
Robbed-bit
Copyright 2005 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P 528
Config#interface t1 1/2 config-t11/2#test-pattern ones
Test-pattern ones zeros
Ones Generate continous ones Zeros Generate continous zeros
E1 Interface Configuration Command SET
E1 Interface Configuration Command Set
Config#interface e1 1/1 config-e1 1/1#clock source line
Clock source internal line through
Config#interface e1 1/1 config-e1 1/1#coding ami
Coding ami hdb3
Ami
Hdb3
Config#interface e1 1/1
Framing crc4
Crc4
Loop-alarm-detect
Config#interface e1 1/1 Config-e1 1/1#loopback network line
Loopback network line
Loopback remote
Remote-alarm rai ais
Ais
Config-interface# Interface configuration mode
Config#interface e1 1/1 config-e11/1#sa4tx-bit
Sa4tx-bit 0
Config-e1 1/1#show test-pattern Qrss Errored Seconds
Copyright 2005 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P 541
Tdm-group group number timeslots 1-31speed 56
Config#interface e1 1/1 config-e11/1#test-pattern ones
Test-pattern ones zeros clear insert p215 p220 p511
Config#interface e1 1/1 config-e1 1/1#ts16
Ts16
Interface Configuration Command SET
Interface Configuration Command set
Config#interface e1 1/2 config-e1 1/2#coding ami
Config#interface e1 1/2
Config#interface e1 1/2 Config-e1 1/2#loopback network line
Copyright 2005 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P 549
Config#interface e1 1/2 config-e11/2#test-pattern ones
511
Show
Show qrss
Config#interface e1 1/2 config-e1 1/2#ts16
Modem Interface Configuration Command SET
Router#configure terminal Routerconfig#interface modem 1/2
Caller-id override always number if-no-cid number
Config#interface modem 1/2 config-modem 1/2#dialin
Dialin
Modem countrycode countryname
BRI Interface Configuration Command SET
BRI Interface Configuration Command set
Bonding txadd-timer seconds
Config#interface bri 1/2 Config-bri 1/2#bonding txadd-timer
Bonding txcid-timer seconds
Bonding txdeq-timer seconds
Config#interface bri 1/2 Config-bri 1/2#bonding txdeq-timer
Bonding txfa-timer seconds
Bonding txinit-timer seconds
Config#interface bri 1/2 Config-bri 1/2#bonding txinit-timer
Bonding txnull-timer seconds
Copyright 2005 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P 563
Isdn spid1 spid ldn
Isdn spid2 spid ldn
Isdn switch-type type
Typebasic-ni
Frame Relay Interface Config Command SET
Config#interface frame-relay 1 config-fr 1#bandwidth
Encapsulation frame-relay ietf
Config#interface frame-relay
Fair-queue threshold
Frame-relay intf-type type
Dce
Frame-relay lmi-n391dce polls
Frame-relay lmi-n391dte polls
Frame-relay lmi-n392dce threshold
Frame-relay lmi-n392dte threshold
Frame-relay lmi-n393dce counter
Frame-relay lmi-n393dte counter
Frame-relay lmi-t391dte seconds
Frame-relay lmi-t392dce seconds
Frame-relay lmi-type type
Ansi
Cisco
Q933a
Functional Note
Following example specifies Class B operation
Config#interface frame-relay 1 config-fr1#hold-queue
Hold-queue queue size out
Qos-policy out mapname
Config-fr 1#snmp trap
Copyright 2005 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P 586
Frame Relay SUB-INTERFACE Config Command SET
Spanning-tree commands begin on
Copyright 2005 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P 588
Create the access list this is the packet selector
Copyright 2005 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P 590
Backup auto-backup
Backup auto-restore
Backup backup-delay seconds
Config#interface atm Config-atm 1.1#backup backup-delay
Backup call-mode role
Sample config for central router dialing
Ip address 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.252 backup call-mode answer
Backup connect-timeout seconds
Config#interface atm Config-atm 1.1#backup connect-timeout
Backup force state
Config#interface frame-relay 1.7 config-fr 1.7#bandwidth
Config-fr 1.16#bridge-group
Copyright 2005 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P 601
Copyright 2005 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P 602
Following enables automatic backup on the endpoint
Copyright 2005 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P 604
Copyright 2005 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P 605
Roleoriginate-answer
Copyright 2005 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P 607
Copyright 2005 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P 608
Config#interface fr Config-fr 1.16#backup connect-timeout
Config#interface fr Config-fr 1.16#backup force backup
Copyright 2005 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P 611
Usage Examples
Config#interface fr Config-fr1.1#frame-relay bc
Frame-relay bc committed burst value
Config#interface fr Config-fr1.1#frame-relay be
Frame-relay be excessive burst value
Frame-relay fragment threshold
Config#interface fr Config-fr1.16#frame-relay interface-dlci
Frame-relay interface-dlci dlci
Out
Identifier
Address assigned to ethernet 0/1 is used in this field
Hostname command
Hostname
Copyright 2005 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P 621
Ip dhcp release renew
Copyright 2005 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P 623
Copyright 2005 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P 624
2x the query-interval value
Copyright 2005 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P 626
Config-fr 1.16#ip mcast-stub downstream
Page
Copyright 2005 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P 629
Config-fr 1.16#ip ospf authentication null
Config-fr 1.16#ip ospf network broadcast
Following enables proxy-arp on the Frame Relay sub-interface
Copyright 2005 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P 633
Copyright 2005 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P 634
Ip route-cache address
Copyright 2005 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P 636
Size
By default, this command is set to disable
Enable Enable the Bpdu block Disable Disable the Bpdu block
Spanning-tree edgeport disable
By default, a port is set to auto
Spanning-tree path-cost value
Value 128
ATM Interface Config Command SET
ATM Interface Config Command Set
Config#interface atm
Config#interface atm Config-atm 1#no snmp trap link-status
ATM SUB-INTERFACE Config Command SET
Router#configure terminal Routerconfig#interface atm
Copyright 2005 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P 648
Atm routed-bridged ip
Use ip protocol to be route bridged
Config#interface atm Config-atm1.1#access-policy UnTrusted
Copyright 2005 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P 651
Copyright 2005 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P 652
Copyright 2005 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P 653
Copyright 2005 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P 654
Copyright 2005 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P 655
Copyright 2005 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P 656
Copyright 2005 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P 657
Copyright 2005 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P 658
Copyright 2005 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P 659
Config#interface atm 1.1 config-atm 1.1#bandwidth
Config#interface atm 1.1 config-atm1.1#bridge-group
Copyright 2005 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P 662
Copyright 2005 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P 663
See Functional Notes, below, for argument descriptions
Copyright 2005 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P 665
Config-atm 1.1#encapsulation aal5snap
Encapsulation aal5mux aal5snap
Encapsulation aal5mux ip ppp encapsulation aal5snap
Copyright 2005 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P 667
Copyright 2005 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P 668
Copyright 2005 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P 669
Host name
MAC Address assigned to ethernet 0/1 is used in this field
Config#interface atm 1.1 config-atm 1.1#ip address dhcp
Copyright 2005 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P 673
Config#interface atm 1.1 config-atm 1.1#ip dhcp release
Copyright 2005 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P 675
Copyright 2005 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P 676
Copyright 2005 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P 677
Copyright 2005 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P 678
Config-atm 1.1#ip mcast-stub downstream
Ip mcast-stub helper-enable
Page
Copyright 2005 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P 682
Config-atm 1.1#ip ospf authentication null
Config-atm 1.1#ip ospf network broadcast
Config#interface atm 1.1 config-atm 1.1#ip proxy-arp
Copyright 2005 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P 686
Copyright 2005 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P 687
Config#interface atm 1.1 config-atm 1.1#ip route-cache
Copyright 2005 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P 689
Config-atm 1.1#mtu
Config#interface atm 1.1 config-atm1.1#oam-pvc manage
Oam-pvc managed frequency
Config#interface atm 1.1 config-atm 1.1#oam retry 2 2
Oam retry up-count down-count retry-frequency
Config#interface atm 1.1 config-atm 1.1#pvc 8/35
Pvc VPI/VCI
Mapnamesequence number on page 326 for more information
Copyright 2005 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P 695
Copyright 2005 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P 696
Copyright 2005 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P 697
Copyright 2005 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P 698
Config#interface atm Config-atm1.1#spanning-tree path-cost
Spanning-tree port-priority value
Adsl Interface Config Command SET
Adsl Interface Config Command Set
Retrain
Config-adsl0/1#snr-margin showtime monitor
Snr-margin showtime monitor training monitor margin
Showtime monitor
Training monitor
Specifies Ansi full rate mode
Specifies Ansi splitterless mode
Config-adsl0/1#training-mode T1.413
Training-mode G.DMT G.LITE Multi-Mode T1.413
BGP Configuration Command SET
BGP Configuration Command Set
Config-bgp#bgp fast-external-fallover
Bgp fast-external-fallover
Config-bgp#bgp log-neighbor-changes
Bgp log-neighbor-changes
Config-bgp#bgp router-id
Bgp router-id ip address
Config-bgp#distance bgp 30 200
Distance bgp external internal local
Hold-timer hold time
Config-bgp#hold-timer
BGP Neighbor Configuration Command SET
BGP Neighbor Configuration Command Set
Config-bgp-neighbor#advertisement-interval
Advertisement-interval seconds
Ebgp-multihop hop count
By default, the hold time is 90 seconds
PPP Interface Configuration Command SET
Mtu size on Peer default ip address address on
Config#interface ppp Config-ppp1#access-policy UnTrusted
Copyright 2005 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P 718
Copyright 2005 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P 719
Alias linktext
Config#interface ppp 1 config-ppp 1#bandwidth
Multiple binds
This Step is only Valid for T1 Interfaces
Copyright 2005 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P 724
Config#interface ppp 1 config-ppp1#bridge-group
Bridge-group group# bpdufilter enable disable
Bridge-group group# bpduguard enable disable
Bridge-group group# edgeport disable
Config#interface ppp Config-ppp1#bridge-group 1 edgeport
Bridge-group group# link-type auto point-to-point shared
Bridge-group group# spanning-disabled
Copyright 2005 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P 731
Config-ppp 1#crypto map MyMap
Copyright 2005 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P 733
Copyright 2005 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P 734
Config#interface ppp Config-ppp 1#backup backup-delay
Sample config for remote router dialing out
Copyright 2005 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P 737
Copyright 2005 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P 738
Dialing Out
Dialing
Config#interface ppp Config-ppp 1#backup connect-timeout
State Selects the forced backup state of the link
Copyright 2005 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P 742
Copyright 2005 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P 743
Config-ppp 1#fair-queue
Config#interface ppp 1 config-ppp1#hold-queue
Copyright 2005 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P 746
Ip address negotiated
Copyright 2005 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P 748
Copyright 2005 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P 749
Copyright 2005 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P 750
Copyright 2005 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P 751
Copyright 2005 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P 752
Config-ppp 1#ip mcast-stub downstream
Config-ppp 1#ip mcast-stub upstream
Copyright 2005 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P 755
Config-ppp 1#ip ospf authentication null
Config-ppp 1#ip ospf network broadcast
By default, proxy-arp is enabled
Copyright 2005 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P 759
Version Specifies the RIP version
Config-ppp 1#ip route-cache
Copyright 2005 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P 762
Keepalive seconds
Config#interface ppp 1 config-ppp 1#mtu
Peer default ip address address
Config#interface ppp Config-ppp 1#peer default ip address
Ppp authentication protocol
Defining PAP
Peerconfig-ppp 1#ppp pap sent-username farend password same
Defining Chap
Both ends must have identical passwords
Peerconfig-ppp 1#username Local password same
Peerconfig-ppp 1#ppp chap password different
Config#interface ppp Config-ppp 1#ppp chap hostname myhost
Ppp chap hostname hostname
Ppp chap password password
Ppp multilink
Ppp pap sent-username username password password
Pppoe ac-name name
Pppoe service-name name
Config#interface ppp Config-ppp1#qos-policy out Voicemap
Config#interface ppp Config-ppp 1#no snmp trap link-status
Tunnel Configuration Command SET
Tunnel Configuration Command Set
Router#configure terminal Routerconfig#interface tunnel
Copyright 2005 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P 779
Config#ip policy-class UnTrusted
Copyright 2005 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P 781
Config#interface tunnel 1 config-tunnel 1#bandwidth
Bandwidth
Refer to Functional Notes below for argument descriptions
Copyright 2005 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P 784
Copyright 2005 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P 785
Copyright 2005 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P 786
Copyright 2005 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P 787
Copyright 2005 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P 788
Leave-group message Igmp Version 2, the router sends a
Copyright 2005 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P 790
Copyright 2005 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P 791
Copyright 2005 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P 792
Following example sets the helper address as the Igmp proxy
Copyright 2005 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P 794
Command Reference GuideTunnel Configuration Command Set
Cost value
Copyright 2005 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P 796
Optional. Selects message-digest authentication type
Sets the network type for broadcast
Config#interface tunnel 1 config-tunnel 1#ip proxy-arp
Ip proxy-arpip address subnet mask
Ip rip receive version 1
Ip rip send version 1
Only transmits RIP version 1 packets on the interface
Only transmits RIP version 2 packets on the interface
Config#interface tunnel 1 config-tunnel 1#ip route-cache
Config#interface tunnel
Keepalive period retries
Config#interface tunnel 1 config-tunnel 1#tunnel checksum
Tunnel checksum
Config#interface tunnel Config-tunnel 1#tunnel destination
Tunnel destination ip address
Config#interface tunnel 1 config-tunnel 1#tunnel key
Tunnel key value
Tunnel mode gre
Config#interface tunnel 1 config-tunnel 1#tunnel mode gre
Tunnel sequence-datagrams
Tunnel source ip address interface
Config#interface tunnel Config-tunnel 1#tunnel source
Hdlc Command SET
Hdlc Command Set
Copyright 2005 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P 812
Copyright 2005 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P 813
Config#interface hdlc Config-hdlc1#access-policy UnTrusted
Copyright 2005 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P 815
Config#interface hdlc 1 config-hdlc 1#bandwidth
Config#interface hdlc 1 config-hdlc1#bridge-group
Copyright 2005 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P 818
Config#interface hdlc 1 config-hdlc 1#crypto map MyMap
See Functional Notes below for syntax descriptions
Copyright 2005 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P 821
Config-hdlc 1#fair-queue
Config-hdlc 1#hold-queue
Copyright 2005 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P 824
Copyright 2005 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P 825
Copyright 2005 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P 826
Copyright 2005 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P 827
Sros Command Line Interface Reference GuideHDLC Command Set
Copyright 2005 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P 829
Config#interface hdlc Config-hdlc 1#ip mcast-stub downstream
Copyright 2005 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P 831
Copyright 2005 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P 832
Config#interface hdlc Config-hdlc 1#ip ospf dead-interval
Copyright 2005 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P 834
Copyright 2005 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P 835
Following enables proxy ARP on the Hdlc interface
Copyright 2005 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P 837
Copyright 2005 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P 838
Config-hdlc 1#ip route-cache
Copyright 2005 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P 840
Config#interface hdlc 1 config-hdlc 1#keepalive
Config#interface hdlc 1 config-hdlc 1#lldp receive
Config#interface hdlc 1 config-hdlc 1#lldp send
Config-interface# Interface Configuration Mode
Config#interface hdlc 1 config-hdlc 1#mtu
Config#interface hdlc Config-hdlc1#qos-policy out Voicemap
Config#interface hdlc Config-hdlc 1#no snmp trap link-status
Loopback Interface Configuration Command SET
Router#configure terminal Routerconfig#interface loopback
Copyright 2005 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P 848
Copyright 2005 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P 849
Copyright 2005 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P 850
Config#interface loopback 1 config-loop 1#bandwidth
Copyright 2005 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P 852
Copyright 2005 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P 853
Copyright 2005 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P 854
Copyright 2005 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P 855
Copyright 2005 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P 856
Copyright 2005 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P 857
Copyright 2005 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P 858
Copyright 2005 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P 859
Copyright 2005 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P 860
Copyright 2005 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P 861
Copyright 2005 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P 862
Config-loop 1#ip mcast-stub downstream
Page
Assign a simple-text authentication password to be used by
Config-loop 1#ip ospf authentication null
Config-loop 1#ip ospf network broadcast
Following enables proxy-arp on the loopback interface
Copyright 2005 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P 869
Copyright 2005 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P 870
Config#interface loopback 1 config-loop 1#ip route-cache
Config#interface loopback 1 config-loop 1#ip unnumbered ppp
Config#interface loopback 1 config-loop 1#mtu
Config-eth 0/1#snmp trap
Copyright 2005 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P 875
Line Console Interface Config Command SET
Line Console Interface Config Command Set
Config#line console 0 config-con 0#databits
Databits option
Config#line console 0 config-con 0#flowcontrol none
Flowcontrol none software
Line-timeout minutes
Config#line console
Login
Login authentication aaa login list
Config#line console Config-con 0#login authentication myList
Login local-userlist
Config#line console 0 config-con 0#parity mark
Parity option
Password md5 password
Config-con 0#password mypassword
Speed rate
Config#line console 0 config-con 0#stopbits
Stopbits option
Line Telnet Interface Config Command SET
Line Telnet Interface Config Command Set
Access-class listname
Config#line telnet 0
Config-telnet0-4#access-class Trusted
Config#line telnet 0 config-telnet0#line-timeout
Copyright 2005 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P 890
Copyright 2005 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P 891
Copyright 2005 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P 892
Config#line telnet
Router RIP Configuration Command SET
Router RIP Configuration Command Set
Config#router rip config-rip#no auto-summary
Auto-summary
Default-metric value
Network address subnet mask
Passive-interface interface
Config#router rip Config-rip#redistribute connected
Redistribute connected metric value
Metric value
Config#router rip config-rip#redistribute ospf
Redistribute ospf metric value
Redistribute static metric value
Config#router rip config-rip#version
Version version
Router Ospf Configuration Command SET
Router Ospf Configuration Command Set
Area area id default-cost value
Config#router ospf Config-ospf#area 192.22.72.0 default-cost
Area area id range ip address network mask advertise
Not-advertise
Config#router ospf
Area area id stub no-summary
Config#router ospf Config-ospf#auto-cost reference-bandwidth
Auto-cost reference-bandwidth rate
Always Always advertise default route Metric value
Metric type type Configure metric type 1 or
Metric value Metric type type
Value Set the default metric value range
Network ip address wildcard area area id
Config#router ospf config-ospf#redistribute connected
Redistribute connected
Config#router ospf config-ospf#redistribute rip
Redistribute rip
Config#router ospf config-ospf#redistribute static
Redistribute static
Summary-addressaddress mask prefix mask not-advertise
Timers lsa-group-pacing seconds
Timers spf delay hold
Config#router ospf config-ospf#timers spf 10
Quality of Service QOS MAP Commands
Quality of Service QoS Map Commands
Match
Match dscp 0-63match ip rtp port #
Priority
Priority unlimited
Config#qos map Voicemap 10 config-qos-map#set dscp
Set dscp
Config#qos map Voicemap 10 config-qos-map#set precedence
Set precedence
Common Commands
Common Commands
Alias text
Copyright 2005 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P 924
Copyright 2005 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P 925
Copyright 2005 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P 926
Description
Config#do clear arp-cache
End
Exit
Copyright 2005 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P 931
#ping
Show running-config
Policy-class
Qos-map
Checksum
Enable #show running-config Building configuration
Config#interface modem 1/2
Index
CLI
Command security levels
Fair-queue570, 667, 744, 822 fdl
Nat-traversal 382 netbios-name-server 366
Copyright 2005 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P 940
VT100 configuration Warranty 2 write